Xiaojiang Huang
PAFFA: Premeditated Actions For Fast Agents
Dec 10, 2024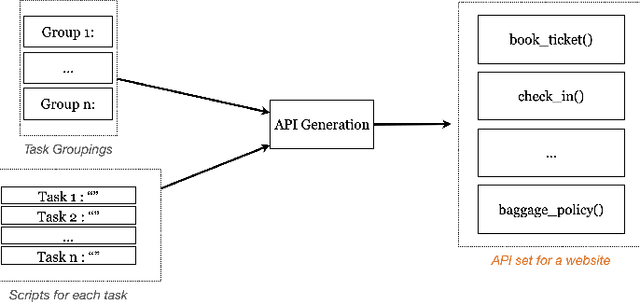
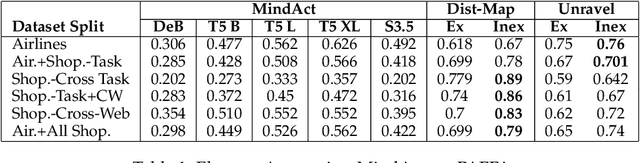
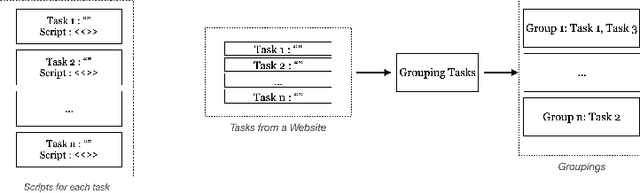
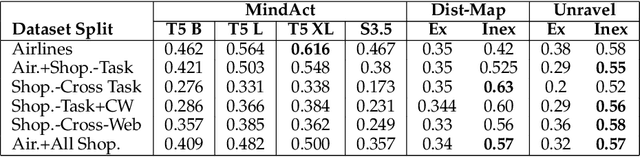
Abstract:Modern AI assistants have made significant progress in natural language understanding and API/tool integration, with emerging efforts to incorporate diverse interfaces (such as Web interfaces) for enhanced scalability and functionality. However, current approaches that heavily rely on repeated LLM-driven HTML parsing are computationally expensive and error-prone, particularly when handling dynamic web interfaces and multi-step tasks. To overcome these challenges, we introduce PAFFA (Premeditated Actions For Fast Agents), a framework designed to enhance web interaction capabilities through an Action API Library of reusable, verified browser interaction functions. By pre-computing interaction patterns and employing two core methodologies - "Dist-Map" for task-agnostic element distillation and "Unravel" for incremental page-wise exploration - PAFFA reduces inference calls by 87% while maintaining robust performance even as website structures evolve. This framework accelerates multi-page task execution and offers a scalable solution to advance autonomous web agent research.
RecMind: Large Language Model Powered Agent For Recommendation
Aug 28, 2023



Abstract:Recent advancements in instructing Large Language Models (LLMs) to utilize external tools and execute multi-step plans have significantly enhanced their ability to solve intricate tasks, ranging from mathematical problems to creative writing. Yet, there remains a notable gap in studying the capacity of LLMs in responding to personalized queries such as a recommendation request. To bridge this gap, we have designed an LLM-powered autonomous recommender agent, RecMind, which is capable of providing precise personalized recommendations through careful planning, utilizing tools for obtaining external knowledge, and leveraging individual data. We propose a novel algorithm, Self-Inspiring, to improve the planning ability of the LLM agent. At each intermediate planning step, the LLM 'self-inspires' to consider all previously explored states to plan for next step. This mechanism greatly improves the model's ability to comprehend and utilize historical planning information for recommendation. We evaluate RecMind's performance in various recommendation scenarios, including rating prediction, sequential recommendation, direct recommendation, explanation generation, and review summarization. Our experiment shows that RecMind outperforms existing zero/few-shot LLM-based recommendation methods in different recommendation tasks and achieves competitive performance to a recent model P5, which requires fully pre-train for the recommendation tasks.
Pattern-aware Data Augmentation for Query Rewriting in Voice Assistant Systems
Dec 21, 2020



Abstract:Query rewriting (QR) systems are widely used to reduce the friction caused by errors in a spoken language understanding pipeline. However, the underlying supervised models require a large number of labeled pairs, and these pairs are hard and costly to be collected. Therefore, We propose an augmentation framework that learns patterns from existing training pairs and generates rewrite candidates from rewrite labels inversely to compensate for insufficient QR training data. The proposed framework casts the augmentation problem as a sequence-to-sequence generation task and enforces the optimization process with a policy gradient technique for controllable rewarding. This approach goes beyond the traditional heuristics or rule-based augmentation methods and is not constrained to generate predefined patterns of swapping/replacing words. Our experimental results show its effectiveness compared with a fully trained QR baseline and demonstrate its potential application in boosting the QR performance on low-resource domains or locales.
Learning to Mine Chinese Coordinate Terms Using the Web
Jul 13, 2015



Abstract:Coordinate relation refers to the relation between instances of a concept and the relation between the directly hyponyms of a concept. In this paper, we focus on the task of extracting terms which are coordinate with a user given seed term in Chinese, and grouping the terms which belong to different concepts if the seed term has several meanings. We propose a semi-supervised method that integrates manually defined linguistic patterns and automatically learned semi-structural patterns to extract coordinate terms in Chinese from web search results. In addition, terms are grouped into different concepts based on their co-occurring terms and contexts. We further calculate the saliency scores of extracted terms and rank them accordingly. Experimental results demonstrate that our proposed method generates results with high quality and wide coverage.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge