Chengyuan Ma
ReIn: Conversational Error Recovery with Reasoning Inception
Feb 19, 2026Abstract:Conversational agents powered by large language models (LLMs) with tool integration achieve strong performance on fixed task-oriented dialogue datasets but remain vulnerable to unanticipated, user-induced errors. Rather than focusing on error prevention, this work focuses on error recovery, which necessitates the accurate diagnosis of erroneous dialogue contexts and execution of proper recovery plans. Under realistic constraints precluding model fine-tuning or prompt modification due to significant cost and time requirements, we explore whether agents can recover from contextually flawed interactions and how their behavior can be adapted without altering model parameters and prompts. To this end, we propose Reasoning Inception (ReIn), a test-time intervention method that plants an initial reasoning into the agent's decision-making process. Specifically, an external inception module identifies predefined errors within the dialogue context and generates recovery plans, which are subsequently integrated into the agent's internal reasoning process to guide corrective actions, without modifying its parameters or system prompts. We evaluate ReIn by systematically simulating conversational failure scenarios that directly hinder successful completion of user goals: user's ambiguous and unsupported requests. Across diverse combinations of agent models and inception modules, ReIn substantially improves task success and generalizes to unseen error types. Moreover, it consistently outperforms explicit prompt-modification approaches, underscoring its utility as an efficient, on-the-fly method. In-depth analysis of its operational mechanism, particularly in relation to instruction hierarchy, indicates that jointly defining recovery tools with ReIn can serve as a safe and effective strategy for improving the resilience of conversational agents without modifying the backbone models or system prompts.
VividVoice: A Unified Framework for Scene-Aware Visually-Driven Speech Synthesis
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:We introduce and define a novel task-Scene-Aware Visually-Driven Speech Synthesis, aimed at addressing the limitations of existing speech generation models in creating immersive auditory experiences that align with the real physical world. To tackle the two core challenges of data scarcity and modality decoupling, we propose VividVoice, a unified generative framework. First, we constructed a large-scale, high-quality hybrid multimodal dataset, Vivid-210K, which, through an innovative programmatic pipeline, establishes a strong correlation between visual scenes, speaker identity, and audio for the first time. Second, we designed a core alignment module, D-MSVA, which leverages a decoupled memory bank architecture and a cross-modal hybrid supervision strategy to achieve fine-grained alignment from visual scenes to timbre and environmental acoustic features. Both subjective and objective experimental results provide strong evidence that VividVoice significantly outperforms existing baseline models in terms of audio fidelity, content clarity, and multimodal consistency. Our demo is available at https://chengyuann.github.io/VividVoice/.
TLDiffGAN: A Latent Diffusion-GAN Framework with Temporal Information Fusion for Anomalous Sound Detection
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:Existing generative models for unsupervised anomalous sound detection are limited by their inability to fully capture the complex feature distribution of normal sounds, while the potential of powerful diffusion models in this domain remains largely unexplored. To address this challenge, we propose a novel framework, TLDiffGAN, which consists of two complementary branches. One branch incorporates a latent diffusion model into the GAN generator for adversarial training, thereby making the discriminator's task more challenging and improving the quality of generated samples. The other branch leverages pretrained audio model encoders to extract features directly from raw audio waveforms for auxiliary discrimination. This framework effectively captures feature representations of normal sounds from both raw audio and Mel spectrograms. Moreover, we introduce a TMixup spectrogram augmentation technique to enhance sensitivity to subtle and localized temporal patterns that are often overlooked. Extensive experiments on the DCASE 2020 Challenge Task 2 dataset demonstrate the superior detection performance of TLDiffGAN, as well as its strong capability in anomalous time-frequency localization.
Robustness and Resilience Evaluation of Eco-Driving Strategies at Signalized Intersections
Jan 19, 2026Abstract:Eco-driving strategies have demonstrated substantial potential for improving energy efficiency and reducing emissions, especially at signalized intersections. However, evaluations of eco-driving methods typically rely on simplified simulation or experimental conditions, where certain assumptions are made to manage complexity and experimental control. This study introduces a unified framework to evaluate eco-driving strategies through the lens of two complementary criteria: control robustness and environmental resilience. We define formal indicators that quantify performance degradation caused by internal execution variability and external environmental disturbances, respectively. These indicators are then applied to assess multiple eco-driving controllers through real-world vehicle experiments. The results reveal key tradeoffs between tracking accuracy and adaptability, showing that optimization-based controllers offer more consistent performance across varying disturbance levels, while analytical controllers may perform comparably under nominal conditions but exhibit greater sensitivity to execution and timing variability.
SpeakRL: Synergizing Reasoning, Speaking, and Acting in Language Models with Reinforcement Learning
Dec 15, 2025
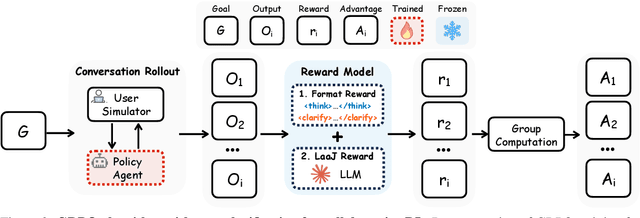
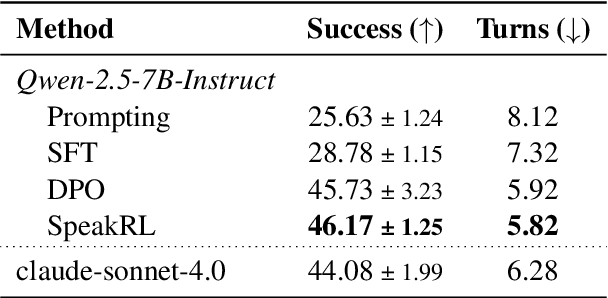
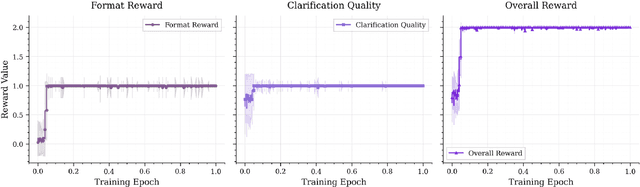
Abstract:Effective human-agent collaboration is increasingly prevalent in real-world applications. Current trends in such collaborations are predominantly unidirectional, with users providing instructions or posing questions to agents, where agents respond directly without seeking necessary clarifications or confirmations. However, the evolving capabilities of these agents require more proactive engagement, where agents should dynamically participate in conversations to clarify user intents, resolve ambiguities, and adapt to changing circumstances. Existing prior work under-utilize the conversational capabilities of language models (LMs), thereby optimizing agents as better followers rather than effective speakers. In this work, we introduce SpeakRL, a reinforcement learning (RL) method that enhances agents' conversational capabilities by rewarding proactive interactions with users, such as asking right clarification questions when necessary. To support this, we curate SpeakER, a synthetic dataset that includes diverse scenarios from task-oriented dialogues, where tasks are resolved through interactive clarification questions. We present a systematic analysis of reward design for conversational proactivity and propose a principled reward formulation for teaching agents to balance asking with acting. Empirical evaluations demonstrate that our approach achieves a 20.14% absolute improvement in task completion over base models without increasing conversation turns even surpassing even much larger proprietary models, demonstrating the promise of clarification-centric user-agent interactions.
MAC: A Multi-Agent Framework for Interactive User Clarification in Multi-turn Conversations
Dec 15, 2025Abstract:Conversational agents often encounter ambiguous user requests, requiring an effective clarification to successfully complete tasks. While recent advancements in real-world applications favor multi-agent architectures to manage complex conversational scenarios efficiently, ambiguity resolution remains a critical and underexplored challenge--particularly due to the difficulty of determining which agent should initiate a clarification and how agents should coordinate their actions when faced with uncertain or incomplete user input. The fundamental questions of when to interrupt a user and how to formulate the optimal clarification query within the most optimal multi-agent settings remain open. In this paper, we propose MAC (Multi-Agent Clarification), an interactive multi-agent framework specifically optimized to resolve user ambiguities by strategically managing clarification dialogues. We first introduce a novel taxonomy categorizing user ambiguities to systematically guide clarification strategies. Then, we present MAC that autonomously coordinates multiple agents to interact synergistically with users. Empirical evaluations on MultiWOZ 2.4 demonstrate that enabling clarification at both levels increases task success rate 7.8\% (54.5 to 62.3) and reduces the average number of dialogue turns (6.53 to 4.86) by eliciting all required user information up front and minimizing repetition. Our findings highlight the importance of active user interaction and role-aware clarification for more reliable human-agent communication.
CATS-V2V: A Real-World Vehicle-to-Vehicle Cooperative Perception Dataset with Complex Adverse Traffic Scenarios
Nov 14, 2025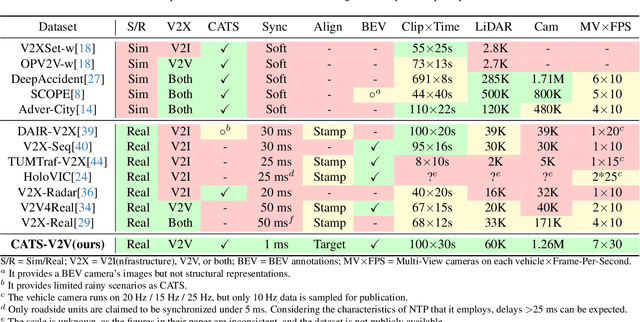

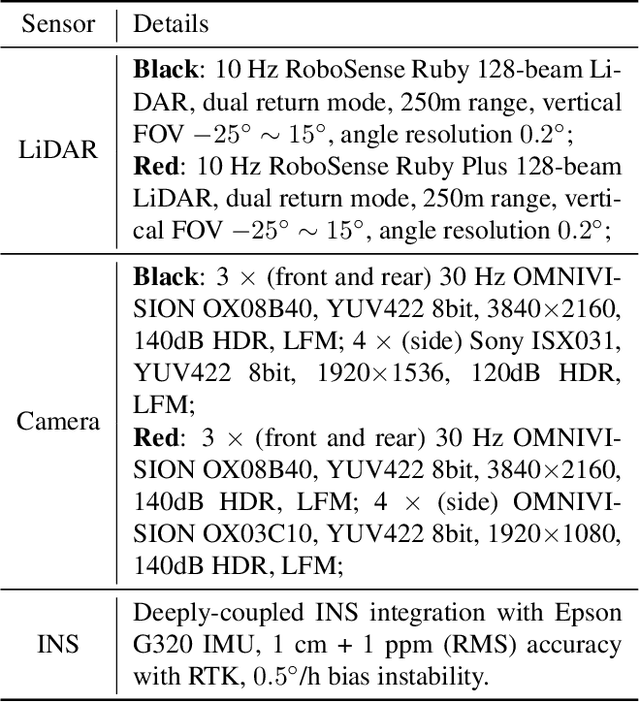
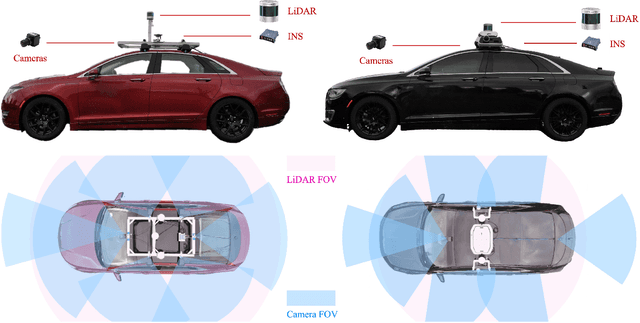
Abstract:Vehicle-to-Vehicle (V2V) cooperative perception has great potential to enhance autonomous driving performance by overcoming perception limitations in complex adverse traffic scenarios (CATS). Meanwhile, data serves as the fundamental infrastructure for modern autonomous driving AI. However, due to stringent data collection requirements, existing datasets focus primarily on ordinary traffic scenarios, constraining the benefits of cooperative perception. To address this challenge, we introduce CATS-V2V, the first-of-its-kind real-world dataset for V2V cooperative perception under complex adverse traffic scenarios. The dataset was collected by two hardware time-synchronized vehicles, covering 10 weather and lighting conditions across 10 diverse locations. The 100-clip dataset includes 60K frames of 10 Hz LiDAR point clouds and 1.26M multi-view 30 Hz camera images, along with 750K anonymized yet high-precision RTK-fixed GNSS and IMU records. Correspondingly, we provide time-consistent 3D bounding box annotations for objects, as well as static scenes to construct a 4D BEV representation. On this basis, we propose a target-based temporal alignment method, ensuring that all objects are precisely aligned across all sensor modalities. We hope that CATS-V2V, the largest-scale, most supportive, and highest-quality dataset of its kind to date, will benefit the autonomous driving community in related tasks.
SLIM: Subtrajectory-Level Elimination for More Effective Reasoning
Aug 27, 2025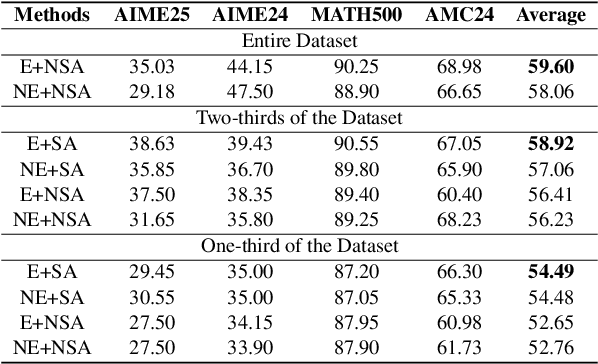
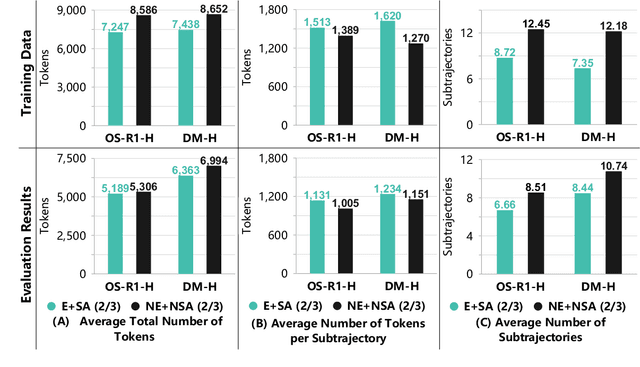
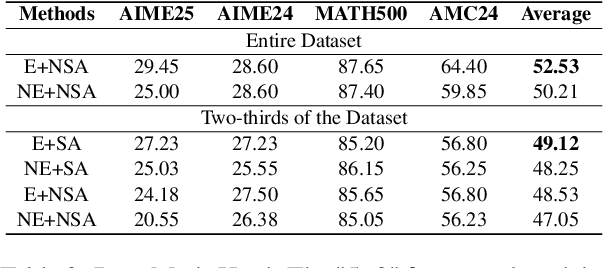
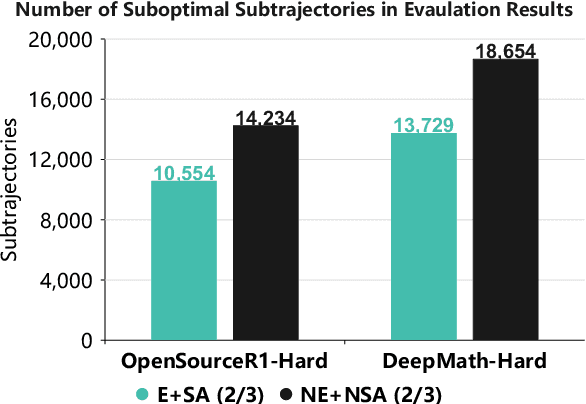
Abstract:In recent months, substantial progress has been made in complex reasoning of Large Language Models, particularly through the application of test-time scaling. Notable examples include o1/o3/o4 series and DeepSeek-R1. When responding to a query, these models generate an extended reasoning trajectory, during which the model explores, reflects, backtracks, and self-verifies before arriving at a conclusion. However, fine-tuning models with such reasoning trajectories may not always be optimal. Our findings indicate that not all components within these reasoning trajectories contribute positively to the reasoning process; in fact, some components may affect the overall performance negatively. In this study, we divide a reasoning trajectory into individual subtrajectories and develop a "5+2" framework to: (1) systematically identify suboptimal subtrajectories within the reasoning trajectory based on five human-established criteria; (2) assess the independence of the suboptimal subtrajectories identified in (1) from the subsequent content, ensuring that their elimination does not compromise overall flow and coherence of the reasoning process. Additionally, a sampling algorithm, built upon the "5+2" framework, is employed to select data whose reasoning process is free from suboptimal subtrajectories to the highest degree. Experimental results demonstrate that our method can reduce the number of suboptimal subtrajectories by 25.9\% during the inference. Furthermore, our method achieves an average accuracy of 58.92\% on highly challenging math benchmarks with only two thirds of training data, surpassing the average accuracy of 58.06\% achieved with the entire data, and outperforming open-source datasets, when fine-tuning Qwen2.5-Math-7B. Finally, We validated our method under resource constraints and observed improved performance across various inference token limits.
Towards Full-Scenario Safety Evaluation of Automated Vehicles: A Volume-Based Method
Jun 10, 2025Abstract:With the rapid development of automated vehicles (AVs) in recent years, commercially available AVs are increasingly demonstrating high-level automation capabilities. However, most existing AV safety evaluation methods are primarily designed for simple maneuvers such as car-following and lane-changing. While suitable for basic tests, these methods are insufficient for assessing high-level automation functions deployed in more complex environments. First, these methods typically use crash rate as the evaluation metric, whose accuracy heavily depends on the quality and completeness of naturalistic driving environment data used to estimate scenario probabilities. Such data is often difficult and expensive to collect. Second, when applied to diverse scenarios, these methods suffer from the curse of dimensionality, making large-scale evaluation computationally intractable. To address these challenges, this paper proposes a novel framework for full-scenario AV safety evaluation. A unified model is first introduced to standardize the representation of diverse driving scenarios. This modeling approach constrains the dimension of most scenarios to a regular highway setting with three lanes and six surrounding background vehicles, significantly reducing dimensionality. To further avoid the limitations of probability-based method, we propose a volume-based evaluation method that quantifies the proportion of risky scenarios within the entire scenario space. For car-following scenarios, we prove that the set of safe scenarios is convex under specific settings, enabling exact volume computation. Experimental results validate the effectiveness of the proposed volume-based method using both AV behavior models from existing literature and six production AV models calibrated from field-test trajectory data in the Ultra-AV dataset. Code and data will be made publicly available upon acceptance of this paper.
AutoStyle-TTS: Retrieval-Augmented Generation based Automatic Style Matching Text-to-Speech Synthesis
Apr 14, 2025Abstract:With the advancement of speech synthesis technology, users have higher expectations for the naturalness and expressiveness of synthesized speech. But previous research ignores the importance of prompt selection. This study proposes a text-to-speech (TTS) framework based on Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) technology, which can dynamically adjust the speech style according to the text content to achieve more natural and vivid communication effects. We have constructed a speech style knowledge database containing high-quality speech samples in various contexts and developed a style matching scheme. This scheme uses embeddings, extracted by Llama, PER-LLM-Embedder,and Moka, to match with samples in the knowledge database, selecting the most appropriate speech style for synthesis. Furthermore, our empirical research validates the effectiveness of the proposed method. Our demo can be viewed at: https://thuhcsi.github.io/icme2025-AutoStyle-TTS
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge