Zhuowen Tu
Soft Tail-dropping for Adaptive Visual Tokenization
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:We present Soft Tail-dropping Adaptive Tokenizer (STAT), a 1D discrete visual tokenizer that adaptively chooses the number of output tokens per image according to its structural complexity and level of detail. STAT encodes an image into a sequence of discrete codes together with per-token keep probabilities. Beyond standard autoencoder objectives, we regularize these keep probabilities to be monotonically decreasing along the sequence and explicitly align their distribution with an image-level complexity measure. As a result, STAT produces length-adaptive 1D visual tokens that are naturally compatible with causal 1D autoregressive (AR) visual generative models. On ImageNet-1k, equipping vanilla causal AR models with STAT yields competitive or superior visual generation quality compared to other probabilistic model families, while also exhibiting favorable scaling behavior that has been elusive in prior vanilla AR visual generation attempts.
Talk2Move: Reinforcement Learning for Text-Instructed Object-Level Geometric Transformation in Scenes
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:We introduce Talk2Move, a reinforcement learning (RL) based diffusion framework for text-instructed spatial transformation of objects within scenes. Spatially manipulating objects in a scene through natural language poses a challenge for multimodal generation systems. While existing text-based manipulation methods can adjust appearance or style, they struggle to perform object-level geometric transformations-such as translating, rotating, or resizing objects-due to scarce paired supervision and pixel-level optimization limits. Talk2Move employs Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) to explore geometric actions through diverse rollouts generated from input images and lightweight textual variations, removing the need for costly paired data. A spatial reward guided model aligns geometric transformations with linguistic description, while off-policy step evaluation and active step sampling improve learning efficiency by focusing on informative transformation stages. Furthermore, we design object-centric spatial rewards that evaluate displacement, rotation, and scaling behaviors directly, enabling interpretable and coherent transformations. Experiments on curated benchmarks demonstrate that Talk2Move achieves precise, consistent, and semantically faithful object transformations, outperforming existing text-guided editing approaches in both spatial accuracy and scene coherence.
CVP: Central-Peripheral Vision-Inspired Multimodal Model for Spatial Reasoning
Dec 09, 2025Abstract:We present a central-peripheral vision-inspired framework (CVP), a simple yet effective multimodal model for spatial reasoning that draws inspiration from the two types of human visual fields -- central vision and peripheral vision. Existing approaches primarily rely on unstructured representations, such as point clouds, voxels, or patch features, and inject scene context implicitly via coordinate embeddings. However, this often results in limited spatial reasoning capabilities due to the lack of explicit, high-level structural understanding. To address this limitation, we introduce two complementary components into a Large Multimodal Model-based architecture: target-affinity token, analogous to central vision, that guides the model's attention toward query-relevant objects; and allocentric grid, akin to peripheral vision, that captures global scene context and spatial arrangements. These components work in tandem to enable structured, context-aware understanding of complex 3D environments. Experiments show that CVP achieves state-of-the-art performance across a range of 3D scene understanding benchmarks.
Real Deep Research for AI, Robotics and Beyond
Oct 23, 2025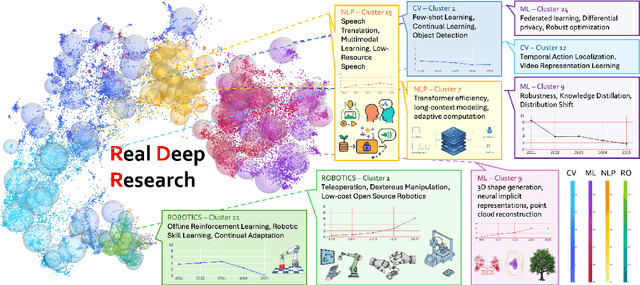
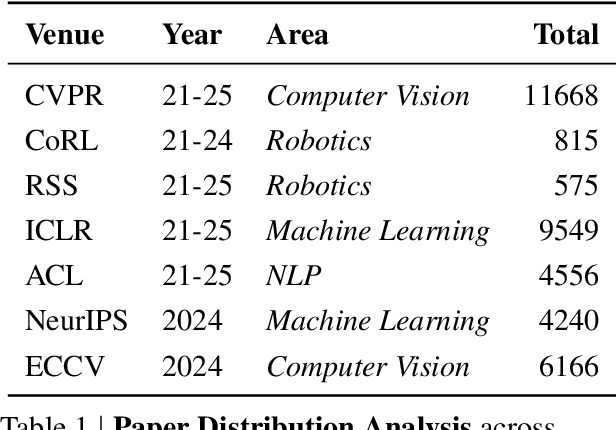
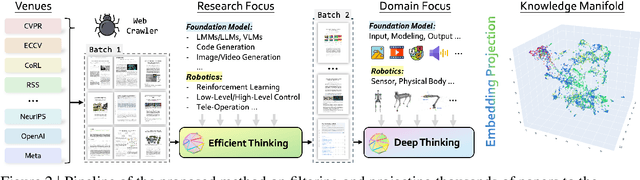
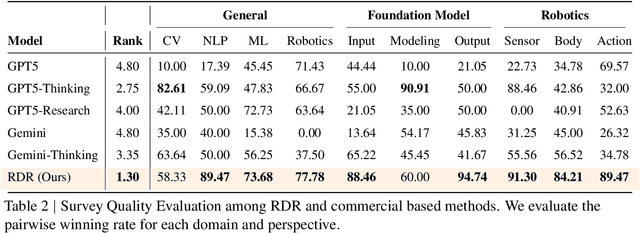
Abstract:With the rapid growth of research in AI and robotics now producing over 10,000 papers annually it has become increasingly difficult for researchers to stay up to date. Fast evolving trends, the rise of interdisciplinary work, and the need to explore domains beyond one's expertise all contribute to this challenge. To address these issues, we propose a generalizable pipeline capable of systematically analyzing any research area: identifying emerging trends, uncovering cross domain opportunities, and offering concrete starting points for new inquiry. In this work, we present Real Deep Research (RDR) a comprehensive framework applied to the domains of AI and robotics, with a particular focus on foundation models and robotics advancements. We also briefly extend our analysis to other areas of science. The main paper details the construction of the RDR pipeline, while the appendix provides extensive results across each analyzed topic. We hope this work sheds light for researchers working in the field of AI and beyond.
C3Editor: Achieving Controllable Consistency in 2D Model for 3D Editing
Oct 06, 2025Abstract:Existing 2D-lifting-based 3D editing methods often encounter challenges related to inconsistency, stemming from the lack of view-consistent 2D editing models and the difficulty of ensuring consistent editing across multiple views. To address these issues, we propose C3Editor, a controllable and consistent 2D-lifting-based 3D editing framework. Given an original 3D representation and a text-based editing prompt, our method selectively establishes a view-consistent 2D editing model to achieve superior 3D editing results. The process begins with the controlled selection of a ground truth (GT) view and its corresponding edited image as the optimization target, allowing for user-defined manual edits. Next, we fine-tune the 2D editing model within the GT view and across multiple views to align with the GT-edited image while ensuring multi-view consistency. To meet the distinct requirements of GT view fitting and multi-view consistency, we introduce separate LoRA modules for targeted fine-tuning. Our approach delivers more consistent and controllable 2D and 3D editing results than existing 2D-lifting-based methods, outperforming them in both qualitative and quantitative evaluations.
VideoNSA: Native Sparse Attention Scales Video Understanding
Oct 02, 2025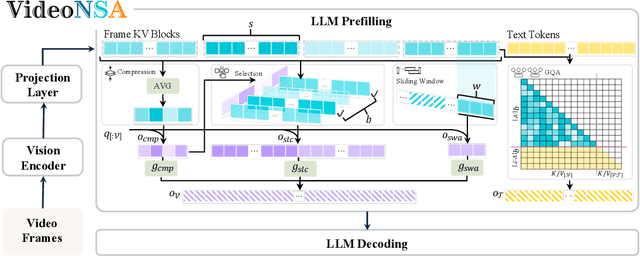
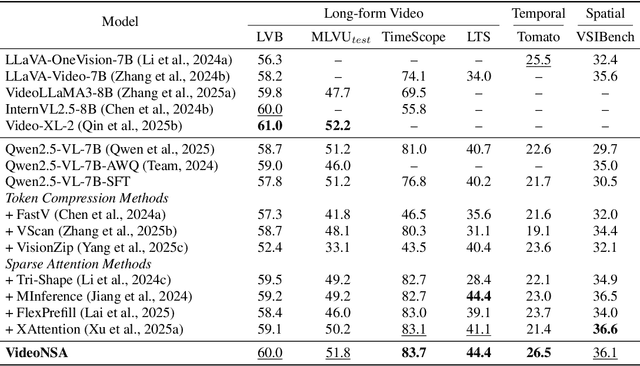
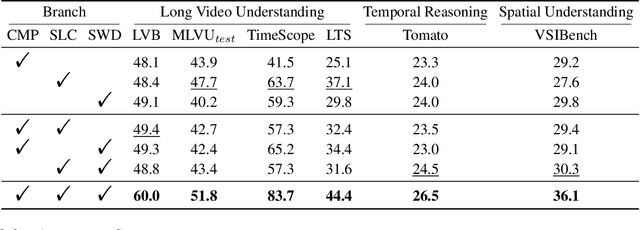
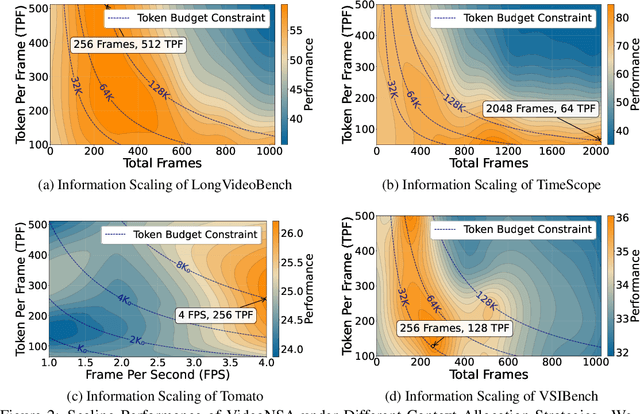
Abstract:Video understanding in multimodal language models remains limited by context length: models often miss key transition frames and struggle to maintain coherence across long time scales. To address this, we adapt Native Sparse Attention (NSA) to video-language models. Our method, VideoNSA, adapts Qwen2.5-VL through end-to-end training on a 216K video instruction dataset. We employ a hardware-aware hybrid approach to attention, preserving dense attention for text, while employing NSA for video. Compared to token-compression and training-free sparse baselines, VideoNSA achieves improved performance on long-video understanding, temporal reasoning, and spatial benchmarks. Further ablation analysis reveals four key findings: (1) reliable scaling to 128K tokens; (2) an optimal global-local attention allocation at a fixed budget; (3) task-dependent branch usage patterns; and (4) the learnable combined sparse attention help induce dynamic attention sinks.
YOLO-Count: Differentiable Object Counting for Text-to-Image Generation
Aug 01, 2025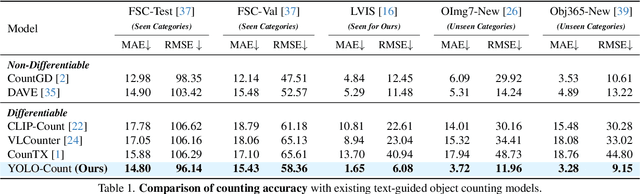
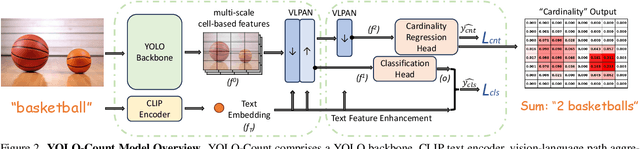
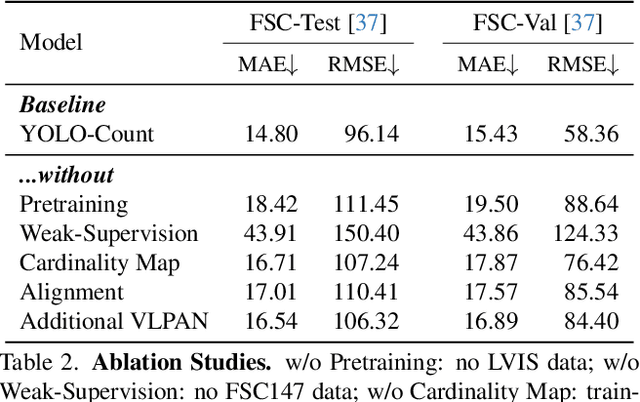
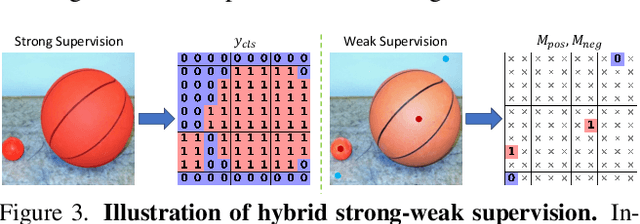
Abstract:We propose YOLO-Count, a differentiable open-vocabulary object counting model that tackles both general counting challenges and enables precise quantity control for text-to-image (T2I) generation. A core contribution is the 'cardinality' map, a novel regression target that accounts for variations in object size and spatial distribution. Leveraging representation alignment and a hybrid strong-weak supervision scheme, YOLO-Count bridges the gap between open-vocabulary counting and T2I generation control. Its fully differentiable architecture facilitates gradient-based optimization, enabling accurate object count estimation and fine-grained guidance for generative models. Extensive experiments demonstrate that YOLO-Count achieves state-of-the-art counting accuracy while providing robust and effective quantity control for T2I systems.
DepR: Depth Guided Single-view Scene Reconstruction with Instance-level Diffusion
Jul 30, 2025Abstract:We propose DepR, a depth-guided single-view scene reconstruction framework that integrates instance-level diffusion within a compositional paradigm. Instead of reconstructing the entire scene holistically, DepR generates individual objects and subsequently composes them into a coherent 3D layout. Unlike previous methods that use depth solely for object layout estimation during inference and therefore fail to fully exploit its rich geometric information, DepR leverages depth throughout both training and inference. Specifically, we introduce depth-guided conditioning to effectively encode shape priors into diffusion models. During inference, depth further guides DDIM sampling and layout optimization, enhancing alignment between the reconstruction and the input image. Despite being trained on limited synthetic data, DepR achieves state-of-the-art performance and demonstrates strong generalization in single-view scene reconstruction, as shown through evaluations on both synthetic and real-world datasets.
AuthGuard: Generalizable Deepfake Detection via Language Guidance
Jun 04, 2025Abstract:Existing deepfake detection techniques struggle to keep-up with the ever-evolving novel, unseen forgeries methods. This limitation stems from their reliance on statistical artifacts learned during training, which are often tied to specific generation processes that may not be representative of samples from new, unseen deepfake generation methods encountered at test time. We propose that incorporating language guidance can improve deepfake detection generalization by integrating human-like commonsense reasoning -- such as recognizing logical inconsistencies and perceptual anomalies -- alongside statistical cues. To achieve this, we train an expert deepfake vision encoder by combining discriminative classification with image-text contrastive learning, where the text is generated by generalist MLLMs using few-shot prompting. This allows the encoder to extract both language-describable, commonsense deepfake artifacts and statistical forgery artifacts from pixel-level distributions. To further enhance robustness, we integrate data uncertainty learning into vision-language contrastive learning, mitigating noise in image-text supervision. Our expert vision encoder seamlessly interfaces with an LLM, further enabling more generalized and interpretable deepfake detection while also boosting accuracy. The resulting framework, AuthGuard, achieves state-of-the-art deepfake detection accuracy in both in-distribution and out-of-distribution settings, achieving AUC gains of 6.15% on the DFDC dataset and 16.68% on the DF40 dataset. Additionally, AuthGuard significantly enhances deepfake reasoning, improving performance by 24.69% on the DDVQA dataset.
Ground-V: Teaching VLMs to Ground Complex Instructions in Pixels
May 20, 2025Abstract:This work presents a simple yet effective workflow for automatically scaling instruction-following data to elicit pixel-level grounding capabilities of VLMs under complex instructions. In particular, we address five critical real-world challenges in text-instruction-based grounding: hallucinated references, multi-object scenarios, reasoning, multi-granularity, and part-level references. By leveraging knowledge distillation from a pre-trained teacher model, our approach generates high-quality instruction-response pairs linked to existing pixel-level annotations, minimizing the need for costly human annotation. The resulting dataset, Ground-V, captures rich object localization knowledge and nuanced pixel-level referring expressions. Experiment results show that models trained on Ground-V exhibit substantial improvements across diverse grounding tasks. Specifically, incorporating Ground-V during training directly achieves an average accuracy boost of 4.4% for LISA and a 7.9% for PSALM across six benchmarks on the gIoU metric. It also sets new state-of-the-art results on standard benchmarks such as RefCOCO/+/g. Notably, on gRefCOCO, we achieve an N-Acc of 83.3%, exceeding the previous state-of-the-art by more than 20%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge