Yakun Song
Towards Reliable Large Audio Language Model
May 25, 2025Abstract:Recent advancements in large audio language models (LALMs) have demonstrated impressive results and promising prospects in universal understanding and reasoning across speech, music, and general sound. However, these models still lack the ability to recognize their knowledge boundaries and refuse to answer questions they don't know proactively. While there have been successful attempts to enhance the reliability of LLMs, reliable LALMs remain largely unexplored. In this paper, we systematically investigate various approaches towards reliable LALMs, including training-free methods such as multi-modal chain-of-thought (MCoT), and training-based methods such as supervised fine-tuning (SFT). Besides, we identify the limitations of previous evaluation metrics and propose a new metric, the Reliability Gain Index (RGI), to assess the effectiveness of different reliable methods. Our findings suggest that both training-free and training-based methods enhance the reliability of LALMs to different extents. Moreover, we find that awareness of reliability is a "meta ability", which can be transferred across different audio modalities, although significant structural and content differences exist among sound, music, and speech.
Language Model Can Listen While Speaking
Aug 05, 2024



Abstract:Dialogue serves as the most natural manner of human-computer interaction (HCI). Recent advancements in speech language models (SLM) have significantly enhanced speech-based conversational AI. However, these models are limited to turn-based conversation, lacking the ability to interact with humans in real-time spoken scenarios, for example, being interrupted when the generated content is not satisfactory. To address these limitations, we explore full duplex modeling (FDM) in interactive speech language models (iSLM), focusing on enhancing real-time interaction and, more explicitly, exploring the quintessential ability of interruption. We introduce a novel model design, namely listening-while-speaking language model (LSLM), an end-to-end system equipped with both listening and speaking channels. Our LSLM employs a token-based decoder-only TTS for speech generation and a streaming self-supervised learning (SSL) encoder for real-time audio input. LSLM fuses both channels for autoregressive generation and detects turn-taking in real time. Three fusion strategies -- early fusion, middle fusion, and late fusion -- are explored, with middle fusion achieving an optimal balance between speech generation and real-time interaction. Two experimental settings, command-based FDM and voice-based FDM, demonstrate LSLM's robustness to noise and sensitivity to diverse instructions. Our results highlight LSLM's capability to achieve duplex communication with minimal impact on existing systems. This study aims to advance the development of interactive speech dialogue systems, enhancing their applicability in real-world contexts.
TacoLM: GaTed Attention Equipped Codec Language Model are Efficient Zero-Shot Text to Speech Synthesizers
Jun 22, 2024Abstract:Neural codec language model (LM) has demonstrated strong capability in zero-shot text-to-speech (TTS) synthesis. However, the codec LM often suffers from limitations in inference speed and stability, due to its auto-regressive nature and implicit alignment between text and audio. In this work, to handle these challenges, we introduce a new variant of neural codec LM, namely TacoLM. Specifically, TacoLM introduces a gated attention mechanism to improve the training and inference efficiency and reduce the model size. Meanwhile, an additional gated cross-attention layer is included for each decoder layer, which improves the efficiency and content accuracy of the synthesized speech. In the evaluation of the Librispeech corpus, the proposed TacoLM achieves a better word error rate, speaker similarity, and mean opinion score, with 90% fewer parameters and 5.2 times speed up, compared with VALL-E. Demo and code is available at https://ereboas.github.io/TacoLM/.
4DBInfer: A 4D Benchmarking Toolbox for Graph-Centric Predictive Modeling on Relational DBs
Apr 28, 2024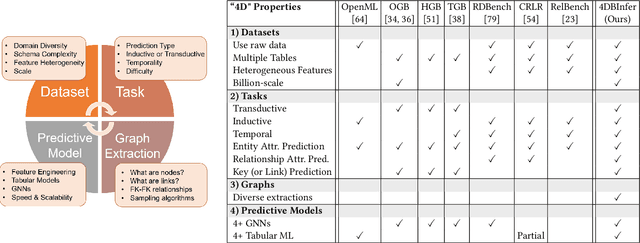
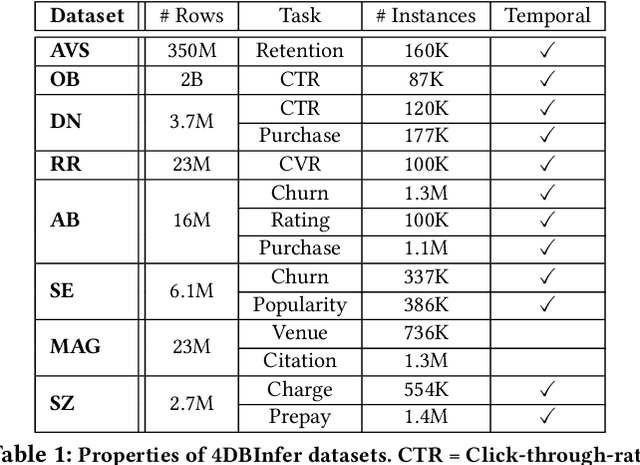
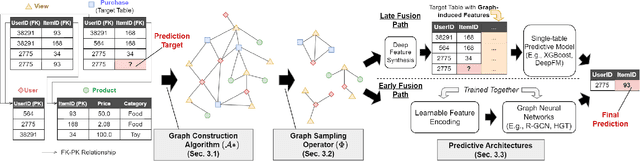
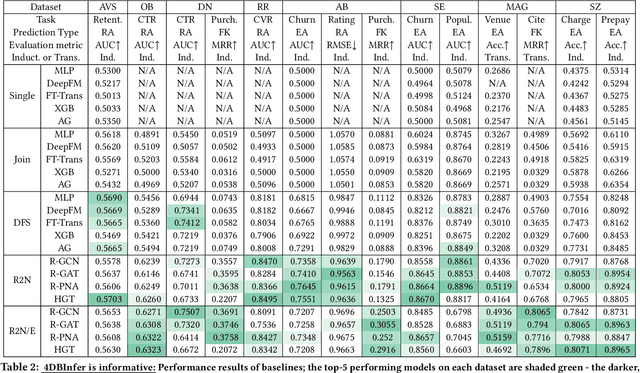
Abstract:Although RDBs store vast amounts of rich, informative data spread across interconnected tables, the progress of predictive machine learning models as applied to such tasks arguably falls well behind advances in other domains such as computer vision or natural language processing. This deficit stems, at least in part, from the lack of established/public RDB benchmarks as needed for training and evaluation purposes. As a result, related model development thus far often defaults to tabular approaches trained on ubiquitous single-table benchmarks, or on the relational side, graph-based alternatives such as GNNs applied to a completely different set of graph datasets devoid of tabular characteristics. To more precisely target RDBs lying at the nexus of these two complementary regimes, we explore a broad class of baseline models predicated on: (i) converting multi-table datasets into graphs using various strategies equipped with efficient subsampling, while preserving tabular characteristics; and (ii) trainable models with well-matched inductive biases that output predictions based on these input subgraphs. Then, to address the dearth of suitable public benchmarks and reduce siloed comparisons, we assemble a diverse collection of (i) large-scale RDB datasets and (ii) coincident predictive tasks. From a delivery standpoint, we operationalize the above four dimensions (4D) of exploration within a unified, scalable open-source toolbox called 4DBInfer. We conclude by presenting evaluations using 4DBInfer, the results of which highlight the importance of considering each such dimension in the design of RDB predictive models, as well as the limitations of more naive approaches such as simply joining adjacent tables. Our source code is released at https://github.com/awslabs/multi-table-benchmark .
ELLA-V: Stable Neural Codec Language Modeling with Alignment-guided Sequence Reordering
Jan 14, 2024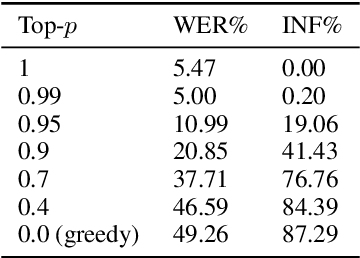
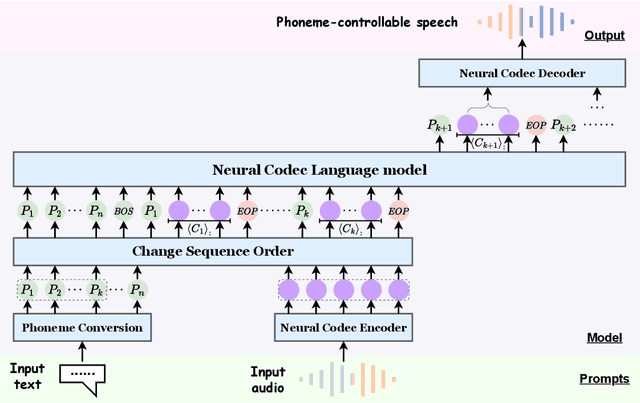
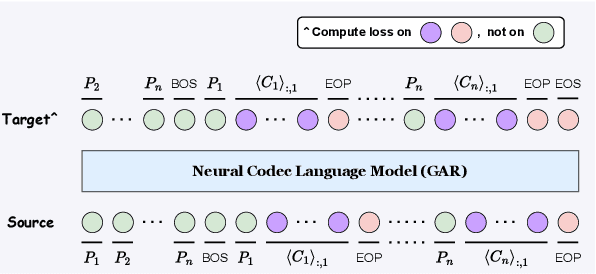
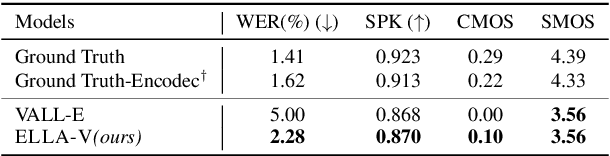
Abstract:The language model (LM) approach based on acoustic and linguistic prompts, such as VALL-E, has achieved remarkable progress in the field of zero-shot audio generation. However, existing methods still have some limitations: 1) repetitions, transpositions, and omissions in the output synthesized speech due to limited alignment constraints between audio and phoneme tokens; 2) challenges of fine-grained control over the synthesized speech with autoregressive (AR) language model; 3) infinite silence generation due to the nature of AR-based decoding, especially under the greedy strategy. To alleviate these issues, we propose ELLA-V, a simple but efficient LM-based zero-shot text-to-speech (TTS) framework, which enables fine-grained control over synthesized audio at the phoneme level. The key to ELLA-V is interleaving sequences of acoustic and phoneme tokens, where phoneme tokens appear ahead of the corresponding acoustic tokens. The experimental findings reveal that our model outperforms VALL-E in terms of accuracy and delivers more stable results using both greedy and sampling-based decoding strategies. The code of ELLA-V will be open-sourced after cleanups. Audio samples are available at https://ereboas.github.io/ELLAV/.
On the Initialization of Graph Neural Networks
Dec 05, 2023



Abstract:Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) have displayed considerable promise in graph representation learning across various applications. The core learning process requires the initialization of model weight matrices within each GNN layer, which is typically accomplished via classic initialization methods such as Xavier initialization. However, these methods were originally motivated to stabilize the variance of hidden embeddings and gradients across layers of Feedforward Neural Networks (FNNs) and Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) to avoid vanishing gradients and maintain steady information flow. In contrast, within the GNN context classical initializations disregard the impact of the input graph structure and message passing on variance. In this paper, we analyze the variance of forward and backward propagation across GNN layers and show that the variance instability of GNN initializations comes from the combined effect of the activation function, hidden dimension, graph structure and message passing. To better account for these influence factors, we propose a new initialization method for Variance Instability Reduction within GNN Optimization (Virgo), which naturally tends to equate forward and backward variances across successive layers. We conduct comprehensive experiments on 15 datasets to show that Virgo can lead to superior model performance and more stable variance at initialization on node classification, link prediction and graph classification tasks. Codes are in https://github.com/LspongebobJH/virgo_icml2023.
Fast-HuBERT: An Efficient Training Framework for Self-Supervised Speech Representation Learning
Sep 29, 2023



Abstract:Recent years have witnessed significant advancements in self-supervised learning (SSL) methods for speech-processing tasks. Various speech-based SSL models have been developed and present promising performance on a range of downstream tasks including speech recognition. However, existing speech-based SSL models face a common dilemma in terms of computational cost, which might hinder their potential application and in-depth academic research. To address this issue, we first analyze the computational cost of different modules during HuBERT pre-training and then introduce a stack of efficiency optimizations, which is named Fast-HuBERT in this paper. The proposed Fast-HuBERT can be trained in 1.1 days with 8 V100 GPUs on the Librispeech 960h benchmark, without performance degradation, resulting in a 5.2x speedup, compared to the original implementation. Moreover, we explore two well-studied techniques in the Fast-HuBERT and demonstrate consistent improvements as reported in previous work.
Set-to-Sequence Ranking-based Concept-aware Learning Path Recommendation
Jun 07, 2023



Abstract:With the development of the online education system, personalized education recommendation has played an essential role. In this paper, we focus on developing path recommendation systems that aim to generating and recommending an entire learning path to the given user in each session. Noticing that existing approaches fail to consider the correlations of concepts in the path, we propose a novel framework named Set-to-Sequence Ranking-based Concept-aware Learning Path Recommendation (SRC), which formulates the recommendation task under a set-to-sequence paradigm. Specifically, we first design a concept-aware encoder module which can capture the correlations among the input learning concepts. The outputs are then fed into a decoder module that sequentially generates a path through an attention mechanism that handles correlations between the learning and target concepts. Our recommendation policy is optimized by policy gradient. In addition, we also introduce an auxiliary module based on knowledge tracing to enhance the model's stability by evaluating students' learning effects on learning concepts. We conduct extensive experiments on two real-world public datasets and one industrial dataset, and the experimental results demonstrate the superiority and effectiveness of SRC. Code will be available at https://gitee.com/mindspore/models/tree/master/research/recommend/SRC.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge