Yi Guo
SHIELD: An Auto-Healing Agentic Defense Framework for LLM Resource Exhaustion Attacks
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Sponge attacks increasingly threaten LLM systems by inducing excessive computation and DoS. Existing defenses either rely on statistical filters that fail on semantically meaningful attacks or use static LLM-based detectors that struggle to adapt as attack strategies evolve. We introduce SHIELD, a multi-agent, auto-healing defense framework centered on a three-stage Defense Agent that integrates semantic similarity retrieval, pattern matching, and LLM-based reasoning. Two auxiliary agents, a Knowledge Updating Agent and a Prompt Optimization Agent, form a closed self-healing loop, when an attack bypasses detection, the system updates an evolving knowledgebase, and refines defense instructions. Extensive experiments show that SHIELD consistently outperforms perplexity-based and standalone LLM defenses, achieving high F1 scores across both non-semantic and semantic sponge attacks, demonstrating the effectiveness of agentic self-healing against evolving resource-exhaustion threats.
Prompt-Induced Over-Generation as Denial-of-Service: A Black-Box Attack-Side Benchmark
Dec 29, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) can be driven into over-generation, emitting thousands of tokens before producing an end-of-sequence (EOS) token. This degrades answer quality, inflates latency and cost, and can be weaponized as a denial-of-service (DoS) attack. Recent work has begun to study DoS-style prompt attacks, but typically focuses on a single attack algorithm or assumes white-box access, without an attack-side benchmark that compares prompt-based attackers in a black-box, query-only regime with a known tokenizer. We introduce such a benchmark and study two prompt-only attackers. The first is Evolutionary Over-Generation Prompt Search (EOGen), which searches the token space for prefixes that suppress EOS and induce long continuations. The second is a goal-conditioned reinforcement learning attacker (RL-GOAL) that trains a network to generate prefixes conditioned on a target length. To characterize behavior, we introduce Over-Generation Factor (OGF), the ratio of produced tokens to a model's context window, along with stall and latency summaries. Our evolutionary attacker achieves mean OGF = 1.38 +/- 1.15 and Success@OGF >= 2 of 24.5 percent on Phi-3. RL-GOAL is stronger: across victims it achieves higher mean OGF (up to 2.81 +/- 1.38).
TinyUSFM: Towards Compact and Efficient Ultrasound Foundation Models
Oct 22, 2025Abstract:Foundation models for medical imaging demonstrate superior generalization capabilities across diverse anatomical structures and clinical applications. Their outstanding performance relies on substantial computational resources, limiting deployment in resource-constrained clinical environments. This paper presents TinyUSFM, the first lightweight ultrasound foundation model that maintains superior organ versatility and task adaptability of our large-scale Ultrasound Foundation Model (USFM) through knowledge distillation with strategically curated small datasets, delivering significant computational efficiency without sacrificing performance. Considering the limited capacity and representation ability of lightweight models, we propose a feature-gradient driven coreset selection strategy to curate high-quality compact training data, avoiding training degradation from low-quality redundant images. To preserve the essential spatial and frequency domain characteristics during knowledge transfer, we develop domain-separated masked image modeling assisted consistency-driven dynamic distillation. This novel framework adaptively transfers knowledge from large foundation models by leveraging teacher model consistency across different domain masks, specifically tailored for ultrasound interpretation. For evaluation, we establish the UniUS-Bench, the largest publicly available ultrasound benchmark comprising 8 classification and 10 segmentation datasets across 15 organs. Using only 200K images in distillation, TinyUSFM matches USFM's performance with just 6.36% of parameters and 6.40% of GFLOPs. TinyUSFM significantly outperforms the vanilla model by 9.45% in classification and 7.72% in segmentation, surpassing all state-of-the-art lightweight models, and achieving 84.91% average classification accuracy and 85.78% average segmentation Dice score across diverse medical devices and centers.
SplitMeanFlow: Interval Splitting Consistency in Few-Step Generative Modeling
Jul 22, 2025
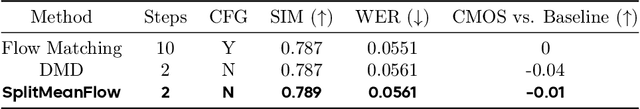
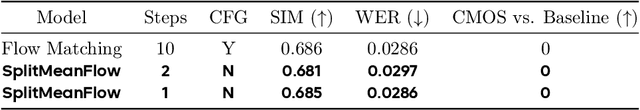
Abstract:Generative models like Flow Matching have achieved state-of-the-art performance but are often hindered by a computationally expensive iterative sampling process. To address this, recent work has focused on few-step or one-step generation by learning the average velocity field, which directly maps noise to data. MeanFlow, a leading method in this area, learns this field by enforcing a differential identity that connects the average and instantaneous velocities. In this work, we argue that this differential formulation is a limiting special case of a more fundamental principle. We return to the first principles of average velocity and leverage the additivity property of definite integrals. This leads us to derive a novel, purely algebraic identity we term Interval Splitting Consistency. This identity establishes a self-referential relationship for the average velocity field across different time intervals without resorting to any differential operators. Based on this principle, we introduce SplitMeanFlow, a new training framework that enforces this algebraic consistency directly as a learning objective. We formally prove that the differential identity at the core of MeanFlow is recovered by taking the limit of our algebraic consistency as the interval split becomes infinitesimal. This establishes SplitMeanFlow as a direct and more general foundation for learning average velocity fields. From a practical standpoint, our algebraic approach is significantly more efficient, as it eliminates the need for JVP computations, resulting in simpler implementation, more stable training, and broader hardware compatibility. One-step and two-step SplitMeanFlow models have been successfully deployed in large-scale speech synthesis products (such as Doubao), achieving speedups of 20x.
Scale-Invariance Drives Convergence in AI and Brain Representations
Jun 13, 2025Abstract:Despite variations in architecture and pretraining strategies, recent studies indicate that large-scale AI models often converge toward similar internal representations that also align with neural activity. We propose that scale-invariance, a fundamental structural principle in natural systems, is a key driver of this convergence. In this work, we propose a multi-scale analytical framework to quantify two core aspects of scale-invariance in AI representations: dimensional stability and structural similarity across scales. We further investigate whether these properties can predict alignment performance with functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) responses in the visual cortex. Our analysis reveals that embeddings with more consistent dimension and higher structural similarity across scales align better with fMRI data. Furthermore, we find that the manifold structure of fMRI data is more concentrated, with most features dissipating at smaller scales. Embeddings with similar scale patterns align more closely with fMRI data. We also show that larger pretraining datasets and the inclusion of language modalities enhance the scale-invariance properties of embeddings, further improving neural alignment. Our findings indicate that scale-invariance is a fundamental structural principle that bridges artificial and biological representations, providing a new framework for evaluating the structural quality of human-like AI systems.
A Topic Modeling Analysis of Stigma Dimensions, Social, and Related Behavioral Circumstances in Clinical Notes Among Patients with HIV
Jun 10, 2025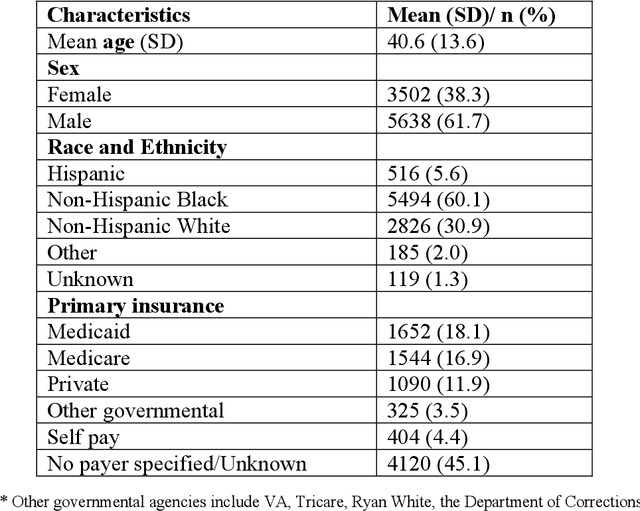
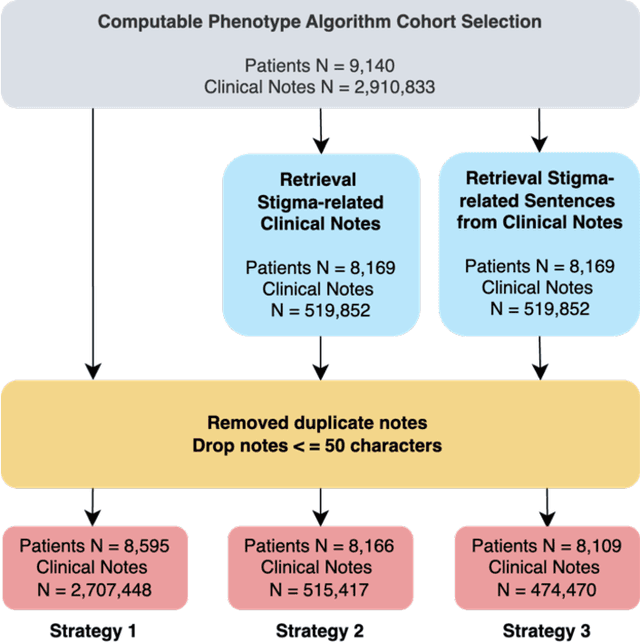
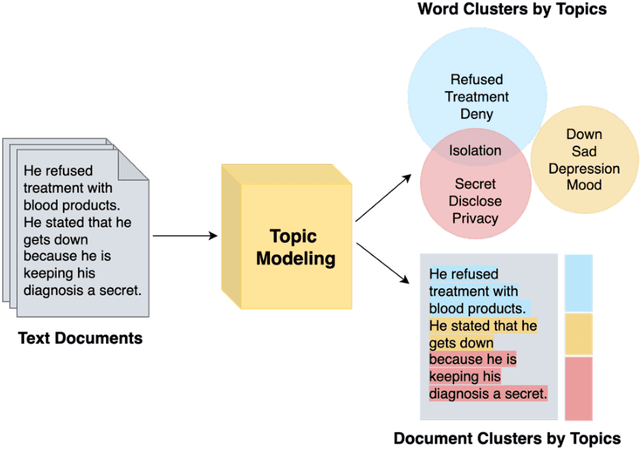
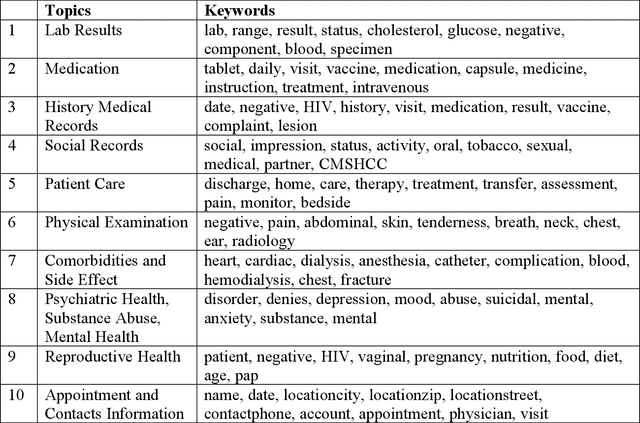
Abstract:Objective: To characterize stigma dimensions, social, and related behavioral circumstances in people living with HIV (PLWHs) seeking care, using natural language processing methods applied to a large collection of electronic health record (EHR) clinical notes from a large integrated health system in the southeast United States. Methods: We identified 9,140 cohort of PLWHs from the UF Health IDR and performed topic modeling analysis using Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA) to uncover stigma dimensions, social, and related behavioral circumstances. Domain experts created a seed list of HIV-related stigma keywords, then applied a snowball strategy to iteratively review notes for additional terms until saturation was reached. To identify more target topics, we tested three keyword-based filtering strategies. Domain experts manually reviewed the detected topics using the prevalent terms and key discussion topics. Word frequency analysis was used to highlight the prevalent terms associated with each topic. In addition, we conducted topic variation analysis among subgroups to examine differences across age and sex-specific demographics. Results and Conclusion: Topic modeling on sentences containing at least one keyword uncovered a wide range of topic themes associated with HIV-related stigma, social, and related behaviors circumstances, including "Mental Health Concern and Stigma", "Social Support and Engagement", "Limited Healthcare Access and Severe Illness", "Treatment Refusal and Isolation" and so on. Topic variation analysis across age subgroups revealed differences. Extracting and understanding the HIV-related stigma dimensions, social, and related behavioral circumstances from EHR clinical notes enables scalable, time-efficient assessment, overcoming the limitations of traditional questionnaires and improving patient outcomes.
Deep Learning-Based Direct Leaf Area Estimation using Two RGBD Datasets for Model Development
Mar 13, 2025



Abstract:Estimation of a single leaf area can be a measure of crop growth and a phenotypic trait to breed new varieties. It has also been used to measure leaf area index and total leaf area. Some studies have used hand-held cameras, image processing 3D reconstruction and unsupervised learning-based methods to estimate the leaf area in plant images. Deep learning works well for object detection and segmentation tasks; however, direct area estimation of objects has not been explored. This work investigates deep learning-based leaf area estimation, for RGBD images taken using a mobile camera setup in real-world scenarios. A dataset for attached leaves captured with a top angle view and a dataset for detached single leaves were collected for model development and testing. First, image processing-based area estimation was tested on manually segmented leaves. Then a Mask R-CNN-based model was investigated, and modified to accept RGBD images and to estimate the leaf area. The detached-leaf data set was then mixed with the attached-leaf plant data set to estimate the single leaf area for plant images, and another network design with two backbones was proposed: one for segmentation and the other for area estimation. Instead of trying all possibilities or random values, an agile approach was used in hyperparameter tuning. The final model was cross-validated with 5-folds and tested with two unseen datasets: detached and attached leaves. The F1 score with 90% IoA for segmentation result on unseen detached-leaf data was 1.0, while R-squared of area estimation was 0.81. For unseen plant data segmentation, the F1 score with 90% IoA was 0.59, while the R-squared score was 0.57. The research suggests using attached leaves with ground truth area to improve the results.
EEG-ReMinD: Enhancing Neurodegenerative EEG Decoding through Self-Supervised State Reconstruction-Primed Riemannian Dynamics
Jan 14, 2025



Abstract:The development of EEG decoding algorithms confronts challenges such as data sparsity, subject variability, and the need for precise annotations, all of which are vital for advancing brain-computer interfaces and enhancing the diagnosis of diseases. To address these issues, we propose a novel two-stage approach named Self-Supervised State Reconstruction-Primed Riemannian Dynamics (EEG-ReMinD) , which mitigates reliance on supervised learning and integrates inherent geometric features. This approach efficiently handles EEG data corruptions and reduces the dependency on labels. EEG-ReMinD utilizes self-supervised and geometric learning techniques, along with an attention mechanism, to analyze the temporal dynamics of EEG features within the framework of Riemannian geometry, referred to as Riemannian dynamics. Comparative analyses on both intact and corrupted datasets from two different neurodegenerative disorders underscore the enhanced performance of EEG-ReMinD.
Cycle-Consistent Bridge Diffusion Model for Accelerated MRI Reconstruction
Dec 13, 2024



Abstract:Accelerated MRI reconstruction techniques aim to reduce examination time while maintaining high image fidelity, which is highly desirable in clinical settings for improving patient comfort and hospital efficiency. Existing deep learning methods typically reconstruct images from under-sampled data with traditional reconstruction approaches, but they still struggle to provide high-fidelity results. Diffusion models show great potential to improve fidelity of generated images in recent years. However, their inference process starting with a random Gaussian noise introduces instability into the results and usually requires thousands of sampling steps, resulting in sub-optimal reconstruction quality and low efficiency. To address these challenges, we propose Cycle-Consistent Bridge Diffusion Model (CBDM). CBDM employs two bridge diffusion models to construct a cycle-consistent diffusion process with a consistency loss, enhancing the fine-grained details of reconstructed images and reducing the number of diffusion steps. Moreover, CBDM incorporates a Contourlet Decomposition Embedding Module (CDEM) which captures multi-scale structural texture knowledge in images through frequency domain decomposition pyramids and directional filter banks to improve structural fidelity. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superiority of our model by higher reconstruction quality and fewer training iterations, achieving a new state of the art for accelerated MRI reconstruction in both fastMRI and IXI datasets.
Defensive Dual Masking for Robust Adversarial Defense
Dec 10, 2024Abstract:The field of textual adversarial defenses has gained considerable attention in recent years due to the increasing vulnerability of natural language processing (NLP) models to adversarial attacks, which exploit subtle perturbations in input text to deceive models. This paper introduces the Defensive Dual Masking (DDM) algorithm, a novel approach designed to enhance model robustness against such attacks. DDM utilizes a unique adversarial training strategy where [MASK] tokens are strategically inserted into training samples to prepare the model to handle adversarial perturbations more effectively. During inference, potentially adversarial tokens are dynamically replaced with [MASK] tokens to neutralize potential threats while preserving the core semantics of the input. The theoretical foundation of our approach is explored, demonstrating how the selective masking mechanism strengthens the model's ability to identify and mitigate adversarial manipulations. Our empirical evaluation across a diverse set of benchmark datasets and attack mechanisms consistently shows that DDM outperforms state-of-the-art defense techniques, improving model accuracy and robustness. Moreover, when applied to Large Language Models (LLMs), DDM also enhances their resilience to adversarial attacks, providing a scalable defense mechanism for large-scale NLP applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge