Guanghui Qin
Scaling medical imaging report generation with multimodal reinforcement learning
Jan 23, 2026Abstract:Frontier models have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in understanding and reasoning with natural-language text, but they still exhibit major competency gaps in multimodal understanding and reasoning especially in high-value verticals such as biomedicine. Medical imaging report generation is a prominent example. Supervised fine-tuning can substantially improve performance, but they are prone to overfitting to superficial boilerplate patterns. In this paper, we introduce Universal Report Generation (UniRG) as a general framework for medical imaging report generation. By leveraging reinforcement learning as a unifying mechanism to directly optimize for evaluation metrics designed for end applications, UniRG can significantly improve upon supervised fine-tuning and attain durable generalization across diverse institutions and clinical practices. We trained UniRG-CXR on publicly available chest X-ray (CXR) data and conducted a thorough evaluation in CXR report generation with rigorous evaluation scenarios. On the authoritative ReXrank benchmark, UniRG-CXR sets new overall SOTA, outperforming prior state of the art by a wide margin.
X-Reasoner: Towards Generalizable Reasoning Across Modalities and Domains
May 06, 2025Abstract:Recent proprietary models (e.g., o3) have begun to demonstrate strong multimodal reasoning capabilities. Yet, most existing open-source research concentrates on training text-only reasoning models, with evaluations limited to mainly mathematical and general-domain tasks. Therefore, it remains unclear how to effectively extend reasoning capabilities beyond text input and general domains. This paper explores a fundamental research question: Is reasoning generalizable across modalities and domains? Our findings support an affirmative answer: General-domain text-based post-training can enable such strong generalizable reasoning. Leveraging this finding, we introduce X-Reasoner, a vision-language model post-trained solely on general-domain text for generalizable reasoning, using a two-stage approach: an initial supervised fine-tuning phase with distilled long chain-of-thoughts, followed by reinforcement learning with verifiable rewards. Experiments show that X-Reasoner successfully transfers reasoning capabilities to both multimodal and out-of-domain settings, outperforming existing state-of-the-art models trained with in-domain and multimodal data across various general and medical benchmarks (Figure 1). Additionally, we find that X-Reasoner's performance in specialized domains can be further enhanced through continued training on domain-specific text-only data. Building upon this, we introduce X-Reasoner-Med, a medical-specialized variant that achieves new state of the art on numerous text-only and multimodal medical benchmarks.
KV-Distill: Nearly Lossless Learnable Context Compression for LLMs
Mar 13, 2025Abstract:Sequence-to-sequence tasks often benefit from long contexts, but the quadratic complexity of self-attention in standard Transformers renders this non-trivial. During generation, temporary representations -stored in the so-called KV cache-account for a large portion of GPU memory usage and scale linearly with context length. We introduce KV-Distill, a Transformer compression framework that distills long context KV caches into significantly shorter representations in a question-independent fashion. KV-Distill can be trained as a parameter-efficient adaptor for pretrained models, and enables the compression of arbitrary spans of a context while preserving pre-trained model capabilities. We treat a compressed-uncompressed cache as a student-teacher pairing and apply a KL-type divergence to match the generated outputs. KV-Distill outperforms other compression techniques in worst-case extractive tasks and approaches uncompressed performance in long context question answering and summarization, and it can be fine-tuned on domain-specific contexts to reduce lengths by up to 99% while preserving downstream performance. We demonstrate the generalizability of KV-Distill across various model sizes and architectures.
Med-RLVR: Emerging Medical Reasoning from a 3B base model via reinforcement Learning
Feb 27, 2025



Abstract:Reinforcement learning from verifiable rewards (RLVR) has recently gained attention for its ability to elicit self-evolved reasoning capabilitie from base language models without explicit reasoning supervisions, as demonstrated by DeepSeek-R1. While prior work on RLVR has primarily focused on mathematical and coding domains, its applicability to other tasks and domains remains unexplored. In this work, we investigate whether medical reasoning can emerge from RLVR. We introduce Med-RLVR as an initial study of RLVR in the medical domain leveraging medical multiple-choice question answering (MCQA) data as verifiable labels. Our results demonstrate that RLVR is not only effective for math and coding but also extends successfully to medical question answering. Notably, Med-RLVR achieves performance comparable to traditional supervised fine-tuning (SFT) on in-distribution tasks while significantly improving out-of-distribution generalization, with an 8-point accuracy gain. Further analysis of training dynamics reveals that, with no explicit reasoning supervision, reasoning emerges from the 3B-parameter base model. These findings underscore the potential of RLVR in domains beyond math and coding, opening new avenues for its application in knowledge-intensive fields such as medicine.
CLERC: A Dataset for Legal Case Retrieval and Retrieval-Augmented Analysis Generation
Jun 24, 2024
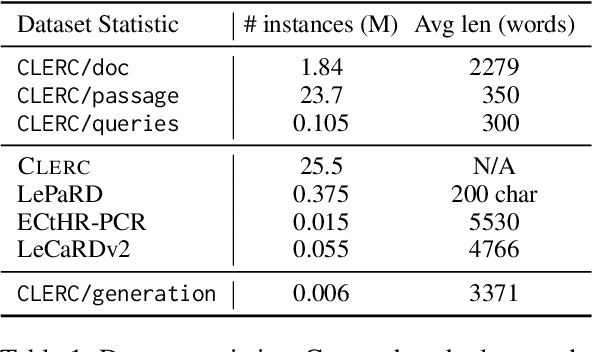
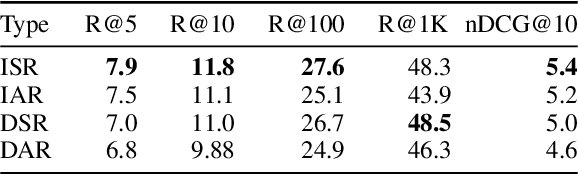

Abstract:Legal professionals need to write analyses that rely on citations to relevant precedents, i.e., previous case decisions. Intelligent systems assisting legal professionals in writing such documents provide great benefits but are challenging to design. Such systems need to help locate, summarize, and reason over salient precedents in order to be useful. To enable systems for such tasks, we work with legal professionals to transform a large open-source legal corpus into a dataset supporting two important backbone tasks: information retrieval (IR) and retrieval-augmented generation (RAG). This dataset CLERC (Case Law Evaluation Retrieval Corpus), is constructed for training and evaluating models on their ability to (1) find corresponding citations for a given piece of legal analysis and to (2) compile the text of these citations (as well as previous context) into a cogent analysis that supports a reasoning goal. We benchmark state-of-the-art models on CLERC, showing that current approaches still struggle: GPT-4o generates analyses with the highest ROUGE F-scores but hallucinates the most, while zero-shot IR models only achieve 48.3% recall@1000.
Researchy Questions: A Dataset of Multi-Perspective, Decompositional Questions for LLM Web Agents
Feb 27, 2024



Abstract:Existing question answering (QA) datasets are no longer challenging to most powerful Large Language Models (LLMs). Traditional QA benchmarks like TriviaQA, NaturalQuestions, ELI5 and HotpotQA mainly study ``known unknowns'' with clear indications of both what information is missing, and how to find it to answer the question. Hence, good performance on these benchmarks provides a false sense of security. A yet unmet need of the NLP community is a bank of non-factoid, multi-perspective questions involving a great deal of unclear information needs, i.e. ``unknown uknowns''. We claim we can find such questions in search engine logs, which is surprising because most question-intent queries are indeed factoid. We present Researchy Questions, a dataset of search engine queries tediously filtered to be non-factoid, ``decompositional'' and multi-perspective. We show that users spend a lot of ``effort'' on these questions in terms of signals like clicks and session length, and that they are also challenging for GPT-4. We also show that ``slow thinking'' answering techniques, like decomposition into sub-questions shows benefit over answering directly. We release $\sim$ 100k Researchy Questions, along with the Clueweb22 URLs that were clicked.
Streaming Sequence Transduction through Dynamic Compression
Feb 02, 2024Abstract:We introduce STAR (Stream Transduction with Anchor Representations), a novel Transformer-based model designed for efficient sequence-to-sequence transduction over streams. STAR dynamically segments input streams to create compressed anchor representations, achieving nearly lossless compression (12x) in Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) and outperforming existing methods. Moreover, STAR demonstrates superior segmentation and latency-quality trade-offs in simultaneous speech-to-text tasks, optimizing latency, memory footprint, and quality.
Nugget: Neural Agglomerative Embeddings of Text
Oct 03, 2023Abstract:Embedding text sequences is a widespread requirement in modern language understanding. Existing approaches focus largely on constant-size representations. This is problematic, as the amount of information contained in text often varies with the length of the input. We propose a solution called Nugget, which encodes language into a representation based on a dynamically selected subset of input tokens. These nuggets are learned through tasks like autoencoding and machine translation, and intuitively segment language into meaningful units. We demonstrate Nugget outperforms related approaches in tasks involving semantic comparison. Finally, we illustrate these compact units allow for expanding the contextual window of a language model (LM), suggesting new future LMs that can condition on significantly larger amounts of content.
* Appeared at ICML 2023
Nugget 2D: Dynamic Contextual Compression for Scaling Decoder-only Language Models
Oct 03, 2023



Abstract:Standard Transformer-based language models (LMs) scale poorly to long contexts. We propose a solution based on dynamic contextual compression, which extends the Nugget approach of Qin & Van Durme (2023) from BERT-like frameworks to decoder-only LMs. Our method models history as compressed "nuggets" which are trained to allow for reconstruction, and it can be initialized with off-the-shelf models such as LLaMA. We demonstrate through experiments in language modeling, question answering, and summarization that Nugget2D retains capabilities in these tasks, while drastically reducing the overhead during decoding in terms of time and space. For example, in the experiments of autoencoding, Nugget2D can shrink context at a 20x compression ratio with a BLEU score of 98% for reconstruction, achieving nearly lossless encoding.
The NLP Task Effectiveness of Long-Range Transformers
Feb 16, 2022
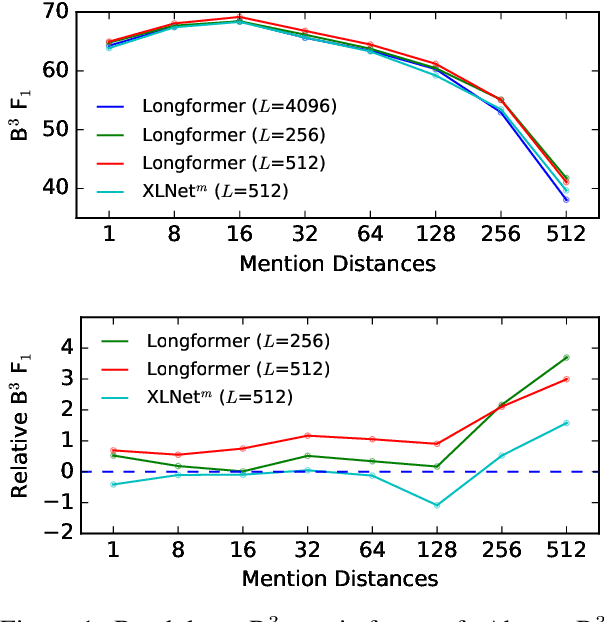


Abstract:Transformer models cannot easily scale to long sequences due to their O(N^2) time and space complexity. This has led to Transformer variants seeking to lessen computational complexity, such as Longformer and Performer. While such models have theoretically greater efficiency, their effectiveness on real NLP tasks has not been well studied. We benchmark 7 variants of Transformer models on 5 difficult NLP tasks and 7 datasets. We design experiments to isolate the effect of pretraining and hyperparameter settings, to focus on their capacity for long-range attention. Moreover, we present various methods to investigate attention behaviors, to illuminate model details beyond metric scores. We find that attention of long-range transformers has advantages on content selection and query-guided decoding, but they come with previously unrecognized drawbacks such as insufficient attention to distant tokens.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge