Tao Liu
IESR:Efficient MCTS-Based Modular Reasoning for Text-to-SQL with Large Language Models
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Text-to-SQL is a key natural language processing task that maps natural language questions to SQL queries, enabling intuitive interaction with web-based databases. Although current methods perform well on benchmarks like BIRD and Spider, they struggle with complex reasoning, domain knowledge, and hypothetical queries, and remain costly in enterprise deployment. To address these issues, we propose a framework named IESR(Information Enhanced Structured Reasoning) for lightweight large language models: (i) leverages LLMs for key information understanding and schema linking, and decoupling mathematical computation and SQL generation, (ii) integrates a multi-path reasoning mechanism based on Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS) with majority voting, and (iii) introduces a trajectory consistency verification module with a discriminator model to ensure accuracy and consistency. Experimental results demonstrate that IESR achieves state-of-the-art performance on the complex reasoning benchmark LogicCat (24.28 EX) and the Archer dataset (37.28 EX) using only compact lightweight models without fine-tuning. Furthermore, our analysis reveals that current coder models exhibit notable biases and deficiencies in physical knowledge, mathematical computation, and common-sense reasoning, highlighting important directions for future research. We released code at https://github.com/Ffunkytao/IESR-SLM.
AGILE: Hand-Object Interaction Reconstruction from Video via Agentic Generation
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Reconstructing dynamic hand-object interactions from monocular videos is critical for dexterous manipulation data collection and creating realistic digital twins for robotics and VR. However, current methods face two prohibitive barriers: (1) reliance on neural rendering often yields fragmented, non-simulation-ready geometries under heavy occlusion, and (2) dependence on brittle Structure-from-Motion (SfM) initialization leads to frequent failures on in-the-wild footage. To overcome these limitations, we introduce AGILE, a robust framework that shifts the paradigm from reconstruction to agentic generation for interaction learning. First, we employ an agentic pipeline where a Vision-Language Model (VLM) guides a generative model to synthesize a complete, watertight object mesh with high-fidelity texture, independent of video occlusions. Second, bypassing fragile SfM entirely, we propose a robust anchor-and-track strategy. We initialize the object pose at a single interaction onset frame using a foundation model and propagate it temporally by leveraging the strong visual similarity between our generated asset and video observations. Finally, a contact-aware optimization integrates semantic, geometric, and interaction stability constraints to enforce physical plausibility. Extensive experiments on HO3D, DexYCB, and in-the-wild videos reveal that AGILE outperforms baselines in global geometric accuracy while demonstrating exceptional robustness on challenging sequences where prior art frequently collapses. By prioritizing physical validity, our method produces simulation-ready assets validated via real-to-sim retargeting for robotic applications.
ProFit: Leveraging High-Value Signals in SFT via Probability-Guided Token Selection
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:Supervised fine-tuning (SFT) is a fundamental post-training strategy to align Large Language Models (LLMs) with human intent. However, traditional SFT often ignores the one-to-many nature of language by forcing alignment with a single reference answer, leading to the model overfitting to non-core expressions. Although our empirical analysis suggests that introducing multiple reference answers can mitigate this issue, the prohibitive data and computational costs necessitate a strategic shift: prioritizing the mitigation of single-reference overfitting over the costly pursuit of answer diversity. To achieve this, we reveal the intrinsic connection between token probability and semantic importance: high-probability tokens carry the core logical framework, while low-probability tokens are mostly replaceable expressions. Based on this insight, we propose ProFit, which selectively masks low-probability tokens to prevent surface-level overfitting. Extensive experiments confirm that ProFit consistently outperforms traditional SFT baselines on general reasoning and mathematical benchmarks.
DiffusionUavLoc: Visually Prompted Diffusion for Cross-View UAV Localization
Nov 09, 2025



Abstract:With the rapid growth of the low-altitude economy, unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) have become key platforms for measurement and tracking in intelligent patrol systems. However, in GNSS-denied environments, localization schemes that rely solely on satellite signals are prone to failure. Cross-view image retrieval-based localization is a promising alternative, yet substantial geometric and appearance domain gaps exist between oblique UAV views and nadir satellite orthophotos. Moreover, conventional approaches often depend on complex network architectures, text prompts, or large amounts of annotation, which hinders generalization. To address these issues, we propose DiffusionUavLoc, a cross-view localization framework that is image-prompted, text-free, diffusion-centric, and employs a VAE for unified representation. We first use training-free geometric rendering to synthesize pseudo-satellite images from UAV imagery as structural prompts. We then design a text-free conditional diffusion model that fuses multimodal structural cues to learn features robust to viewpoint changes. At inference, descriptors are computed at a fixed time step t and compared using cosine similarity. On University-1652 and SUES-200, the method performs competitively for cross-view localization, especially for satellite-to-drone in University-1652.Our data and code will be published at the following URL: https://github.com/liutao23/DiffusionUavLoc.git.
ArchPilot: A Proxy-Guided Multi-Agent Approach for Machine Learning Engineering
Nov 06, 2025Abstract:Recent LLM-based agents have demonstrated strong capabilities in automated ML engineering. However, they heavily rely on repeated full training runs to evaluate candidate solutions, resulting in significant computational overhead, limited scalability to large search spaces, and slow iteration cycles. To address these challenges, we introduce ArchPilot, a multi-agent system that integrates architecture generation, proxy-based evaluation, and adaptive search into a unified framework. ArchPilot consists of three specialized agents: an orchestration agent that coordinates the search process using a Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS)-inspired novel algorithm with a restart mechanism and manages memory of previous candidates; a generation agent that iteratively generates, improves, and debugs candidate architectures; and an evaluation agent that executes proxy training runs, generates and optimizes proxy functions, and aggregates the proxy scores into a fidelity-aware performance metric. This multi-agent collaboration allows ArchPilot to prioritize high-potential candidates with minimal reliance on expensive full training runs, facilitating efficient ML engineering under limited budgets. Experiments on MLE-Bench demonstrate that ArchPilot outperforms SOTA baselines such as AIDE and ML-Master, validating the effectiveness of our multi-agent system.
GUI-Rise: Structured Reasoning and History Summarization for GUI Navigation
Oct 31, 2025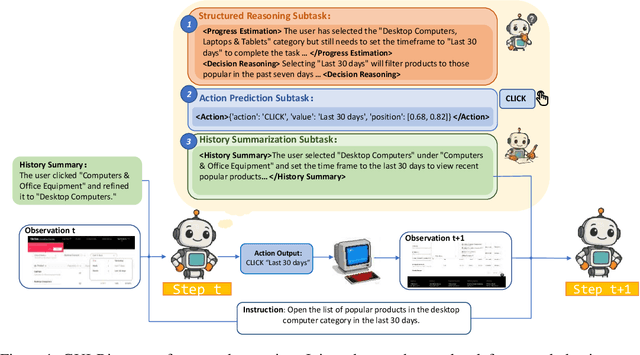
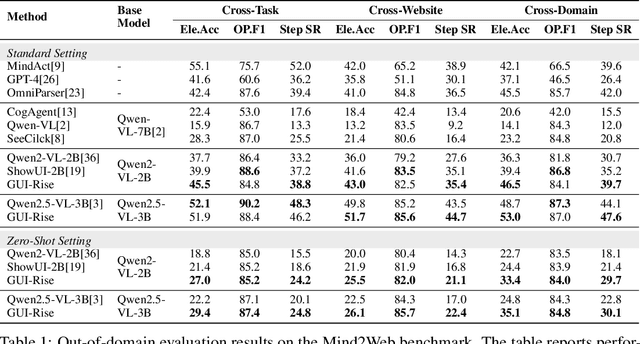
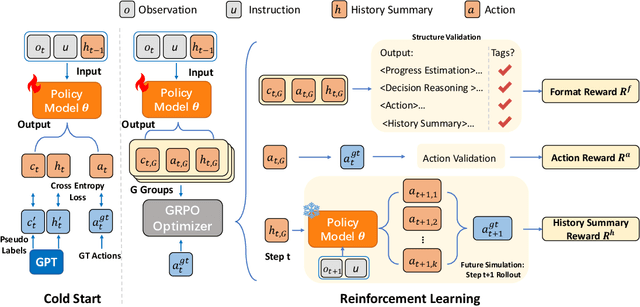
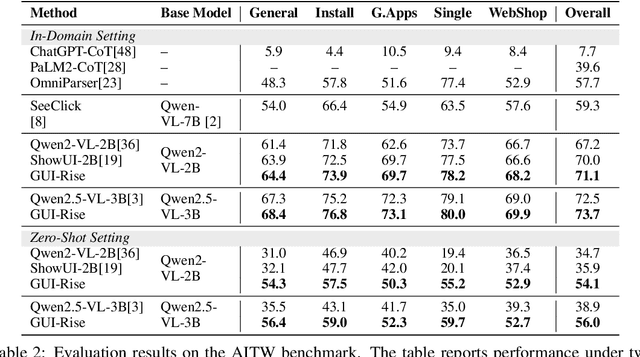
Abstract:While Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have advanced GUI navigation agents, current approaches face limitations in cross-domain generalization and effective history utilization. We present a reasoning-enhanced framework that systematically integrates structured reasoning, action prediction, and history summarization. The structured reasoning component generates coherent Chain-of-Thought analyses combining progress estimation and decision reasoning, which inform both immediate action predictions and compact history summaries for future steps. Based on this framework, we train a GUI agent, \textbf{GUI-Rise}, through supervised fine-tuning on pseudo-labeled trajectories and reinforcement learning with Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO). This framework employs specialized rewards, including a history-aware objective, directly linking summary quality to subsequent action performance. Comprehensive evaluations on standard benchmarks demonstrate state-of-the-art results under identical training data conditions, with particularly strong performance in out-of-domain scenarios. These findings validate our framework's ability to maintain robust reasoning and generalization across diverse GUI navigation tasks. Code is available at https://leon022.github.io/GUI-Rise.
MatchAttention: Matching the Relative Positions for High-Resolution Cross-View Matching
Oct 16, 2025Abstract:Cross-view matching is fundamentally achieved through cross-attention mechanisms. However, matching of high-resolution images remains challenging due to the quadratic complexity and lack of explicit matching constraints in the existing cross-attention. This paper proposes an attention mechanism, MatchAttention, that dynamically matches relative positions. The relative position determines the attention sampling center of the key-value pairs given a query. Continuous and differentiable sliding-window attention sampling is achieved by the proposed BilinearSoftmax. The relative positions are iteratively updated through residual connections across layers by embedding them into the feature channels. Since the relative position is exactly the learning target for cross-view matching, an efficient hierarchical cross-view decoder, MatchDecoder, is designed with MatchAttention as its core component. To handle cross-view occlusions, gated cross-MatchAttention and a consistency-constrained loss are proposed. These two components collectively mitigate the impact of occlusions in both forward and backward passes, allowing the model to focus more on learning matching relationships. When applied to stereo matching, MatchStereo-B ranked 1st in average error on the public Middlebury benchmark and requires only 29ms for KITTI-resolution inference. MatchStereo-T can process 4K UHD images in 0.1 seconds using only 3GB of GPU memory. The proposed models also achieve state-of-the-art performance on KITTI 2012, KITTI 2015, ETH3D, and Spring flow datasets. The combination of high accuracy and low computational complexity makes real-time, high-resolution, and high-accuracy cross-view matching possible. Code is available at https://github.com/TingmanYan/MatchAttention.
ACPO: Adaptive Curriculum Policy Optimization for Aligning Vision-Language Models in Complex Reasoning
Oct 01, 2025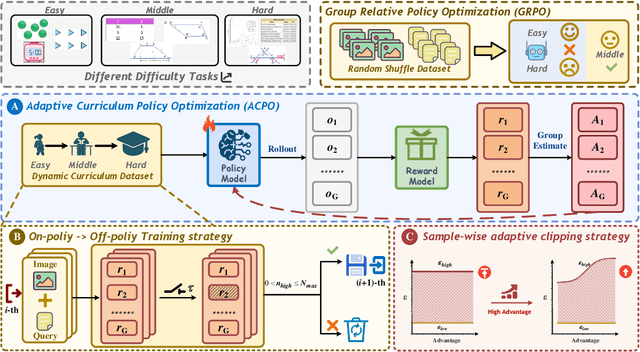
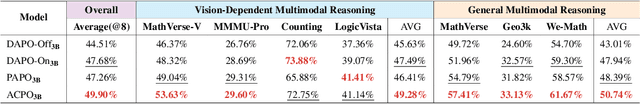
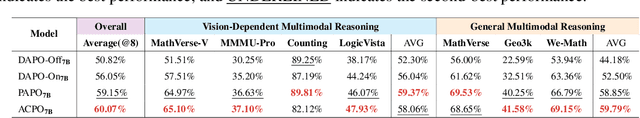
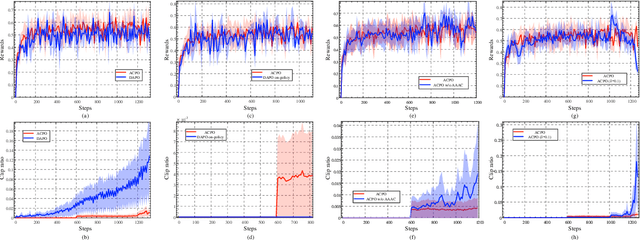
Abstract:Aligning large-scale vision-language models (VLMs) for complex reasoning via reinforcement learning is often hampered by the limitations of existing policy optimization algorithms, such as static training schedules and the rigid, uniform clipping mechanism in Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO). In this work, we introduce Adaptive Curriculum Policy Optimization (ACPO), a novel framework that addresses these challenges through a dual-component adaptive learning strategy. First, ACPO employs a dynamic curriculum that orchestrates a principled transition from a stable, near on-policy exploration phase to an efficient, off-policy exploitation phase by progressively increasing sample reuse. Second, we propose an Advantage-Aware Adaptive Clipping (AAAC) mechanism that replaces the fixed clipping hyperparameter with dynamic, sample-wise bounds modulated by the normalized advantage of each token. This allows for more granular and robust policy updates, enabling larger gradients for high-potential samples while safeguarding against destructive ones. We conduct extensive experiments on a suite of challenging multimodal reasoning benchmarks, including MathVista, LogicVista, and MMMU-Pro. Results demonstrate that ACPO consistently outperforms strong baselines such as DAPO and PAPO, achieving state-of-the-art performance, accelerated convergence, and superior training stability.
Mini-o3: Scaling Up Reasoning Patterns and Interaction Turns for Visual Search
Sep 09, 2025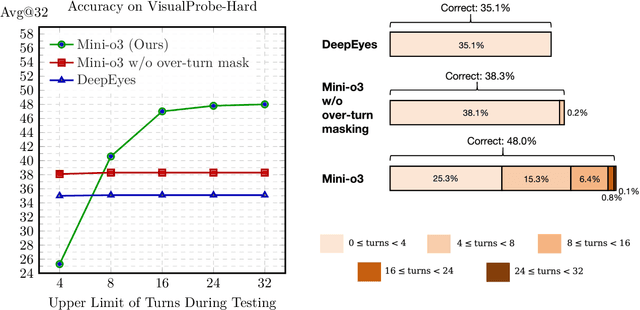
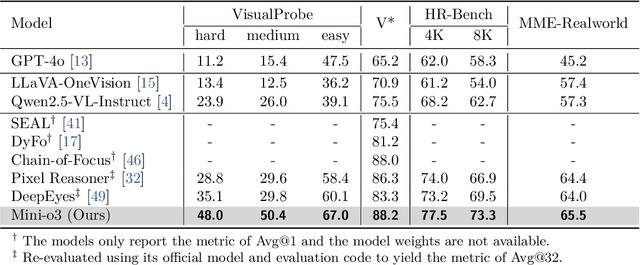
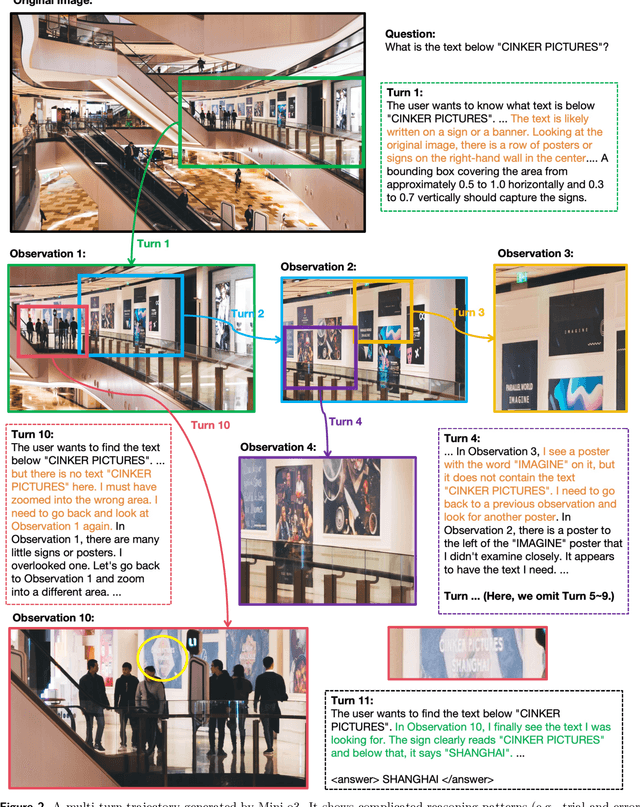
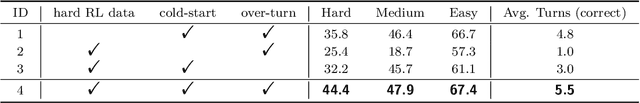
Abstract:Recent advances in large multimodal models have leveraged image-based tools with reinforcement learning to tackle visual problems. However, existing open-source approaches often exhibit monotonous reasoning patterns and allow only a limited number of interaction turns, making them inadequate for difficult tasks that require trial-and-error exploration. In this work, we address this limitation by scaling up tool-based interactions and introduce Mini-o3, a system that executes deep, multi-turn reasoning -- spanning tens of steps -- and achieves state-of-the-art performance on challenging visual search tasks. Our recipe for reproducing OpenAI o3-style behaviors comprises three key components. First, we construct the Visual Probe Dataset, a collection of thousands of challenging visual search problems designed for exploratory reasoning. Second, we develop an iterative data collection pipeline to obtain cold-start trajectories that exhibit diverse reasoning patterns, including depth-first search, trial-and-error, and goal maintenance. Third, we propose an over-turn masking strategy that prevents penalization of over-turn responses (those that hit the maximum number of turns) during reinforcement learning, thereby balancing training-time efficiency with test-time scalability. Despite training with an upper bound of only six interaction turns, our model generates trajectories that naturally scale to tens of turns at inference time, with accuracy improving as the number of turns increases. Extensive experiments demonstrate that Mini-o3 produces rich reasoning patterns and deep thinking paths, effectively solving challenging visual search problems.
Degree of Staleness-Aware Data Updating in Federated Learning
Aug 23, 2025Abstract:Handling data staleness remains a significant challenge in federated learning with highly time-sensitive tasks, where data is generated continuously and data staleness largely affects model performance. Although recent works attempt to optimize data staleness by determining local data update frequency or client selection strategy, none of them explore taking both data staleness and data volume into consideration. In this paper, we propose DUFL(Data Updating in Federated Learning), an incentive mechanism featuring an innovative local data update scheme manipulated by three knobs: the server's payment, outdated data conservation rate, and clients' fresh data collection volume, to coordinate staleness and volume of local data for best utilities. To this end, we introduce a novel metric called DoS(the Degree of Staleness) to quantify data staleness and conduct a theoretic analysis illustrating the quantitative relationship between DoS and model performance. We model DUFL as a two-stage Stackelberg game with dynamic constraint, deriving the optimal local data update strategy for each client in closed-form and the approximately optimal strategy for the server. Experimental results on real-world datasets demonstrate the significant performance of our approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge