Huayi Wang
Towards Adaptable Humanoid Control via Adaptive Motion Tracking
Oct 16, 2025Abstract:Humanoid robots are envisioned to adapt demonstrated motions to diverse real-world conditions while accurately preserving motion patterns. Existing motion prior approaches enable well adaptability with a few motions but often sacrifice imitation accuracy, whereas motion-tracking methods achieve accurate imitation yet require many training motions and a test-time target motion to adapt. To combine their strengths, we introduce AdaMimic, a novel motion tracking algorithm that enables adaptable humanoid control from a single reference motion. To reduce data dependence while ensuring adaptability, our method first creates an augmented dataset by sparsifying the single reference motion into keyframes and applying light editing with minimal physical assumptions. A policy is then initialized by tracking these sparse keyframes to generate dense intermediate motions, and adapters are subsequently trained to adjust tracking speed and refine low-level actions based on the adjustment, enabling flexible time warping that further improves imitation accuracy and adaptability. We validate these significant improvements in our approach in both simulation and the real-world Unitree G1 humanoid robot in multiple tasks across a wide range of adaptation conditions. Videos and code are available at https://taohuang13.github.io/adamimic.github.io/.
VB-Com: Learning Vision-Blind Composite Humanoid Locomotion Against Deficient Perception
Feb 20, 2025Abstract:The performance of legged locomotion is closely tied to the accuracy and comprehensiveness of state observations. Blind policies, which rely solely on proprioception, are considered highly robust due to the reliability of proprioceptive observations. However, these policies significantly limit locomotion speed and often require collisions with the terrain to adapt. In contrast, Vision policies allows the robot to plan motions in advance and respond proactively to unstructured terrains with an online perception module. However, perception is often compromised by noisy real-world environments, potential sensor failures, and the limitations of current simulations in presenting dynamic or deformable terrains. Humanoid robots, with high degrees of freedom and inherently unstable morphology, are particularly susceptible to misguidance from deficient perception, which can result in falls or termination on challenging dynamic terrains. To leverage the advantages of both vision and blind policies, we propose VB-Com, a composite framework that enables humanoid robots to determine when to rely on the vision policy and when to switch to the blind policy under perceptual deficiency. We demonstrate that VB-Com effectively enables humanoid robots to traverse challenging terrains and obstacles despite perception deficiencies caused by dynamic terrains or perceptual noise.
Learning Humanoid Standing-up Control across Diverse Postures
Feb 12, 2025Abstract:Standing-up control is crucial for humanoid robots, with the potential for integration into current locomotion and loco-manipulation systems, such as fall recovery. Existing approaches are either limited to simulations that overlook hardware constraints or rely on predefined ground-specific motion trajectories, failing to enable standing up across postures in real-world scenes. To bridge this gap, we present HoST (Humanoid Standing-up Control), a reinforcement learning framework that learns standing-up control from scratch, enabling robust sim-to-real transfer across diverse postures. HoST effectively learns posture-adaptive motions by leveraging a multi-critic architecture and curriculum-based training on diverse simulated terrains. To ensure successful real-world deployment, we constrain the motion with smoothness regularization and implicit motion speed bound to alleviate oscillatory and violent motions on physical hardware, respectively. After simulation-based training, the learned control policies are directly deployed on the Unitree G1 humanoid robot. Our experimental results demonstrate that the controllers achieve smooth, stable, and robust standing-up motions across a wide range of laboratory and outdoor environments. Videos are available at https://taohuang13.github.io/humanoid-standingup.github.io/.
P3: A Policy-Driven, Pace-Adaptive, and Diversity-Promoted Framework for Optimizing LLM Training
Aug 10, 2024



Abstract:In the rapidly evolving field of Large Language Models (LLMs), selecting high-quality data for fine-tuning is essential. This paper focuses on task-specific data pruning and selection to enhance fine-tuning. We introduce an innovative framework, termed P3, which improves LLM performance through a dynamic, adaptive training strategy. Specifically, P3 comprises the following components: (1) Policy-driven Difficulty Measurement: we begin by measuring the difficulty of data based on the model's real-time performance, transitioning from static, predefined metrics to more dynamic and adaptable ones. (2) Pace-adaptive Selection: we employ self-paced learning (SPL) to gradually select increasingly challenging data, thereby progressively enhancing the model's performance. (3) Diversity Promotion: we integrate Determinantal Point Process (DPP) into the selection process to promote the diversity within and between samples, enriching the learning process. We have validated our method on two well-known LLM datasets, APPS and MATH, designed for logical reasoning scenarios. The results show that our P3 framework significantly improves training outcomes compared to traditional methods. By fundamentally refining data selection and utilization strategies, P3 not only advances theoretical understanding of dynamic training approaches but also provides a versatile framework that can revolutionize model training in natural language processing.
Rethinking Similarity Search: Embracing Smarter Mechanisms over Smarter Data
Aug 02, 2023



Abstract:In this vision paper, we propose a shift in perspective for improving the effectiveness of similarity search. Rather than focusing solely on enhancing the data quality, particularly machine learning-generated embeddings, we advocate for a more comprehensive approach that also enhances the underpinning search mechanisms. We highlight three novel avenues that call for a redefinition of the similarity search problem: exploiting implicit data structures and distributions, engaging users in an iterative feedback loop, and moving beyond a single query vector. These novel pathways have gained relevance in emerging applications such as large-scale language models, video clip retrieval, and data labeling. We discuss the corresponding research challenges posed by these new problem areas and share insights from our preliminary discoveries.
Image-free multi-character recognition
Dec 20, 2021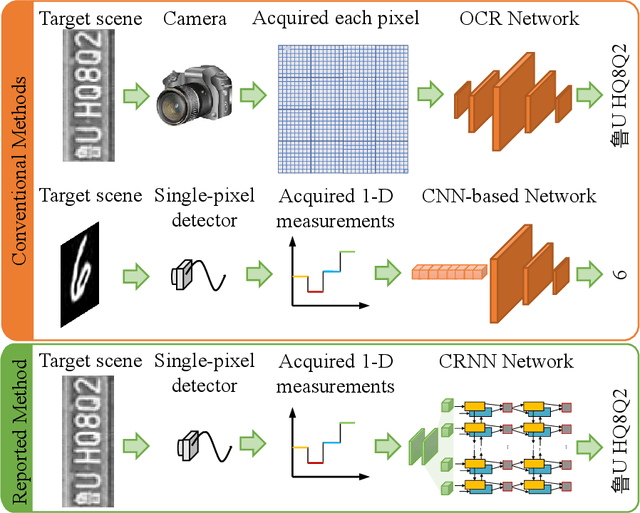
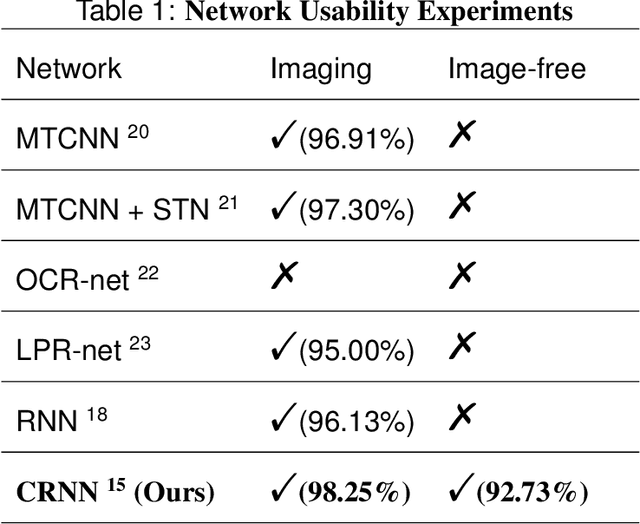
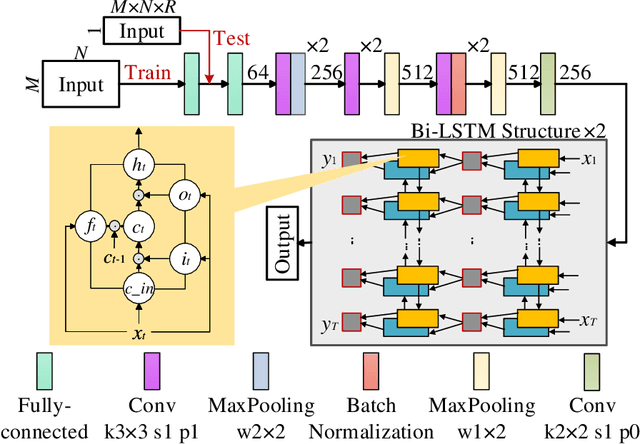
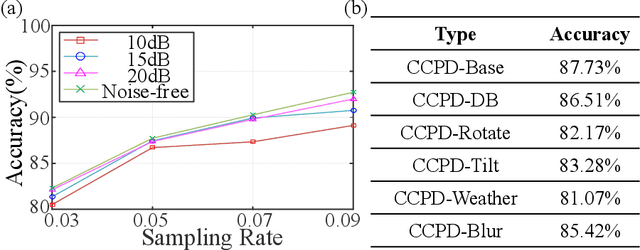
Abstract:The recently developed image-free sensing technique maintains the advantages of both the light hardware and software, which has been applied in simple target classification and motion tracking. In practical applications, however, there usually exist multiple targets in the field of view, where existing trials fail to produce multi-semantic information. In this letter, we report a novel image-free sensing technique to tackle the multi-target recognition challenge for the first time. Different from the convolutional layer stack of image-free single-pixel networks, the reported CRNN network utilities the bidirectional LSTM architecture to predict the distribution of multiple characters simultaneously. The framework enables to capture the long-range dependencies, providing a high recognition accuracy of multiple characters. We demonstrated the technique's effectiveness in license plate detection, which achieved 87.60% recognition accuracy at a 5% sampling rate with a higher than 100 FPS refresh rate.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge