Eugene Yang
Overview of the TREC 2025 RAGTIME Track
Feb 10, 2026Abstract:The principal goal of the RAG TREC Instrument for Multilingual Evaluation (RAGTIME) track at TREC is to study report generation from multilingual source documents. The track has created a document collection containing Arabic, Chinese, English, and Russian news stories. RAGTIME includes three task types: Multilingual Report Generation, English Report Generation, and Multilingual Information Retrieval (MLIR). A total of 125 runs were submitted by 13 participating teams (and as baselines by the track coordinators) for three tasks. This overview describes these three tasks and presents the available results.
NeuCLIRTech: Chinese Monolingual and Cross-Language Information Retrieval Evaluation in a Challenging Domain
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Measuring advances in retrieval requires test collections with relevance judgments that can faithfully distinguish systems. This paper presents NeuCLIRTech, an evaluation collection for cross-language retrieval over technical information. The collection consists of technical documents written natively in Chinese and those same documents machine translated into English. It includes 110 queries with relevance judgments. The collection supports two retrieval scenarios: monolingual retrieval in Chinese, and cross-language retrieval with English as the query language. NeuCLIRTech combines the TREC NeuCLIR track topics of 2023 and 2024. The 110 queries with 35,962 document judgments provide strong statistical discriminatory power when trying to distinguish retrieval approaches. A fusion baseline of strong neural retrieval systems is included so that developers of reranking algorithms are not reliant on BM25 as their first stage retriever. The dataset and artifacts are released on Huggingface Datasets
LANCER: LLM Reranking for Nugget Coverage
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Unlike short-form retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), such as factoid question answering, long-form RAG requires retrieval to provide documents covering a wide range of relevant information. Automated report generation exemplifies this setting: it requires not only relevant information but also a more elaborate response with comprehensive information. Yet, existing retrieval methods are primarily optimized for relevance ranking rather than information coverage. To address this limitation, we propose LANCER, an LLM-based reranking method for nugget coverage. LANCER predicts what sub-questions should be answered to satisfy an information need, predicts which documents answer these sub-questions, and reranks documents in order to provide a ranked list covering as many information nuggets as possible. Our empirical results show that LANCER enhances the quality of retrieval as measured by nugget coverage metrics, achieving higher $α$-nDCG and information coverage than other LLM-based reranking methods. Our oracle analysis further reveals that sub-question generation plays an essential role.
Insider Knowledge: How Much Can RAG Systems Gain from Evaluation Secrets?
Jan 19, 2026Abstract:RAG systems are increasingly evaluated and optimized using LLM judges, an approach that is rapidly becoming the dominant paradigm for system assessment. Nugget-based approaches in particular are now embedded not only in evaluation frameworks but also in the architectures of RAG systems themselves. While this integration can lead to genuine improvements, it also creates a risk of faulty measurements due to circularity. In this paper, we investigate this risk through comparative experiments with nugget-based RAG systems, including Ginger and Crucible, against strong baselines such as GPT-Researcher. By deliberately modifying Crucible to generate outputs optimized for an LLM judge, we show that near-perfect evaluation scores can be achieved when elements of the evaluation - such as prompt templates or gold nuggets - are leaked or can be predicted. Our results highlight the importance of blind evaluation settings and methodological diversity to guard against mistaking metric overfitting for genuine system progress.
Incorporating Q&A Nuggets into Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Jan 19, 2026Abstract:RAGE systems integrate ideas from automatic evaluation (E) into Retrieval-augmented Generation (RAG). As one such example, we present Crucible, a Nugget-Augmented Generation System that preserves explicit citation provenance by constructing a bank of Q&A nuggets from retrieved documents and uses them to guide extraction, selection, and report generation. Reasoning on nuggets avoids repeated information through clear and interpretable Q&A semantics - instead of opaque cluster abstractions - while maintaining citation provenance throughout the entire generation process. Evaluated on the TREC NeuCLIR 2024 collection, our Crucible system substantially outperforms Ginger, a recent nugget-based RAG system, in nugget recall, density, and citation grounding.
RoutIR: Fast Serving of Retrieval Pipelines for Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:Retrieval models are key components of Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems, which generate search queries, process the documents returned, and generate a response. RAG systems are often dynamic and may involve multiple rounds of retrieval. While many state-of-the-art retrieval methods are available through academic IR platforms, these platforms are typically designed for the Cranfield paradigm in which all queries are known up front and can be batch processed offline. This simplification accelerates research but leaves state-of-the-art retrieval models unable to support downstream applications that require online services, such as arbitrary dynamic RAG pipelines that involve looping, feedback, or even self-organizing agents. In this work, we introduce RoutIR, a Python package that provides a simple and efficient HTTP API that wraps arbitrary retrieval methods, including first stage retrieval, reranking, query expansion, and result fusion. By providing a minimal JSON configuration file specifying the retrieval models to serve, RoutIR can be used to construct and query retrieval pipelines on-the-fly using any permutation of available models (e.g., fusing the results of several first-stage retrieval methods followed by reranking). The API automatically performs asynchronous query batching and caches results by default. While many state-of-the-art retrieval methods are already supported by the package, RoutIR is also easily expandable by implementing the Engine abstract class. The package is open-sourced and publicly available on GitHub: http://github.com/hltcoe/routir.
NeuCLIRBench: A Modern Evaluation Collection for Monolingual, Cross-Language, and Multilingual Information Retrieval
Nov 18, 2025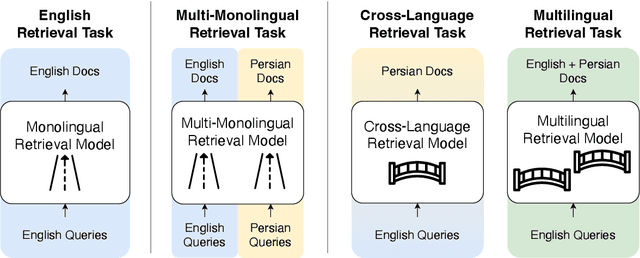
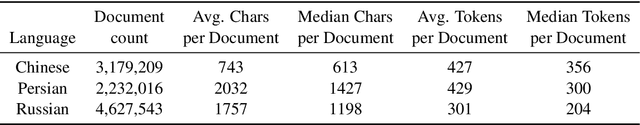
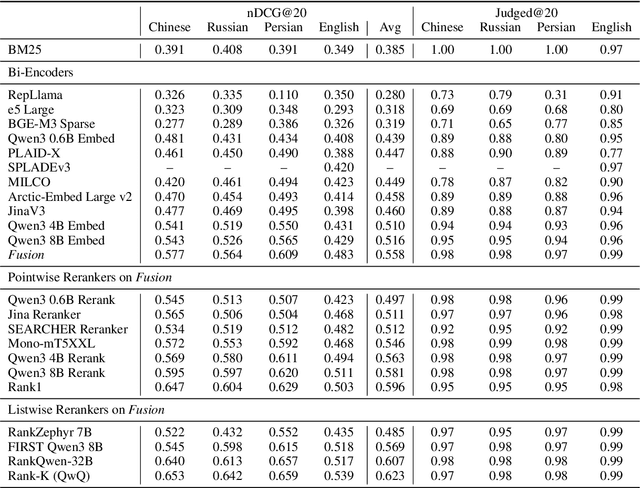
Abstract:To measure advances in retrieval, test collections with relevance judgments that can faithfully distinguish systems are required. This paper presents NeuCLIRBench, an evaluation collection for cross-language and multilingual retrieval. The collection consists of documents written natively in Chinese, Persian, and Russian, as well as those same documents machine translated into English. The collection supports several retrieval scenarios including: monolingual retrieval in English, Chinese, Persian, or Russian; cross-language retrieval with English as the query language and one of the other three languages as the document language; and multilingual retrieval, again with English as the query language and relevant documents in all three languages. NeuCLIRBench combines the TREC NeuCLIR track topics of 2022, 2023, and 2024. The 250,128 judgments across approximately 150 queries for the monolingual and cross-language tasks and 100 queries for multilingual retrieval provide strong statistical discriminatory power to distinguish retrieval approaches. A fusion baseline of strong neural retrieval systems is included with the collection so that developers of reranking algorithms are no longer reliant on BM25 as their first-stage retriever. NeuCLIRBench is publicly available.
Topic-Specific Classifiers are Better Relevance Judges than Prompted LLMs
Oct 06, 2025Abstract:The unjudged document problem, where pooled test collections have incomplete relevance judgments for evaluating new retrieval systems, is a key obstacle to the reusability of test collections in information retrieval. While the de facto standard to deal with the problem is to treat unjudged documents as non-relevant, many alternatives have been proposed, including the use of large language models (LLMs) as a relevance judge (LLM-as-a-judge). However, this has been criticized as circular, since the same LLM can be used as a judge and as a ranker at the same time. We propose to train topic-specific relevance classifiers instead: By finetuning monoT5 with independent LoRA weight adaptation on the judgments of a single assessor for a single topic's pool, we align it to that assessor's notion of relevance for the topic. The system rankings obtained through our classifier's relevance judgments achieve a Spearmans' $\rho$ correlation of $>0.95$ with ground truth system rankings. As little as 128 initial human judgments per topic suffice to improve the comparability of models, compared to treating unjudged documents as non-relevant, while achieving more reliability than existing LLM-as-a-judge approaches. Topic-specific relevance classifiers thus are a lightweight and straightforward way to tackle the unjudged document problem, while maintaining human judgments as the gold standard for retrieval evaluation. Code, models, and data are made openly available.
Milco: Learned Sparse Retrieval Across Languages via a Multilingual Connector
Oct 01, 2025Abstract:Learned Sparse Retrieval (LSR) combines the efficiency of bi-encoders with the transparency of lexical matching, but existing approaches struggle to scale beyond English. We introduce MILCO, an LSR architecture that maps queries and documents from different languages into a shared English lexical space via a multilingual connector. MILCO is trained with a specialized two-stage regime that combines Sparse Alignment Pretraining with contrastive training to provide representation transparency and effectiveness while mitigating semantic collapse. Motivated by the observation that uncommon entities are often lost when projected into English, we propose a new LexEcho head, which enhances robustness by augmenting the English lexical representation with a source-language view obtained through a special [ECHO] token. MILCO achieves state-of-the-art multilingual and cross-lingual LSR performance, outperforming leading dense, sparse, and multi-vector baselines such as BGE-M3 and Qwen3-Embed on standard multilingual benchmarks, while supporting dynamic efficiency through post-hoc pruning. Notably, when using mass-based pruning to reduce document representations to only 30 active dimensions on average, MILCO 560M outperforms the similarly-sized Qwen3-Embed 0.6B with 1024 dimensions.
Overview of the TREC 2024 NeuCLIR Track
Sep 17, 2025Abstract:The principal goal of the TREC Neural Cross-Language Information Retrieval (NeuCLIR) track is to study the effect of neural approaches on cross-language information access. The track has created test collections containing Chinese, Persian, and Russian news stories and Chinese academic abstracts. NeuCLIR includes four task types: Cross-Language Information Retrieval (CLIR) from news, Multilingual Information Retrieval (MLIR) from news, Report Generation from news, and CLIR from technical documents. A total of 274 runs were submitted by five participating teams (and as baselines by the track coordinators) for eight tasks across these four task types. Task descriptions and the available results are presented.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge