Haohan Weng
refer to the report for detailed contributions
Hunyuan3D Studio: End-to-End AI Pipeline for Game-Ready 3D Asset Generation
Sep 16, 2025



Abstract:The creation of high-quality 3D assets, a cornerstone of modern game development, has long been characterized by labor-intensive and specialized workflows. This paper presents Hunyuan3D Studio, an end-to-end AI-powered content creation platform designed to revolutionize the game production pipeline by automating and streamlining the generation of game-ready 3D assets. At its core, Hunyuan3D Studio integrates a suite of advanced neural modules (such as Part-level 3D Generation, Polygon Generation, Semantic UV, etc.) into a cohesive and user-friendly system. This unified framework allows for the rapid transformation of a single concept image or textual description into a fully-realized, production-quality 3D model complete with optimized geometry and high-fidelity PBR textures. We demonstrate that assets generated by Hunyuan3D Studio are not only visually compelling but also adhere to the stringent technical requirements of contemporary game engines, significantly reducing iteration time and lowering the barrier to entry for 3D content creation. By providing a seamless bridge from creative intent to technical asset, Hunyuan3D Studio represents a significant leap forward for AI-assisted workflows in game development and interactive media.
Mesh Silksong: Auto-Regressive Mesh Generation as Weaving Silk
Jul 03, 2025Abstract:We introduce Mesh Silksong, a compact and efficient mesh representation tailored to generate the polygon mesh in an auto-regressive manner akin to silk weaving. Existing mesh tokenization methods always produce token sequences with repeated vertex tokens, wasting the network capability. Therefore, our approach tokenizes mesh vertices by accessing each mesh vertice only once, reduces the token sequence's redundancy by 50\%, and achieves a state-of-the-art compression rate of approximately 22\%. Furthermore, Mesh Silksong produces polygon meshes with superior geometric properties, including manifold topology, watertight detection, and consistent face normals, which are critical for practical applications. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach, showcasing not only intricate mesh generation but also significantly improved geometric integrity.
Mesh-RFT: Enhancing Mesh Generation via Fine-grained Reinforcement Fine-Tuning
May 22, 2025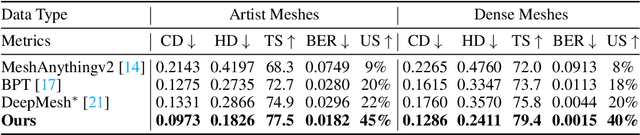
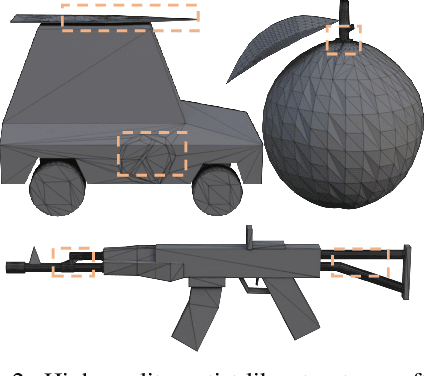
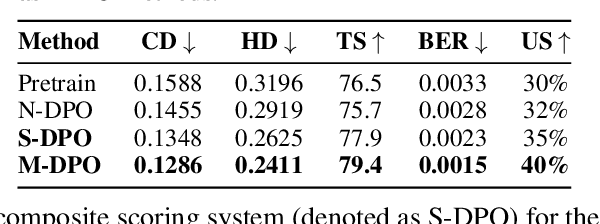
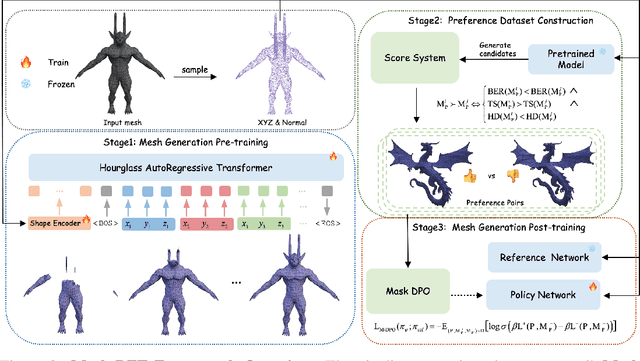
Abstract:Existing pretrained models for 3D mesh generation often suffer from data biases and produce low-quality results, while global reinforcement learning (RL) methods rely on object-level rewards that struggle to capture local structure details. To address these challenges, we present \textbf{Mesh-RFT}, a novel fine-grained reinforcement fine-tuning framework that employs Masked Direct Preference Optimization (M-DPO) to enable localized refinement via quality-aware face masking. To facilitate efficient quality evaluation, we introduce an objective topology-aware scoring system to evaluate geometric integrity and topological regularity at both object and face levels through two metrics: Boundary Edge Ratio (BER) and Topology Score (TS). By integrating these metrics into a fine-grained RL strategy, Mesh-RFT becomes the first method to optimize mesh quality at the granularity of individual faces, resolving localized errors while preserving global coherence. Experiment results show that our M-DPO approach reduces Hausdorff Distance (HD) by 24.6\% and improves Topology Score (TS) by 3.8\% over pre-trained models, while outperforming global DPO methods with a 17.4\% HD reduction and 4.9\% TS gain. These results demonstrate Mesh-RFT's ability to improve geometric integrity and topological regularity, achieving new state-of-the-art performance in production-ready mesh generation. Project Page: \href{https://hitcslj.github.io/mesh-rft/}{this https URL}.
FreeMesh: Boosting Mesh Generation with Coordinates Merging
May 19, 2025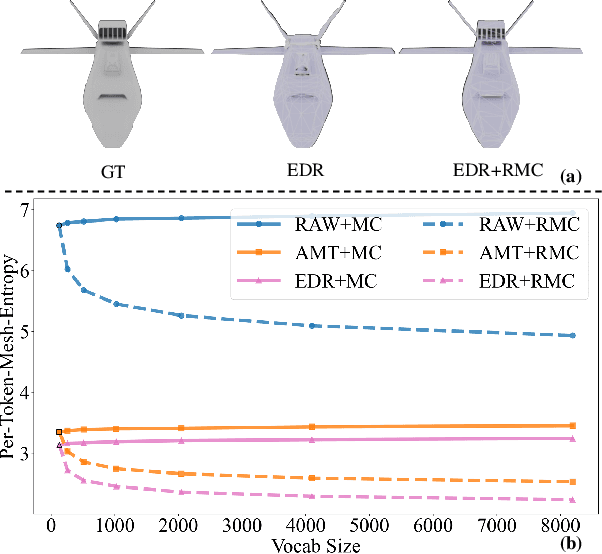
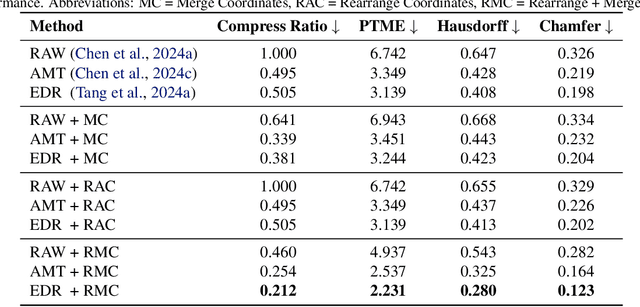
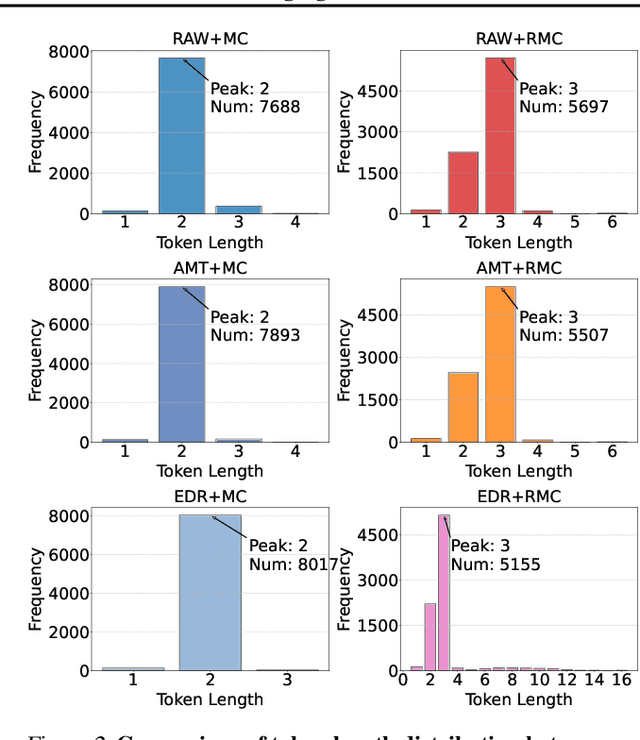
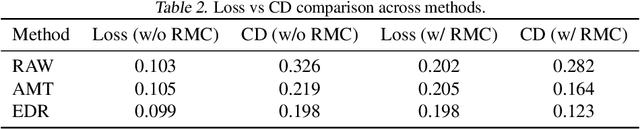
Abstract:The next-coordinate prediction paradigm has emerged as the de facto standard in current auto-regressive mesh generation methods. Despite their effectiveness, there is no efficient measurement for the various tokenizers that serialize meshes into sequences. In this paper, we introduce a new metric Per-Token-Mesh-Entropy (PTME) to evaluate the existing mesh tokenizers theoretically without any training. Building upon PTME, we propose a plug-and-play tokenization technique called coordinate merging. It further improves the compression ratios of existing tokenizers by rearranging and merging the most frequent patterns of coordinates. Through experiments on various tokenization methods like MeshXL, MeshAnything V2, and Edgerunner, we further validate the performance of our method. We hope that the proposed PTME and coordinate merging can enhance the existing mesh tokenizers and guide the further development of native mesh generation.
Nautilus: Locality-aware Autoencoder for Scalable Mesh Generation
Jan 27, 2025



Abstract:Triangle meshes are fundamental to 3D applications, enabling efficient modification and rasterization while maintaining compatibility with standard rendering pipelines. However, current automatic mesh generation methods typically rely on intermediate representations that lack the continuous surface quality inherent to meshes. Converting these representations into meshes produces dense, suboptimal outputs. Although recent autoregressive approaches demonstrate promise in directly modeling mesh vertices and faces, they are constrained by the limitation in face count, scalability, and structural fidelity. To address these challenges, we propose Nautilus, a locality-aware autoencoder for artist-like mesh generation that leverages the local properties of manifold meshes to achieve structural fidelity and efficient representation. Our approach introduces a novel tokenization algorithm that preserves face proximity relationships and compresses sequence length through locally shared vertices and edges, enabling the generation of meshes with an unprecedented scale of up to 5,000 faces. Furthermore, we develop a Dual-stream Point Conditioner that provides multi-scale geometric guidance, ensuring global consistency and local structural fidelity by capturing fine-grained geometric features. Extensive experiments demonstrate that Nautilus significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods in both fidelity and scalability. The project page will be released to https://nautilusmeshgen.github.io.
Hunyuan3D 2.0: Scaling Diffusion Models for High Resolution Textured 3D Assets Generation
Jan 21, 2025



Abstract:We present Hunyuan3D 2.0, an advanced large-scale 3D synthesis system for generating high-resolution textured 3D assets. This system includes two foundation components: a large-scale shape generation model -- Hunyuan3D-DiT, and a large-scale texture synthesis model -- Hunyuan3D-Paint. The shape generative model, built on a scalable flow-based diffusion transformer, aims to create geometry that properly aligns with a given condition image, laying a solid foundation for downstream applications. The texture synthesis model, benefiting from strong geometric and diffusion priors, produces high-resolution and vibrant texture maps for either generated or hand-crafted meshes. Furthermore, we build Hunyuan3D-Studio -- a versatile, user-friendly production platform that simplifies the re-creation process of 3D assets. It allows both professional and amateur users to manipulate or even animate their meshes efficiently. We systematically evaluate our models, showing that Hunyuan3D 2.0 outperforms previous state-of-the-art models, including the open-source models and closed-source models in geometry details, condition alignment, texture quality, and etc. Hunyuan3D 2.0 is publicly released in order to fill the gaps in the open-source 3D community for large-scale foundation generative models. The code and pre-trained weights of our models are available at: https://github.com/Tencent/Hunyuan3D-2
Scaling Mesh Generation via Compressive Tokenization
Nov 11, 2024



Abstract:We propose a compressive yet effective mesh representation, Blocked and Patchified Tokenization (BPT), facilitating the generation of meshes exceeding 8k faces. BPT compresses mesh sequences by employing block-wise indexing and patch aggregation, reducing their length by approximately 75\% compared to the original sequences. This compression milestone unlocks the potential to utilize mesh data with significantly more faces, thereby enhancing detail richness and improving generation robustness. Empowered with the BPT, we have built a foundation mesh generative model training on scaled mesh data to support flexible control for point clouds and images. Our model demonstrates the capability to generate meshes with intricate details and accurate topology, achieving SoTA performance on mesh generation and reaching the level for direct product usage.
PivotMesh: Generic 3D Mesh Generation via Pivot Vertices Guidance
May 27, 2024



Abstract:Generating compact and sharply detailed 3D meshes poses a significant challenge for current 3D generative models. Different from extracting dense meshes from neural representation, some recent works try to model the native mesh distribution (i.e., a set of triangles), which generates more compact results as humans crafted. However, due to the complexity and variety of mesh topology, these methods are typically limited to small datasets with specific categories and are hard to extend. In this paper, we introduce a generic and scalable mesh generation framework PivotMesh, which makes an initial attempt to extend the native mesh generation to large-scale datasets. We employ a transformer-based auto-encoder to encode meshes into discrete tokens and decode them from face level to vertex level hierarchically. Subsequently, to model the complex typology, we first learn to generate pivot vertices as coarse mesh representation and then generate the complete mesh tokens with the same auto-regressive Transformer. This reduces the difficulty compared with directly modeling the mesh distribution and further improves the model controllability. PivotMesh demonstrates its versatility by effectively learning from both small datasets like Shapenet, and large-scale datasets like Objaverse and Objaverse-xl. Extensive experiments indicate that PivotMesh can generate compact and sharp 3D meshes across various categories, highlighting its great potential for native mesh modeling.
Desigen: A Pipeline for Controllable Design Template Generation
Mar 14, 2024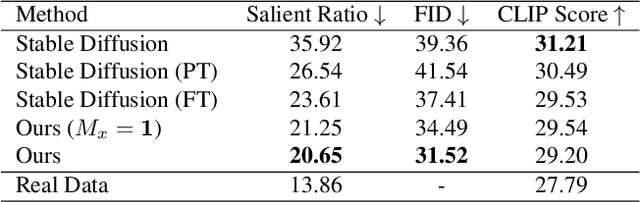
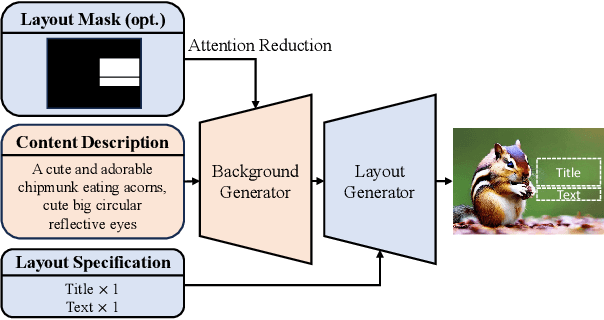
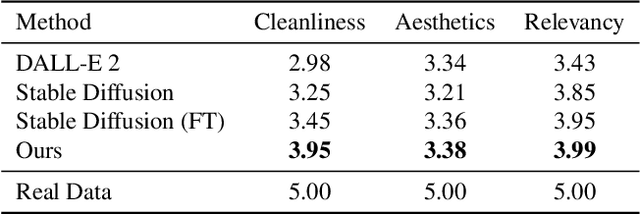
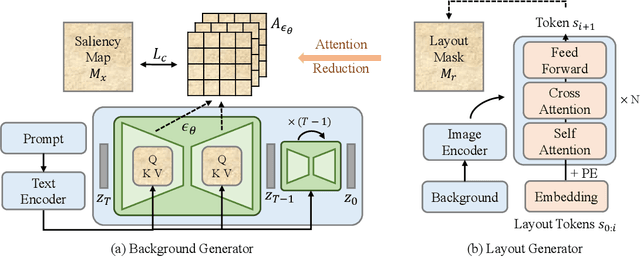
Abstract:Templates serve as a good starting point to implement a design (e.g., banner, slide) but it takes great effort from designers to manually create. In this paper, we present Desigen, an automatic template creation pipeline which generates background images as well as harmonious layout elements over the background. Different from natural images, a background image should preserve enough non-salient space for the overlaying layout elements. To equip existing advanced diffusion-based models with stronger spatial control, we propose two simple but effective techniques to constrain the saliency distribution and reduce the attention weight in desired regions during the background generation process. Then conditioned on the background, we synthesize the layout with a Transformer-based autoregressive generator. To achieve a more harmonious composition, we propose an iterative inference strategy to adjust the synthesized background and layout in multiple rounds. We constructed a design dataset with more than 40k advertisement banners to verify our approach. Extensive experiments demonstrate that the proposed pipeline generates high-quality templates comparable to human designers. More than a single-page design, we further show an application of presentation generation that outputs a set of theme-consistent slides. The data and code are available at https://whaohan.github.io/desigen.
Consistent123: Improve Consistency for One Image to 3D Object Synthesis
Oct 12, 2023Abstract:Large image diffusion models enable novel view synthesis with high quality and excellent zero-shot capability. However, such models based on image-to-image translation have no guarantee of view consistency, limiting the performance for downstream tasks like 3D reconstruction and image-to-3D generation. To empower consistency, we propose Consistent123 to synthesize novel views simultaneously by incorporating additional cross-view attention layers and the shared self-attention mechanism. The proposed attention mechanism improves the interaction across all synthesized views, as well as the alignment between the condition view and novel views. In the sampling stage, such architecture supports simultaneously generating an arbitrary number of views while training at a fixed length. We also introduce a progressive classifier-free guidance strategy to achieve the trade-off between texture and geometry for synthesized object views. Qualitative and quantitative experiments show that Consistent123 outperforms baselines in view consistency by a large margin. Furthermore, we demonstrate a significant improvement of Consistent123 on varying downstream tasks, showing its great potential in the 3D generation field. The project page is available at consistent-123.github.io.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge