Ethan C. Chau
Researchy Questions: A Dataset of Multi-Perspective, Decompositional Questions for LLM Web Agents
Feb 27, 2024



Abstract:Existing question answering (QA) datasets are no longer challenging to most powerful Large Language Models (LLMs). Traditional QA benchmarks like TriviaQA, NaturalQuestions, ELI5 and HotpotQA mainly study ``known unknowns'' with clear indications of both what information is missing, and how to find it to answer the question. Hence, good performance on these benchmarks provides a false sense of security. A yet unmet need of the NLP community is a bank of non-factoid, multi-perspective questions involving a great deal of unclear information needs, i.e. ``unknown uknowns''. We claim we can find such questions in search engine logs, which is surprising because most question-intent queries are indeed factoid. We present Researchy Questions, a dataset of search engine queries tediously filtered to be non-factoid, ``decompositional'' and multi-perspective. We show that users spend a lot of ``effort'' on these questions in terms of signals like clicks and session length, and that they are also challenging for GPT-4. We also show that ``slow thinking'' answering techniques, like decomposition into sub-questions shows benefit over answering directly. We release $\sim$ 100k Researchy Questions, along with the Clueweb22 URLs that were clicked.
Nugget 2D: Dynamic Contextual Compression for Scaling Decoder-only Language Models
Oct 03, 2023



Abstract:Standard Transformer-based language models (LMs) scale poorly to long contexts. We propose a solution based on dynamic contextual compression, which extends the Nugget approach of Qin & Van Durme (2023) from BERT-like frameworks to decoder-only LMs. Our method models history as compressed "nuggets" which are trained to allow for reconstruction, and it can be initialized with off-the-shelf models such as LLaMA. We demonstrate through experiments in language modeling, question answering, and summarization that Nugget2D retains capabilities in these tasks, while drastically reducing the overhead during decoding in terms of time and space. For example, in the experiments of autoencoding, Nugget2D can shrink context at a 20x compression ratio with a BLEU score of 98% for reconstruction, achieving nearly lossless encoding.
Specializing Multilingual Language Models: An Empirical Study
Jun 22, 2021
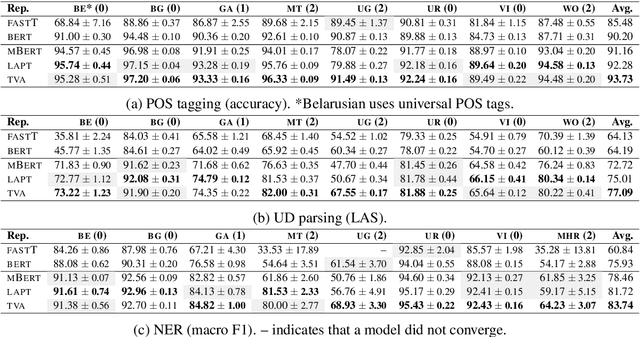

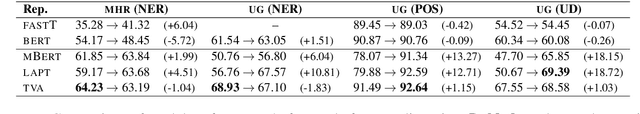
Abstract:Contextualized word representations from pretrained multilingual language models have become the de facto standard for addressing natural language tasks in many different languages, but the success of this approach is far from universal. For languages rarely or never seen by these models, directly using such models often results in suboptimal representation or use of data, motivating additional model adaptations to achieve reasonably strong performance. In this work, we study the performance, extensibility, and interaction of two such adaptations for this low-resource setting: vocabulary augmentation and script transliteration. Our evaluations on a set of three tasks in nine diverse low-resource languages yield a mixed result, upholding the viability of these approaches while raising new questions around how to optimally adapt multilingual models to low-resource settings.
Parsing with Multilingual BERT, a Small Corpus, and a Small Treebank
Sep 29, 2020
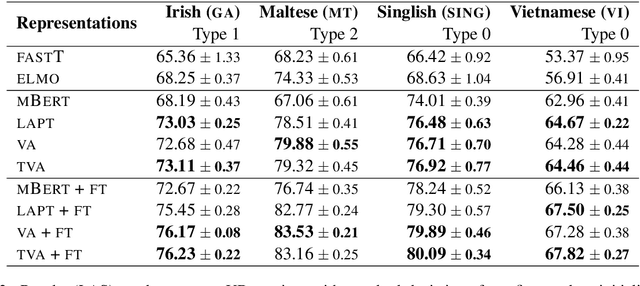

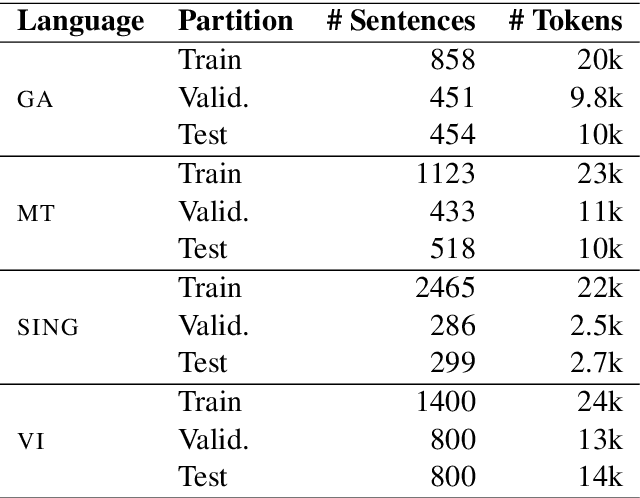
Abstract:Pretrained multilingual contextual representations have shown great success, but due to the limits of their pretraining data, their benefits do not apply equally to all language varieties. This presents a challenge for language varieties unfamiliar to these models, whose labeled \emph{and unlabeled} data is too limited to train a monolingual model effectively. We propose the use of additional language-specific pretraining and vocabulary augmentation to adapt multilingual models to low-resource settings. Using dependency parsing of four diverse low-resource language varieties as a case study, we show that these methods significantly improve performance over baselines, especially in the lowest-resource cases, and demonstrate the importance of the relationship between such models' pretraining data and target language varieties.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge