Sixing Lu
Feedback Control for Multi-Objective Graph Self-Supervision
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Can multi-task self-supervised learning on graphs be coordinated without the usual tug-of-war between objectives? Graph self-supervised learning (SSL) offers a growing toolbox of pretext objectives: mutual information, reconstruction, contrastive learning; yet combining them reliably remains a challenge due to objective interference and training instability. Most multi-pretext pipelines use per-update mixing, forcing every parameter update to be a compromise, leading to three failure modes: Disagreement (conflict-induced negative transfer), Drift (nonstationary objective utility), and Drought (hidden starvation of underserved objectives). We argue that coordination is fundamentally a temporal allocation problem: deciding when each objective receives optimization budget, not merely how to weigh them. We introduce ControlG, a control-theoretic framework that recasts multi-objective graph SSL as feedback-controlled temporal allocation by estimating per-objective difficulty and pairwise antagonism, planning target budgets via a Pareto-aware log-hypervolume planner, and scheduling with a Proportional-Integral-Derivative (PID) controller. Across 9 datasets, ControlG consistently outperforms state-of-the-art baselines, while producing an auditable schedule that reveals which objectives drove learning.
MEND: Meta dEmonstratioN Distillation for Efficient and Effective In-Context Learning
Mar 12, 2024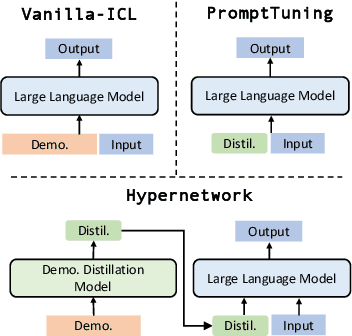
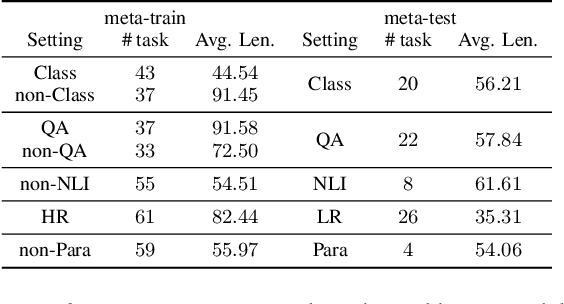
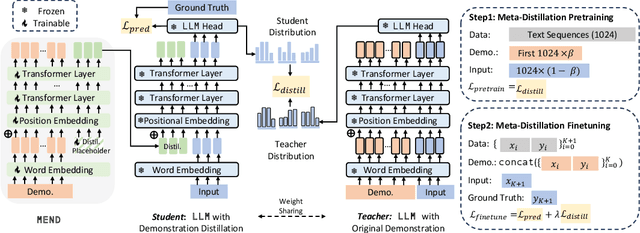
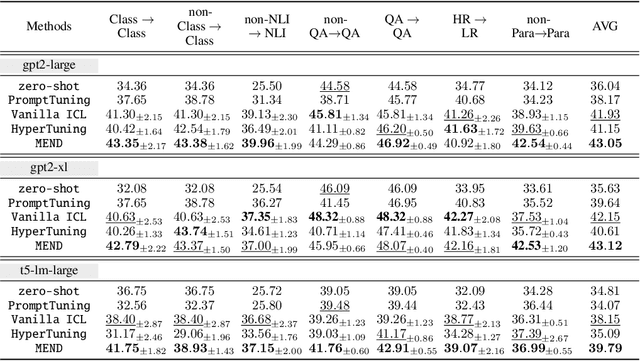
Abstract:Large Language models (LLMs) have demonstrated impressive in-context learning (ICL) capabilities, where a LLM makes predictions for a given test input together with a few input-output pairs (demonstrations). Nevertheless, the inclusion of demonstrations leads to a quadratic increase in the computational overhead of the self-attention mechanism. Existing solutions attempt to distill lengthy demonstrations into compact vectors. However, they often require task-specific retraining or compromise LLM's in-context learning performance. To mitigate these challenges, we present Meta dEmonstratioN Distillation (MEND), where a language model learns to distill any lengthy demonstrations into vectors without retraining for a new downstream task. We exploit the knowledge distillation to enhance alignment between MEND and LLM, achieving both efficiency and effectiveness simultaneously. MEND is endowed with the meta-knowledge of distilling demonstrations through a two-stage training process, which includes meta-distillation pretraining and fine-tuning. Comprehensive evaluations across seven diverse ICL task partitions using decoder-only (GPT-2) and encoder-decoder (T5) attest to MEND's prowess. It not only matches but often outperforms the Vanilla ICL as well as other state-of-the-art distillation models, while significantly reducing the computational demands. This innovation promises enhanced scalability and efficiency for the practical deployment of large language models
CLICKER: Attention-Based Cross-Lingual Commonsense Knowledge Transfer
Feb 26, 2023Abstract:Recent advances in cross-lingual commonsense reasoning (CSR) are facilitated by the development of multilingual pre-trained models (mPTMs). While mPTMs show the potential to encode commonsense knowledge for different languages, transferring commonsense knowledge learned in large-scale English corpus to other languages is challenging. To address this problem, we propose the attention-based Cross-LIngual Commonsense Knowledge transfER (CLICKER) framework, which minimizes the performance gaps between English and non-English languages in commonsense question-answering tasks. CLICKER effectively improves commonsense reasoning for non-English languages by differentiating non-commonsense knowledge from commonsense knowledge. Experimental results on public benchmarks demonstrate that CLICKER achieves remarkable improvements in the cross-lingual CSR task for languages other than English.
Query Expansion and Entity Weighting for Query Reformulation Retrieval in Voice Assistant Systems
Feb 22, 2022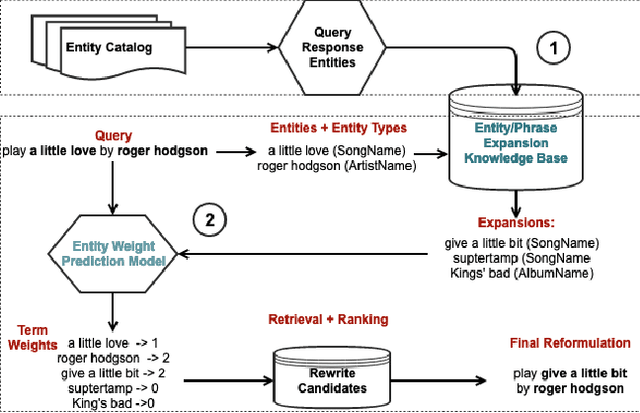
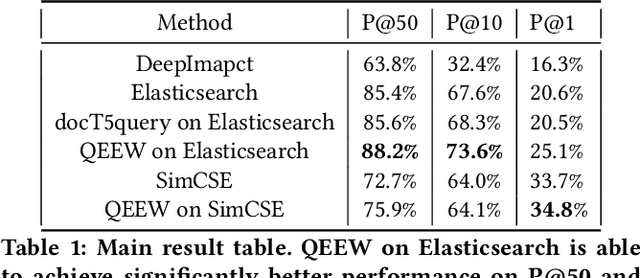
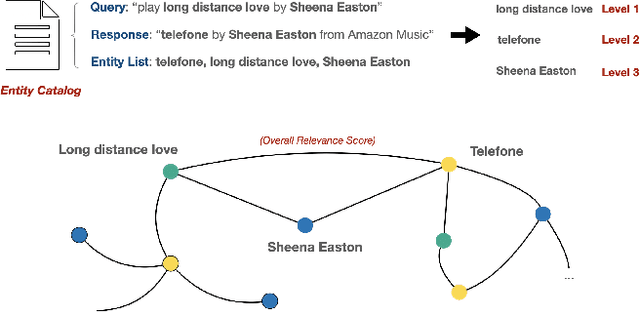
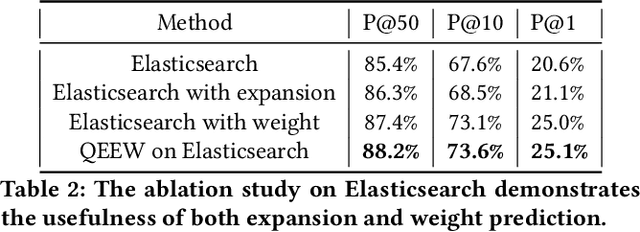
Abstract:Voice assistants such as Alexa, Siri, and Google Assistant have become increasingly popular worldwide. However, linguistic variations, variability of speech patterns, ambient acoustic conditions, and other such factors are often correlated with the assistants misinterpreting the user's query. In order to provide better customer experience, retrieval based query reformulation (QR) systems are widely used to reformulate those misinterpreted user queries. Current QR systems typically focus on neural retrieval model training or direct entities retrieval for the reformulating. However, these methods rarely focus on query expansion and entity weighting simultaneously, which may limit the scope and accuracy of the query reformulation retrieval. In this work, we propose a novel Query Expansion and Entity Weighting method (QEEW), which leverages the relationships between entities in the entity catalog (consisting of users' queries, assistant's responses, and corresponding entities), to enhance the query reformulation performance. Experiments on Alexa annotated data demonstrate that QEEW improves all top precision metrics, particularly 6% improvement in top10 precision, compared with baselines not using query expansion and weighting; and more than 5% improvement in top10 precision compared with other baselines using query expansion and weighting.
VAE based Text Style Transfer with Pivot Words Enhancement Learning
Dec 06, 2021
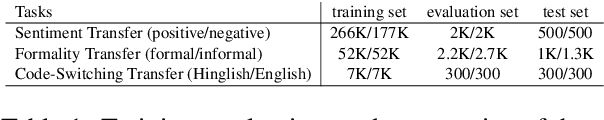
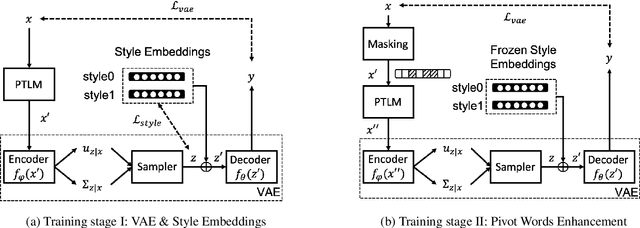
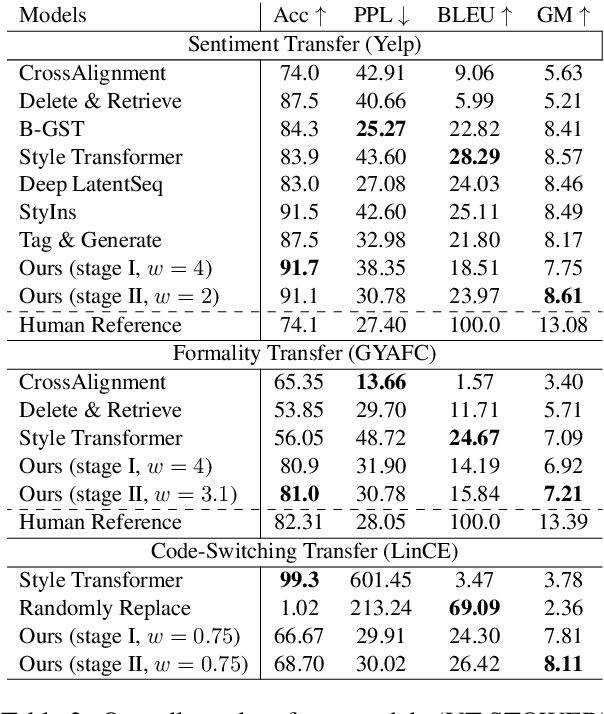
Abstract:Text Style Transfer (TST) aims to alter the underlying style of the source text to another specific style while keeping the same content. Due to the scarcity of high-quality parallel training data, unsupervised learning has become a trending direction for TST tasks. In this paper, we propose a novel VAE based Text Style Transfer with pivOt Words Enhancement leaRning (VT-STOWER) method which utilizes Variational AutoEncoder (VAE) and external style embeddings to learn semantics and style distribution jointly. Additionally, we introduce pivot words learning, which is applied to learn decisive words for a specific style and thereby further improve the overall performance of the style transfer. The proposed VT-STOWER can be scaled to different TST scenarios given very limited and non-parallel training data with a novel and flexible style strength control mechanism. Experiments demonstrate that the VT-STOWER outperforms the state-of-the-art on sentiment, formality, and code-switching TST tasks.
Pattern-aware Data Augmentation for Query Rewriting in Voice Assistant Systems
Dec 21, 2020



Abstract:Query rewriting (QR) systems are widely used to reduce the friction caused by errors in a spoken language understanding pipeline. However, the underlying supervised models require a large number of labeled pairs, and these pairs are hard and costly to be collected. Therefore, We propose an augmentation framework that learns patterns from existing training pairs and generates rewrite candidates from rewrite labels inversely to compensate for insufficient QR training data. The proposed framework casts the augmentation problem as a sequence-to-sequence generation task and enforces the optimization process with a policy gradient technique for controllable rewarding. This approach goes beyond the traditional heuristics or rule-based augmentation methods and is not constrained to generate predefined patterns of swapping/replacing words. Our experimental results show its effectiveness compared with a fully trained QR baseline and demonstrate its potential application in boosting the QR performance on low-resource domains or locales.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge