Junhao Jiang
Video Compression with Hierarchical Temporal Neural Representation
Jan 25, 2026Abstract:Video compression has recently benefited from implicit neural representations (INRs), which model videos as continuous functions. INRs offer compact storage and flexible reconstruction, providing a promising alternative to traditional codecs. However, most existing INR-based methods treat the temporal dimension as an independent input, limiting their ability to capture complex temporal dependencies. To address this, we propose a Hierarchical Temporal Neural Representation for Videos, TeNeRV. TeNeRV integrates short- and long-term dependencies through two key components. First, an Inter-Frame Feature Fusion (IFF) module aggregates features from adjacent frames, enforcing local temporal coherence and capturing fine-grained motion. Second, a GoP-Adaptive Modulation (GAM) mechanism partitions videos into Groups-of-Pictures and learns group-specific priors. The mechanism modulates network parameters, enabling adaptive representations across different GoPs. Extensive experiments demonstrate that TeNeRV consistently outperforms existing INR-based methods in rate-distortion performance, validating the effectiveness of our proposed approach.
Frequency-aware Neural Representation for Videos
Jan 25, 2026Abstract:Implicit Neural Representations (INRs) have emerged as a promising paradigm for video compression. However, existing INR-based frameworks typically suffer from inherent spectral bias, which favors low-frequency components and leads to over-smoothed reconstructions and suboptimal rate-distortion performance. In this paper, we propose FaNeRV, a Frequency-aware Neural Representation for videos, which explicitly decouples low- and high-frequency components to enable efficient and faithful video reconstruction. FaNeRV introduces a multi-resolution supervision strategy that guides the network to progressively capture global structures and fine-grained textures through staged supervision . To further enhance high-frequency reconstruction, we propose a dynamic high-frequency injection mechanism that adaptively emphasizes challenging regions. In addition, we design a frequency-decomposed network module to improve feature modeling across different spectral bands. Extensive experiments on standard benchmarks demonstrate that FaNeRV significantly outperforms state-of-the-art INR methods and achieves competitive rate-distortion performance against traditional codecs.
A Histogram Thresholding Improvement to Mask R-CNN for Scalable Segmentation of New and Old Rural Buildings
Feb 08, 2021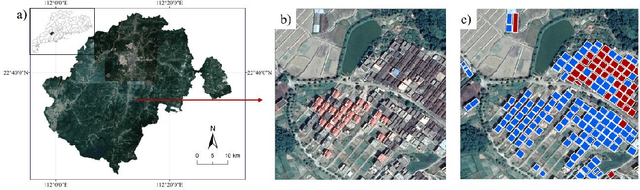

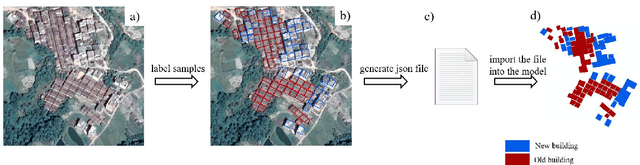

Abstract:Mapping new and old buildings are of great significance for understanding socio-economic development in rural areas. In recent years, deep neural networks have achieved remarkable building segmentation results in high-resolution remote sensing images. However, the scarce training data and the varying geographical environments have posed challenges for scalable building segmentation. This study proposes a novel framework based on Mask R-CNN, named HTMask R-CNN, to extract new and old rural buildings even when the label is scarce. The framework adopts the result of single-object instance segmentation from the orthodox Mask R-CNN. Further, it classifies the rural buildings into new and old ones based on a dynamic grayscale threshold inferred from the result of a two-object instance segmentation task where training data is scarce. We found that the framework can extract more buildings and achieve a much higher mean Average Precision (mAP) than the orthodox Mask R-CNN model. We tested the novel framework's performance with increasing training data and found that it converged even when the training samples were limited. This framework's main contribution is to allow scalable segmentation by using significantly fewer training samples than traditional machine learning practices. That makes mapping China's new and old rural buildings viable.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge