Yuan Yao
Department of Mathematics, Hong Kong University of Science and Technology
Phi-Former: A Pairwise Hierarchical Approach for Compound-Protein Interactions Prediction
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Drug discovery remains time-consuming, labor-intensive, and expensive, often requiring years and substantial investment per drug candidate. Predicting compound-protein interactions (CPIs) is a critical component in this process, enabling the identification of molecular interactions between drug candidates and target proteins. Recent deep learning methods have successfully modeled CPIs at the atomic level, achieving improved efficiency and accuracy over traditional energy-based approaches. However, these models do not always align with chemical realities, as molecular fragments (motifs or functional groups) typically serve as the primary units of biological recognition and binding. In this paper, we propose Phi-former, a pairwise hierarchical interaction representation learning method that addresses this gap by incorporating the biological role of motifs in CPIs. Phi-former represents compounds and proteins hierarchically and employs a pairwise pre-training framework to model interactions systematically across atom-atom, motif-motif, and atom-motif levels, reflecting how biological systems recognize molecular partners. We design intra-level and inter-level learning pipelines that make different interaction levels mutually beneficial. Experimental results demonstrate that Phi-former achieves superior performance on CPI-related tasks. A case study shows that our method accurately identifies specific atoms or motifs activated in CPIs, providing interpretable model explanations. These insights may guide rational drug design and support precision medicine applications.
Prefill vs. Decode Bottlenecks: SRAM-Frequency Tradeoffs and the Memory-Bandwidth Ceiling
Dec 26, 2025



Abstract:Energy consumption dictates the cost and environmental impact of deploying Large Language Models. This paper investigates the impact of on-chip SRAM size and operating frequency on the energy efficiency and performance of LLM inference, focusing on the distinct behaviors of the compute-bound prefill and memory-bound decode phases. Our simulation methodology combines OpenRAM for energy modeling, LLMCompass for latency simulation, and ScaleSIM for systolic array operational intensity. Our findings show that total energy use is predominantly determined by SRAM size in both phases, with larger buffers significantly increasing static energy due to leakage, which is not offset by corresponding latency benefits. We quantitatively explore the memory-bandwidth bottleneck, demonstrating that while high operating frequencies reduce prefill latency, their positive impact on memory-bound decode latency is capped by the external memory bandwidth. Counter-intuitively, high compute frequency can reduce total energy by reducing execution time and consequently decreasing static energy consumption more than the resulting dynamic power increase. We identify an optimal hardware configuration for the simulated workload: high operating frequencies (1200MHz-1400MHz) and a small local buffer size of 32KB to 64KB. This combination achieves the best energy-delay product, balancing low latency with high energy efficiency. Furthermore, we demonstrate how memory bandwidth acts as a performance ceiling, and that increasing compute frequency only yields performance gains up to the point where the workload becomes memory-bound. This analysis provides concrete architectural insights for designing energy-efficient LLM accelerators, especially for datacenters aiming to minimize their energy overhead.
Diffusion Transformer-to-Mamba Distillation for High-Resolution Image Generation
Jun 23, 2025
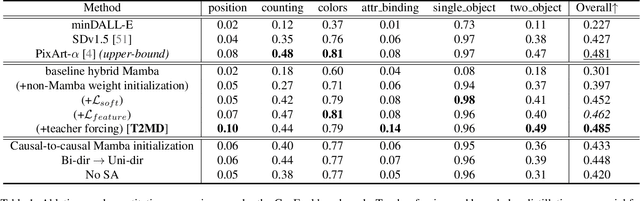
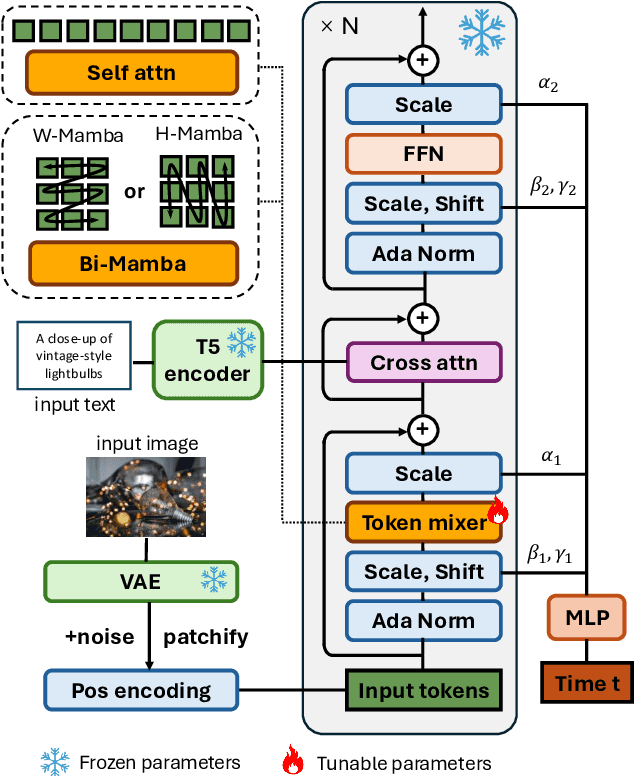
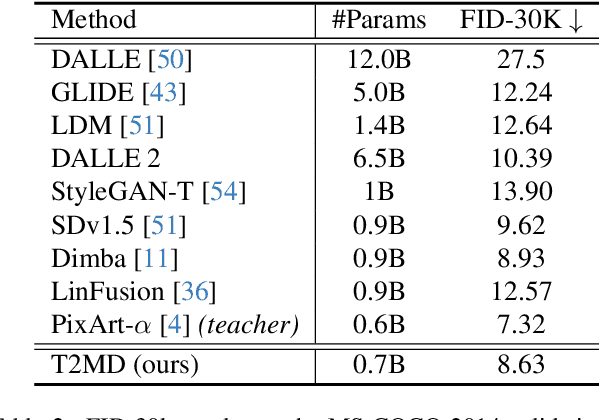
Abstract:The quadratic computational complexity of self-attention in diffusion transformers (DiT) introduces substantial computational costs in high-resolution image generation. While the linear-complexity Mamba model emerges as a potential alternative, direct Mamba training remains empirically challenging. To address this issue, this paper introduces diffusion transformer-to-mamba distillation (T2MD), forming an efficient training pipeline that facilitates the transition from the self-attention-based transformer to the linear complexity state-space model Mamba. We establish a diffusion self-attention and Mamba hybrid model that simultaneously achieves efficiency and global dependencies. With the proposed layer-level teacher forcing and feature-based knowledge distillation, T2MD alleviates the training difficulty and high cost of a state space model from scratch. Starting from the distilled 512$\times$512 resolution base model, we push the generation towards 2048$\times$2048 images via lightweight adaptation and high-resolution fine-tuning. Experiments demonstrate that our training path leads to low overhead but high-quality text-to-image generation. Importantly, our results also justify the feasibility of using sequential and causal Mamba models for generating non-causal visual output, suggesting the potential for future exploration.
Transformer IMU Calibrator: Dynamic On-body IMU Calibration for Inertial Motion Capture
Jun 12, 2025Abstract:In this paper, we propose a novel dynamic calibration method for sparse inertial motion capture systems, which is the first to break the restrictive absolute static assumption in IMU calibration, i.e., the coordinate drift RG'G and measurement offset RBS remain constant during the entire motion, thereby significantly expanding their application scenarios. Specifically, we achieve real-time estimation of RG'G and RBS under two relaxed assumptions: i) the matrices change negligibly in a short time window; ii) the human movements/IMU readings are diverse in such a time window. Intuitively, the first assumption reduces the number of candidate matrices, and the second assumption provides diverse constraints, which greatly reduces the solution space and allows for accurate estimation of RG'G and RBS from a short history of IMU readings in real time. To achieve this, we created synthetic datasets of paired RG'G, RBS matrices and IMU readings, and learned their mappings using a Transformer-based model. We also designed a calibration trigger based on the diversity of IMU readings to ensure that assumption ii) is met before applying our method. To our knowledge, we are the first to achieve implicit IMU calibration (i.e., seamlessly putting IMUs into use without the need for an explicit calibration process), as well as the first to enable long-term and accurate motion capture using sparse IMUs. The code and dataset are available at https://github.com/ZuoCX1996/TIC.
FedAPM: Federated Learning via ADMM with Partial Model Personalization
Jun 05, 2025Abstract:In federated learning (FL), the assumption that datasets from different devices are independent and identically distributed (i.i.d.) often does not hold due to user differences, and the presence of various data modalities across clients makes using a single model impractical. Personalizing certain parts of the model can effectively address these issues by allowing those parts to differ across clients, while the remaining parts serve as a shared model. However, we found that partial model personalization may exacerbate client drift (each client's local model diverges from the shared model), thereby reducing the effectiveness and efficiency of FL algorithms. We propose an FL framework based on the alternating direction method of multipliers (ADMM), referred to as FedAPM, to mitigate client drift. We construct the augmented Lagrangian function by incorporating first-order and second-order proximal terms into the objective, with the second-order term providing fixed correction and the first-order term offering compensatory correction between the local and shared models. Our analysis demonstrates that FedAPM, by using explicit estimates of the Lagrange multiplier, is more stable and efficient in terms of convergence compared to other FL frameworks. We establish the global convergence of FedAPM training from arbitrary initial points to a stationary point, achieving three types of rates: constant, linear, and sublinear, under mild assumptions. We conduct experiments using four heterogeneous and multimodal datasets with different metrics to validate the performance of FedAPM. Specifically, FedAPM achieves faster and more accurate convergence, outperforming the SOTA methods with average improvements of 12.3% in test accuracy, 16.4% in F1 score, and 18.0% in AUC while requiring fewer communication rounds.
TextVidBench: A Benchmark for Long Video Scene Text Understanding
Jun 05, 2025Abstract:Despite recent progress on the short-video Text-Visual Question Answering (ViteVQA) task - largely driven by benchmarks such as M4-ViteVQA - existing datasets still suffer from limited video duration and narrow evaluation scopes, making it difficult to adequately assess the growing capabilities of powerful multimodal large language models (MLLMs). To address these limitations, we introduce TextVidBench, the first benchmark specifically designed for long-video text question answering (>3 minutes). TextVidBench makes three key contributions: 1) Cross-domain long-video coverage: Spanning 9 categories (e.g., news, sports, gaming), with an average video length of 2306 seconds, enabling more realistic evaluation of long-video understanding. 2) A three-stage evaluation framework: "Text Needle-in-Haystack -> Temporal Grounding -> Text Dynamics Captioning". 3) High-quality fine-grained annotations: Containing over 5,000 question-answer pairs with detailed semantic labeling. Furthermore, we propose an efficient paradigm for improving large models through: (i) introducing the IT-Rope mechanism and temporal prompt engineering to enhance temporal perception, (ii) adopting non-uniform positional encoding to better handle long video sequences, and (iii) applying lightweight fine-tuning on video-text data. Extensive experiments on multiple public datasets as well as TextVidBench demonstrate that our new benchmark presents significant challenges to existing models, while our proposed method offers valuable insights into improving long-video scene text understanding capabilities.
Automated Model-Free Sorting of Single-Molecule Fluorescence Events Using a Deep Learning Based Hidden-State Model
May 13, 2025Abstract:Single-molecule fluorescence assays enable high-resolution analysis of biomolecular dynamics, but traditional analysis pipelines are labor-intensive and rely on users' experience, limiting scalability and reproducibility. Recent deep learning models have automated aspects of data processing, yet many still require manual thresholds, complex architectures, or extensive labeled data. Therefore, we present DASH, a fully streamlined architecture for trace classification, state assignment, and automatic sorting that requires no user input. DASH demonstrates robust performance across users and experimental conditions both in equilibrium and non-equilibrium systems such as Cas12a-mediated DNA cleavage. This paper proposes a novel strategy for the automatic and detailed sorting of single-molecule fluorescence events. The dynamic cleavage process of Cas12a is used as an example to provide a comprehensive analysis. This approach is crucial for studying biokinetic structural changes at the single-molecule level.
MoSAM: Motion-Guided Segment Anything Model with Spatial-Temporal Memory Selection
Apr 30, 2025



Abstract:The recent Segment Anything Model 2 (SAM2) has demonstrated exceptional capabilities in interactive object segmentation for both images and videos. However, as a foundational model on interactive segmentation, SAM2 performs segmentation directly based on mask memory from the past six frames, leading to two significant challenges. Firstly, during inference in videos, objects may disappear since SAM2 relies solely on memory without accounting for object motion information, which limits its long-range object tracking capabilities. Secondly, its memory is constructed from fixed past frames, making it susceptible to challenges associated with object disappearance or occlusion, due to potentially inaccurate segmentation results in memory. To address these problems, we present MoSAM, incorporating two key strategies to integrate object motion cues into the model and establish more reliable feature memory. Firstly, we propose Motion-Guided Prompting (MGP), which represents the object motion in both sparse and dense manners, then injects them into SAM2 through a set of motion-guided prompts. MGP enables the model to adjust its focus towards the direction of motion, thereby enhancing the object tracking capabilities. Furthermore, acknowledging that past segmentation results may be inaccurate, we devise a Spatial-Temporal Memory Selection (ST-MS) mechanism that dynamically identifies frames likely to contain accurate segmentation in both pixel- and frame-level. By eliminating potentially inaccurate mask predictions from memory, we can leverage more reliable memory features to exploit similar regions for improving segmentation results. Extensive experiments on various benchmarks of video object segmentation and video instance segmentation demonstrate that our MoSAM achieves state-of-the-art results compared to other competitors.
Instance-Adaptive Keypoint Learning with Local-to-Global Geometric Aggregation for Category-Level Object Pose Estimation
Apr 21, 2025



Abstract:Category-level object pose estimation aims to predict the 6D pose and size of previously unseen instances from predefined categories, requiring strong generalization across diverse object instances. Although many previous methods attempt to mitigate intra-class variations, they often struggle with instances exhibiting complex geometries or significant deviations from canonical shapes. To address this challenge, we propose INKL-Pose, a novel category-level object pose estimation framework that enables INstance-adaptive Keypoint Learning with local-to-global geometric aggregation. Specifically, our approach first predicts semantically consistent and geometric informative keypoints through an Instance-Adaptive Keypoint Generator, then refines them with: (1) a Local Keypoint Feature Aggregator capturing fine-grained geometries, and (2) a Global Keypoint Feature Aggregator using bidirectional Mamba for structural consistency. To enable bidirectional modeling in Mamba, we introduce a Feature Sequence Flipping strategy that preserves spatial coherence while constructing backward feature sequences. Additionally, we design a surface loss and a separation loss to enforce uniform coverage and spatial diversity in keypoint distribution. The generated keypoints are finally mapped to a canonical space for regressing the object's 6D pose and size. Extensive experiments on CAMERA25, REAL275, and HouseCat6D demonstrate that INKL-Pose achieves state-of-the-art performance and significantly outperforms existing methods.
An LMM for Efficient Video Understanding via Reinforced Compression of Video Cubes
Apr 21, 2025



Abstract:Large Multimodal Models (LMMs) uniformly perceive video frames, creating computational inefficiency for videos with inherently varying temporal information density. This paper present \textbf{Quicksviewer}, an LMM with new perceiving paradigm that partitions a video of nonuniform density into varying cubes using Gumbel Softmax, followed by a unified resampling for each cube to achieve efficient video understanding. This simple and intuitive approach dynamically compress video online based on its temporal density, significantly reducing spatiotemporal redundancy (overall 45$\times$ compression rate), while enabling efficient training with large receptive field. We train the model from a language backbone through three progressive stages, each incorporating lengthy videos on average of 420s/1fps thanks to the perceiving efficiency. With only 0.8M total video-text samples for training, our model outperforms the direct baseline employing a fixed partitioning strategy by a maximum of 8.72 in accuracy, demonstrating the effectiveness in performance. On Video-MME, Quicksviewer achieves SOTA under modest sequence lengths using just up to 5\% of tokens per frame required by baselines. With this paradigm, scaling up the number of input frames reveals a clear power law of the model capabilities. It is also empirically verified that the segments generated by the cubing network can help for analyzing continuous events in videos.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge