Ge Yu
UNIKIE-BENCH: Benchmarking Large Multimodal Models for Key Information Extraction in Visual Documents
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Key Information Extraction (KIE) from real-world documents remains challenging due to substantial variations in layout structures, visual quality, and task-specific information requirements. Recent Large Multimodal Models (LMMs) have shown promising potential for performing end-to-end KIE directly from document images. To enable a comprehensive and systematic evaluation across realistic and diverse application scenarios, we introduce UNIKIE-BENCH, a unified benchmark designed to rigorously evaluate the KIE capabilities of LMMs. UNIKIE-BENCH consists of two complementary tracks: a constrained-category KIE track with scenario-predefined schemas that reflect practical application needs, and an open-category KIE track that extracts any key information that is explicitly present in the document. Experiments on 15 state-of-the-art LMMs reveal substantial performance degradation under diverse schema definitions, long-tail key fields, and complex layouts, along with pronounced performance disparities across different document types and scenarios. These findings underscore persistent challenges in grounding accuracy and layout-aware reasoning for LMM-based KIE. All codes and datasets are available at https://github.com/NEUIR/UNIKIE-BENCH.
Teaching LLMs to Learn Tool Trialing and Execution through Environment Interaction
Jan 19, 2026Abstract:Equipping Large Language Models (LLMs) with external tools enables them to solve complex real-world problems. However, the robustness of existing methods remains a critical challenge when confronting novel or evolving tools. Existing trajectory-centric paradigms primarily rely on memorizing static solution paths during training, which limits the ability of LLMs to generalize tool usage to newly introduced or previously unseen tools. In this paper, we propose ToolMaster, a framework that shifts tool use from imitating golden tool-calling trajectories to actively learning tool usage through interaction with the environment. To optimize LLMs for tool planning and invocation, ToolMaster adopts a trial-and-execution paradigm, which trains LLMs to first imitate teacher-generated trajectories containing explicit tool trials and self-correction, followed by reinforcement learning to coordinate the trial and execution phases jointly. This process enables agents to autonomously explore correct tool usage by actively interacting with environments and forming experiential knowledge that benefits tool execution. Experimental results demonstrate that ToolMaster significantly outperforms existing baselines in terms of generalization and robustness across unseen or unfamiliar tools. All code and data are available at https://github.com/NEUIR/ToolMaster.
Long-Chain Reasoning Distillation via Adaptive Prefix Alignment
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable reasoning capabilities, particularly in solving complex mathematical problems. Recent studies show that distilling long reasoning trajectories can effectively enhance the reasoning performance of small-scale student models. However, teacher-generated reasoning trajectories are often excessively long and structurally complex, making them difficult for student models to learn. This mismatch leads to a gap between the provided supervision signal and the learning capacity of the student model. To address this challenge, we propose Prefix-ALIGNment distillation (P-ALIGN), a framework that fully exploits teacher CoTs for distillation through adaptive prefix alignment. Specifically, P-ALIGN adaptively truncates teacher-generated reasoning trajectories by determining whether the remaining suffix is concise and sufficient to guide the student model. Then, P-ALIGN leverages the teacher-generated prefix to supervise the student model, encouraging effective prefix alignment. Experiments on multiple mathematical reasoning benchmarks demonstrate that P-ALIGN outperforms all baselines by over 3%. Further analysis indicates that the prefixes constructed by P-ALIGN provide more effective supervision signals, while avoiding the negative impact of redundant and uncertain reasoning components. All code is available at https://github.com/NEUIR/P-ALIGN.
Structured Knowledge Representation through Contextual Pages for Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) enhances Large Language Models (LLMs) by incorporating external knowledge. Recently, some works have incorporated iterative knowledge accumulation processes into RAG models to progressively accumulate and refine query-related knowledge, thereby constructing more comprehensive knowledge representations. However, these iterative processes often lack a coherent organizational structure, which limits the construction of more comprehensive and cohesive knowledge representations. To address this, we propose PAGER, a page-driven autonomous knowledge representation framework for RAG. PAGER first prompts an LLM to construct a structured cognitive outline for a given question, which consists of multiple slots representing a distinct knowledge aspect. Then, PAGER iteratively retrieves and refines relevant documents to populate each slot, ultimately constructing a coherent page that serves as contextual input for guiding answer generation. Experiments on multiple knowledge-intensive benchmarks and backbone models show that PAGER consistently outperforms all RAG baselines. Further analyses demonstrate that PAGER constructs higher-quality and information-dense knowledge representations, better mitigates knowledge conflicts, and enables LLMs to leverage external knowledge more effectively. All code is available at https://github.com/OpenBMB/PAGER.
Revealing the Attention Floating Mechanism in Masked Diffusion Models
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:Masked diffusion models (MDMs), which leverage bidirectional attention and a denoising process, are narrowing the performance gap with autoregressive models (ARMs). However, their internal attention mechanisms remain under-explored. This paper investigates the attention behaviors in MDMs, revealing the phenomenon of Attention Floating. Unlike ARMs, where attention converges to a fixed sink, MDMs exhibit dynamic, dispersed attention anchors that shift across denoising steps and layers. Further analysis reveals its Shallow Structure-Aware, Deep Content-Focused attention mechanism: shallow layers utilize floating tokens to build a global structural framework, while deeper layers allocate more capability toward capturing semantic content. Empirically, this distinctive attention pattern provides a mechanistic explanation for the strong in-context learning capabilities of MDMs, allowing them to double the performance compared to ARMs in knowledge-intensive tasks. All codes and datasets are available at https://github.com/NEUIR/Attention-Floating.
MSC-180: A Benchmark for Automated Formal Theorem Proving from Mathematical Subject Classification
Dec 20, 2025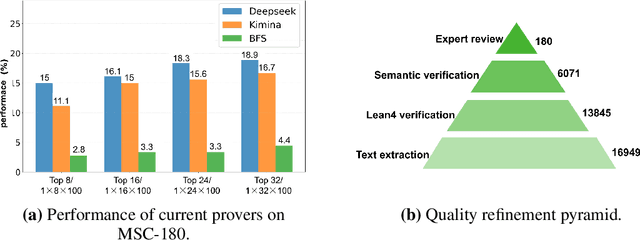


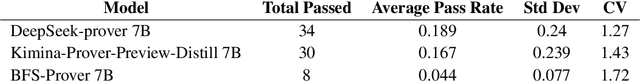
Abstract:Automated Theorem Proving (ATP) represents a core research direction in artificial intelligence for achieving formal reasoning and verification, playing a significant role in advancing machine intelligence. However, current large language model (LLM)-based theorem provers suffer from limitations such as restricted domain coverage and weak generalization in mathematical reasoning. To address these issues, we propose MSC-180, a benchmark for evaluation based on the MSC2020 mathematical subject classification. It comprises 180 formal verification problems, 3 advanced problems from each of 60 mathematical branches, spanning from undergraduate to graduate levels. Each problem has undergone multiple rounds of verification and refinement by domain experts to ensure formal accuracy. Evaluations of state-of-the-art LLM-based theorem provers under the pass@32 setting reveal that the best model achieves only an 18.89% overall pass rate, with prominent issues including significant domain bias (maximum domain coverage 41.7%) and a difficulty gap (significantly lower pass rates on graduate-level problems). To further quantify performance variability across mathematical domains, we introduce the coefficient of variation (CV) as an evaluation metric. The observed CV values are 4-6 times higher than the statistical high-variability threshold, indicating that the models still rely on pattern matching from training corpora rather than possessing transferable reasoning mechanisms and systematic generalization capabilities. MSC-180, together with its multi-dimensional evaluation framework, provides a discriminative and systematic benchmark for driving the development of next-generation AI systems with genuine mathematical reasoning abilities.
Legal$Δ$: Enhancing Legal Reasoning in LLMs via Reinforcement Learning with Chain-of-Thought Guided Information Gain
Aug 17, 2025
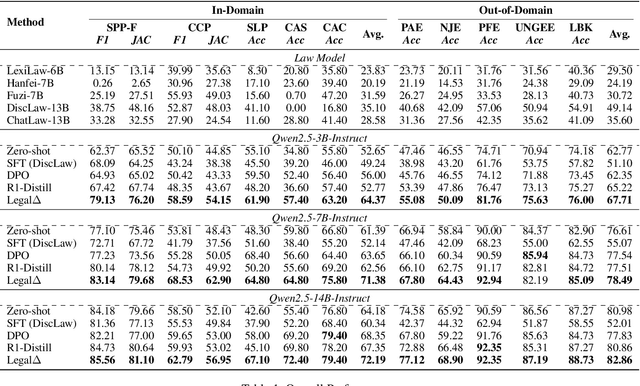

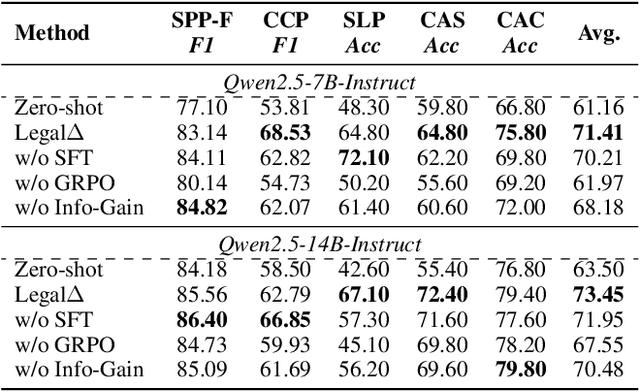
Abstract:Legal Artificial Intelligence (LegalAI) has achieved notable advances in automating judicial decision-making with the support of Large Language Models (LLMs). However, existing legal LLMs still struggle to generate reliable and interpretable reasoning processes. They often default to fast-thinking behavior by producing direct answers without explicit multi-step reasoning, limiting their effectiveness in complex legal scenarios that demand rigorous justification. To address this challenge, we propose Legal$\Delta$, a reinforcement learning framework designed to enhance legal reasoning through chain-of-thought guided information gain. During training, Legal$\Delta$ employs a dual-mode input setup-comprising direct answer and reasoning-augmented modes-and maximizes the information gain between them. This encourages the model to acquire meaningful reasoning patterns rather than generating superficial or redundant explanations. Legal$\Delta$ follows a two-stage approach: (1) distilling latent reasoning capabilities from a powerful Large Reasoning Model (LRM), DeepSeek-R1, and (2) refining reasoning quality via differential comparisons, combined with a multidimensional reward mechanism that assesses both structural coherence and legal-domain specificity. Experimental results on multiple legal reasoning tasks demonstrate that Legal$\Delta$ outperforms strong baselines in both accuracy and interpretability. It consistently produces more robust and trustworthy legal judgments without relying on labeled preference data. All code and data will be released at https://github.com/NEUIR/LegalDelta.
Advancing Knowledge Tracing by Exploring Follow-up Performance Trends
Aug 11, 2025


Abstract:Intelligent Tutoring Systems (ITS), such as Massive Open Online Courses, offer new opportunities for human learning. At the core of such systems, knowledge tracing (KT) predicts students' future performance by analyzing their historical learning activities, enabling an accurate evaluation of students' knowledge states over time. We show that existing KT methods often encounter correlation conflicts when analyzing the relationships between historical learning sequences and future performance. To address such conflicts, we propose to extract so-called Follow-up Performance Trends (FPTs) from historical ITS data and to incorporate them into KT. We propose a method called Forward-Looking Knowledge Tracing (FINER) that combines historical learning sequences with FPTs to enhance student performance prediction accuracy. FINER constructs learning patterns that facilitate the retrieval of FPTs from historical ITS data in linear time; FINER includes a novel similarity-aware attention mechanism that aggregates FPTs based on both frequency and contextual similarity; and FINER offers means of combining FPTs and historical learning sequences to enable more accurate prediction of student future performance. Experiments on six real-world datasets show that FINER can outperform ten state-of-the-art KT methods, increasing accuracy by 8.74% to 84.85%.
Automated Formalization via Conceptual Retrieval-Augmented LLMs
Aug 09, 2025
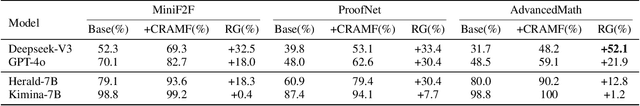

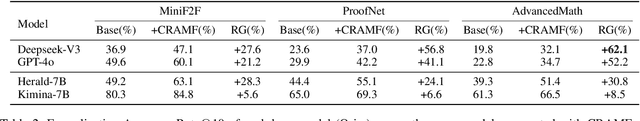
Abstract:Interactive theorem provers (ITPs) require manual formalization, which is labor-intensive and demands expert knowledge. While automated formalization offers a potential solution, it faces two major challenges: model hallucination (e.g., undefined predicates, symbol misuse, and version incompatibility) and the semantic gap caused by ambiguous or missing premises in natural language descriptions. To address these issues, we propose CRAMF, a Concept-driven Retrieval-Augmented Mathematical Formalization framework. CRAMF enhances LLM-based autoformalization by retrieving formal definitions of core mathematical concepts, providing contextual grounding during code generation. However, applying retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) in this setting is non-trivial due to the lack of structured knowledge bases, the polymorphic nature of mathematical concepts, and the high precision required in formal retrieval. We introduce a framework for automatically constructing a concept-definition knowledge base from Mathlib4, the standard mathematical library for the Lean 4 theorem prover, indexing over 26,000 formal definitions and 1,000+ core mathematical concepts. To address conceptual polymorphism, we propose contextual query augmentation with domain- and application-level signals. In addition, we design a dual-channel hybrid retrieval strategy with reranking to ensure accurate and relevant definition retrieval. Experiments on miniF2F, ProofNet, and our newly proposed AdvancedMath benchmark show that CRAMF can be seamlessly integrated into LLM-based autoformalizers, yielding consistent improvements in translation accuracy, achieving up to 62.1% and an average of 29.9% relative improvement.
Resource-Limited Joint Multimodal Sentiment Reasoning and Classification via Chain-of-Thought Enhancement and Distillation
Aug 07, 2025Abstract:The surge in rich multimodal content on social media platforms has greatly advanced Multimodal Sentiment Analysis (MSA), with Large Language Models (LLMs) further accelerating progress in this field. Current approaches primarily leverage the knowledge and reasoning capabilities of parameter-heavy (Multimodal) LLMs for sentiment classification, overlooking autonomous multimodal sentiment reasoning generation in resource-constrained environments. Therefore, we focus on the Resource-Limited Joint Multimodal Sentiment Reasoning and Classification task, JMSRC, which simultaneously performs multimodal sentiment reasoning chain generation and sentiment classification only with a lightweight model. We propose a Multimodal Chain-of-Thought Reasoning Distillation model, MulCoT-RD, designed for JMSRC that employs a "Teacher-Assistant-Student" distillation paradigm to address deployment constraints in resource-limited environments. We first leverage a high-performance Multimodal Large Language Model (MLLM) to generate the initial reasoning dataset and train a medium-sized assistant model with a multi-task learning mechanism. A lightweight student model is jointly trained to perform efficient multimodal sentiment reasoning generation and classification. Extensive experiments on four datasets demonstrate that MulCoT-RD with only 3B parameters achieves strong performance on JMSRC, while exhibiting robust generalization and enhanced interpretability.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge