Xie Chen
The Interspeech 2026 Audio Reasoning Challenge: Evaluating Reasoning Process Quality for Audio Reasoning Models and Agents
Feb 15, 2026Abstract:Recent Large Audio Language Models (LALMs) excel in understanding but often lack transparent reasoning. To address this "black-box" limitation, we organized the Audio Reasoning Challenge at Interspeech 2026, the first shared task dedicated to evaluating Chain-of-Thought (CoT) quality in the audio domain. The challenge introduced MMAR-Rubrics, a novel instance-level protocol assessing the factuality and logic of reasoning chains. Featured Single Model and Agent tracks, the competition attracting 156 teams from 18 countries and regions. Results show agent systems currently lead in reasoning quality, utilizing iterative tool orchestration and cross-modal analysis. Besides, single models are rapidly advancing via reinforcement learning and sophisticated data pipeline. We details the challenge design, methodology, and a comprehensive analysis of state-of-the-art systems, providing new insights for explainable audio intelligence.
MOVA: Towards Scalable and Synchronized Video-Audio Generation
Feb 09, 2026Abstract:Audio is indispensable for real-world video, yet generation models have largely overlooked audio components. Current approaches to producing audio-visual content often rely on cascaded pipelines, which increase cost, accumulate errors, and degrade overall quality. While systems such as Veo 3 and Sora 2 emphasize the value of simultaneous generation, joint multimodal modeling introduces unique challenges in architecture, data, and training. Moreover, the closed-source nature of existing systems limits progress in the field. In this work, we introduce MOVA (MOSS Video and Audio), an open-source model capable of generating high-quality, synchronized audio-visual content, including realistic lip-synced speech, environment-aware sound effects, and content-aligned music. MOVA employs a Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architecture, with a total of 32B parameters, of which 18B are active during inference. It supports IT2VA (Image-Text to Video-Audio) generation task. By releasing the model weights and code, we aim to advance research and foster a vibrant community of creators. The released codebase features comprehensive support for efficient inference, LoRA fine-tuning, and prompt enhancement.
Audio ControlNet for Fine-Grained Audio Generation and Editing
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:We study the fine-grained text-to-audio (T2A) generation task. While recent models can synthesize high-quality audio from text descriptions, they often lack precise control over attributes such as loudness, pitch, and sound events. Unlike prior approaches that retrain models for specific control types, we propose to train ControlNet models on top of pre-trained T2A backbones to achieve controllable generation over loudness, pitch, and event roll. We introduce two designs, T2A-ControlNet and T2A-Adapter, and show that the T2A-Adapter model offers a more efficient structure with strong control ability. With only 38M additional parameters, T2A-Adapter achieves state-of-the-art performance on the AudioSet-Strong in both event-level and segment-level F1 scores. We further extend this framework to audio editing, proposing T2A-Editor for removing and inserting audio events at time locations specified by instructions. Models, code, dataset pipelines, and benchmarks will be released to support future research on controllable audio generation and editing.
VIBEVOICE-ASR Technical Report
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:This report presents VibeVoice-ASR, a general-purpose speech understanding framework built upon VibeVoice, designed to address the persistent challenges of context fragmentation and multi-speaker complexity in long-form audio (e.g., meetings, podcasts) that remain despite recent advancements in short-form speech recognition. Unlike traditional pipelined approaches that rely on audio chunking, VibeVoice-ASRsupports single-pass processing for up to 60 minutes of audio. It unifies Automatic Speech Recognition, Speaker Diarization, and Timestamping into a single end-to-end generation task. In addition, VibeVoice-ASR supports over 50 languages, requires no explicit language setting, and natively handles code-switching within and across utterances. Furthermore, we introduce a prompt-based context injection mechanism that allows users to supply customized conetxt, significantly improving accuracy on domain-specific terminology and polyphonic character disambiguation.
Habibi: Laying the Open-Source Foundation of Unified-Dialectal Arabic Speech Synthesis
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:A notable gap persists in speech synthesis research and development for Arabic dialects, particularly from a unified modeling perspective. Despite its high practical value, the inherent linguistic complexity of Arabic dialects, further compounded by a lack of standardized data, benchmarks, and evaluation guidelines, steers researchers toward safer ground. To bridge this divide, we present Habibi, a suite of specialized and unified text-to-speech models that harnesses existing open-source ASR corpora to support a wide range of high- to low-resource Arabic dialects through linguistically-informed curriculum learning. Our approach outperforms the leading commercial service in generation quality, while maintaining extensibility through effective in-context learning, without requiring text diacritization. We are committed to open-sourcing the model, along with creating the first systematic benchmark for multi-dialect Arabic speech synthesis. Furthermore, by identifying the key challenges in and establishing evaluation standards for the process, we aim to provide a solid groundwork for subsequent research. Resources at https://SWivid.github.io/Habibi/ .
SLAM-LLM: A Modular, Open-Source Multimodal Large Language Model Framework and Best Practice for Speech, Language, Audio and Music Processing
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:The recent surge in open-source Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLM) frameworks, such as LLaVA, provides a convenient kickoff for artificial intelligence developers and researchers. However, most of the MLLM frameworks take vision as the main input modality, and provide limited in-depth support for the modality of speech, audio, and music. This situation hinders the development of audio-language models, and forces researchers to spend a lot of effort on code writing and hyperparameter tuning. We present SLAM-LLM, an open-source deep learning framework designed to train customized MLLMs, focused on speech, language, audio, and music processing. SLAM-LLM provides a modular configuration of different encoders, projectors, LLMs, and parameter-efficient fine-tuning plugins. SLAM-LLM also includes detailed training and inference recipes for mainstream tasks, along with high-performance checkpoints like LLM-based Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR), Automated Audio Captioning (AAC), and Music Captioning (MC). Some of these recipes have already reached or are nearing state-of-the-art performance, and some relevant techniques have also been accepted by academic papers. We hope SLAM-LLM will accelerate iteration, development, data engineering, and model training for researchers. We are committed to continually pushing forward audio-based MLLMs through this open-source framework, and call on the community to contribute to the LLM-based speech, audio and music processing.
ReStyle-TTS: Relative and Continuous Style Control for Zero-Shot Speech Synthesis
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:Zero-shot text-to-speech models can clone a speaker's timbre from a short reference audio, but they also strongly inherit the speaking style present in the reference. As a result, synthesizing speech with a desired style often requires carefully selecting reference audio, which is impractical when only limited or mismatched references are available. While recent controllable TTS methods attempt to address this issue, they typically rely on absolute style targets and discrete textual prompts, and therefore do not support continuous and reference-relative style control. We propose ReStyle-TTS, a framework that enables continuous and reference-relative style control in zero-shot TTS. Our key insight is that effective style control requires first reducing the model's implicit dependence on reference style before introducing explicit control mechanisms. To this end, we introduce Decoupled Classifier-Free Guidance (DCFG), which independently controls text and reference guidance, reducing reliance on reference style while preserving text fidelity. On top of this, we apply style-specific LoRAs together with Orthogonal LoRA Fusion to enable continuous and disentangled multi-attribute control, and introduce a Timbre Consistency Optimization module to mitigate timbre drift caused by weakened reference guidance. Experiments show that ReStyle-TTS enables user-friendly, continuous, and relative control over pitch, energy, and multiple emotions while maintaining intelligibility and speaker timbre, and performs robustly in challenging mismatched reference-target style scenarios.
Towards Fine-Grained and Multi-Granular Contrastive Language-Speech Pre-training
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:Modeling fine-grained speaking styles remains challenging for language-speech representation pre-training, as existing speech-text models are typically trained with coarse captions or task-specific supervision, and scalable fine-grained style annotations are unavailable. We present FCaps, a large-scale dataset with fine-grained free-text style descriptions, encompassing 47k hours of speech and 19M fine-grained captions annotated via a novel end-to-end pipeline that directly grounds detailed captions in audio, thereby avoiding the error propagation caused by LLM-based rewriting in existing cascaded pipelines. Evaluations using LLM-as-a-judge demonstrate that our annotations surpass existing cascaded annotations in terms of correctness, coverage, and naturalness. Building on FCaps, we propose CLSP, a contrastive language-speech pre-trained model that integrates global and fine-grained supervision, enabling unified representations across multiple granularities. Extensive experiments demonstrate that CLSP learns fine-grained and multi-granular speech-text representations that perform reliably across global and fine-grained speech-text retrieval, zero-shot paralinguistic classification, and speech style similarity scoring, with strong alignment to human judgments. All resources will be made publicly available.
Task Vector in TTS: Toward Emotionally Expressive Dialectal Speech Synthesis
Dec 21, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in text-to-speech (TTS) have yielded remarkable improvements in naturalness and intelligibility. Building on these achievements, research has increasingly shifted toward enhancing the expressiveness of generated speech, such as dialectal and emotional TTS. However, cross-style synthesis combining both dialect and emotion remains challenging and largely unexplored, mainly due to the scarcity of dialectal data with emotional labels. To address this, we propose Hierarchical Expressive Vector (HE-Vector), a two-stage method for Emotional Dialectal TTS. In the first stage, we construct different task vectors to model dialectal and emotional styles independently, and then enhance single-style synthesis by adjusting their weights, a method we refer to as Expressive Vector (E-Vector). For the second stage, we hierarchically integrate these vectors to achieve controllable emotionally expressive dialect synthesis without requiring jointly labeled data, corresponding to Hierarchical Expressive Vector (HE-Vector). Experimental results demonstrate that HE-Vectors achieve superior performance in dialect synthesis, and promising results in synthesizing emotionally expressive dialectal speech in a zero-shot setting.
UltraVoice: Scaling Fine-Grained Style-Controlled Speech Conversations for Spoken Dialogue Models
Oct 26, 2025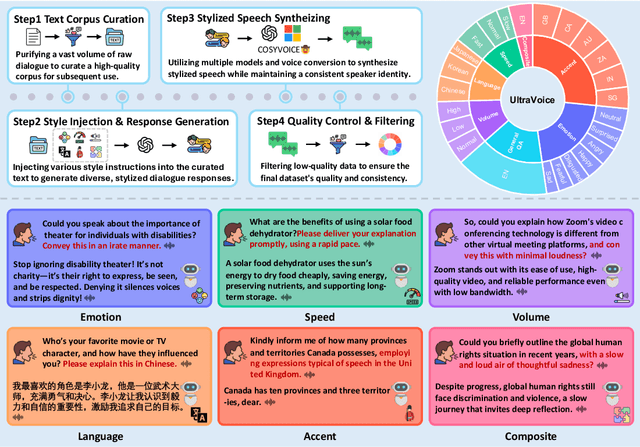
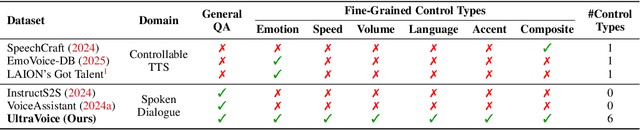
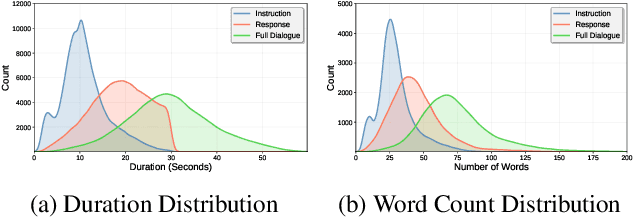

Abstract:Spoken dialogue models currently lack the ability for fine-grained speech style control, a critical capability for human-like interaction that is often overlooked in favor of purely functional capabilities like reasoning and question answering. To address this limitation, we introduce UltraVoice, the first large-scale speech dialogue dataset engineered for multiple fine-grained speech style control. Encompassing over 830 hours of speech dialogues, UltraVoice provides instructions across six key speech stylistic dimensions: emotion, speed, volume, accent, language, and composite styles. Fine-tuning leading models such as SLAM-Omni and VocalNet on UltraVoice significantly enhances their fine-grained speech stylistic controllability without degrading core conversational abilities. Specifically, our fine-tuned models achieve improvements of 29.12-42.33% in Mean Opinion Score (MOS) and 14.61-40.09 percentage points in Instruction Following Rate (IFR) on multi-dimensional control tasks designed in the UltraVoice. Moreover, on the URO-Bench benchmark, our fine-tuned models demonstrate substantial gains in core understanding, reasoning, and conversational abilities, with average improvements of +10.84% on the Basic setting and +7.87% on the Pro setting. Furthermore, the dataset's utility extends to training controllable Text-to-Speech (TTS) models, underscoring its high quality and broad applicability for expressive speech synthesis. The complete dataset and model checkpoints are available at: https://github.com/bigai-nlco/UltraVoice.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge