Tianyu Yang
Alibaba DAMO Academy
Infinite-World: Scaling Interactive World Models to 1000-Frame Horizons via Pose-Free Hierarchical Memory
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:We propose Infinite-World, a robust interactive world model capable of maintaining coherent visual memory over 1000+ frames in complex real-world environments. While existing world models can be efficiently optimized on synthetic data with perfect ground-truth, they lack an effective training paradigm for real-world videos due to noisy pose estimations and the scarcity of viewpoint revisits. To bridge this gap, we first introduce a Hierarchical Pose-free Memory Compressor (HPMC) that recursively distills historical latents into a fixed-budget representation. By jointly optimizing the compressor with the generative backbone, HPMC enables the model to autonomously anchor generations in the distant past with bounded computational cost, eliminating the need for explicit geometric priors. Second, we propose an Uncertainty-aware Action Labeling module that discretizes continuous motion into a tri-state logic. This strategy maximizes the utilization of raw video data while shielding the deterministic action space from being corrupted by noisy trajectories, ensuring robust action-response learning. Furthermore, guided by insights from a pilot toy study, we employ a Revisit-Dense Finetuning Strategy using a compact, 30-minute dataset to efficiently activate the model's long-range loop-closure capabilities. Extensive experiments, including objective metrics and user studies, demonstrate that Infinite-World achieves superior performance in visual quality, action controllability, and spatial consistency.
ReCALL: Recalibrating Capability Degradation for MLLM-based Composed Image Retrieval
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Composed Image Retrieval (CIR) aims to retrieve target images based on a hybrid query comprising a reference image and a modification text. Early dual-tower Vision-Language Models (VLMs) struggle with cross-modality compositional reasoning required for this task. Recently, adapting generative Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) for retrieval offers a promising direction. However, we identify that this adaptation strategy overlooks a fundamental issue: adapting a generative MLLM into a single-embedding discriminative retriever triggers a paradigm conflict, which leads to Capability Degradation - the deterioration of native fine-grained reasoning after retrieval adaptation. To address this challenge, we propose ReCALL (Recalibrating Capability Degradation), a model-agnostic framework that follows a diagnose-generate-refine pipeline: Firstly, we diagnose cognitive blind spots of the retriever via self-guided informative instance mining. Next, we generate corrective instructions and triplets by CoT prompting the foundation MLLM and conduct quality control with VQA-based consistency filtering. Finally, we refine the retriever through continual training on these triplets with a grouped contrastive scheme, thereby internalizing fine-grained visual-semantic distinctions and realigning the discriminative embedding space of retriever with intrinsic compositional reasoning within the MLLM. Extensive experiments on CIRR and FashionIQ show that ReCALL consistently recalibrates degraded capabilities and achieves state-of-the-art performance. Code will be released soon.
Active Intelligence in Video Avatars via Closed-loop World Modeling
Dec 23, 2025Abstract:Current video avatar generation methods excel at identity preservation and motion alignment but lack genuine agency, they cannot autonomously pursue long-term goals through adaptive environmental interaction. We address this by introducing L-IVA (Long-horizon Interactive Visual Avatar), a task and benchmark for evaluating goal-directed planning in stochastic generative environments, and ORCA (Online Reasoning and Cognitive Architecture), the first framework enabling active intelligence in video avatars. ORCA embodies Internal World Model (IWM) capabilities through two key innovations: (1) a closed-loop OTAR cycle (Observe-Think-Act-Reflect) that maintains robust state tracking under generative uncertainty by continuously verifying predicted outcomes against actual generations, and (2) a hierarchical dual-system architecture where System 2 performs strategic reasoning with state prediction while System 1 translates abstract plans into precise, model-specific action captions. By formulating avatar control as a POMDP and implementing continuous belief updating with outcome verification, ORCA enables autonomous multi-step task completion in open-domain scenarios. Extensive experiments demonstrate that ORCA significantly outperforms open-loop and non-reflective baselines in task success rate and behavioral coherence, validating our IWM-inspired design for advancing video avatar intelligence from passive animation to active, goal-oriented behavior.
Explainable AI-Generated Image Detection RewardBench
Nov 15, 2025Abstract:Conventional, classification-based AI-generated image detection methods cannot explain why an image is considered real or AI-generated in a way a human expert would, which reduces the trustworthiness and persuasiveness of these detection tools for real-world applications. Leveraging Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) has recently become a trending solution to this issue. Further, to evaluate the quality of generated explanations, a common approach is to adopt an "MLLM as a judge" methodology to evaluate explanations generated by other MLLMs. However, how well those MLLMs perform when judging explanations for AI-generated image detection generated by themselves or other MLLMs has not been well studied. We therefore propose \textbf{XAIGID-RewardBench}, the first benchmark designed to evaluate the ability of current MLLMs to judge the quality of explanations about whether an image is real or AI-generated. The benchmark consists of approximately 3,000 annotated triplets sourced from various image generation models and MLLMs as policy models (detectors) to assess the capabilities of current MLLMs as reward models (judges). Our results show that the current best reward model scored 88.76\% on this benchmark (while human inter-annotator agreement reaches 98.30\%), demonstrating that a visible gap remains between the reasoning abilities of today's MLLMs and human-level performance. In addition, we provide an analysis of common pitfalls that these models frequently encounter. Code and benchmark are available at https://github.com/RewardBench/XAIGID-RewardBench.
Near-Field Integrated Imaging and Communication in Distributed MIMO Networks
Aug 24, 2025Abstract:In this work, we propose a general framework for wireless imaging in distributed MIMO wideband communication systems, considering multi-view non-isotropic targets and near-field propagation effects. For indoor scenarios where the objective is to image small-scale objects with high resolution, we propose a range migration algorithm (RMA)-based scheme using three kinds of array architectures: the full array, boundary array, and distributed boundary array. With non-isotropic near-field channels, we establish the Fourier transformation (FT)-based relationship between the imaging reflectivity and the distributed spatial-domain signals and discuss the corresponding theoretical properties. Next, for outdoor scenarios where the objective is to reconstruct the large-scale three-dimensional (3D) environment with coarse resolution, we propose a sparse Bayesian learning (SBL)-based algorithm to solve the multiple measurement vector (MMV) problem, which further addresses the non-isotropic reflectivity across different subcarriers. Numerical results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed algorithms in acquiring high-resolution small objects and accurately reconstructing large-scale environments.
LlamaSeg: Image Segmentation via Autoregressive Mask Generation
May 26, 2025Abstract:We present LlamaSeg, a visual autoregressive framework that unifies multiple image segmentation tasks via natural language instructions. We reformulate image segmentation as a visual generation problem, representing masks as "visual" tokens and employing a LLaMA-style Transformer to predict them directly from image inputs. By adhering to the next-token prediction paradigm, our approach naturally integrates segmentation tasks into autoregressive architectures. To support large-scale training, we introduce a data annotation pipeline and construct the SA-OVRS dataset, which contains 2M segmentation masks annotated with over 5,800 open-vocabulary labels or diverse textual descriptions, covering a wide spectrum of real-world scenarios. This enables our model to localize objects in images based on text prompts and to generate fine-grained masks. To more accurately evaluate the quality of masks produced by visual generative models, we further propose a composite metric that combines Intersection over Union (IoU) with Average Hausdorff Distance (AHD), offering a more precise assessment of contour fidelity. Experimental results demonstrate that our method surpasses existing generative models across multiple datasets and yields more detailed segmentation masks.
ReEx-SQL: Reasoning with Execution-Aware Reinforcement Learning for Text-to-SQL
May 19, 2025Abstract:In Text-to-SQL, execution feedback is essential for guiding large language models (LLMs) to reason accurately and generate reliable SQL queries. However, existing methods treat execution feedback solely as a post-hoc signal for correction or selection, failing to integrate it into the generation process. This limitation hinders their ability to address reasoning errors as they occur, ultimately reducing query accuracy and robustness. To address this issue, we propose ReEx-SQL (Reasoning with Execution-Aware Reinforcement Learning), a framework for Text-to-SQL that enables models to interact with the database during decoding and dynamically adjust their reasoning based on execution feedback. ReEx-SQL introduces an execution-aware reasoning paradigm that interleaves intermediate SQL execution into reasoning paths, facilitating context-sensitive revisions. It achieves this through structured prompts with markup tags and a stepwise rollout strategy that integrates execution feedback into each stage of generation. To supervise policy learning, we develop a composite reward function that includes an exploration reward, explicitly encouraging effective database interaction. Additionally, ReEx-SQL adopts a tree-based decoding strategy to support exploratory reasoning, enabling dynamic expansion of alternative reasoning paths. Notably, ReEx-SQL achieves 88.8% on Spider and 64.9% on BIRD at the 7B scale, surpassing the standard reasoning baseline by 2.7% and 2.6%, respectively. It also shows robustness, achieving 85.2% on Spider-Realistic with leading performance. In addition, its tree-structured decoding improves efficiency and performance over linear decoding, reducing inference time by 51.9% on the BIRD development set.
Holographic MIMO Multi-Cell Communications
Feb 23, 2025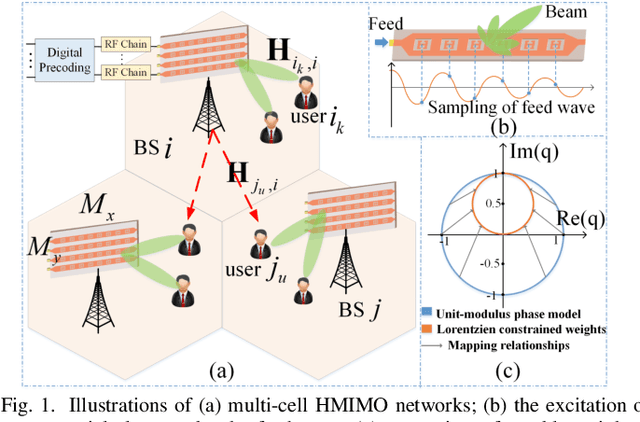
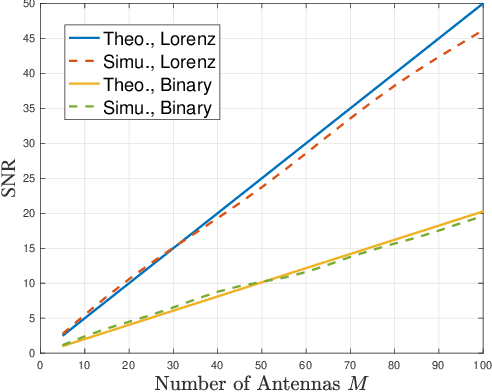
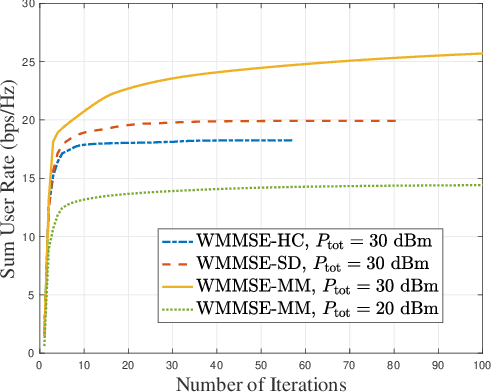
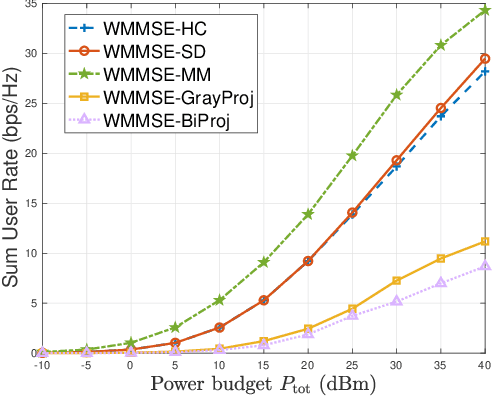
Abstract:Metamaterial antennas are appealing for next-generation wireless networks due to their simplified hardware and much-reduced size, power, and cost. This paper investigates the holographic multiple-input multiple-output (HMIMO)-aided multi-cell systems with practical per-radio frequency (RF) chain power constraints. With multiple antennas at both base stations (BSs) and users, we design the baseband digital precoder and the tuning response of HMIMO metamaterial elements to maximize the weighted sum user rate. Specifically, under the framework of block coordinate descent (BCD) and weighted minimum mean square error (WMMSE) techniques, we derive the low-complexity closed-form solution for baseband precoder without requiring bisection search and matrix inversion. Then, for the design of HMIMO metamaterial elements under binary tuning constraints, we first propose a low-complexity suboptimal algorithm with closed-form solutions by exploiting the hidden convexity (HC) in the quadratic problem and then further propose an accelerated sphere decoding (SD)-based algorithm which yields global optimal solution in the iteration. For HMIMO metamaterial element design under the Lorentzian-constrained phase model, we propose a maximization-minorization (MM) algorithm with closed-form solutions at each iteration step. Furthermore, in a simplified multiple-input single-output (MISO) scenario, we derive the scaling law of downlink single-to-noise (SNR) for HMIMO with binary and Lorentzian tuning constraints and theoretically compare it with conventional fully digital/hybrid arrays. Simulation results demonstrate the effectiveness of our algorithms compared to benchmarks and the benefits of HMIMO compared to conventional arrays.
Beyond Single-Value Metrics: Evaluating and Enhancing LLM Unlearning with Cognitive Diagnosis
Feb 19, 2025Abstract:Due to the widespread use of LLMs and the rising critical ethical and safety concerns, LLM unlearning methods have been developed to remove harmful knowledge and undesirable capabilities. In this context, evaluations are mostly based on single-value metrics such as QA accuracy. However, these metrics often fail to capture the nuanced retention of harmful knowledge components, making it difficult to assess the true effectiveness of unlearning. To address this issue, we propose UNCD (UNlearning evaluation via Cognitive Diagnosis), a novel framework that leverages Cognitive Diagnosis Modeling for fine-grained evaluation of LLM unlearning. Our dedicated benchmark, UNCD-Cyber, provides a detailed assessment of the removal of dangerous capabilities. Moreover, we introduce UNCD-Agent, which refines unlearning by diagnosing knowledge remnants and generating targeted unlearning data. Extensive experiments across eight unlearning methods and two base models demonstrate that UNCD not only enhances evaluation but also effectively facilitates the removal of harmful LLM abilities.
CLIPErase: Efficient Unlearning of Visual-Textual Associations in CLIP
Oct 30, 2024



Abstract:Machine unlearning (MU) has gained significant attention as a means to remove specific data from trained models without requiring a full retraining process. While progress has been made in unimodal domains like text and image classification, unlearning in multimodal models remains relatively underexplored. In this work, we address the unique challenges of unlearning in CLIP, a prominent multimodal model that aligns visual and textual representations. We introduce CLIPErase, a novel approach that disentangles and selectively forgets both visual and textual associations, ensuring that unlearning does not compromise model performance. CLIPErase consists of three key modules: a Forgetting Module that disrupts the associations in the forget set, a Retention Module that preserves performance on the retain set, and a Consistency Module that maintains consistency with the original model. Extensive experiments on the CIFAR-100 and Flickr30K datasets across four CLIP downstream tasks demonstrate that CLIPErase effectively forgets designated associations in zero-shot tasks for multimodal samples, while preserving the model's performance on the retain set after unlearning.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge