Zirui Wang
VisGym: Diverse, Customizable, Scalable Environments for Multimodal Agents
Jan 23, 2026Abstract:Modern Vision-Language Models (VLMs) remain poorly characterized in multi-step visual interactions, particularly in how they integrate perception, memory, and action over long horizons. We introduce VisGym, a gymnasium of 17 environments for evaluating and training VLMs. The suite spans symbolic puzzles, real-image understanding, navigation, and manipulation, and provides flexible controls over difficulty, input representation, planning horizon, and feedback. We also provide multi-step solvers that generate structured demonstrations, enabling supervised finetuning. Our evaluations show that all frontier models struggle in interactive settings, achieving low success rates in both the easy (46.6%) and hard (26.0%) configurations. Our experiments reveal notable limitations: models struggle to effectively leverage long context, performing worse with an unbounded history than with truncated windows. Furthermore, we find that several text-based symbolic tasks become substantially harder once rendered visually. However, explicit goal observations, textual feedback, and exploratory demonstrations in partially observable or unknown-dynamics settings for supervised finetuning yield consistent gains, highlighting concrete failure modes and pathways for improving multi-step visual decision-making. Code, data, and models can be found at: https://visgym.github.io/.
Why Does the LLM Stop Computing: An Empirical Study of User-Reported Failures in Open-Source LLMs
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:The democratization of open-source Large Language Models (LLMs) allows users to fine-tune and deploy models on local infrastructure but exposes them to a First Mile deployment landscape. Unlike black-box API consumption, the reliability of user-managed orchestration remains a critical blind spot. To bridge this gap, we conduct the first large-scale empirical study of 705 real-world failures from the open-source DeepSeek, Llama, and Qwen ecosystems. Our analysis reveals a paradigm shift: white-box orchestration relocates the reliability bottleneck from model algorithmic defects to the systemic fragility of the deployment stack. We identify three key phenomena: (1) Diagnostic Divergence: runtime crashes distinctively signal infrastructure friction, whereas incorrect functionality serves as a signature for internal tokenizer defects. (2) Systemic Homogeneity: Root causes converge across divergent series, confirming reliability barriers are inherent to the shared ecosystem rather than specific architectures. (3) Lifecycle Escalation: Barriers escalate from intrinsic configuration struggles during fine-tuning to compounded environmental incompatibilities during inference. Supported by our publicly available dataset, these insights provide actionable guidance for enhancing the reliability of the LLM landscape.
FrontierCS: Evolving Challenges for Evolving Intelligence
Dec 17, 2025



Abstract:We introduce FrontierCS, a benchmark of 156 open-ended problems across diverse areas of computer science, designed and reviewed by experts, including CS PhDs and top-tier competitive programming participants and problem setters. Unlike existing benchmarks that focus on tasks with known optimal solutions, FrontierCS targets problems where the optimal solution is unknown, but the quality of a solution can be objectively evaluated. Models solve these tasks by implementing executable programs rather than outputting a direct answer. FrontierCS includes algorithmic problems, which are often NP-hard variants of competitive programming problems with objective partial scoring, and research problems with the same property. For each problem we provide an expert reference solution and an automatic evaluator. Combining open-ended design, measurable progress, and expert curation, FrontierCS provides a benchmark at the frontier of computer-science difficulty. Empirically, we find that frontier reasoning models still lag far behind human experts on both the algorithmic and research tracks, that increasing reasoning budgets alone does not close this gap, and that models often over-optimize for generating merely workable code instead of discovering high-quality algorithms and system designs.
Unveiling the Impact of Data and Model Scaling on High-Level Control for Humanoid Robots
Nov 12, 2025
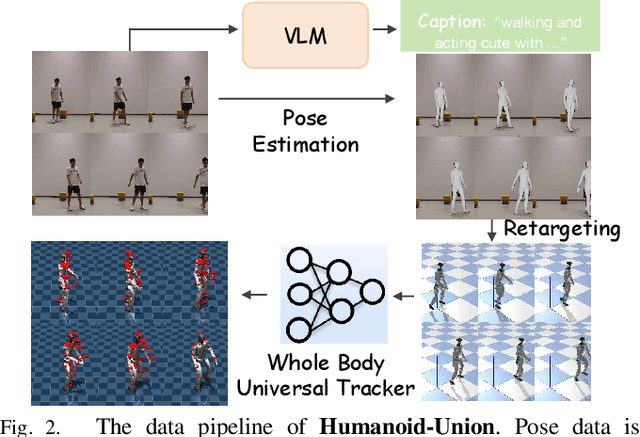
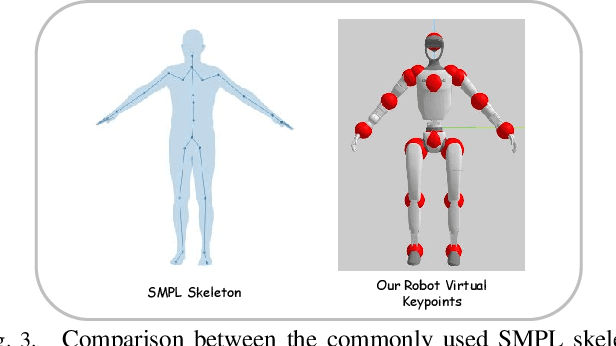
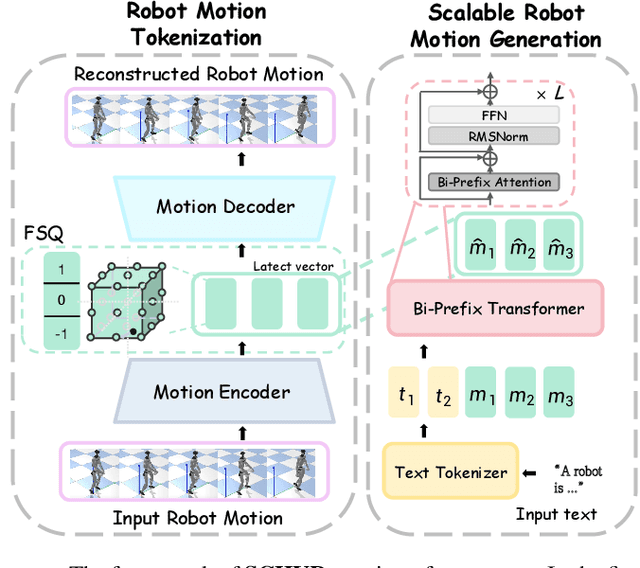
Abstract:Data scaling has long remained a critical bottleneck in robot learning. For humanoid robots, human videos and motion data are abundant and widely available, offering a free and large-scale data source. Besides, the semantics related to the motions enable modality alignment and high-level robot control learning. However, how to effectively mine raw video, extract robot-learnable representations, and leverage them for scalable learning remains an open problem. To address this, we introduce Humanoid-Union, a large-scale dataset generated through an autonomous pipeline, comprising over 260 hours of diverse, high-quality humanoid robot motion data with semantic annotations derived from human motion videos. The dataset can be further expanded via the same pipeline. Building on this data resource, we propose SCHUR, a scalable learning framework designed to explore the impact of large-scale data on high-level control in humanoid robots. Experimental results demonstrate that SCHUR achieves high robot motion generation quality and strong text-motion alignment under data and model scaling, with 37\% reconstruction improvement under MPJPE and 25\% alignment improvement under FID comparing with previous methods. Its effectiveness is further validated through deployment in real-world humanoid robot.
Towards Adaptable Humanoid Control via Adaptive Motion Tracking
Oct 16, 2025Abstract:Humanoid robots are envisioned to adapt demonstrated motions to diverse real-world conditions while accurately preserving motion patterns. Existing motion prior approaches enable well adaptability with a few motions but often sacrifice imitation accuracy, whereas motion-tracking methods achieve accurate imitation yet require many training motions and a test-time target motion to adapt. To combine their strengths, we introduce AdaMimic, a novel motion tracking algorithm that enables adaptable humanoid control from a single reference motion. To reduce data dependence while ensuring adaptability, our method first creates an augmented dataset by sparsifying the single reference motion into keyframes and applying light editing with minimal physical assumptions. A policy is then initialized by tracking these sparse keyframes to generate dense intermediate motions, and adapters are subsequently trained to adjust tracking speed and refine low-level actions based on the adjustment, enabling flexible time warping that further improves imitation accuracy and adaptability. We validate these significant improvements in our approach in both simulation and the real-world Unitree G1 humanoid robot in multiple tasks across a wide range of adaptation conditions. Videos and code are available at https://taohuang13.github.io/adamimic.github.io/.
COMPASS: A Multi-Turn Benchmark for Tool-Mediated Planning & Preference Optimization
Oct 08, 2025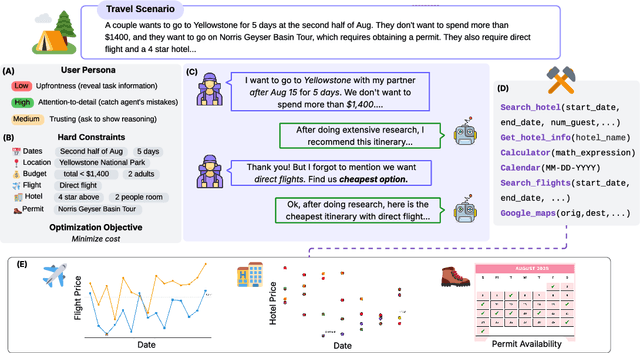
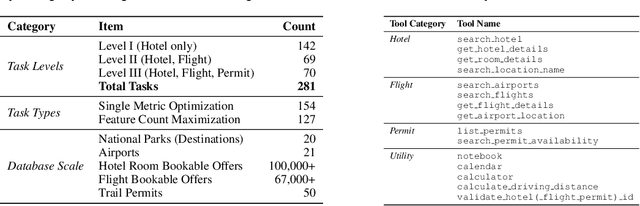
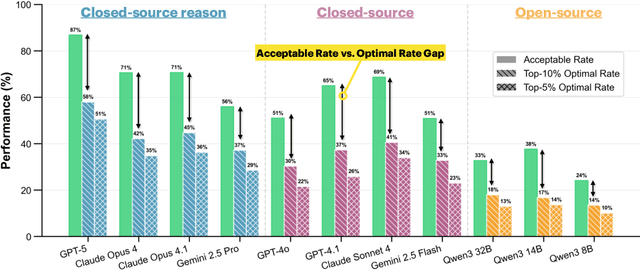
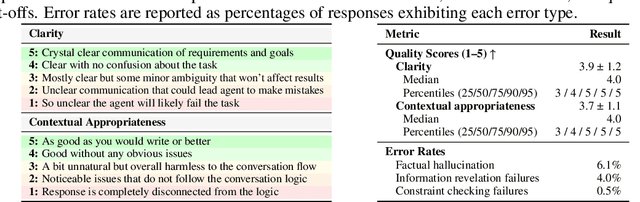
Abstract:Real-world large language model (LLM) agents must master strategic tool use and user preference optimization through multi-turn interactions to assist users with complex planning tasks. We introduce COMPASS (Constrained Optimization through Multi-turn Planning and Strategic Solutions), a benchmark that evaluates agents on realistic travel-planning scenarios. We cast travel planning as a constrained preference optimization problem, where agents must satisfy hard constraints while simultaneously optimizing soft user preferences. To support this, we build a realistic travel database covering transportation, accommodation, and ticketing for 20 U.S. National Parks, along with a comprehensive tool ecosystem that mirrors commercial booking platforms. Evaluating state-of-the-art models, we uncover two critical gaps: (i) an acceptable-optimal gap, where agents reliably meet constraints but fail to optimize preferences, and (ii) a plan-coordination gap, where performance collapses on multi-service (flight and hotel) coordination tasks, especially for open-source models. By grounding reasoning and planning in a practical, user-facing domain, COMPASS provides a benchmark that directly measures an agent's ability to optimize user preferences in realistic tasks, bridging theoretical advances with real-world impact.
MANZANO: A Simple and Scalable Unified Multimodal Model with a Hybrid Vision Tokenizer
Sep 19, 2025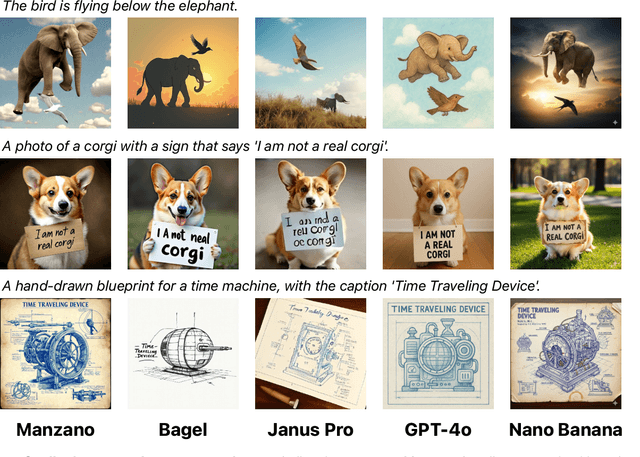
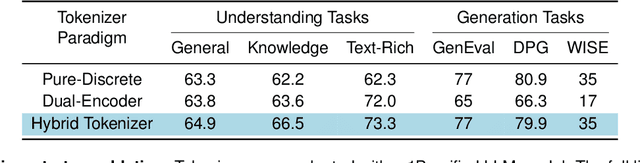
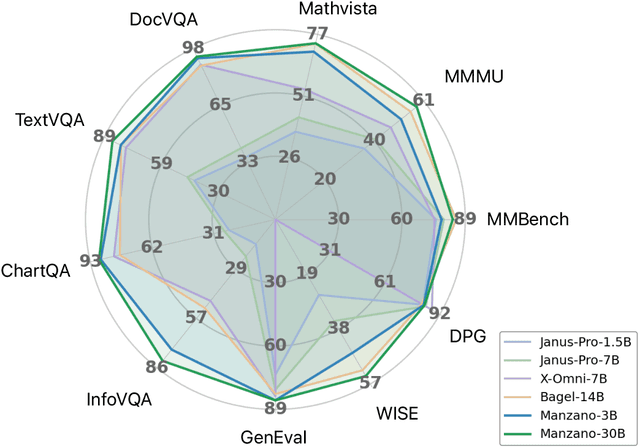
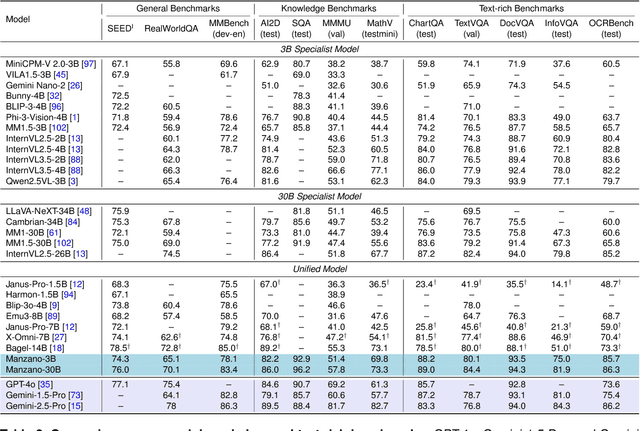
Abstract:Unified multimodal Large Language Models (LLMs) that can both understand and generate visual content hold immense potential. However, existing open-source models often suffer from a performance trade-off between these capabilities. We present Manzano, a simple and scalable unified framework that substantially reduces this tension by coupling a hybrid image tokenizer with a well-curated training recipe. A single shared vision encoder feeds two lightweight adapters that produce continuous embeddings for image-to-text understanding and discrete tokens for text-to-image generation within a common semantic space. A unified autoregressive LLM predicts high-level semantics in the form of text and image tokens, with an auxiliary diffusion decoder subsequently translating the image tokens into pixels. The architecture, together with a unified training recipe over understanding and generation data, enables scalable joint learning of both capabilities. Manzano achieves state-of-the-art results among unified models, and is competitive with specialist models, particularly on text-rich evaluation. Our studies show minimal task conflicts and consistent gains from scaling model size, validating our design choice of a hybrid tokenizer.
YOLO-Count: Differentiable Object Counting for Text-to-Image Generation
Aug 01, 2025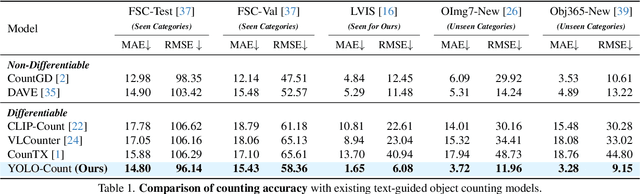
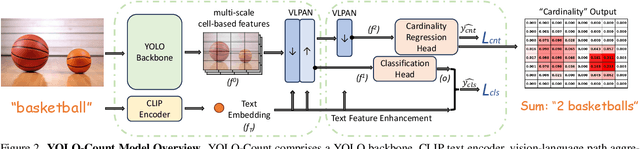
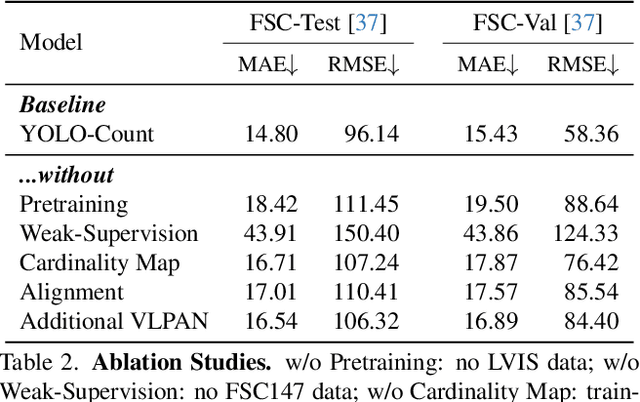
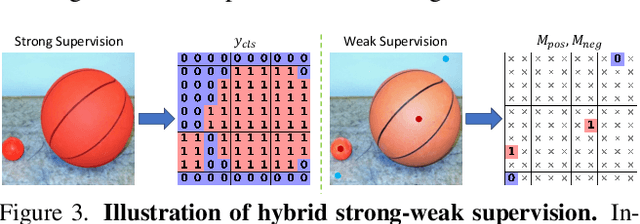
Abstract:We propose YOLO-Count, a differentiable open-vocabulary object counting model that tackles both general counting challenges and enables precise quantity control for text-to-image (T2I) generation. A core contribution is the 'cardinality' map, a novel regression target that accounts for variations in object size and spatial distribution. Leveraging representation alignment and a hybrid strong-weak supervision scheme, YOLO-Count bridges the gap between open-vocabulary counting and T2I generation control. Its fully differentiable architecture facilitates gradient-based optimization, enabling accurate object count estimation and fine-grained guidance for generative models. Extensive experiments demonstrate that YOLO-Count achieves state-of-the-art counting accuracy while providing robust and effective quantity control for T2I systems.
UniTracker: Learning Universal Whole-Body Motion Tracker for Humanoid Robots
Jul 10, 2025Abstract:Humanoid robots must achieve diverse, robust, and generalizable whole-body control to operate effectively in complex, human-centric environments. However, existing methods, particularly those based on teacher-student frameworks often suffer from a loss of motion diversity during policy distillation and exhibit limited generalization to unseen behaviors. In this work, we present UniTracker, a simplified yet powerful framework that integrates a Conditional Variational Autoencoder (CVAE) into the student policy to explicitly model the latent diversity of human motion. By leveraging a learned CVAE prior, our method enables the student to retain expressive motion characteristics while improving robustness and adaptability under partial observations. The result is a single policy capable of tracking a wide spectrum of whole-body motions with high fidelity and stability. Comprehensive experiments in both simulation and real-world deployments demonstrate that UniTracker significantly outperforms MLP-based DAgger baselines in motion quality, generalization to unseen references, and deployment robustness, offering a practical and scalable solution for expressive humanoid control.
Active View Selector: Fast and Accurate Active View Selection with Cross Reference Image Quality Assessment
Jun 24, 2025Abstract:We tackle active view selection in novel view synthesis and 3D reconstruction. Existing methods like FisheRF and ActiveNeRF select the next best view by minimizing uncertainty or maximizing information gain in 3D, but they require specialized designs for different 3D representations and involve complex modelling in 3D space. Instead, we reframe this as a 2D image quality assessment (IQA) task, selecting views where current renderings have the lowest quality. Since ground-truth images for candidate views are unavailable, full-reference metrics like PSNR and SSIM are inapplicable, while no-reference metrics, such as MUSIQ and MANIQA, lack the essential multi-view context. Inspired by a recent cross-referencing quality framework CrossScore, we train a model to predict SSIM within a multi-view setup and use it to guide view selection. Our cross-reference IQA framework achieves substantial quantitative and qualitative improvements across standard benchmarks, while being agnostic to 3D representations, and runs 14-33 times faster than previous methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge