Zhipeng Xu
MiMo-V2-Flash Technical Report
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:We present MiMo-V2-Flash, a Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) model with 309B total parameters and 15B active parameters, designed for fast, strong reasoning and agentic capabilities. MiMo-V2-Flash adopts a hybrid attention architecture that interleaves Sliding Window Attention (SWA) with global attention, with a 128-token sliding window under a 5:1 hybrid ratio. The model is pre-trained on 27 trillion tokens with Multi-Token Prediction (MTP), employing a native 32k context length and subsequently extended to 256k. To efficiently scale post-training compute, MiMo-V2-Flash introduces a novel Multi-Teacher On-Policy Distillation (MOPD) paradigm. In this framework, domain-specialized teachers (e.g., trained via large-scale reinforcement learning) provide dense and token-level reward, enabling the student model to perfectly master teacher expertise. MiMo-V2-Flash rivals top-tier open-weight models such as DeepSeek-V3.2 and Kimi-K2, despite using only 1/2 and 1/3 of their total parameters, respectively. During inference, by repurposing MTP as a draft model for speculative decoding, MiMo-V2-Flash achieves up to 3.6 acceptance length and 2.6x decoding speedup with three MTP layers. We open-source both the model weights and the three-layer MTP weights to foster open research and community collaboration.
MiMo-Audio: Audio Language Models are Few-Shot Learners
Dec 29, 2025Abstract:Existing audio language models typically rely on task-specific fine-tuning to accomplish particular audio tasks. In contrast, humans are able to generalize to new audio tasks with only a few examples or simple instructions. GPT-3 has shown that scaling next-token prediction pretraining enables strong generalization capabilities in text, and we believe this paradigm is equally applicable to the audio domain. By scaling MiMo-Audio's pretraining data to over one hundred million of hours, we observe the emergence of few-shot learning capabilities across a diverse set of audio tasks. We develop a systematic evaluation of these capabilities and find that MiMo-Audio-7B-Base achieves SOTA performance on both speech intelligence and audio understanding benchmarks among open-source models. Beyond standard metrics, MiMo-Audio-7B-Base generalizes to tasks absent from its training data, such as voice conversion, style transfer, and speech editing. MiMo-Audio-7B-Base also demonstrates powerful speech continuation capabilities, capable of generating highly realistic talk shows, recitations, livestreaming and debates. At the post-training stage, we curate a diverse instruction-tuning corpus and introduce thinking mechanisms into both audio understanding and generation. MiMo-Audio-7B-Instruct achieves open-source SOTA on audio understanding benchmarks (MMSU, MMAU, MMAR, MMAU-Pro), spoken dialogue benchmarks (Big Bench Audio, MultiChallenge Audio) and instruct-TTS evaluations, approaching or surpassing closed-source models. Model checkpoints and full evaluation suite are available at https://github.com/XiaomiMiMo/MiMo-Audio.
Prompt Disentanglement via Language Guidance and Representation Alignment for Domain Generalization
Jul 03, 2025Abstract:Domain Generalization (DG) seeks to develop a versatile model capable of performing effectively on unseen target domains. Notably, recent advances in pre-trained Visual Foundation Models (VFMs), such as CLIP, have demonstrated considerable potential in enhancing the generalization capabilities of deep learning models. Despite the increasing attention toward VFM-based domain prompt tuning within DG, the effective design of prompts capable of disentangling invariant features across diverse domains remains a critical challenge. In this paper, we propose addressing this challenge by leveraging the controllable and flexible language prompt of the VFM. Noting that the text modality of VFMs is naturally easier to disentangle, we introduce a novel framework for text feature-guided visual prompt tuning. This framework first automatically disentangles the text prompt using a large language model (LLM) and then learns domain-invariant visual representation guided by the disentangled text feature. However, relying solely on language to guide visual feature disentanglement has limitations, as visual features can sometimes be too complex or nuanced to be fully captured by descriptive text. To address this, we introduce Worst Explicit Representation Alignment (WERA), which extends text-guided visual prompts by incorporating an additional set of abstract prompts. These prompts enhance source domain diversity through stylized image augmentations, while alignment constraints ensure that visual representations remain consistent across both the original and augmented distributions. Experiments conducted on major DG datasets, including PACS, VLCS, OfficeHome, DomainNet, and TerraInc, demonstrate that our proposed method outperforms state-of-the-art DG methods.
Learning to Route Queries Across Knowledge Bases for Step-wise Retrieval-Augmented Reasoning
May 28, 2025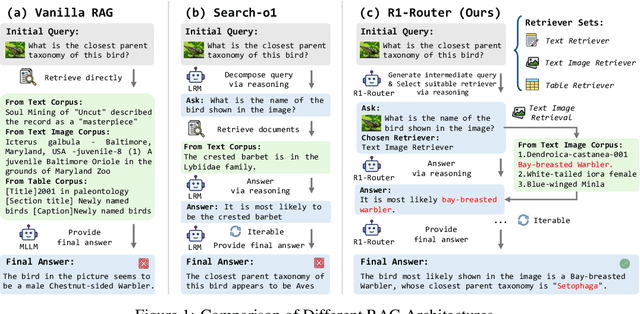
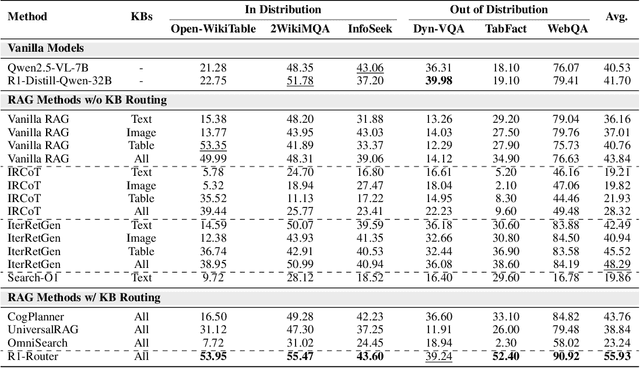
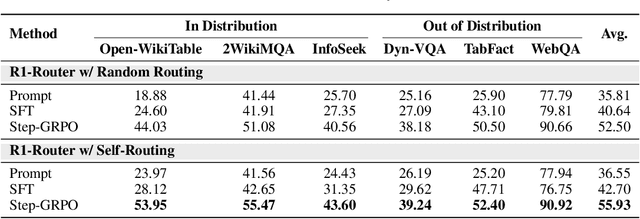
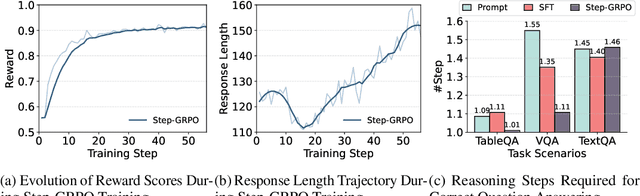
Abstract:Multimodal Retrieval-Augmented Generation (MRAG) has shown promise in mitigating hallucinations in Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) by incorporating external knowledge during generation. Existing MRAG methods typically adopt a static retrieval pipeline that fetches relevant information from multiple Knowledge Bases (KBs), followed by a refinement step. However, these approaches overlook the reasoning and planning capabilities of MLLMs to dynamically determine how to interact with different KBs during the reasoning process. To address this limitation, we propose R1-Router, a novel MRAG framework that learns to decide when and where to retrieve knowledge based on the evolving reasoning state. Specifically, R1-Router can generate follow-up queries according to the current reasoning step, routing these intermediate queries to the most suitable KB, and integrating external knowledge into a coherent reasoning trajectory to answer the original query. Furthermore, we introduce Step-wise Group Relative Policy Optimization (Step-GRPO), a tailored reinforcement learning algorithm that assigns step-specific rewards to optimize the reasoning behavior of MLLMs. Experimental results on various open-domain QA benchmarks across multiple modalities demonstrate that R1-Router outperforms baseline models by over 7%. Further analysis shows that R1-Router can adaptively and effectively leverage diverse KBs, reducing unnecessary retrievals and improving both efficiency and accuracy.
StPR: Spatiotemporal Preservation and Routing for Exemplar-Free Video Class-Incremental Learning
May 20, 2025Abstract:Video Class-Incremental Learning (VCIL) seeks to develop models that continuously learn new action categories over time without forgetting previously acquired knowledge. Unlike traditional Class-Incremental Learning (CIL), VCIL introduces the added complexity of spatiotemporal structures, making it particularly challenging to mitigate catastrophic forgetting while effectively capturing both frame-shared semantics and temporal dynamics. Existing approaches either rely on exemplar rehearsal, raising concerns over memory and privacy, or adapt static image-based methods that neglect temporal modeling. To address these limitations, we propose Spatiotemporal Preservation and Routing (StPR), a unified and exemplar-free VCIL framework that explicitly disentangles and preserves spatiotemporal information. First, we introduce Frame-Shared Semantics Distillation (FSSD), which identifies semantically stable and meaningful channels by jointly considering semantic sensitivity and classification contribution. These important semantic channels are selectively regularized to maintain prior knowledge while allowing for adaptation. Second, we design a Temporal Decomposition-based Mixture-of-Experts (TD-MoE), which dynamically routes task-specific experts based on their temporal dynamics, enabling inference without task ID or stored exemplars. Together, StPR effectively leverages spatial semantics and temporal dynamics, achieving a unified, exemplar-free VCIL framework. Extensive experiments on UCF101, HMDB51, and Kinetics400 show that our method outperforms existing baselines while offering improved interpretability and efficiency in VCIL. Code is available in the supplementary materials.
Enhancing the Patent Matching Capability of Large Language Models via the Memory Graph
Apr 21, 2025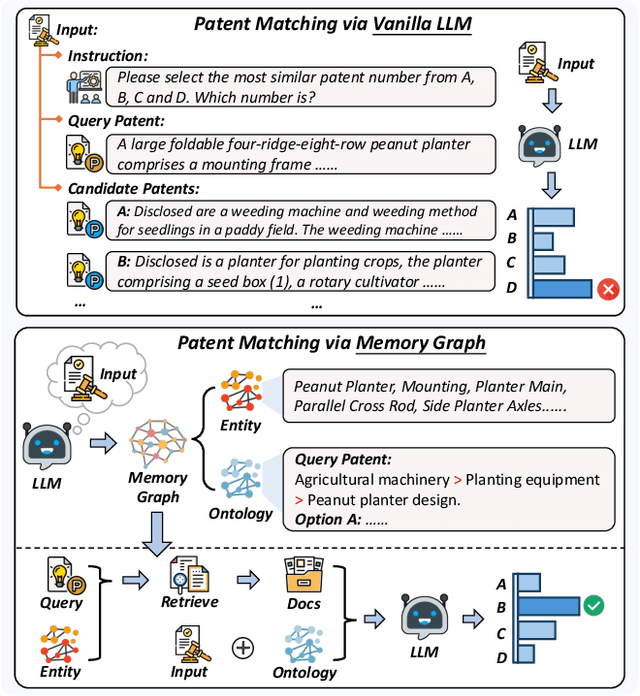

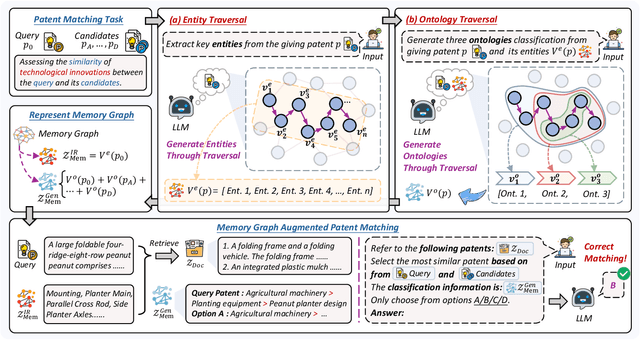
Abstract:Intellectual Property (IP) management involves strategically protecting and utilizing intellectual assets to enhance organizational innovation, competitiveness, and value creation. Patent matching is a crucial task in intellectual property management, which facilitates the organization and utilization of patents. Existing models often rely on the emergent capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) and leverage them to identify related patents directly. However, these methods usually depend on matching keywords and overlook the hierarchical classification and categorical relationships of patents. In this paper, we propose MemGraph, a method that augments the patent matching capabilities of LLMs by incorporating a memory graph derived from their parametric memory. Specifically, MemGraph prompts LLMs to traverse their memory to identify relevant entities within patents, followed by attributing these entities to corresponding ontologies. After traversing the memory graph, we utilize extracted entities and ontologies to improve the capability of LLM in comprehending the semantics of patents. Experimental results on the PatentMatch dataset demonstrate the effectiveness of MemGraph, achieving a 17.68% performance improvement over baseline LLMs. The further analysis highlights the generalization ability of MemGraph across various LLMs, both in-domain and out-of-domain, and its capacity to enhance the internal reasoning processes of LLMs during patent matching. All data and codes are available at https://github.com/NEUIR/MemGraph.
Learning More Effective Representations for Dense Retrieval through Deliberate Thinking Before Search
Feb 18, 2025Abstract:Recent dense retrievers usually thrive on the emergency capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs), using them to encode queries and documents into an embedding space for retrieval. These LLM-based dense retrievers have shown promising performance across various retrieval scenarios. However, relying on a single embedding to represent documents proves less effective in capturing different perspectives of documents for matching. In this paper, we propose Deliberate Thinking based Dense Retriever (DEBATER), which enhances these LLM-based retrievers by enabling them to learn more effective document representations through a step-by-step thinking process. DEBATER introduces the Chain-of-Deliberation mechanism to iteratively optimize document representations using a continuous chain of thought. To consolidate information from various thinking steps, DEBATER also incorporates the Self Distillation mechanism, which identifies the most informative thinking steps and integrates them into a unified text embedding. Experimental results show that DEBATER significantly outperforms existing methods across several retrieval benchmarks, demonstrating superior accuracy and robustness. All codes are available at https://github.com/OpenBMB/DEBATER.
Code-Vision: Evaluating Multimodal LLMs Logic Understanding and Code Generation Capabilities
Feb 17, 2025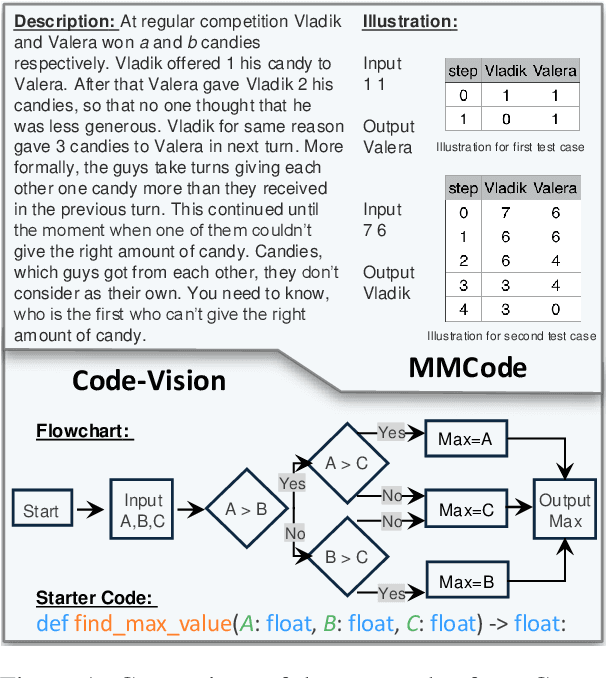
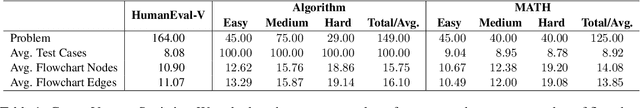
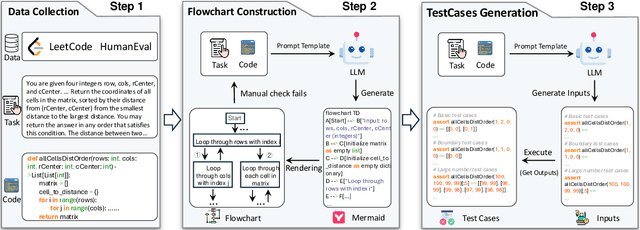
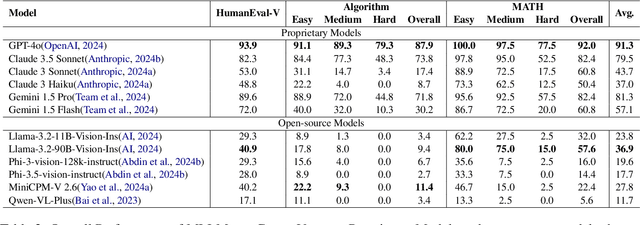
Abstract:This paper introduces Code-Vision, a benchmark designed to evaluate the logical understanding and code generation capabilities of Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs). It challenges MLLMs to generate a correct program that fulfills specific functionality requirements based on a given flowchart, which visually represents the desired algorithm or process. Code-Vision comprises three subsets: HumanEval-V, Algorithm, and MATH, which evaluate MLLMs' coding abilities across basic programming, algorithmic, and mathematical problem-solving domains. Our experiments evaluate 12 MLLMs on Code-Vision. Experimental results demonstrate that there is a large performance difference between proprietary and open-source models. On Hard problems, GPT-4o can achieve 79.3% pass@1, but the best open-source model only achieves 15%. Further experiments reveal that Code-Vision can pose unique challenges compared to other multimodal reasoning benchmarks MMCode and MathVista. We also explore the reason for the poor performance of the open-source models. All data and codes are available at https://github.com/wanghanbinpanda/CodeVision.
DeepSeek-V3 Technical Report
Dec 27, 2024



Abstract:We present DeepSeek-V3, a strong Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) language model with 671B total parameters with 37B activated for each token. To achieve efficient inference and cost-effective training, DeepSeek-V3 adopts Multi-head Latent Attention (MLA) and DeepSeekMoE architectures, which were thoroughly validated in DeepSeek-V2. Furthermore, DeepSeek-V3 pioneers an auxiliary-loss-free strategy for load balancing and sets a multi-token prediction training objective for stronger performance. We pre-train DeepSeek-V3 on 14.8 trillion diverse and high-quality tokens, followed by Supervised Fine-Tuning and Reinforcement Learning stages to fully harness its capabilities. Comprehensive evaluations reveal that DeepSeek-V3 outperforms other open-source models and achieves performance comparable to leading closed-source models. Despite its excellent performance, DeepSeek-V3 requires only 2.788M H800 GPU hours for its full training. In addition, its training process is remarkably stable. Throughout the entire training process, we did not experience any irrecoverable loss spikes or perform any rollbacks. The model checkpoints are available at https://github.com/deepseek-ai/DeepSeek-V3.
Cleaner Pretraining Corpus Curation with Neural Web Scraping
Feb 22, 2024



Abstract:The web contains large-scale, diverse, and abundant information to satisfy the information-seeking needs of humans. Through meticulous data collection, preprocessing, and curation, webpages can be used as a fundamental data resource for language model pretraining. However, when confronted with the progressively revolutionized and intricate nature of webpages, rule-based/feature-based web scrapers are becoming increasingly inadequate. This paper presents a simple, fast, and effective Neural web Scraper (NeuScraper) to help extract primary and clean text contents from webpages. Experimental results show that NeuScraper surpasses the baseline scrapers by achieving more than a 20% improvement, demonstrating its potential in extracting higher-quality data to facilitate the language model pretraining. All of the code is available at https://github.com/OpenMatch/NeuScraper.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge