Dan Luo
Lehigh University
LFD: Layer Fused Decoding to Exploit External Knowledge in Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Aug 27, 2025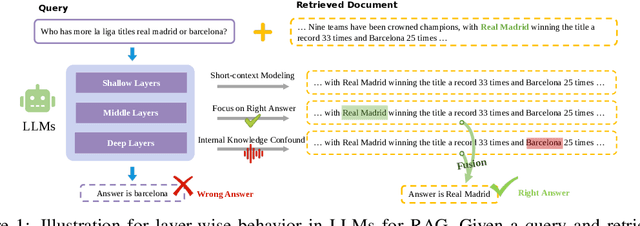
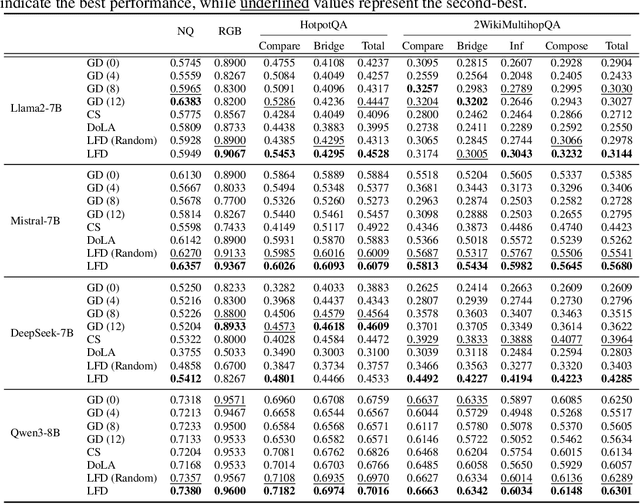
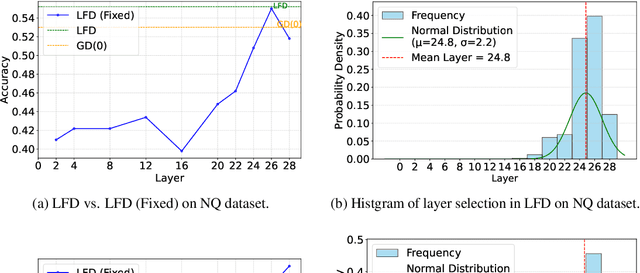

Abstract:Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) incorporates external knowledge into large language models (LLMs), improving their adaptability to downstream tasks and enabling information updates. Surprisingly, recent empirical evidence demonstrates that injecting noise into retrieved relevant documents paradoxically facilitates exploitation of external knowledge and improves generation quality. Although counterintuitive and challenging to apply in practice, this phenomenon enables granular control and rigorous analysis of how LLMs integrate external knowledge. Therefore, in this paper, we intervene on noise injection and establish a layer-specific functional demarcation within the LLM: shallow layers specialize in local context modeling, intermediate layers focus on integrating long-range external factual knowledge, and deeper layers primarily rely on parametric internal knowledge. Building on this insight, we propose Layer Fused Decoding (LFD), a simple decoding strategy that directly combines representations from an intermediate layer with final-layer decoding outputs to fully exploit the external factual knowledge. To identify the optimal intermediate layer, we introduce an internal knowledge score (IKS) criterion that selects the layer with the lowest IKS value in the latter half of layers. Experimental results across multiple benchmarks demonstrate that LFD helps RAG systems more effectively surface retrieved context knowledge with minimal cost.
Flow Matching based Sequential Recommender Model
May 22, 2025Abstract:Generative models, particularly diffusion model, have emerged as powerful tools for sequential recommendation. However, accurately modeling user preferences remains challenging due to the noise perturbations inherent in the forward and reverse processes of diffusion-based methods. Towards this end, this study introduces FMRec, a Flow Matching based model that employs a straight flow trajectory and a modified loss tailored for the recommendation task. Additionally, from the diffusion-model perspective, we integrate a reconstruction loss to improve robustness against noise perturbations, thereby retaining user preferences during the forward process. In the reverse process, we employ a deterministic reverse sampler, specifically an ODE-based updating function, to eliminate unnecessary randomness, thereby ensuring that the generated recommendations closely align with user needs. Extensive evaluations on four benchmark datasets reveal that FMRec achieves an average improvement of 6.53% over state-of-the-art methods. The replication code is available at https://github.com/FengLiu-1/FMRec.
DynamicDTA: Drug-Target Binding Affinity Prediction Using Dynamic Descriptors and Graph Representation
May 13, 2025Abstract:Predicting drug-target binding affinity (DTA) is essential for identifying potential therapeutic candidates in drug discovery. However, most existing models rely heavily on static protein structures, often overlooking the dynamic nature of proteins, which is crucial for capturing conformational flexibility that will be beneficial for protein binding interactions. We introduce DynamicDTA, an innovative deep learning framework that incorporates static and dynamic protein features to enhance DTA prediction. The proposed DynamicDTA takes three types of inputs, including drug sequence, protein sequence, and dynamic descriptors. A molecular graph representation of the drug sequence is generated and subsequently processed through graph convolutional network, while the protein sequence is encoded using dilated convolutions. Dynamic descriptors, such as root mean square fluctuation, are processed through a multi-layer perceptron. These embedding features are fused with static protein features using cross-attention, and a tensor fusion network integrates all three modalities for DTA prediction. Extensive experiments on three datasets demonstrate that DynamicDTA achieves by at least 3.4% improvement in RMSE score with comparison to seven state-of-the-art baseline methods. Additionally, predicting novel drugs for Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 and visualizing the docking complexes further demonstrates the reliability and biological relevance of DynamicDTA.
AutoStyle-TTS: Retrieval-Augmented Generation based Automatic Style Matching Text-to-Speech Synthesis
Apr 14, 2025Abstract:With the advancement of speech synthesis technology, users have higher expectations for the naturalness and expressiveness of synthesized speech. But previous research ignores the importance of prompt selection. This study proposes a text-to-speech (TTS) framework based on Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) technology, which can dynamically adjust the speech style according to the text content to achieve more natural and vivid communication effects. We have constructed a speech style knowledge database containing high-quality speech samples in various contexts and developed a style matching scheme. This scheme uses embeddings, extracted by Llama, PER-LLM-Embedder,and Moka, to match with samples in the knowledge database, selecting the most appropriate speech style for synthesis. Furthermore, our empirical research validates the effectiveness of the proposed method. Our demo can be viewed at: https://thuhcsi.github.io/icme2025-AutoStyle-TTS
UniSep: Universal Target Audio Separation with Language Models at Scale
Mar 31, 2025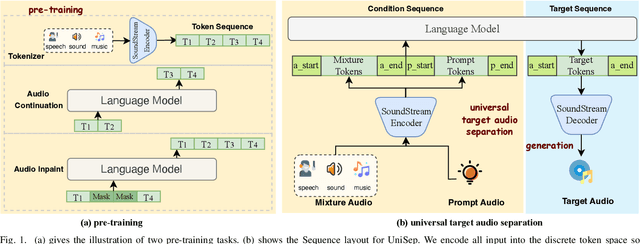
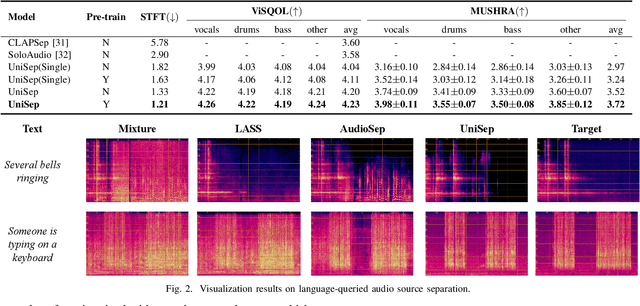

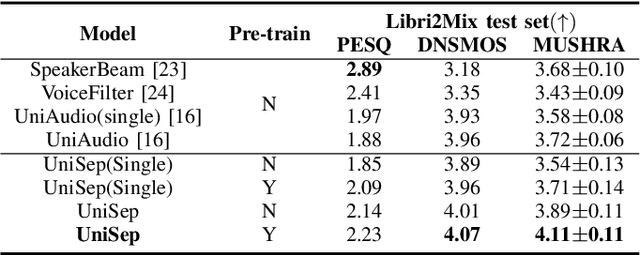
Abstract:We propose Universal target audio Separation (UniSep), addressing the separation task on arbitrary mixtures of different types of audio. Distinguished from previous studies, UniSep is performed on unlimited source domains and unlimited source numbers. We formulate the separation task as a sequence-to-sequence problem, and a large language model (LLM) is used to model the audio sequence in the discrete latent space, leveraging the power of LLM in handling complex mixture audios with large-scale data. Moreover, a novel pre-training strategy is proposed to utilize audio-only data, which reduces the efforts of large-scale data simulation and enhances the ability of LLMs to understand the consistency and correlation of information within audio sequences. We also demonstrate the effectiveness of scaling datasets in an audio separation task: we use large-scale data (36.5k hours), including speech, music, and sound, to train a universal target audio separation model that is not limited to a specific domain. Experiments show that UniSep achieves competitive subjective and objective evaluation results compared with single-task models.
From Documents to Dialogue: Building KG-RAG Enhanced AI Assistants
Feb 21, 2025Abstract:The Adobe Experience Platform AI Assistant is a conversational tool that enables organizations to interact seamlessly with proprietary enterprise data through a chatbot. However, due to access restrictions, Large Language Models (LLMs) cannot retrieve these internal documents, limiting their ability to generate accurate zero-shot responses. To overcome this limitation, we use a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) framework powered by a Knowledge Graph (KG) to retrieve relevant information from external knowledge sources, enabling LLMs to answer questions over private or previously unseen document collections. In this paper, we propose a novel approach for building a high-quality, low-noise KG. We apply several techniques, including incremental entity resolution using seed concepts, similarity-based filtering to deduplicate entries, assigning confidence scores to entity-relation pairs to filter for high-confidence pairs, and linking facts to source documents for provenance. Our KG-RAG system retrieves relevant tuples, which are added to the user prompts context before being sent to the LLM generating the response. Our evaluation demonstrates that this approach significantly enhances response relevance, reducing irrelevant answers by over 50% and increasing fully relevant answers by 88% compared to the existing production system.
Generating Negative Samples for Multi-Modal Recommendation
Jan 25, 2025Abstract:Multi-modal recommender systems (MMRS) have gained significant attention due to their ability to leverage information from various modalities to enhance recommendation quality. However, existing negative sampling techniques often struggle to effectively utilize the multi-modal data, leading to suboptimal performance. In this paper, we identify two key challenges in negative sampling for MMRS: (1) producing cohesive negative samples contrasting with positive samples and (2) maintaining a balanced influence across different modalities. To address these challenges, we propose NegGen, a novel framework that utilizes multi-modal large language models (MLLMs) to generate balanced and contrastive negative samples. We design three different prompt templates to enable NegGen to analyze and manipulate item attributes across multiple modalities, and then generate negative samples that introduce better supervision signals and ensure modality balance. Furthermore, NegGen employs a causal learning module to disentangle the effect of intervened key features and irrelevant item attributes, enabling fine-grained learning of user preferences. Extensive experiments on real-world datasets demonstrate the superior performance of NegGen compared to state-of-the-art methods in both negative sampling and multi-modal recommendation.
Federated Retrieval Augmented Generation for Multi-Product Question Answering
Jan 25, 2025



Abstract:Recent advancements in Large Language Models and Retrieval-Augmented Generation have boosted interest in domain-specific question-answering for enterprise products. However, AI Assistants often face challenges in multi-product QA settings, requiring accurate responses across diverse domains. Existing multi-domain RAG-QA approaches either query all domains indiscriminately, increasing computational costs and LLM hallucinations, or rely on rigid resource selection, which can limit search results. We introduce MKP-QA, a novel multi-product knowledge-augmented QA framework with probabilistic federated search across domains and relevant knowledge. This method enhances multi-domain search quality by aggregating query-domain and query-passage probabilistic relevance. To address the lack of suitable benchmarks for multi-product QAs, we also present new datasets focused on three Adobe products: Adobe Experience Platform, Target, and Customer Journey Analytics. Our experiments show that MKP-QA significantly boosts multi-product RAG-QA performance in terms of both retrieval accuracy and response quality.
NT-LLM: A Novel Node Tokenizer for Integrating Graph Structure into Large Language Models
Oct 14, 2024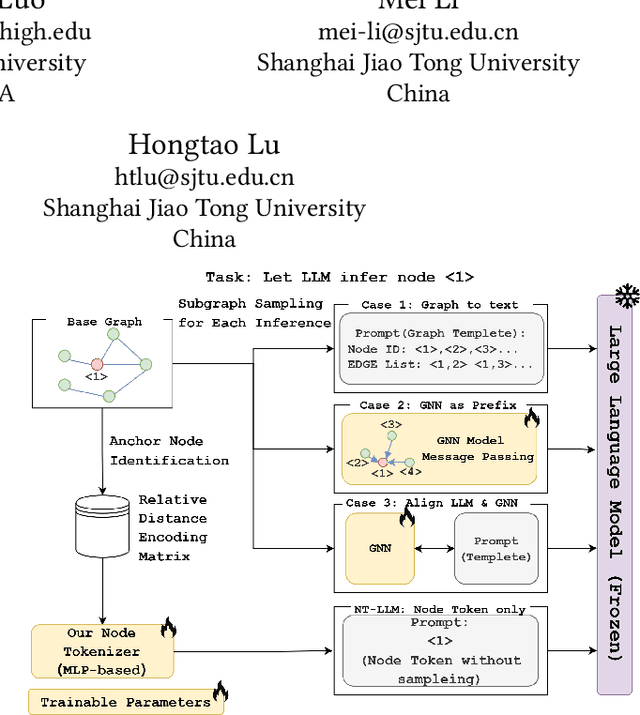

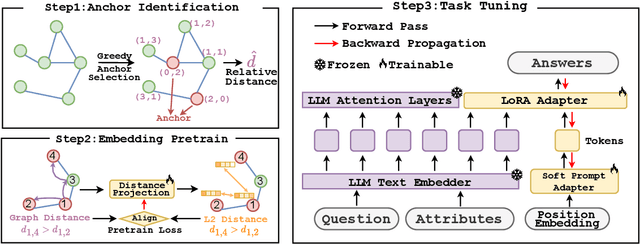

Abstract:Graphs are a fundamental data structure for representing relationships in real-world scenarios. With the success of Large Language Models (LLMs) across various natural language processing (NLP) tasks, there has been growing interest in integrating LLMs for graph learning. However, applying LLMs to graph-related tasks poses significant challenges, as these models are not inherently designed to capture the complex structural information present in graphs. Existing approaches address this challenge through two strategies: the chain of tasks approach, which uses Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) to encode the graph structure so that LLMs are relieved from understanding spatial positions; and Graph-to-Text Conversion, which translates graph structures into semantic text representations that LLMs can process. Despite their progress, these methods often struggle to fully preserve the topological information of graphs or require extensive computational resources, limiting their practical applicability. In this work, we introduce Node Tokenizer for Large Language Models (NT-LLM), a novel framework that efficiently encodes graph structures by selecting key nodes as anchors and representing each node based on its relative distance to these anchors. This position-anchored encoding effectively captures the graph topology, enabling enhanced reasoning capabilities in LLMs over graph data. Additionally, we implement a task-specific tuning procedure to further improve structural understanding within LLMs. Through extensive empirical evaluations, NT-LLM demonstrates significant performance improvements across a variety of graph-related tasks.
Rhythmic Foley: A Framework For Seamless Audio-Visual Alignment In Video-to-Audio Synthesis
Sep 13, 2024



Abstract:Our research introduces an innovative framework for video-to-audio synthesis, which solves the problems of audio-video desynchronization and semantic loss in the audio. By incorporating a semantic alignment adapter and a temporal synchronization adapter, our method significantly improves semantic integrity and the precision of beat point synchronization, particularly in fast-paced action sequences. Utilizing a contrastive audio-visual pre-trained encoder, our model is trained with video and high-quality audio data, improving the quality of the generated audio. This dual-adapter approach empowers users with enhanced control over audio semantics and beat effects, allowing the adjustment of the controller to achieve better results. Extensive experiments substantiate the effectiveness of our framework in achieving seamless audio-visual alignment.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge