Xun Li
Federated Distillation Assisted Vehicle Edge Caching Scheme Based on Lightweight DDPM
Dec 10, 2025



Abstract:Vehicle edge caching is a promising technology that can significantly reduce the latency for vehicle users (VUs) to access content by pre-caching user-interested content at edge nodes. It is crucial to accurately predict the content that VUs are interested in without exposing their privacy. Traditional federated learning (FL) can protect user privacy by sharing models rather than raw data. However, the training of FL requires frequent model transmission, which can result in significant communication overhead. Additionally, vehicles may leave the road side unit (RSU) coverage area before training is completed, leading to training failures. To address these issues, in this letter, we propose a federated distillation-assisted vehicle edge caching scheme based on lightweight denoising diffusion probabilistic model (LDPM). The simulation results demonstrate that the proposed vehicle edge caching scheme has good robustness to variations in vehicle speed, significantly reducing communication overhead and improving cache hit percentage.
Estimating Pasture Biomass from Top-View Images: A Dataset for Precision Agriculture
Oct 27, 2025Abstract:Accurate estimation of pasture biomass is important for decision-making in livestock production systems. Estimates of pasture biomass can be used to manage stocking rates to maximise pasture utilisation, while minimising the risk of overgrazing and promoting overall system health. We present a comprehensive dataset of 1,162 annotated top-view images of pastures collected across 19 locations in Australia. The images were taken across multiple seasons and include a range of temperate pasture species. Each image captures a 70cm * 30cm quadrat and is paired with on-ground measurements including biomass sorted by component (green, dead, and legume fraction), vegetation height, and Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) from Active Optical Sensors (AOS). The multidimensional nature of the data, which combines visual, spectral, and structural information, opens up new possibilities for advancing the use of precision grazing management. The dataset is released and hosted in a Kaggle competition that challenges the international Machine Learning community with the task of pasture biomass estimation. The dataset is available on the official Kaggle webpage: https://www.kaggle.com/competitions/csiro-biomass
From Drone Imagery to Livability Mapping: AI-powered Environment Perception in Rural China
Aug 29, 2025



Abstract:With the deepening of poverty alleviation and rural revitalization strategies, improving the rural living environment and enhancing the quality of life have become key priorities. Rural livability is a key indicator for measuring the effectiveness of these efforts. Current measurement approaches face significant limitations, as questionnaire-based methods are difficult to scale, while urban-oriented visual perception methods are poorly suited for rural contexts. In this paper, a rural-specific livability assessment framework was proposed based on drone imagery and multimodal large language models (MLLMs). To comprehensively assess village livability, this study first used a top-down approach to collect large-scale drone imagery of 1,766 villages in 146 counties across China. In terms of the model framework, an efficient image comparison mechanism was developed, incorporating binary search interpolation to determine effective image pairs while reducing comparison iterations. Building on expert knowledge, a chain-of-thought prompting suitable for nationwide rural livability measurement was constructed, considering both living quality and ecological habitability dimensions. This approach enhanced the rationality and reliability of the livability assessment. Finally, this study characterized the spatial heterogeneity of rural livability across China and thoroughly analyzed its influential factors. The results show that: (1) The rural livability in China demonstrates a dual-core-periphery spatial pattern, radiating outward from Sichuan and Zhejiang provinces with declining gradients; (2) Among various influential factors, government fiscal expenditure emerged as the core determinant, with each unit increase corresponding to a 3.9 - 4.9 unit enhancement in livability. The findings provide valuable insights for rural construction policy-making.
Federated Learning Assisted Edge Caching Scheme Based on Lightweight Architecture DDPM
Jun 05, 2025Abstract:Edge caching is an emerging technology that empowers caching units at edge nodes, allowing users to fetch contents of interest that have been pre-cached at the edge nodes. The key to pre-caching is to maximize the cache hit percentage for cached content without compromising users' privacy. In this letter, we propose a federated learning (FL) assisted edge caching scheme based on lightweight architecture denoising diffusion probabilistic model (LDPM). Our simulation results verify that our proposed scheme achieves a higher cache hit percentage compared to existing FL-based methods and baseline methods.
NeuroLoc: Encoding Navigation Cells for 6-DOF Camera Localization
May 02, 2025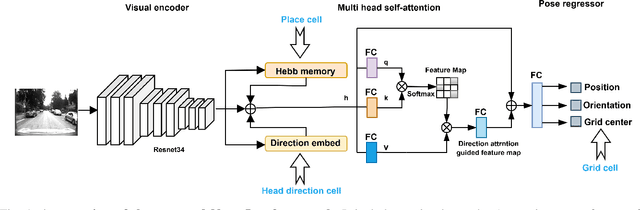
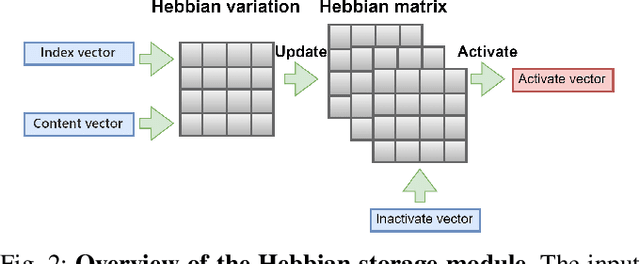
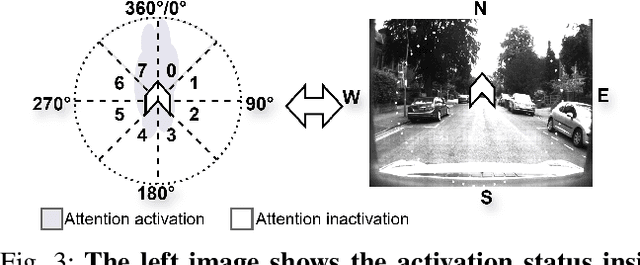
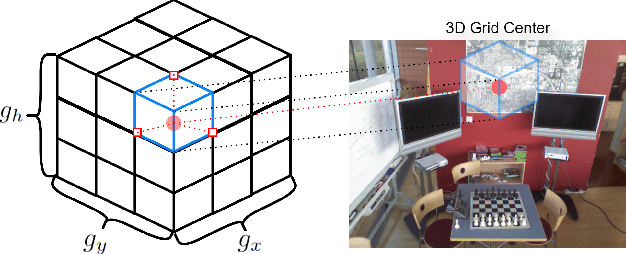
Abstract:Recently, camera localization has been widely adopted in autonomous robotic navigation due to its efficiency and convenience. However, autonomous navigation in unknown environments often suffers from scene ambiguity, environmental disturbances, and dynamic object transformation in camera localization. To address this problem, inspired by the biological brain navigation mechanism (such as grid cells, place cells, and head direction cells), we propose a novel neurobiological camera location method, namely NeuroLoc. Firstly, we designed a Hebbian learning module driven by place cells to save and replay historical information, aiming to restore the details of historical representations and solve the issue of scene fuzziness. Secondly, we utilized the head direction cell-inspired internal direction learning as multi-head attention embedding to help restore the true orientation in similar scenes. Finally, we added a 3D grid center prediction in the pose regression module to reduce the final wrong prediction. We evaluate the proposed NeuroLoc on commonly used benchmark indoor and outdoor datasets. The experimental results show that our NeuroLoc can enhance the robustness in complex environments and improve the performance of pose regression by using only a single image.
Interpreting core forms of urban morphology linked to urban functions with explainable graph neural network
Feb 22, 2025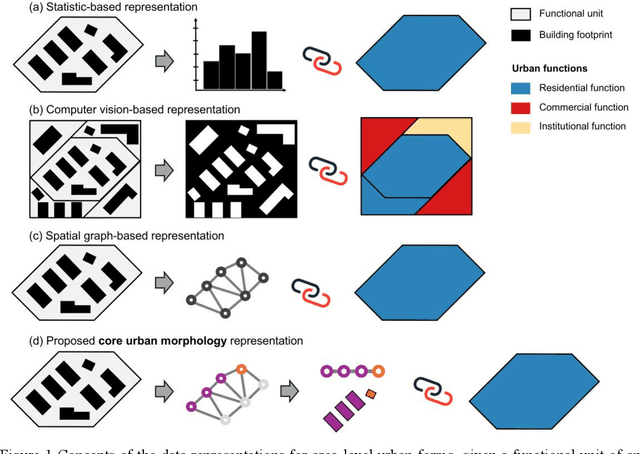
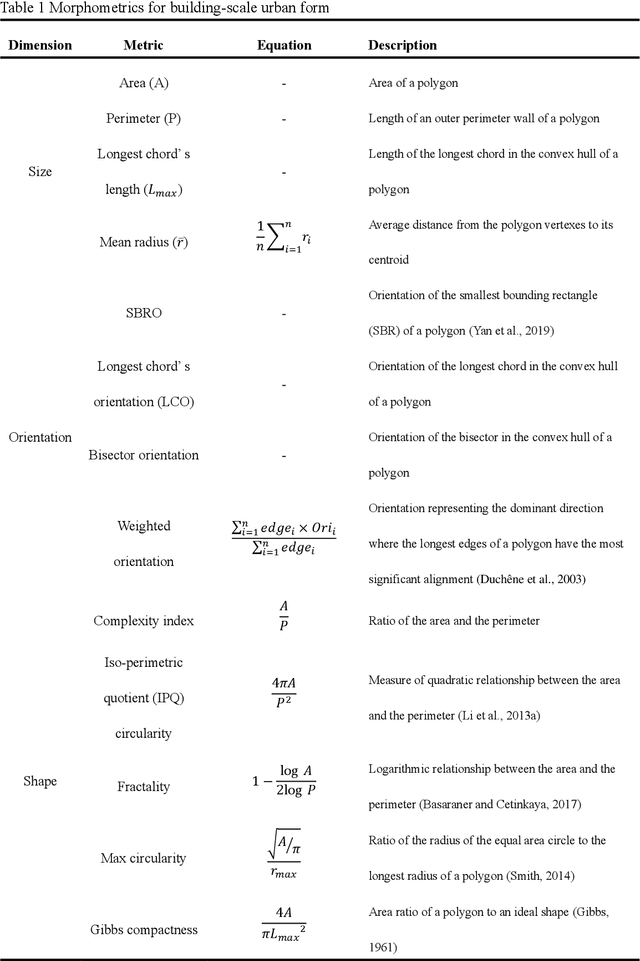
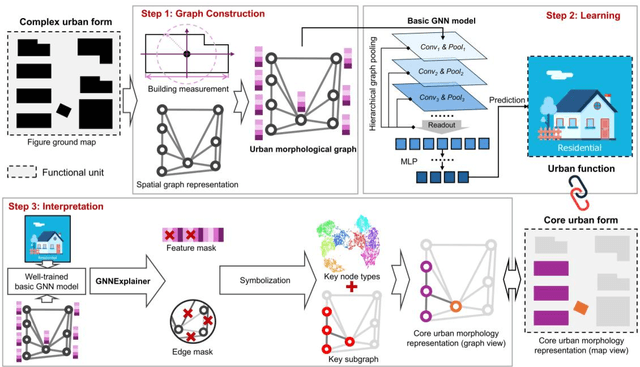
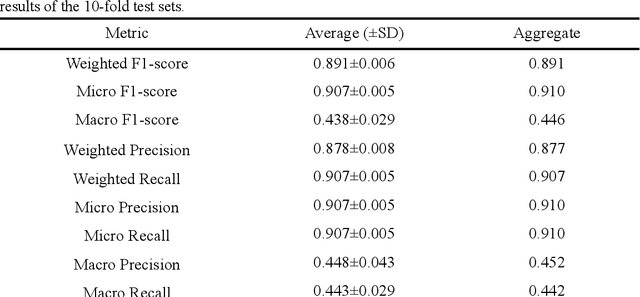
Abstract:Understanding the high-order relationship between urban form and function is essential for modeling the underlying mechanisms of sustainable urban systems. Nevertheless, it is challenging to establish an accurate data representation for complex urban forms that are readily explicable in human terms. This study proposed the concept of core urban morphology representation and developed an explainable deep learning framework for explicably symbolizing complex urban forms into the novel representation, which we call CoMo. By interpretating the well-trained deep learning model with a stable weighted F1-score of 89.14%, CoMo presents a promising approach for revealing links between urban function and urban form in terms of core urban morphology representation. Using Boston as a study area, we analyzed the core urban forms at the individual-building, block, and neighborhood level that are important to corresponding urban functions. The residential core forms follow a gradual morphological pattern along the urban spine, which is consistent with a center-urban-suburban transition. Furthermore, we prove that urban morphology directly affects land use efficiency, which has a significantly strong correlation with the location (R2=0.721, p<0.001). Overall, CoMo can explicably symbolize urban forms, provide evidence for the classic urban location theory, and offer mechanistic insights for digital twins.
Facial Expression Recognition with Controlled Privacy Preservation and Feature Compensation
Dec 03, 2024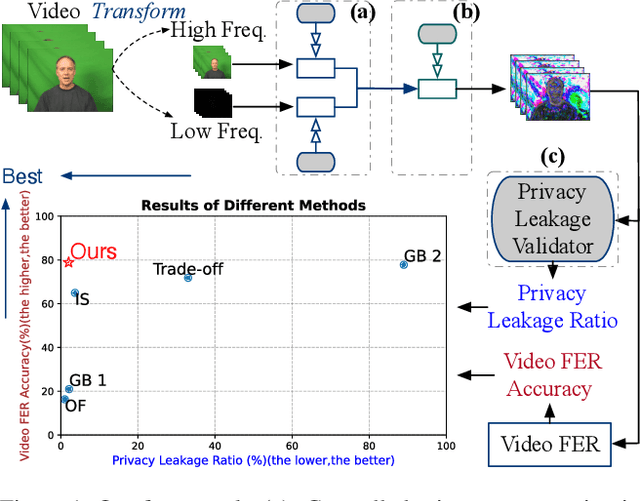
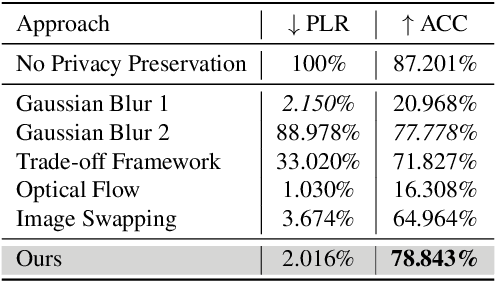
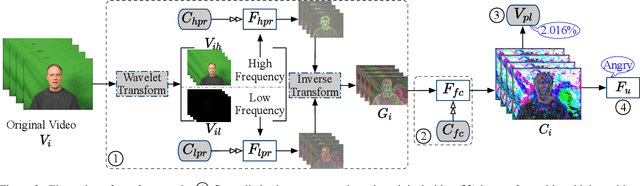
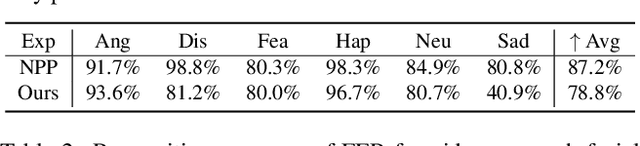
Abstract:Facial expression recognition (FER) systems raise significant privacy concerns due to the potential exposure of sensitive identity information. This paper presents a study on removing identity information while preserving FER capabilities. Drawing on the observation that low-frequency components predominantly contain identity information and high-frequency components capture expression, we propose a novel two-stream framework that applies privacy enhancement to each component separately. We introduce a controlled privacy enhancement mechanism to optimize performance and a feature compensator to enhance task-relevant features without compromising privacy. Furthermore, we propose a novel privacy-utility trade-off, providing a quantifiable measure of privacy preservation efficacy in closed-set FER tasks. Extensive experiments on the benchmark CREMA-D dataset demonstrate that our framework achieves 78.84% recognition accuracy with a privacy (facial identity) leakage ratio of only 2.01%, highlighting its potential for secure and reliable video-based FER applications.
Discrete-Time Mean-Variance Strategy Based on Reinforcement Learning
Dec 24, 2023Abstract:This paper studies a discrete-time mean-variance model based on reinforcement learning. Compared with its continuous-time counterpart in \cite{zhou2020mv}, the discrete-time model makes more general assumptions about the asset's return distribution. Using entropy to measure the cost of exploration, we derive the optimal investment strategy, whose density function is also Gaussian type. Additionally, we design the corresponding reinforcement learning algorithm. Both simulation experiments and empirical analysis indicate that our discrete-time model exhibits better applicability when analyzing real-world data than the continuous-time model.
Combining deep learning and crowdsourcing geo-images to predict housing quality in rural China
Aug 15, 2022
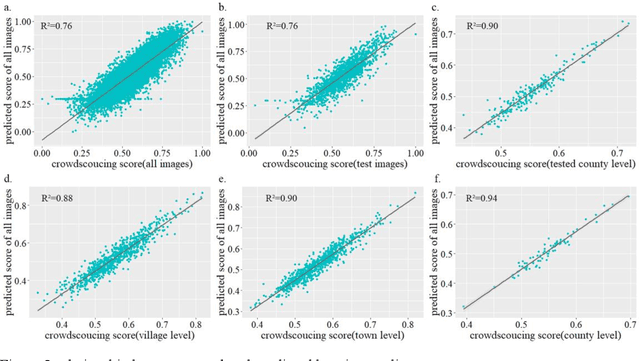

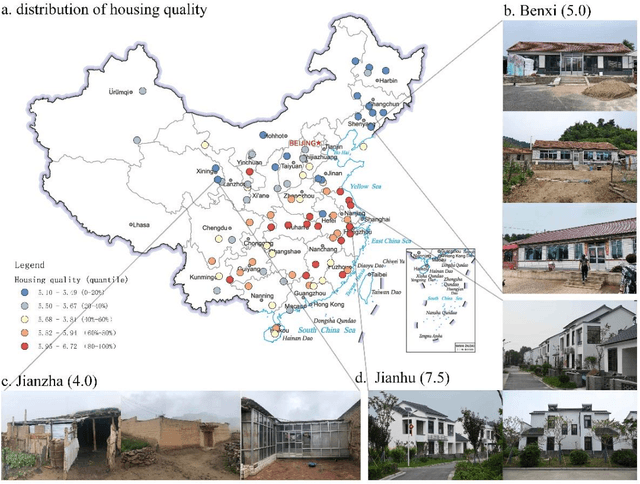
Abstract:Housing quality is an essential proxy for regional wealth, security and health. Understanding the distribution of housing quality is crucial for unveiling rural development status and providing political proposals. However,present rural house quality data highly depends on a top-down, time-consuming survey at the national or provincial level but fails to unpack the housing quality at the village level. To fill the gap between accurately depicting rural housing quality conditions and deficient data,we collect massive rural images and invite users to assess their housing quality at scale. Furthermore, a deep learning framework is proposed to automatically and efficiently predict housing quality based on crowd-sourcing rural images.
A Histogram Thresholding Improvement to Mask R-CNN for Scalable Segmentation of New and Old Rural Buildings
Feb 08, 2021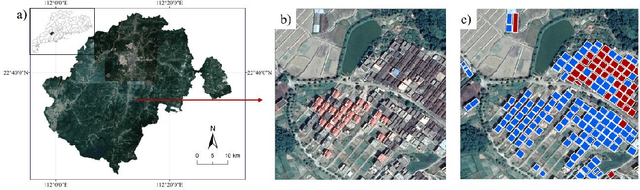

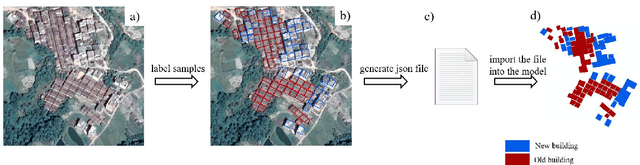

Abstract:Mapping new and old buildings are of great significance for understanding socio-economic development in rural areas. In recent years, deep neural networks have achieved remarkable building segmentation results in high-resolution remote sensing images. However, the scarce training data and the varying geographical environments have posed challenges for scalable building segmentation. This study proposes a novel framework based on Mask R-CNN, named HTMask R-CNN, to extract new and old rural buildings even when the label is scarce. The framework adopts the result of single-object instance segmentation from the orthodox Mask R-CNN. Further, it classifies the rural buildings into new and old ones based on a dynamic grayscale threshold inferred from the result of a two-object instance segmentation task where training data is scarce. We found that the framework can extract more buildings and achieve a much higher mean Average Precision (mAP) than the orthodox Mask R-CNN model. We tested the novel framework's performance with increasing training data and found that it converged even when the training samples were limited. This framework's main contribution is to allow scalable segmentation by using significantly fewer training samples than traditional machine learning practices. That makes mapping China's new and old rural buildings viable.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge