Jiazhe Guo
Scaling Up Occupancy-centric Driving Scene Generation: Dataset and Method
Oct 27, 2025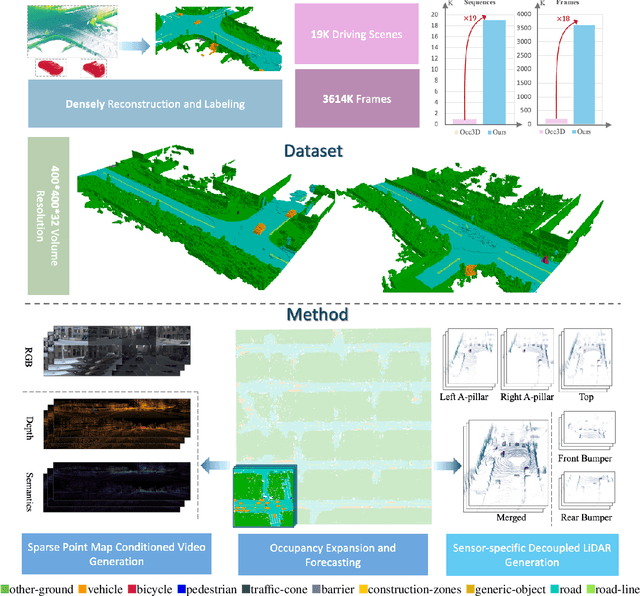
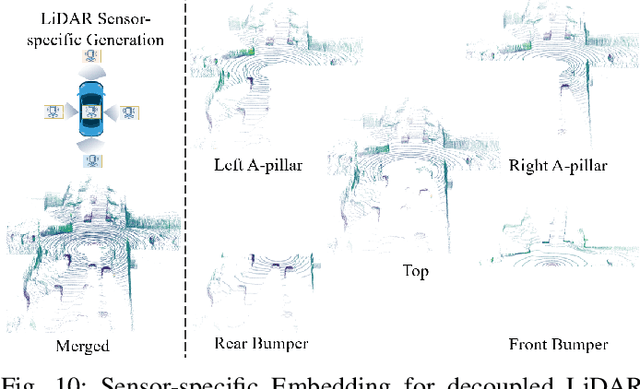
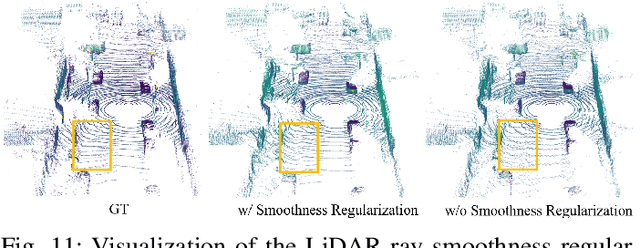
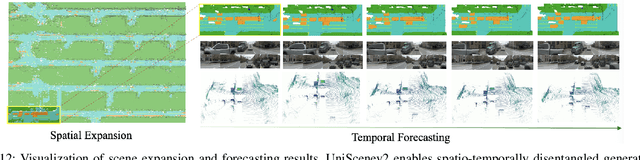
Abstract:Driving scene generation is a critical domain for autonomous driving, enabling downstream applications, including perception and planning evaluation. Occupancy-centric methods have recently achieved state-of-the-art results by offering consistent conditioning across frames and modalities; however, their performance heavily depends on annotated occupancy data, which still remains scarce. To overcome this limitation, we curate Nuplan-Occ, the largest semantic occupancy dataset to date, constructed from the widely used Nuplan benchmark. Its scale and diversity facilitate not only large-scale generative modeling but also autonomous driving downstream applications. Based on this dataset, we develop a unified framework that jointly synthesizes high-quality semantic occupancy, multi-view videos, and LiDAR point clouds. Our approach incorporates a spatio-temporal disentangled architecture to support high-fidelity spatial expansion and temporal forecasting of 4D dynamic occupancy. To bridge modal gaps, we further propose two novel techniques: a Gaussian splatting-based sparse point map rendering strategy that enhances multi-view video generation, and a sensor-aware embedding strategy that explicitly models LiDAR sensor properties for realistic multi-LiDAR simulation. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method achieves superior generation fidelity and scalability compared to existing approaches, and validates its practical value in downstream tasks. Repo: https://github.com/Arlo0o/UniScene-Unified-Occupancy-centric-Driving-Scene-Generation/tree/v2
Driving-RAG: Driving Scenarios Embedding, Search, and RAG Applications
Apr 06, 2025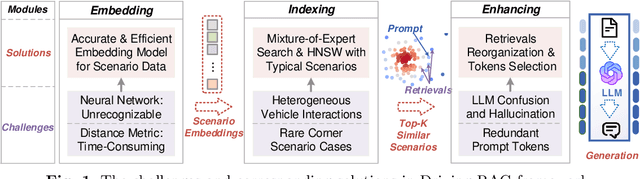
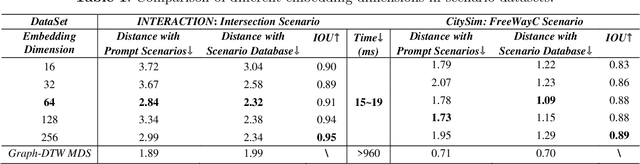
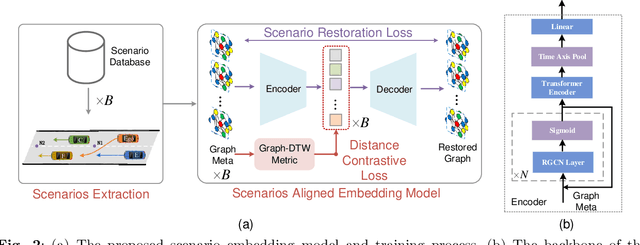
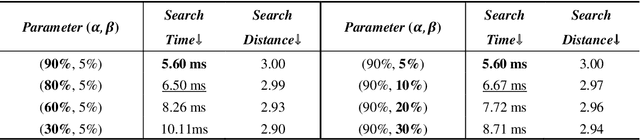
Abstract:Driving scenario data play an increasingly vital role in the development of intelligent vehicles and autonomous driving. Accurate and efficient scenario data search is critical for both online vehicle decision-making and planning, and offline scenario generation and simulations, as it allows for leveraging the scenario experiences to improve the overall performance. Especially with the application of large language models (LLMs) and Retrieval-Augmented-Generation (RAG) systems in autonomous driving, urgent requirements are put forward. In this paper, we introduce the Driving-RAG framework to address the challenges of efficient scenario data embedding, search, and applications for RAG systems. Our embedding model aligns fundamental scenario information and scenario distance metrics in the vector space. The typical scenario sampling method combined with hierarchical navigable small world can perform efficient scenario vector search to achieve high efficiency without sacrificing accuracy. In addition, the reorganization mechanism by graph knowledge enhances the relevance to the prompt scenarios and augment LLM generation. We demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed framework on typical trajectory planning task for complex interactive scenarios such as ramps and intersections, showcasing its advantages for RAG applications.
DiST-4D: Disentangled Spatiotemporal Diffusion with Metric Depth for 4D Driving Scene Generation
Mar 19, 2025



Abstract:Current generative models struggle to synthesize dynamic 4D driving scenes that simultaneously support temporal extrapolation and spatial novel view synthesis (NVS) without per-scene optimization. A key challenge lies in finding an efficient and generalizable geometric representation that seamlessly connects temporal and spatial synthesis. To address this, we propose DiST-4D, the first disentangled spatiotemporal diffusion framework for 4D driving scene generation, which leverages metric depth as the core geometric representation. DiST-4D decomposes the problem into two diffusion processes: DiST-T, which predicts future metric depth and multi-view RGB sequences directly from past observations, and DiST-S, which enables spatial NVS by training only on existing viewpoints while enforcing cycle consistency. This cycle consistency mechanism introduces a forward-backward rendering constraint, reducing the generalization gap between observed and unseen viewpoints. Metric depth is essential for both accurate reliable forecasting and accurate spatial NVS, as it provides a view-consistent geometric representation that generalizes well to unseen perspectives. Experiments demonstrate that DiST-4D achieves state-of-the-art performance in both temporal prediction and NVS tasks, while also delivering competitive performance in planning-related evaluations.
MuDG: Taming Multi-modal Diffusion with Gaussian Splatting for Urban Scene Reconstruction
Mar 13, 2025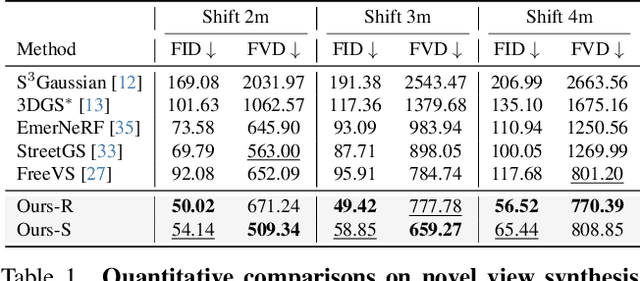
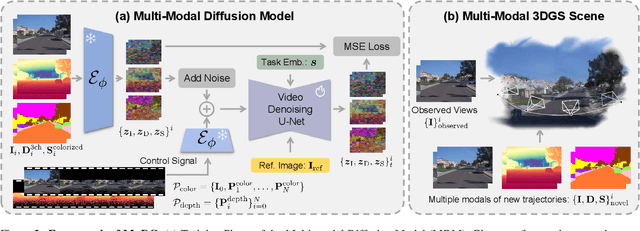
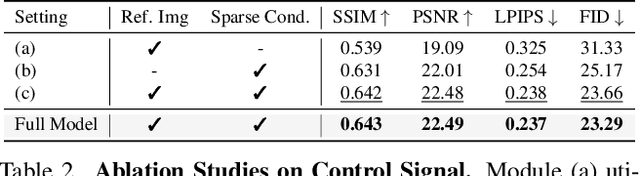
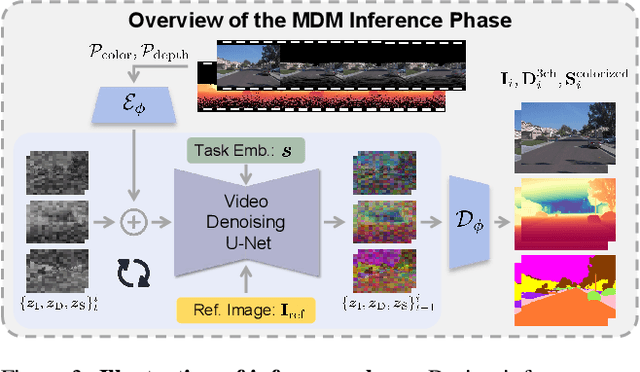
Abstract:Recent breakthroughs in radiance fields have significantly advanced 3D scene reconstruction and novel view synthesis (NVS) in autonomous driving. Nevertheless, critical limitations persist: reconstruction-based methods exhibit substantial performance deterioration under significant viewpoint deviations from training trajectories, while generation-based techniques struggle with temporal coherence and precise scene controllability. To overcome these challenges, we present MuDG, an innovative framework that integrates Multi-modal Diffusion model with Gaussian Splatting (GS) for Urban Scene Reconstruction. MuDG leverages aggregated LiDAR point clouds with RGB and geometric priors to condition a multi-modal video diffusion model, synthesizing photorealistic RGB, depth, and semantic outputs for novel viewpoints. This synthesis pipeline enables feed-forward NVS without computationally intensive per-scene optimization, providing comprehensive supervision signals to refine 3DGS representations for rendering robustness enhancement under extreme viewpoint changes. Experiments on the Open Waymo Dataset demonstrate that MuDG outperforms existing methods in both reconstruction and synthesis quality.
UniScene: Unified Occupancy-centric Driving Scene Generation
Dec 06, 2024Abstract:Generating high-fidelity, controllable, and annotated training data is critical for autonomous driving. Existing methods typically generate a single data form directly from a coarse scene layout, which not only fails to output rich data forms required for diverse downstream tasks but also struggles to model the direct layout-to-data distribution. In this paper, we introduce UniScene, the first unified framework for generating three key data forms - semantic occupancy, video, and LiDAR - in driving scenes. UniScene employs a progressive generation process that decomposes the complex task of scene generation into two hierarchical steps: (a) first generating semantic occupancy from a customized scene layout as a meta scene representation rich in both semantic and geometric information, and then (b) conditioned on occupancy, generating video and LiDAR data, respectively, with two novel transfer strategies of Gaussian-based Joint Rendering and Prior-guided Sparse Modeling. This occupancy-centric approach reduces the generation burden, especially for intricate scenes, while providing detailed intermediate representations for the subsequent generation stages. Extensive experiments demonstrate that UniScene outperforms previous SOTAs in the occupancy, video, and LiDAR generation, which also indeed benefits downstream driving tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge