Yu Gu
OJBKQ: Objective-Joint Babai-Klein Quantization
Feb 09, 2026Abstract:Post-training quantization (PTQ) is widely used to compress large language models without retraining. However, many existing weight-only methods rely on heuristic objectives and greedy rounding, thus leading to noticeable degradation under low-bit quantization. In this work, we introduce OJBKQ (Objective-Joint Babai-Klein Quantization with K-Best Sampling), a layer-wise PTQ method that formulates weight quantization as a joint optimization problem over activations and weights. This formulation results in a multiple-right-hand-side box-constrained integer least squares (BILS) problem in each layer, which is NP-hard. For each column of the weight matrix, we apply an extended Babai nearest-plane algorithm and an extended version of Klein's randomized Babai algorithm to find the minimum-residual Babai-Klein point, a sub-optimal solution to the BILS problem. Experimental results on large language models show that OJBKQ achieves lower perplexity at 3-4 bits compared to existing PTQ approaches, while maintaining comparable computational cost.
UNIKIE-BENCH: Benchmarking Large Multimodal Models for Key Information Extraction in Visual Documents
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Key Information Extraction (KIE) from real-world documents remains challenging due to substantial variations in layout structures, visual quality, and task-specific information requirements. Recent Large Multimodal Models (LMMs) have shown promising potential for performing end-to-end KIE directly from document images. To enable a comprehensive and systematic evaluation across realistic and diverse application scenarios, we introduce UNIKIE-BENCH, a unified benchmark designed to rigorously evaluate the KIE capabilities of LMMs. UNIKIE-BENCH consists of two complementary tracks: a constrained-category KIE track with scenario-predefined schemas that reflect practical application needs, and an open-category KIE track that extracts any key information that is explicitly present in the document. Experiments on 15 state-of-the-art LMMs reveal substantial performance degradation under diverse schema definitions, long-tail key fields, and complex layouts, along with pronounced performance disparities across different document types and scenarios. These findings underscore persistent challenges in grounding accuracy and layout-aware reasoning for LMM-based KIE. All codes and datasets are available at https://github.com/NEUIR/UNIKIE-BENCH.
Scaling medical imaging report generation with multimodal reinforcement learning
Jan 23, 2026Abstract:Frontier models have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in understanding and reasoning with natural-language text, but they still exhibit major competency gaps in multimodal understanding and reasoning especially in high-value verticals such as biomedicine. Medical imaging report generation is a prominent example. Supervised fine-tuning can substantially improve performance, but they are prone to overfitting to superficial boilerplate patterns. In this paper, we introduce Universal Report Generation (UniRG) as a general framework for medical imaging report generation. By leveraging reinforcement learning as a unifying mechanism to directly optimize for evaluation metrics designed for end applications, UniRG can significantly improve upon supervised fine-tuning and attain durable generalization across diverse institutions and clinical practices. We trained UniRG-CXR on publicly available chest X-ray (CXR) data and conducted a thorough evaluation in CXR report generation with rigorous evaluation scenarios. On the authoritative ReXrank benchmark, UniRG-CXR sets new overall SOTA, outperforming prior state of the art by a wide margin.
Beyond Hard Writes and Rigid Preservation: Soft Recursive Least-Squares for Lifelong LLM Editing
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:Model editing updates a pre-trained LLM with new facts or rules without re-training, while preserving unrelated behavior. In real deployment, edits arrive as long streams, and existing editors often face a plasticity-stability dilemma: locate-then-edit "hard writes" can accumulate interference over time, while null-space-style "hard preservation" preserves only what is explicitly constrained, so past edits can be overwritten and unconstrained behaviors may deviate, degrading general capabilities in the many-edits regime. We propose RLSEdit, a recursive least-squares editor for long sequential editing. RLSEdit formulates editing as an online quadratic optimization with soft constraints, minimizing a cumulative key-value fitting objective with two regularizers that control for both deviation from the pre-trained weights and from a designated anchor mapping. The resulting update admits an efficient online recursion via the Woodbury identity, with per-edit cost independent of history length and scaling only with the current edit size. We further provide deviation bounds and an asymptotic characterization of the adherence-preservation trade-off in the many-edits regime. Experiments on multiple model families demonstrate stable scaling to 10K edits, outperforming strong baselines in both edit success and holistic stability -- crucially retaining early edits, and preserving general capabilities on GLUE and held-out reasoning/code benchmarks.
Teaching LLMs to Learn Tool Trialing and Execution through Environment Interaction
Jan 19, 2026Abstract:Equipping Large Language Models (LLMs) with external tools enables them to solve complex real-world problems. However, the robustness of existing methods remains a critical challenge when confronting novel or evolving tools. Existing trajectory-centric paradigms primarily rely on memorizing static solution paths during training, which limits the ability of LLMs to generalize tool usage to newly introduced or previously unseen tools. In this paper, we propose ToolMaster, a framework that shifts tool use from imitating golden tool-calling trajectories to actively learning tool usage through interaction with the environment. To optimize LLMs for tool planning and invocation, ToolMaster adopts a trial-and-execution paradigm, which trains LLMs to first imitate teacher-generated trajectories containing explicit tool trials and self-correction, followed by reinforcement learning to coordinate the trial and execution phases jointly. This process enables agents to autonomously explore correct tool usage by actively interacting with environments and forming experiential knowledge that benefits tool execution. Experimental results demonstrate that ToolMaster significantly outperforms existing baselines in terms of generalization and robustness across unseen or unfamiliar tools. All code and data are available at https://github.com/NEUIR/ToolMaster.
Long-Chain Reasoning Distillation via Adaptive Prefix Alignment
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable reasoning capabilities, particularly in solving complex mathematical problems. Recent studies show that distilling long reasoning trajectories can effectively enhance the reasoning performance of small-scale student models. However, teacher-generated reasoning trajectories are often excessively long and structurally complex, making them difficult for student models to learn. This mismatch leads to a gap between the provided supervision signal and the learning capacity of the student model. To address this challenge, we propose Prefix-ALIGNment distillation (P-ALIGN), a framework that fully exploits teacher CoTs for distillation through adaptive prefix alignment. Specifically, P-ALIGN adaptively truncates teacher-generated reasoning trajectories by determining whether the remaining suffix is concise and sufficient to guide the student model. Then, P-ALIGN leverages the teacher-generated prefix to supervise the student model, encouraging effective prefix alignment. Experiments on multiple mathematical reasoning benchmarks demonstrate that P-ALIGN outperforms all baselines by over 3%. Further analysis indicates that the prefixes constructed by P-ALIGN provide more effective supervision signals, while avoiding the negative impact of redundant and uncertain reasoning components. All code is available at https://github.com/NEUIR/P-ALIGN.
Revealing the Attention Floating Mechanism in Masked Diffusion Models
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:Masked diffusion models (MDMs), which leverage bidirectional attention and a denoising process, are narrowing the performance gap with autoregressive models (ARMs). However, their internal attention mechanisms remain under-explored. This paper investigates the attention behaviors in MDMs, revealing the phenomenon of Attention Floating. Unlike ARMs, where attention converges to a fixed sink, MDMs exhibit dynamic, dispersed attention anchors that shift across denoising steps and layers. Further analysis reveals its Shallow Structure-Aware, Deep Content-Focused attention mechanism: shallow layers utilize floating tokens to build a global structural framework, while deeper layers allocate more capability toward capturing semantic content. Empirically, this distinctive attention pattern provides a mechanistic explanation for the strong in-context learning capabilities of MDMs, allowing them to double the performance compared to ARMs in knowledge-intensive tasks. All codes and datasets are available at https://github.com/NEUIR/Attention-Floating.
JoyVoice: Long-Context Conditioning for Anthropomorphic Multi-Speaker Conversational Synthesis
Dec 22, 2025Abstract:Large speech generation models are evolving from single-speaker, short sentence synthesis to multi-speaker, long conversation geneartion. Current long-form speech generation models are predominately constrained to dyadic, turn-based interactions. To address this, we introduce JoyVoice, a novel anthropomorphic foundation model designed for flexible, boundary-free synthesis of up to eight speakers. Unlike conventional cascaded systems, JoyVoice employs a unified E2E-Transformer-DiT architecture that utilizes autoregressive hidden representations directly for diffusion inputs, enabling holistic end-to-end optimization. We further propose a MM-Tokenizer operating at a low bitrate of 12.5 Hz, which integrates multitask semantic and MMSE losses to effectively model both semantic and acoustic information. Additionally, the model incorporates robust text front-end processing via large-scale data perturbation. Experiments show that JoyVoice achieves state-of-the-art results in multilingual generation (Chinese, English, Japanese, Korean) and zero-shot voice cloning. JoyVoice achieves top-tier results on both the Seed-TTS-Eval Benchmark and multi-speaker long-form conversational voice cloning tasks, demonstrating superior audio quality and generalization. It achieves significant improvements in prosodic continuity for long-form speech, rhythm richness in multi-speaker conversations, paralinguistic naturalness, besides superior intelligibility. We encourage readers to listen to the demo at https://jea-speech.github.io/JoyVoice
DAIEN-TTS: Disentangled Audio Infilling for Environment-Aware Text-to-Speech Synthesis
Sep 18, 2025


Abstract:This paper presents DAIEN-TTS, a zero-shot text-to-speech (TTS) framework that enables ENvironment-aware synthesis through Disentangled Audio Infilling. By leveraging separate speaker and environment prompts, DAIEN-TTS allows independent control over the timbre and the background environment of the synthesized speech. Built upon F5-TTS, the proposed DAIEN-TTS first incorporates a pretrained speech-environment separation (SES) module to disentangle the environmental speech into mel-spectrograms of clean speech and environment audio. Two random span masks of varying lengths are then applied to both mel-spectrograms, which, together with the text embedding, serve as conditions for infilling the masked environmental mel-spectrogram, enabling the simultaneous continuation of personalized speech and time-varying environmental audio. To further enhance controllability during inference, we adopt dual class-free guidance (DCFG) for the speech and environment components and introduce a signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) adaptation strategy to align the synthesized speech with the environment prompt. Experimental results demonstrate that DAIEN-TTS generates environmental personalized speech with high naturalness, strong speaker similarity, and high environmental fidelity.
AURAD: Anatomy-Pathology Unified Radiology Synthesis with Progressive Representations
Sep 05, 2025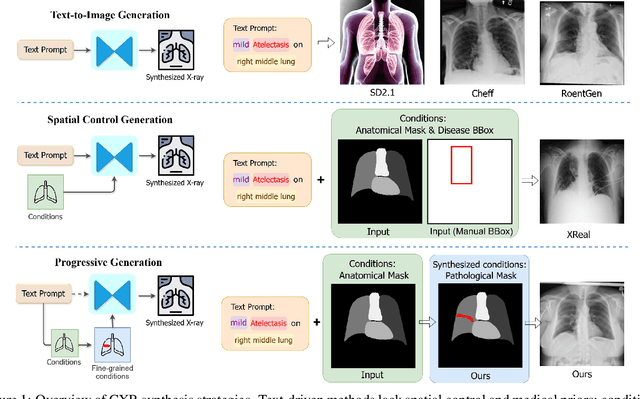

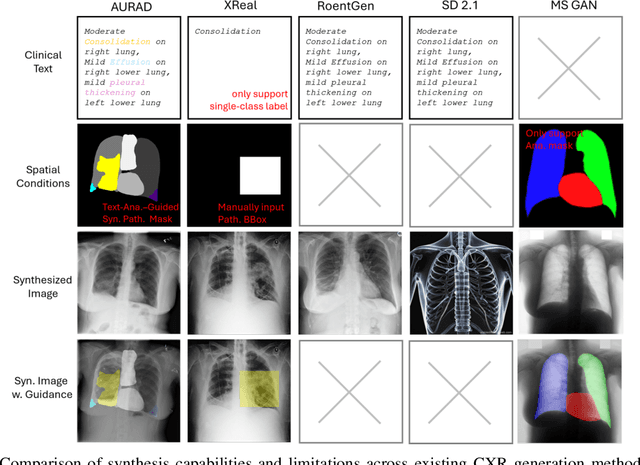
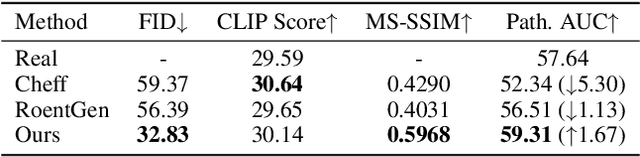
Abstract:Medical image synthesis has become an essential strategy for augmenting datasets and improving model generalization in data-scarce clinical settings. However, fine-grained and controllable synthesis remains difficult due to limited high-quality annotations and domain shifts across datasets. Existing methods, often designed for natural images or well-defined tumors, struggle to generalize to chest radiographs, where disease patterns are morphologically diverse and tightly intertwined with anatomical structures. To address these challenges, we propose AURAD, a controllable radiology synthesis framework that jointly generates high-fidelity chest X-rays and pseudo semantic masks. Unlike prior approaches that rely on randomly sampled masks-limiting diversity, controllability, and clinical relevance-our method learns to generate masks that capture multi-pathology coexistence and anatomical-pathological consistency. It follows a progressive pipeline: pseudo masks are first generated from clinical prompts conditioned on anatomical structures, and then used to guide image synthesis. We also leverage pretrained expert medical models to filter outputs and ensure clinical plausibility. Beyond visual realism, the synthesized masks also serve as labels for downstream tasks such as detection and segmentation, bridging the gap between generative modeling and real-world clinical applications. Extensive experiments and blinded radiologist evaluations demonstrate the effectiveness and generalizability of our method across tasks and datasets. In particular, 78% of our synthesized images are classified as authentic by board-certified radiologists, and over 40% of predicted segmentation overlays are rated as clinically useful. All code, pre-trained models, and the synthesized dataset will be released upon publication.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge