Zhuo Chen
refer to the report for detailed contributions
ROG: Retrieval-Augmented LLM Reasoning for Complex First-Order Queries over Knowledge Graphs
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Answering first-order logic (FOL) queries over incomplete knowledge graphs (KGs) is difficult, especially for complex query structures that compose projection, intersection, union, and negation. We propose ROG, a retrieval-augmented framework that combines query-aware neighborhood retrieval with large language model (LLM) chain-of-thought reasoning. ROG decomposes a multi-operator query into a sequence of single-operator sub-queries and grounds each step in compact, query-relevant neighborhood evidence. Intermediate answer sets are cached and reused across steps, improving consistency on deep reasoning chains. This design reduces compounding errors and yields more robust inference on complex and negation-heavy queries. Overall, ROG provides a practical alternative to embedding-based logical reasoning by replacing learned operators with retrieval-grounded, step-wise inference. Experiments on standard KG reasoning benchmarks show consistent gains over strong embedding-based baselines, with the largest improvements on high-complexity and negation-heavy query types.
UniForce: A Unified Latent Force Model for Robot Manipulation with Diverse Tactile Sensors
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:Force sensing is essential for dexterous robot manipulation, but scaling force-aware policy learning is hindered by the heterogeneity of tactile sensors. Differences in sensing principles (e.g., optical vs. magnetic), form factors, and materials typically require sensor-specific data collection, calibration, and model training, thereby limiting generalisability. We propose UniForce, a novel unified tactile representation learning framework that learns a shared latent force space across diverse tactile sensors. UniForce reduces cross-sensor domain shift by jointly modeling inverse dynamics (image-to-force) and forward dynamics (force-to-image), constrained by force equilibrium and image reconstruction losses to produce force-grounded representations. To avoid reliance on expensive external force/torque (F/T) sensors, we exploit static equilibrium and collect force-paired data via direct sensor--object--sensor interactions, enabling cross-sensor alignment with contact force. The resulting universal tactile encoder can be plugged into downstream force-aware robot manipulation tasks with zero-shot transfer, without retraining or finetuning. Extensive experiments on heterogeneous tactile sensors including GelSight, TacTip, and uSkin, demonstrate consistent improvements in force estimation over prior methods, and enable effective cross-sensor coordination in Vision-Tactile-Language-Action (VTLA) models for a robotic wiping task. Code and datasets will be released.
UniMorphGrasp: Diffusion Model with Morphology-Awareness for Cross-Embodiment Dexterous Grasp Generation
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:Cross-embodiment dexterous grasping aims to generate stable and diverse grasps for robotic hands with heterogeneous kinematic structures. Existing methods are often tailored to specific hand designs and fail to generalize to unseen hand morphologies outside the training distribution. To address these limitations, we propose \textbf{UniMorphGrasp}, a diffusion-based framework that incorporates hand morphological information into the grasp generation process for unified cross-embodiment grasp synthesis. The proposed approach maps grasps from diverse robotic hands into a unified human-like canonical hand pose representation, providing a common space for learning. Grasp generation is then conditioned on structured representations of hand kinematics, encoded as graphs derived from hand configurations, together with object geometry. In addition, a loss function is introduced that exploits the hierarchical organization of hand kinematics to guide joint-level supervision. Extensive experiments demonstrate that UniMorphGrasp achieves state-of-the-art performance on existing dexterous grasp benchmarks and exhibits strong zero-shot generalization to previously unseen hand structures, enabling scalable and practical cross-embodiment grasp deployment.
Efficient Multimodal Planning Agent for Visual Question-Answering
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Visual Question-Answering (VQA) is a challenging multimodal task that requires integrating visual and textual information to generate accurate responses. While multimodal Retrieval-Augmented Generation (mRAG) has shown promise in enhancing VQA systems by providing more evidence on both image and text sides, the default procedure that addresses VQA queries, especially the knowledge-intensive ones, often relies on multi-stage pipelines of mRAG with inherent dependencies. To mitigate the inefficiency limitations while maintaining VQA task performance, this paper proposes a method that trains a multimodal planning agent, dynamically decomposing the mRAG pipeline to solve the VQA task. Our method optimizes the trade-off between efficiency and effectiveness by training the agent to intelligently determine the necessity of each mRAG step. In our experiments, the agent can help reduce redundant computations, cutting search time by over 60\% compared to existing methods and decreasing costly tool calls. Meanwhile, experiments demonstrate that our method outperforms all baselines, including a Deep Research agent and a carefully designed prompt-based method, on average over six various datasets. Code will be released.
RAIR: A Rule-Aware Benchmark Uniting Challenging Long-Tail and Visual Salience Subset for E-commerce Relevance Assessment
Dec 31, 2025Abstract:Search relevance plays a central role in web e-commerce. While large language models (LLMs) have shown significant results on relevance task, existing benchmarks lack sufficient complexity for comprehensive model assessment, resulting in an absence of standardized relevance evaluation metrics across the industry. To address this limitation, we propose Rule-Aware benchmark with Image for Relevance assessment(RAIR), a Chinese dataset derived from real-world scenarios. RAIR established a standardized framework for relevance assessment and provides a set of universal rules, which forms the foundation for standardized evaluation. Additionally, RAIR analyzes essential capabilities required for current relevance models and introduces a comprehensive dataset consists of three subset: (1) a general subset with industry-balanced sampling to evaluate fundamental model competencies; (2) a long-tail hard subset focus on challenging cases to assess performance limits; (3) a visual salience subset for evaluating multimodal understanding capabilities. We conducted experiments on RAIR using 14 open and closed-source models. The results demonstrate that RAIR presents sufficient challenges even for GPT-5, which achieved the best performance. RAIR data are now available, serving as an industry benchmark for relevance assessment while providing new insights into general LLM and Visual Language Model(VLM) evaluation.
RobustMask: Certified Robustness against Adversarial Neural Ranking Attack via Randomized Masking
Dec 29, 2025Abstract:Neural ranking models have achieved remarkable progress and are now widely deployed in real-world applications such as Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG). However, like other neural architectures, they remain vulnerable to adversarial manipulations: subtle character-, word-, or phrase-level perturbations can poison retrieval results and artificially promote targeted candidates, undermining the integrity of search engines and downstream systems. Existing defenses either rely on heuristics with poor generalization or on certified methods that assume overly strong adversarial knowledge, limiting their practical use. To address these challenges, we propose RobustMask, a novel defense that combines the context-prediction capability of pretrained language models with a randomized masking-based smoothing mechanism. Our approach strengthens neural ranking models against adversarial perturbations at the character, word, and phrase levels. Leveraging both the pairwise comparison ability of ranking models and probabilistic statistical analysis, we provide a theoretical proof of RobustMask's certified top-K robustness. Extensive experiments further demonstrate that RobustMask successfully certifies over 20% of candidate documents within the top-10 ranking positions against adversarial perturbations affecting up to 30% of their content. These results highlight the effectiveness of RobustMask in enhancing the adversarial robustness of neural ranking models, marking a significant step toward providing stronger security guarantees for real-world retrieval systems.
Seedance 1.5 pro: A Native Audio-Visual Joint Generation Foundation Model
Dec 23, 2025Abstract:Recent strides in video generation have paved the way for unified audio-visual generation. In this work, we present Seedance 1.5 pro, a foundational model engineered specifically for native, joint audio-video generation. Leveraging a dual-branch Diffusion Transformer architecture, the model integrates a cross-modal joint module with a specialized multi-stage data pipeline, achieving exceptional audio-visual synchronization and superior generation quality. To ensure practical utility, we implement meticulous post-training optimizations, including Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) on high-quality datasets and Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) with multi-dimensional reward models. Furthermore, we introduce an acceleration framework that boosts inference speed by over 10X. Seedance 1.5 pro distinguishes itself through precise multilingual and dialect lip-syncing, dynamic cinematic camera control, and enhanced narrative coherence, positioning it as a robust engine for professional-grade content creation. Seedance 1.5 pro is now accessible on Volcano Engine at https://console.volcengine.com/ark/region:ark+cn-beijing/experience/vision?type=GenVideo.
A Large Language Model Based Method for Complex Logical Reasoning over Knowledge Graphs
Dec 22, 2025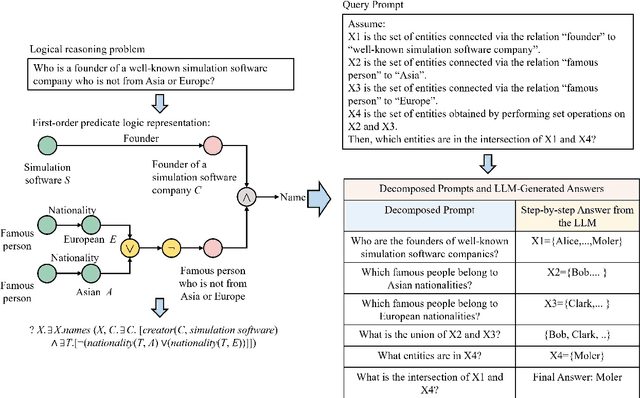
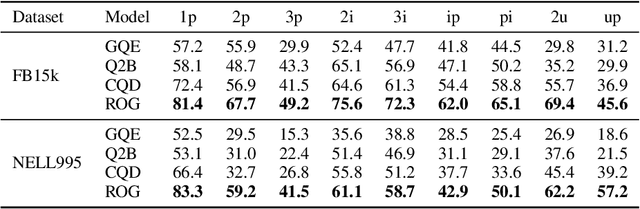
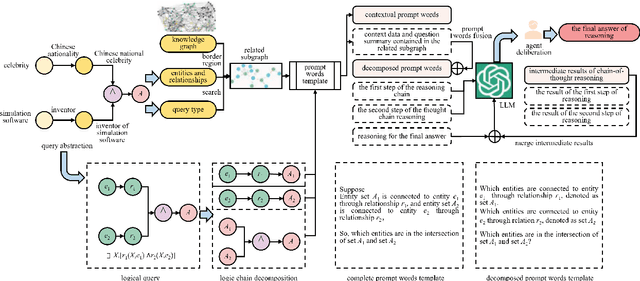
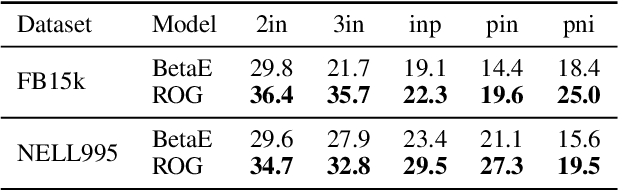
Abstract:Reasoning over knowledge graphs (KGs) with first-order logic (FOL) queries is challenging due to the inherent incompleteness of real-world KGs and the compositional complexity of logical query structures. Most existing methods rely on embedding entities and relations into continuous geometric spaces and answer queries via differentiable set operations. While effective for simple query patterns, these approaches often struggle to generalize to complex queries involving multiple operators, deeper reasoning chains, or heterogeneous KG schemas. We propose ROG (Reasoning Over knowledge Graphs with large language models), an ensemble-style framework that combines query-aware KG neighborhood retrieval with large language model (LLM)-based chain-of-thought reasoning. ROG decomposes complex FOL queries into sequences of simpler sub-queries, retrieves compact, query-relevant subgraphs as contextual evidence, and performs step-by-step logical inference using an LLM, avoiding the need for task-specific embedding optimization. Experiments on standard KG reasoning benchmarks demonstrate that ROG consistently outperforms strong embedding-based baselines in terms of mean reciprocal rank (MRR), with particularly notable gains on high-complexity query types. These results suggest that integrating structured KG retrieval with LLM-driven logical reasoning offers a robust and effective alternative for complex KG reasoning tasks.
The Devil is in Attention Sharing: Improving Complex Non-rigid Image Editing Faithfulness via Attention Synergy
Dec 17, 2025Abstract:Training-free image editing with large diffusion models has become practical, yet faithfully performing complex non-rigid edits (e.g., pose or shape changes) remains highly challenging. We identify a key underlying cause: attention collapse in existing attention sharing mechanisms, where either positional embeddings or semantic features dominate visual content retrieval, leading to over-editing or under-editing. To address this issue, we introduce SynPS, a method that Synergistically leverages Positional embeddings and Semantic information for faithful non-rigid image editing. We first propose an editing measurement that quantifies the required editing magnitude at each denoising step. Based on this measurement, we design an attention synergy pipeline that dynamically modulates the influence of positional embeddings, enabling SynPS to balance semantic modifications and fidelity preservation. By adaptively integrating positional and semantic cues, SynPS effectively avoids both over- and under-editing. Extensive experiments on public and newly curated benchmarks demonstrate the superior performance and faithfulness of our approach.
POLAR: A Portrait OLAT Dataset and Generative Framework for Illumination-Aware Face Modeling
Dec 16, 2025Abstract:Face relighting aims to synthesize realistic portraits under novel illumination while preserving identity and geometry. However, progress remains constrained by the limited availability of large-scale, physically consistent illumination data. To address this, we introduce POLAR, a large-scale and physically calibrated One-Light-at-a-Time (OLAT) dataset containing over 200 subjects captured under 156 lighting directions, multiple views, and diverse expressions. Building upon POLAR, we develop a flow-based generative model POLARNet that predicts per-light OLAT responses from a single portrait, capturing fine-grained and direction-aware illumination effects while preserving facial identity. Unlike diffusion or background-conditioned methods that rely on statistical or contextual cues, our formulation models illumination as a continuous, physically interpretable transformation between lighting states, enabling scalable and controllable relighting. Together, POLAR and POLARNet form a unified illumination learning framework that links real data, generative synthesis, and physically grounded relighting, establishing a self-sustaining "chicken-and-egg" cycle for scalable and reproducible portrait illumination. Our project page: https://rex0191.github.io/POLAR/.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge