Zhiheng Li
GLASS: A Generative Recommender for Long-sequence Modeling via SID-Tier and Semantic Search
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Leveraging long-term user behavioral patterns is a key trajectory for enhancing the accuracy of modern recommender systems. While generative recommender systems have emerged as a transformative paradigm, they face hurdles in effectively modeling extensive historical sequences. To address this challenge, we propose GLASS, a novel framework that integrates long-term user interests into the generative process via SID-Tier and Semantic Search. We first introduce SID-Tier, a module that maps long-term interactions into a unified interest vector to enhance the prediction of the initial SID token. Unlike traditional retrieval models that struggle with massive item spaces, SID-Tier leverages the compact nature of the semantic codebook to incorporate cross features between the user's long-term history and candidate semantic codes. Furthermore, we present semantic hard search, which utilizes generated coarse-grained semantic ID as dynamic keys to extract relevant historical behaviors, which are then fused via an adaptive gated fusion module to recalibrate the trajectory of subsequent fine-grained tokens. To address the inherent data sparsity in semantic hard search, we propose two strategies: semantic neighbor augmentation and codebook resizing. Extensive experiments on two large-scale real-world datasets, TAOBAO-MM and KuaiRec, demonstrate that GLASS outperforms state-of-the-art baselines, achieving significant gains in recommendation quality. Our codes are made publicly available to facilitate further research in generative recommendation.
MIRROR: Manifold Ideal Reference ReconstructOR for Generalizable AI-Generated Image Detection
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:High-fidelity generative models have narrowed the perceptual gap between synthetic and real images, posing serious threats to media security. Most existing AI-generated image (AIGI) detectors rely on artifact-based classification and struggle to generalize to evolving generative traces. In contrast, human judgment relies on stable real-world regularities, with deviations from the human cognitive manifold serving as a more generalizable signal of forgery. Motivated by this insight, we reformulate AIGI detection as a Reference-Comparison problem that verifies consistency with the real-image manifold rather than fitting specific forgery cues. We propose MIRROR (Manifold Ideal Reference ReconstructOR), a framework that explicitly encodes reality priors using a learnable discrete memory bank. MIRROR projects an input into a manifold-consistent ideal reference via sparse linear combination, and uses the resulting residuals as robust detection signals. To evaluate whether detectors reach the "superhuman crossover" required to replace human experts, we introduce the Human-AIGI benchmark, featuring a psychophysically curated human-imperceptible subset. Across 14 benchmarks, MIRROR consistently outperforms prior methods, achieving gains of 2.1% on six standard benchmarks and 8.1% on seven in-the-wild benchmarks. On Human-AIGI, MIRROR reaches 89.6% accuracy across 27 generators, surpassing both lay users and visual experts, and further approaching the human perceptual limit as pretrained backbones scale. The code is publicly available at: https://github.com/349793927/MIRROR
Super4DR: 4D Radar-centric Self-supervised Odometry and Gaussian-based Map Optimization
Dec 10, 2025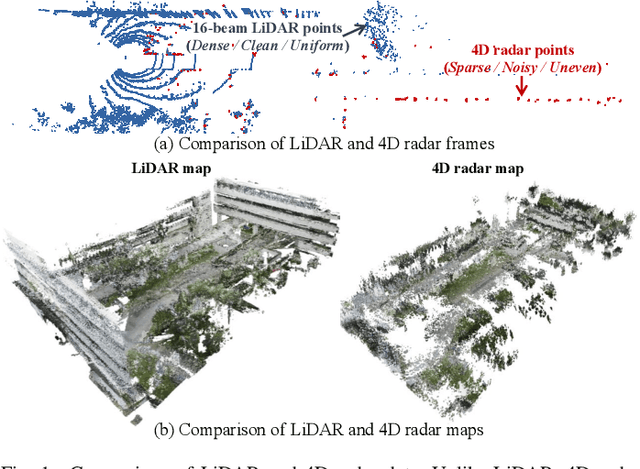

Abstract:Conventional SLAM systems using visual or LiDAR data often struggle in poor lighting and severe weather. Although 4D radar is suited for such environments, its sparse and noisy point clouds hinder accurate odometry estimation, while the radar maps suffer from obscure and incomplete structures. Thus, we propose Super4DR, a 4D radar-centric framework for learning-based odometry estimation and gaussian-based map optimization. First, we design a cluster-aware odometry network that incorporates object-level cues from the clustered radar points for inter-frame matching, alongside a hierarchical self-supervision mechanism to overcome outliers through spatio-temporal consistency, knowledge transfer, and feature contrast. Second, we propose using 3D gaussians as an intermediate representation, coupled with a radar-specific growth strategy, selective separation, and multi-view regularization, to recover blurry map areas and those undetected based on image texture. Experiments show that Super4DR achieves a 67% performance gain over prior self-supervised methods, nearly matches supervised odometry, and narrows the map quality disparity with LiDAR while enabling multi-modal image rendering.
Towards 3D Object-Centric Feature Learning for Semantic Scene Completion
Nov 18, 2025Abstract:Vision-based 3D Semantic Scene Completion (SSC) has received growing attention due to its potential in autonomous driving. While most existing approaches follow an ego-centric paradigm by aggregating and diffusing features over the entire scene, they often overlook fine-grained object-level details, leading to semantic and geometric ambiguities, especially in complex environments. To address this limitation, we propose Ocean, an object-centric prediction framework that decomposes the scene into individual object instances to enable more accurate semantic occupancy prediction. Specifically, we first employ a lightweight segmentation model, MobileSAM, to extract instance masks from the input image. Then, we introduce a 3D Semantic Group Attention module that leverages linear attention to aggregate object-centric features in 3D space. To handle segmentation errors and missing instances, we further design a Global Similarity-Guided Attention module that leverages segmentation features for global interaction. Finally, we propose an Instance-aware Local Diffusion module that improves instance features through a generative process and subsequently refines the scene representation in the BEV space. Extensive experiments on the SemanticKITTI and SSCBench-KITTI360 benchmarks demonstrate that Ocean achieves state-of-the-art performance, with mIoU scores of 17.40 and 20.28, respectively.
LlamaSeg: Image Segmentation via Autoregressive Mask Generation
May 26, 2025Abstract:We present LlamaSeg, a visual autoregressive framework that unifies multiple image segmentation tasks via natural language instructions. We reformulate image segmentation as a visual generation problem, representing masks as "visual" tokens and employing a LLaMA-style Transformer to predict them directly from image inputs. By adhering to the next-token prediction paradigm, our approach naturally integrates segmentation tasks into autoregressive architectures. To support large-scale training, we introduce a data annotation pipeline and construct the SA-OVRS dataset, which contains 2M segmentation masks annotated with over 5,800 open-vocabulary labels or diverse textual descriptions, covering a wide spectrum of real-world scenarios. This enables our model to localize objects in images based on text prompts and to generate fine-grained masks. To more accurately evaluate the quality of masks produced by visual generative models, we further propose a composite metric that combines Intersection over Union (IoU) with Average Hausdorff Distance (AHD), offering a more precise assessment of contour fidelity. Experimental results demonstrate that our method surpasses existing generative models across multiple datasets and yields more detailed segmentation masks.
DiST-4D: Disentangled Spatiotemporal Diffusion with Metric Depth for 4D Driving Scene Generation
Mar 19, 2025



Abstract:Current generative models struggle to synthesize dynamic 4D driving scenes that simultaneously support temporal extrapolation and spatial novel view synthesis (NVS) without per-scene optimization. A key challenge lies in finding an efficient and generalizable geometric representation that seamlessly connects temporal and spatial synthesis. To address this, we propose DiST-4D, the first disentangled spatiotemporal diffusion framework for 4D driving scene generation, which leverages metric depth as the core geometric representation. DiST-4D decomposes the problem into two diffusion processes: DiST-T, which predicts future metric depth and multi-view RGB sequences directly from past observations, and DiST-S, which enables spatial NVS by training only on existing viewpoints while enforcing cycle consistency. This cycle consistency mechanism introduces a forward-backward rendering constraint, reducing the generalization gap between observed and unseen viewpoints. Metric depth is essential for both accurate reliable forecasting and accurate spatial NVS, as it provides a view-consistent geometric representation that generalizes well to unseen perspectives. Experiments demonstrate that DiST-4D achieves state-of-the-art performance in both temporal prediction and NVS tasks, while also delivering competitive performance in planning-related evaluations.
CAO-RONet: A Robust 4D Radar Odometry with Exploring More Information from Low-Quality Points
Mar 03, 2025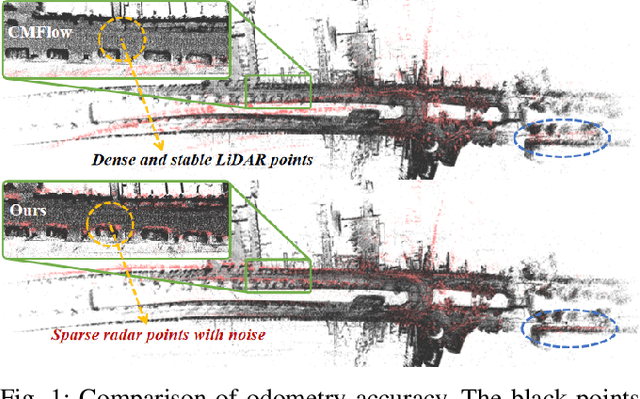
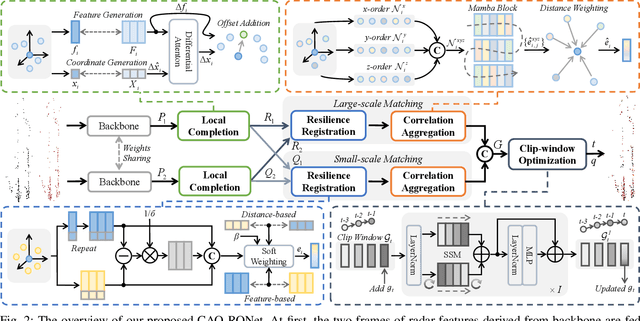
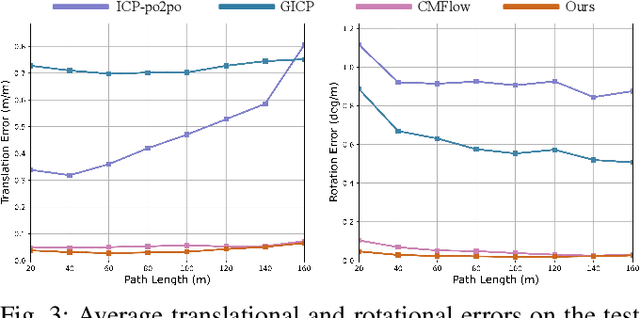
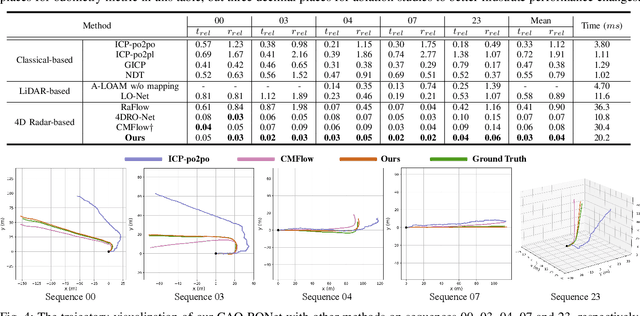
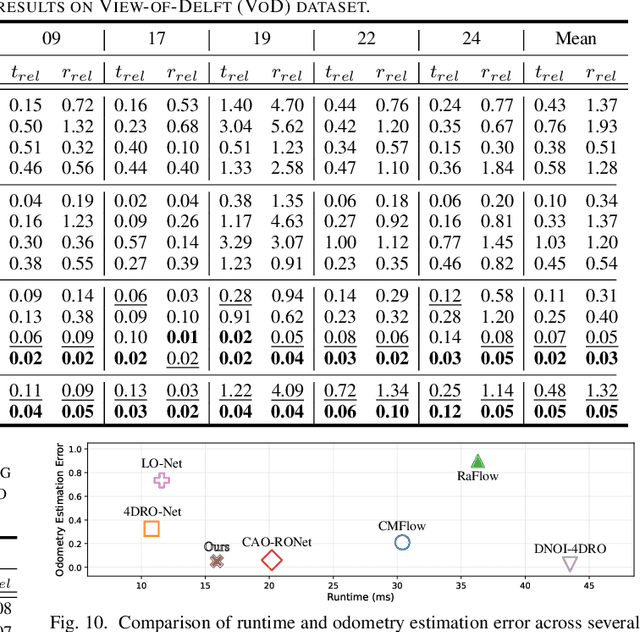
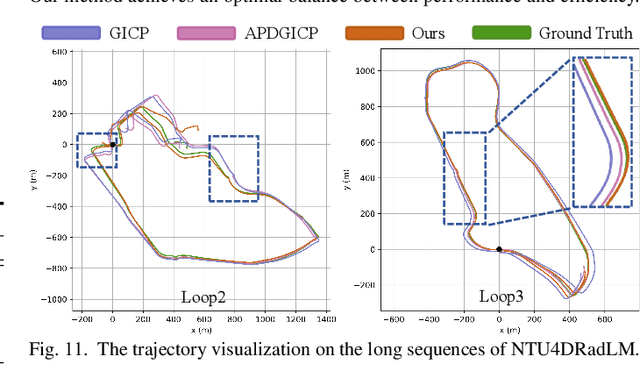
Abstract:Recently, 4D millimetre-wave radar exhibits more stable perception ability than LiDAR and camera under adverse conditions (e.g. rain and fog). However, low-quality radar points hinder its application, especially the odometry task that requires a dense and accurate matching. To fully explore the potential of 4D radar, we introduce a learning-based odometry framework, enabling robust ego-motion estimation from finite and uncertain geometry information. First, for sparse radar points, we propose a local completion to supplement missing structures and provide denser guideline for aligning two frames. Then, a context-aware association with a hierarchical structure flexibly matches points of different scales aided by feature similarity, and improves local matching consistency through correlation balancing. Finally, we present a window-based optimizer that uses historical priors to establish a coupling state estimation and correct errors of inter-frame matching. The superiority of our algorithm is confirmed on View-of-Delft dataset, achieving around a 50% performance improvement over previous approaches and delivering accuracy on par with LiDAR odometry. Our code will be available.
4D-CS: Exploiting Cluster Prior for 4D Spatio-Temporal LiDAR Semantic Segmentation
Jan 06, 2025Abstract:Semantic segmentation of LiDAR points has significant value for autonomous driving and mobile robot systems. Most approaches explore spatio-temporal information of multi-scan to identify the semantic classes and motion states for each point. However, these methods often overlook the segmentation consistency in space and time, which may result in point clouds within the same object being predicted as different categories. To handle this issue, our core idea is to generate cluster labels across multiple frames that can reflect the complete spatial structure and temporal information of objects. These labels serve as explicit guidance for our dual-branch network, 4D-CS, which integrates point-based and cluster-based branches to enable more consistent segmentation. Specifically, in the point-based branch, we leverage historical knowledge to enrich the current feature through temporal fusion on multiple views. In the cluster-based branch, we propose a new strategy to produce cluster labels of foreground objects and apply them to gather point-wise information to derive cluster features. We then merge neighboring clusters across multiple scans to restore missing features due to occlusion. Finally, in the point-cluster fusion stage, we adaptively fuse the information from the two branches to optimize segmentation results. Extensive experiments confirm the effectiveness of the proposed method, and we achieve state-of-the-art results on the multi-scan semantic and moving object segmentation on SemanticKITTI and nuScenes datasets. The code will be available at https://github.com/NEU-REAL/4D-CS.git.
Efficient Scaling of Diffusion Transformers for Text-to-Image Generation
Dec 16, 2024



Abstract:We empirically study the scaling properties of various Diffusion Transformers (DiTs) for text-to-image generation by performing extensive and rigorous ablations, including training scaled DiTs ranging from 0.3B upto 8B parameters on datasets up to 600M images. We find that U-ViT, a pure self-attention based DiT model provides a simpler design and scales more effectively in comparison with cross-attention based DiT variants, which allows straightforward expansion for extra conditions and other modalities. We identify a 2.3B U-ViT model can get better performance than SDXL UNet and other DiT variants in controlled setting. On the data scaling side, we investigate how increasing dataset size and enhanced long caption improve the text-image alignment performance and the learning efficiency.
LOMA: Language-assisted Semantic Occupancy Network via Triplane Mamba
Dec 11, 2024Abstract:Vision-based 3D occupancy prediction has become a popular research task due to its versatility and affordability. Nowadays, conventional methods usually project the image-based vision features to 3D space and learn the geometric information through the attention mechanism, enabling the 3D semantic occupancy prediction. However, these works usually face two main challenges: 1) Limited geometric information. Due to the lack of geometric information in the image itself, it is challenging to directly predict 3D space information, especially in large-scale outdoor scenes. 2) Local restricted interaction. Due to the quadratic complexity of the attention mechanism, they often use modified local attention to fuse features, resulting in a restricted fusion. To address these problems, in this paper, we propose a language-assisted 3D semantic occupancy prediction network, named LOMA. In the proposed vision-language framework, we first introduce a VL-aware Scene Generator (VSG) module to generate the 3D language feature of the scene. By leveraging the vision-language model, this module provides implicit geometric knowledge and explicit semantic information from the language. Furthermore, we present a Tri-plane Fusion Mamba (TFM) block to efficiently fuse the 3D language feature and 3D vision feature. The proposed module not only fuses the two features with global modeling but also avoids too much computation costs. Experiments on the SemanticKITTI and SSCBench-KITTI360 datasets show that our algorithm achieves new state-of-the-art performances in both geometric and semantic completion tasks. Our code will be open soon.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge