Jiamin Wu
Modeling of Human Body-coupled Electric Field Interference in Unshielded Ultra-Low Field MRI
Feb 25, 2026Abstract:Portable ultra-low field MRI (ULF-MRI) systems operated in unshielded environments are susceptible to electromagnetic interference (EMI). Subject presence in the imaging region will lead to substantial noise increases, yet the dominant coupling mechanism remains insufficiently characterized. We develop a lumped-parameter circuit model of the coupled environment-body-receiver system. The model indicates that ambient time-varying electric fields induce a body common-mode potential, which is converted into differential-mode noise through capacitive imbalance between the head and the receive-coil terminals, yielding strong dependence on subject position and geometry. Circuit analysis, simulations, and controlled experiments support the model, with predicted imbalance consistent with measured noise variations. Guided by this mechanism, we implement a capacitive low-impedance bypass to clamp the body potential, achieving an approximately 3.5-fold SNR improvement on a 50 mT prototype. The proposed model offers a compact circuit-based tool for analyzing and mitigating human body-coupled electric-field interference in portable ULF-MRI.
Deeper detection limits in astronomical imaging using self-supervised spatiotemporal denoising
Feb 19, 2026Abstract:The detection limit of astronomical imaging observations is limited by several noise sources. Some of that noise is correlated between neighbouring image pixels and exposures, so in principle could be learned and corrected. We present an astronomical self-supervised transformer-based denoising algorithm (ASTERIS), that integrates spatiotemporal information across multiple exposures. Benchmarking on mock data indicates that ASTERIS improves detection limits by 1.0 magnitude at 90% completeness and purity, while preserving the point spread function and photometric accuracy. Observational validation using data from the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) and Subaru telescope identifies previously undetectable features, including low-surface-brightness galaxy structures and gravitationally-lensed arcs. Applied to deep JWST images, ASTERIS identifies three times more redshift > 9 galaxy candidates, with rest-frame ultraviolet luminosity 1.0 magnitude fainter, than previous methods.
InternAgent-1.5: A Unified Agentic Framework for Long-Horizon Autonomous Scientific Discovery
Feb 09, 2026Abstract:We introduce InternAgent-1.5, a unified system designed for end-to-end scientific discovery across computational and empirical domains. The system is built on a structured architecture composed of three coordinated subsystems for generation, verification, and evolution. These subsystems are supported by foundational capabilities for deep research, solution optimization, and long horizon memory. The architecture allows InternAgent-1.5 to operate continuously across extended discovery cycles while maintaining coherent and improving behavior. It also enables the system to coordinate computational modeling and laboratory experimentation within a single unified system. We evaluate InternAgent-1.5 on scientific reasoning benchmarks such as GAIA, HLE, GPQA, and FrontierScience, and the system achieves leading performance that demonstrates strong foundational capabilities. Beyond these benchmarks, we further assess two categories of discovery tasks. In algorithm discovery tasks, InternAgent-1.5 autonomously designs competitive methods for core machine learning problems. In empirical discovery tasks, it executes complete computational or wet lab experiments and produces scientific findings in earth, life, biological, and physical domains. Overall, these results show that InternAgent-1.5 provides a general and scalable framework for autonomous scientific discovery.
Probing Scientific General Intelligence of LLMs with Scientist-Aligned Workflows
Dec 18, 2025Abstract:Despite advances in scientific AI, a coherent framework for Scientific General Intelligence (SGI)-the ability to autonomously conceive, investigate, and reason across scientific domains-remains lacking. We present an operational SGI definition grounded in the Practical Inquiry Model (PIM: Deliberation, Conception, Action, Perception) and operationalize it via four scientist-aligned tasks: deep research, idea generation, dry/wet experiments, and experimental reasoning. SGI-Bench comprises over 1,000 expert-curated, cross-disciplinary samples inspired by Science's 125 Big Questions, enabling systematic evaluation of state-of-the-art LLMs. Results reveal gaps: low exact match (10--20%) in deep research despite step-level alignment; ideas lacking feasibility and detail; high code executability but low execution result accuracy in dry experiments; low sequence fidelity in wet protocols; and persistent multimodal comparative-reasoning challenges. We further introduce Test-Time Reinforcement Learning (TTRL), which optimizes retrieval-augmented novelty rewards at inference, enhancing hypothesis novelty without reference answer. Together, our PIM-grounded definition, workflow-centric benchmark, and empirical insights establish a foundation for AI systems that genuinely participate in scientific discovery.
ViRC: Enhancing Visual Interleaved Mathematical CoT with Reason Chunking
Dec 17, 2025Abstract:CoT has significantly enhanced the reasoning ability of LLMs while it faces challenges when extended to multimodal domains, particularly in mathematical tasks. Existing MLLMs typically perform textual reasoning solely from a single static mathematical image, overlooking dynamic visual acquisition during reasoning. In contrast, humans repeatedly examine visual image and employ step-by-step reasoning to prove intermediate propositions. This strategy of decomposing the problem-solving process into key logical nodes adheres to Miller's Law in cognitive science. Inspired by this insight, we propose a ViRC framework for multimodal mathematical tasks, introducing a Reason Chunking mechanism that structures multimodal mathematical CoT into consecutive Critical Reasoning Units (CRUs) to simulate human expert problem-solving patterns. CRUs ensure intra-unit textual coherence for intermediate proposition verification while integrating visual information across units to generate subsequent propositions and support structured reasoning. To this end, we present CRUX dataset by using three visual tools and four reasoning patterns to provide explicitly annotated CRUs across multiple reasoning paths for each mathematical problem. Leveraging the CRUX dataset, we propose a progressive training strategy inspired by human cognitive learning, which includes Instructional SFT, Practice SFT, and Strategic RL, aimed at further strengthening the Reason Chunking ability of the model. The resulting ViRC-7B model achieves a 18.8% average improvement over baselines across multiple mathematical benchmarks. Code is available at https://github.com/Leon-LihongWang/ViRC.
EReLiFM: Evidential Reliability-Aware Residual Flow Meta-Learning for Open-Set Domain Generalization under Noisy Labels
Oct 14, 2025
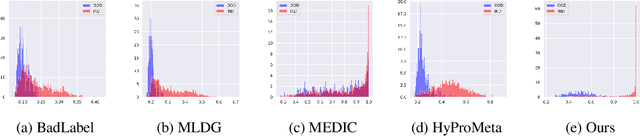


Abstract:Open-Set Domain Generalization (OSDG) aims to enable deep learning models to recognize unseen categories in new domains, which is crucial for real-world applications. Label noise hinders open-set domain generalization by corrupting source-domain knowledge, making it harder to recognize known classes and reject unseen ones. While existing methods address OSDG under Noisy Labels (OSDG-NL) using hyperbolic prototype-guided meta-learning, they struggle to bridge domain gaps, especially with limited clean labeled data. In this paper, we propose Evidential Reliability-Aware Residual Flow Meta-Learning (EReLiFM). We first introduce an unsupervised two-stage evidential loss clustering method to promote label reliability awareness. Then, we propose a residual flow matching mechanism that models structured domain- and category-conditioned residuals, enabling diverse and uncertainty-aware transfer paths beyond interpolation-based augmentation. During this meta-learning process, the model is optimized such that the update direction on the clean set maximizes the loss decrease on the noisy set, using pseudo labels derived from the most confident predicted class for supervision. Experimental results show that EReLiFM outperforms existing methods on OSDG-NL, achieving state-of-the-art performance. The source code is available at https://github.com/KPeng9510/ERELIFM.
A Survey of Scientific Large Language Models: From Data Foundations to Agent Frontiers
Aug 28, 2025



Abstract:Scientific Large Language Models (Sci-LLMs) are transforming how knowledge is represented, integrated, and applied in scientific research, yet their progress is shaped by the complex nature of scientific data. This survey presents a comprehensive, data-centric synthesis that reframes the development of Sci-LLMs as a co-evolution between models and their underlying data substrate. We formulate a unified taxonomy of scientific data and a hierarchical model of scientific knowledge, emphasizing the multimodal, cross-scale, and domain-specific challenges that differentiate scientific corpora from general natural language processing datasets. We systematically review recent Sci-LLMs, from general-purpose foundations to specialized models across diverse scientific disciplines, alongside an extensive analysis of over 270 pre-/post-training datasets, showing why Sci-LLMs pose distinct demands -- heterogeneous, multi-scale, uncertainty-laden corpora that require representations preserving domain invariance and enabling cross-modal reasoning. On evaluation, we examine over 190 benchmark datasets and trace a shift from static exams toward process- and discovery-oriented assessments with advanced evaluation protocols. These data-centric analyses highlight persistent issues in scientific data development and discuss emerging solutions involving semi-automated annotation pipelines and expert validation. Finally, we outline a paradigm shift toward closed-loop systems where autonomous agents based on Sci-LLMs actively experiment, validate, and contribute to a living, evolving knowledge base. Collectively, this work provides a roadmap for building trustworthy, continually evolving artificial intelligence (AI) systems that function as a true partner in accelerating scientific discovery.
SynBrain: Enhancing Visual-to-fMRI Synthesis via Probabilistic Representation Learning
Aug 14, 2025Abstract:Deciphering how visual stimuli are transformed into cortical responses is a fundamental challenge in computational neuroscience. This visual-to-neural mapping is inherently a one-to-many relationship, as identical visual inputs reliably evoke variable hemodynamic responses across trials, contexts, and subjects. However, existing deterministic methods struggle to simultaneously model this biological variability while capturing the underlying functional consistency that encodes stimulus information. To address these limitations, we propose SynBrain, a generative framework that simulates the transformation from visual semantics to neural responses in a probabilistic and biologically interpretable manner. SynBrain introduces two key components: (i) BrainVAE models neural representations as continuous probability distributions via probabilistic learning while maintaining functional consistency through visual semantic constraints; (ii) A Semantic-to-Neural Mapper acts as a semantic transmission pathway, projecting visual semantics into the neural response manifold to facilitate high-fidelity fMRI synthesis. Experimental results demonstrate that SynBrain surpasses state-of-the-art methods in subject-specific visual-to-fMRI encoding performance. Furthermore, SynBrain adapts efficiently to new subjects with few-shot data and synthesizes high-quality fMRI signals that are effective in improving data-limited fMRI-to-image decoding performance. Beyond that, SynBrain reveals functional consistency across trials and subjects, with synthesized signals capturing interpretable patterns shaped by biological neural variability. The code will be made publicly available.
HopaDIFF: Holistic-Partial Aware Fourier Conditioned Diffusion for Referring Human Action Segmentation in Multi-Person Scenarios
Jun 11, 2025Abstract:Action segmentation is a core challenge in high-level video understanding, aiming to partition untrimmed videos into segments and assign each a label from a predefined action set. Existing methods primarily address single-person activities with fixed action sequences, overlooking multi-person scenarios. In this work, we pioneer textual reference-guided human action segmentation in multi-person settings, where a textual description specifies the target person for segmentation. We introduce the first dataset for Referring Human Action Segmentation, i.e., RHAS133, built from 133 movies and annotated with 137 fine-grained actions with 33h video data, together with textual descriptions for this new task. Benchmarking existing action recognition methods on RHAS133 using VLM-based feature extractors reveals limited performance and poor aggregation of visual cues for the target person. To address this, we propose a holistic-partial aware Fourier-conditioned diffusion framework, i.e., HopaDIFF, leveraging a novel cross-input gate attentional xLSTM to enhance holistic-partial long-range reasoning and a novel Fourier condition to introduce more fine-grained control to improve the action segmentation generation. HopaDIFF achieves state-of-the-art results on RHAS133 in diverse evaluation settings. The code is available at https://github.com/KPeng9510/HopaDIFF.git.
Exploring Video-Based Driver Activity Recognition under Noisy Labels
Apr 16, 2025Abstract:As an open research topic in the field of deep learning, learning with noisy labels has attracted much attention and grown rapidly over the past ten years. Learning with label noise is crucial for driver distraction behavior recognition, as real-world video data often contains mislabeled samples, impacting model reliability and performance. However, label noise learning is barely explored in the driver activity recognition field. In this paper, we propose the first label noise learning approach for the driver activity recognition task. Based on the cluster assumption, we initially enable the model to learn clustering-friendly low-dimensional representations from given videos and assign the resultant embeddings into clusters. We subsequently perform co-refinement within each cluster to smooth the classifier outputs. Furthermore, we propose a flexible sample selection strategy that combines two selection criteria without relying on any hyperparameters to filter clean samples from the training dataset. We also incorporate a self-adaptive parameter into the sample selection process to enforce balancing across classes. A comprehensive variety of experiments on the public Drive&Act dataset for all granularity levels demonstrates the superior performance of our method in comparison with other label-denoising methods derived from the image classification field. The source code is available at https://github.com/ilonafan/DAR-noisy-labels.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge