Feng Xu
Feasible strategies for conflict resolution within intuitionistic fuzzy preference-based conflict situations
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:In three-way conflict analysis, preference-based conflict situations characterize agents' attitudes towards issues by formally modeling their preferences over pairs of issues. However, existing preference-based conflict models rely exclusively on three qualitative relations, namely, preference, converse, and indifference, to describe agents' attitudes towards issue pairs, which significantly limits their capacity in capturing the essence of conflict. To overcome this limitation, we introduce the concept of an intuitionistic fuzzy preference-based conflict situation that captures agents' attitudes towards issue pairs with finer granularity than that afforded by classical preference-based models. Afterwards, we develop intuitionistic fuzzy preference-based conflict measures within this framework, and construct three-way conflict analysis models for trisecting the set of agent pairs, the agent set, and the issue set. Additionally, relative loss functions built on the proposed conflict functions are employed to calculate thresholds for three-way conflict analysis. Finally, we present adjustment mechanism-based feasible strategies that simultaneously account for both adjustment magnitudes and conflict degrees, together with an algorithm for constructing such feasible strategies, and provide an illustrative example to demonstrate the validity and effectiveness of the proposed model.
The Llama 4 Herd: Architecture, Training, Evaluation, and Deployment Notes
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:This document consolidates publicly reported technical details about Metas Llama 4 model family. It summarizes (i) released variants (Scout and Maverick) and the broader herd context including the previewed Behemoth teacher model, (ii) architectural characteristics beyond a high-level MoE description covering routed/shared-expert structure, early-fusion multimodality, and long-context design elements reported for Scout (iRoPE and length generalization strategies), (iii) training disclosures spanning pre-training, mid-training for long-context extension, and post-training methodology (lightweight SFT, online RL, and lightweight DPO) as described in release materials, (iv) developer-reported benchmark results for both base and instruction-tuned checkpoints, and (v) practical deployment constraints observed across major serving environments, including provider-specific context limits and quantization packaging. The manuscript also summarizes licensing obligations relevant to redistribution and derivative naming, and reviews publicly described safeguards and evaluation practices. The goal is to provide a compact technical reference for researchers and practitioners who need precise, source-backed facts about Llama 4.
WaveMan: mmWave-Based Room-Scale Human Interaction Perception for Humanoid Robots
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:Reliable humanoid-robot interaction (HRI) in household environments is constrained by two fundamental requirements, namely robustness to unconstrained user positions and preservation of user privacy. Millimeter-wave (mmWave) sensing inherently supports privacy-preserving interaction, making it a promising modality for room-scale HRI. However, existing mmWave-based interaction-sensing systems exhibit poor spatial generalization at unseen distances or viewpoints. To address this challenge, we introduce WaveMan, a spatially adaptive room-scale perception system that restores reliable human interaction sensing across arbitrary user positions. WaveMan integrates viewpoint alignment and spectrogram enhancement for spatial consistency, with dual-channel attention for robust feature extraction. Experiments across five participants show that, under fixed-position evaluation, WaveMan achieves the same cross-position accuracy as the baseline with five times fewer training positions. In random free-position testing, accuracy increases from 33.00% to 94.33%, enabled by the proposed method. These results demonstrate the feasibility of reliable, privacy-preserving interaction for household humanoid robots across unconstrained user positions.
WildCap: Facial Appearance Capture in the Wild via Hybrid Inverse Rendering
Dec 12, 2025Abstract:Existing methods achieve high-quality facial appearance capture under controllable lighting, which increases capture cost and limits usability. We propose WildCap, a novel method for high-quality facial appearance capture from a smartphone video recorded in the wild. To disentangle high-quality reflectance from complex lighting effects in in-the-wild captures, we propose a novel hybrid inverse rendering framework. Specifically, we first apply a data-driven method, i.e., SwitchLight, to convert the captured images into more constrained conditions and then adopt model-based inverse rendering. However, unavoidable local artifacts in network predictions, such as shadow-baking, are non-physical and thus hinder accurate inverse rendering of lighting and material. To address this, we propose a novel texel grid lighting model to explain non-physical effects as clean albedo illuminated by local physical lighting. During optimization, we jointly sample a diffusion prior for reflectance maps and optimize the lighting, effectively resolving scale ambiguity between local lights and albedo. Our method achieves significantly better results than prior arts in the same capture setup, closing the quality gap between in-the-wild and controllable recordings by a large margin. Our code will be released \href{https://yxuhan.github.io/WildCap/index.html}{\textcolor{magenta}{here}}.
Aerial Vision-Language Navigation with a Unified Framework for Spatial, Temporal and Embodied Reasoning
Dec 09, 2025Abstract:Aerial Vision-and-Language Navigation (VLN) aims to enable unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) to interpret natural language instructions and navigate complex urban environments using onboard visual observation. This task holds promise for real-world applications such as low-altitude inspection, search-and-rescue, and autonomous aerial delivery. Existing methods often rely on panoramic images, depth inputs, or odometry to support spatial reasoning and action planning. These requirements increase system cost and integration complexity, thus hindering practical deployment for lightweight UAVs. We present a unified aerial VLN framework that operates solely on egocentric monocular RGB observations and natural language instructions. The model formulates navigation as a next-token prediction problem, jointly optimizing spatial perception, trajectory reasoning, and action prediction through prompt-guided multi-task learning. Moreover, we propose a keyframe selection strategy to reduce visual redundancy by retaining semantically informative frames, along with an action merging and label reweighting mechanism that mitigates long-tailed supervision imbalance and facilitates stable multi-task co-training. Extensive experiments on the Aerial VLN benchmark validate the effectiveness of our method. Under the challenging monocular RGB-only setting, our model achieves strong results across both seen and unseen environments. It significantly outperforms existing RGB-only baselines and narrows the performance gap with state-of-the-art panoramic RGB-D counterparts. Comprehensive ablation studies further demonstrate the contribution of our task design and architectural choices.
Every Step Evolves: Scaling Reinforcement Learning for Trillion-Scale Thinking Model
Oct 21, 2025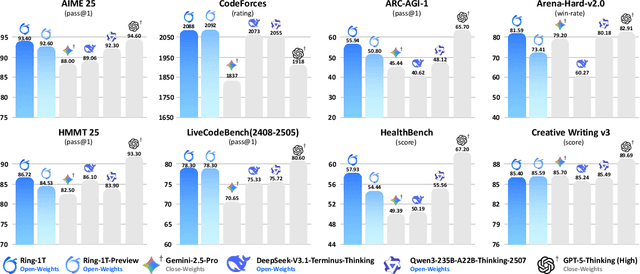
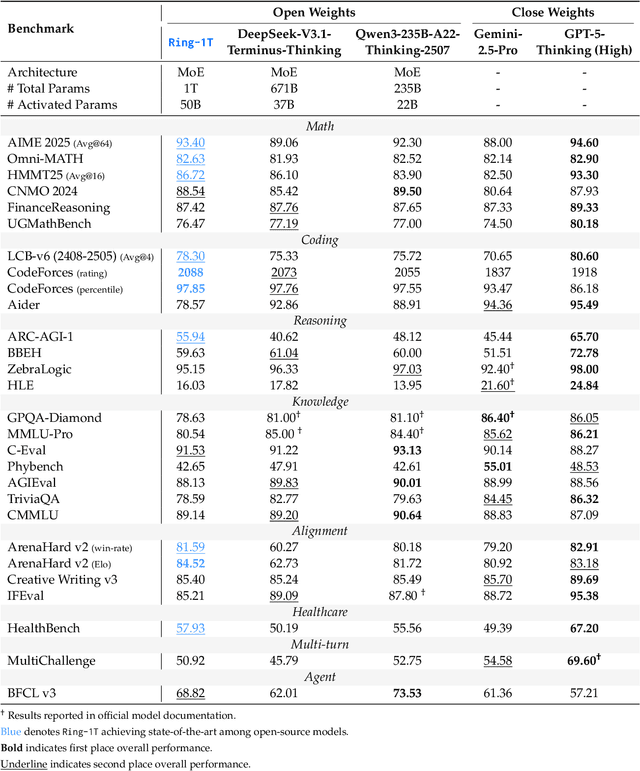
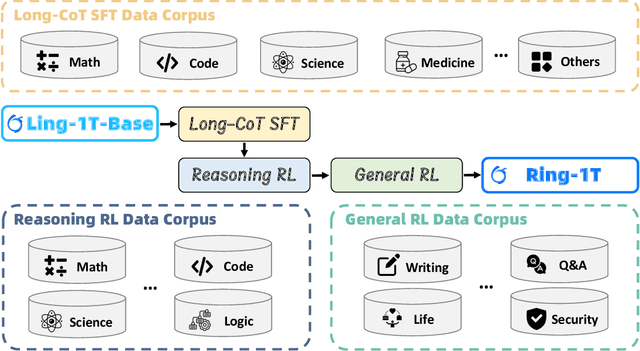
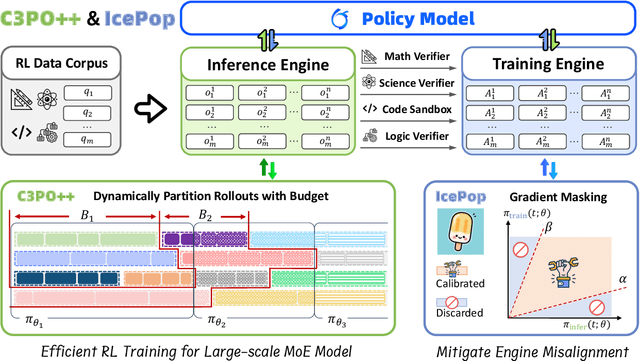
Abstract:We present Ring-1T, the first open-source, state-of-the-art thinking model with a trillion-scale parameter. It features 1 trillion total parameters and activates approximately 50 billion per token. Training such models at a trillion-parameter scale introduces unprecedented challenges, including train-inference misalignment, inefficiencies in rollout processing, and bottlenecks in the RL system. To address these, we pioneer three interconnected innovations: (1) IcePop stabilizes RL training via token-level discrepancy masking and clipping, resolving instability from training-inference mismatches; (2) C3PO++ improves resource utilization for long rollouts under a token budget by dynamically partitioning them, thereby obtaining high time efficiency; and (3) ASystem, a high-performance RL framework designed to overcome the systemic bottlenecks that impede trillion-parameter model training. Ring-1T delivers breakthrough results across critical benchmarks: 93.4 on AIME-2025, 86.72 on HMMT-2025, 2088 on CodeForces, and 55.94 on ARC-AGI-v1. Notably, it attains a silver medal-level result on the IMO-2025, underscoring its exceptional reasoning capabilities. By releasing the complete 1T parameter MoE model to the community, we provide the research community with direct access to cutting-edge reasoning capabilities. This contribution marks a significant milestone in democratizing large-scale reasoning intelligence and establishes a new baseline for open-source model performance.
Effective Gaussian Management for High-fidelity Object Reconstruction
Sep 16, 2025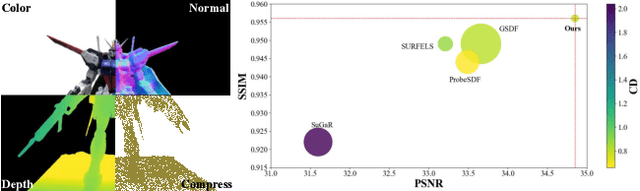
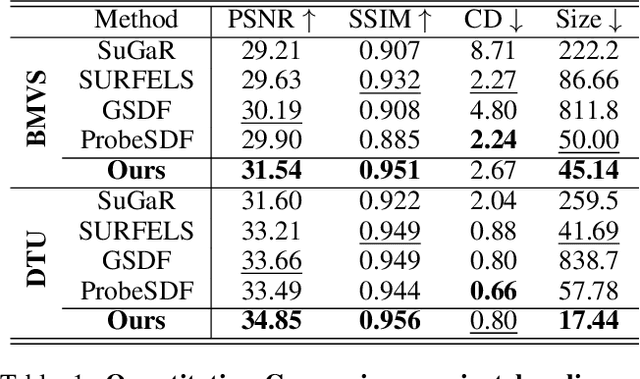
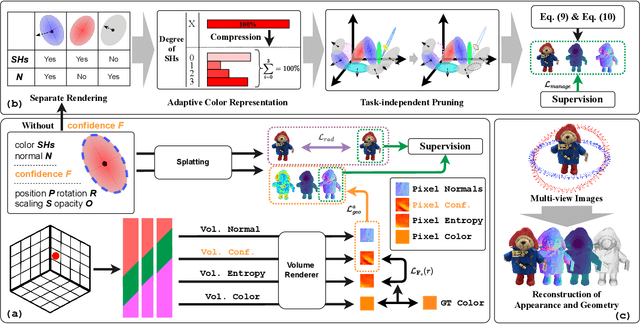
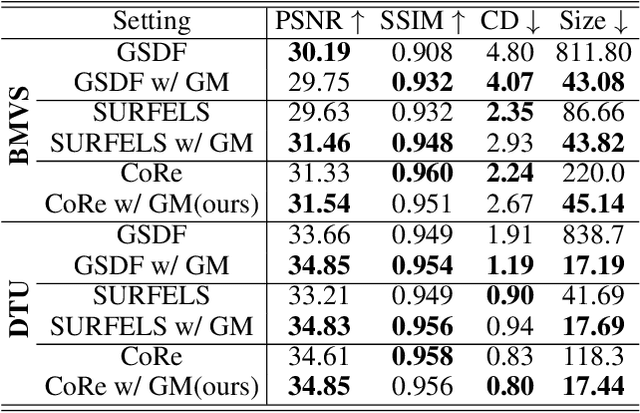
Abstract:This paper proposes an effective Gaussian management approach for high-fidelity object reconstruction. Departing from recent Gaussian Splatting (GS) methods that employ indiscriminate attribute assignment, our approach introduces a novel densification strategy that dynamically activates spherical harmonics (SHs) or normals under the supervision of a surface reconstruction module, which effectively mitigates the gradient conflicts caused by dual supervision and achieves superior reconstruction results. To further improve representation efficiency, we develop a lightweight Gaussian representation that adaptively adjusts the SH orders of each Gaussian based on gradient magnitudes and performs task-decoupled pruning to remove Gaussian with minimal impact on a reconstruction task without sacrificing others, which balances the representational capacity with parameter quantity. Notably, our management approach is model-agnostic and can be seamlessly integrated into other frameworks, enhancing performance while reducing model size. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our approach consistently outperforms state-of-the-art approaches in both reconstruction quality and efficiency, achieving superior performance with significantly fewer parameters.
DiffCap: Diffusion-based Real-time Human Motion Capture using Sparse IMUs and a Monocular Camera
Aug 08, 2025
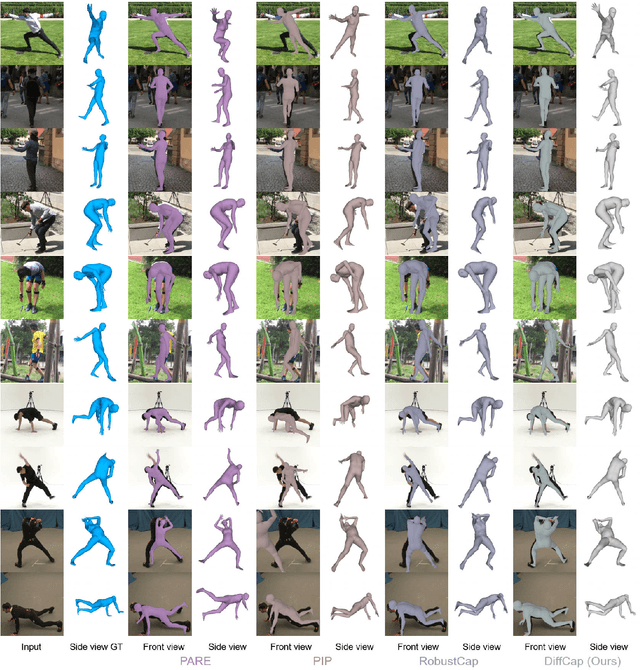
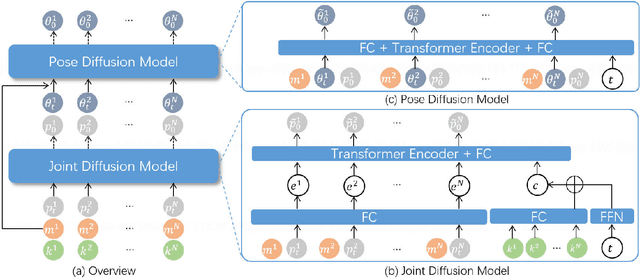
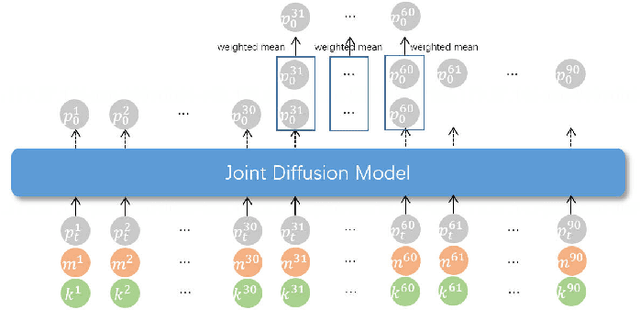

Abstract:Combining sparse IMUs and a monocular camera is a new promising setting to perform real-time human motion capture. This paper proposes a diffusion-based solution to learn human motion priors and fuse the two modalities of signals together seamlessly in a unified framework. By delicately considering the characteristics of the two signals, the sequential visual information is considered as a whole and transformed into a condition embedding, while the inertial measurement is concatenated with the noisy body pose frame by frame to construct a sequential input for the diffusion model. Firstly, we observe that the visual information may be unavailable in some frames due to occlusions or subjects moving out of the camera view. Thus incorporating the sequential visual features as a whole to get a single feature embedding is robust to the occasional degenerations of visual information in those frames. On the other hand, the IMU measurements are robust to occlusions and always stable when signal transmission has no problem. So incorporating them frame-wisely could better explore the temporal information for the system. Experiments have demonstrated the effectiveness of the system design and its state-of-the-art performance in pose estimation compared with the previous works. Our codes are available for research at https://shaohua-pan.github.io/diffcap-page.
Peering into the Unknown: Active View Selection with Neural Uncertainty Maps for 3D Reconstruction
Jun 17, 2025Abstract:Some perspectives naturally provide more information than others. How can an AI system determine which viewpoint offers the most valuable insight for accurate and efficient 3D object reconstruction? Active view selection (AVS) for 3D reconstruction remains a fundamental challenge in computer vision. The aim is to identify the minimal set of views that yields the most accurate 3D reconstruction. Instead of learning radiance fields, like NeRF or 3D Gaussian Splatting, from a current observation and computing uncertainty for each candidate viewpoint, we introduce a novel AVS approach guided by neural uncertainty maps predicted by a lightweight feedforward deep neural network, named UPNet. UPNet takes a single input image of a 3D object and outputs a predicted uncertainty map, representing uncertainty values across all possible candidate viewpoints. By leveraging heuristics derived from observing many natural objects and their associated uncertainty patterns, we train UPNet to learn a direct mapping from viewpoint appearance to uncertainty in the underlying volumetric representations. Next, our approach aggregates all previously predicted neural uncertainty maps to suppress redundant candidate viewpoints and effectively select the most informative one. Using these selected viewpoints, we train 3D neural rendering models and evaluate the quality of novel view synthesis against other competitive AVS methods. Remarkably, despite using half of the viewpoints than the upper bound, our method achieves comparable reconstruction accuracy. In addition, it significantly reduces computational overhead during AVS, achieving up to a 400 times speedup along with over 50\% reductions in CPU, RAM, and GPU usage compared to baseline methods. Notably, our approach generalizes effectively to AVS tasks involving novel object categories, without requiring any additional training.
Transformer IMU Calibrator: Dynamic On-body IMU Calibration for Inertial Motion Capture
Jun 12, 2025Abstract:In this paper, we propose a novel dynamic calibration method for sparse inertial motion capture systems, which is the first to break the restrictive absolute static assumption in IMU calibration, i.e., the coordinate drift RG'G and measurement offset RBS remain constant during the entire motion, thereby significantly expanding their application scenarios. Specifically, we achieve real-time estimation of RG'G and RBS under two relaxed assumptions: i) the matrices change negligibly in a short time window; ii) the human movements/IMU readings are diverse in such a time window. Intuitively, the first assumption reduces the number of candidate matrices, and the second assumption provides diverse constraints, which greatly reduces the solution space and allows for accurate estimation of RG'G and RBS from a short history of IMU readings in real time. To achieve this, we created synthetic datasets of paired RG'G, RBS matrices and IMU readings, and learned their mappings using a Transformer-based model. We also designed a calibration trigger based on the diversity of IMU readings to ensure that assumption ii) is met before applying our method. To our knowledge, we are the first to achieve implicit IMU calibration (i.e., seamlessly putting IMUs into use without the need for an explicit calibration process), as well as the first to enable long-term and accurate motion capture using sparse IMUs. The code and dataset are available at https://github.com/ZuoCX1996/TIC.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge