Yingzhou Lu
Beyond Affinity: A Benchmark of 1D, 2D, and 3D Methods Reveals Critical Trade-offs in Structure-Based Drug Design
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:Currently, the field of structure-based drug design is dominated by three main types of algorithms: search-based algorithms, deep generative models, and reinforcement learning. While existing works have typically focused on comparing models within a single algorithmic category, cross-algorithm comparisons remain scarce. In this paper, to fill the gap, we establish a benchmark to evaluate the performance of fifteen models across these different algorithmic foundations by assessing the pharmaceutical properties of the generated molecules and their docking affinities and poses with specified target proteins. We highlight the unique advantages of each algorithmic approach and offer recommendations for the design of future SBDD models. We emphasize that 1D/2D ligand-centric drug design methods can be used in SBDD by treating the docking function as a black-box oracle, which is typically neglected. Our evaluation reveals distinct patterns across model categories. 3D structure-based models excel in binding affinities but show inconsistencies in chemical validity and pose quality. 1D models demonstrate reliable performance in standard molecular metrics but rarely achieve optimal binding affinities. 2D models offer balanced performance, maintaining high chemical validity while achieving moderate binding scores. Through detailed analysis across multiple protein targets, we identify key improvement areas for each model category, providing insights for researchers to combine strengths of different approaches while addressing their limitations. All the code that are used for benchmarking is available in https://github.com/zkysfls/2025-sbdd-benchmark
Probing Scientific General Intelligence of LLMs with Scientist-Aligned Workflows
Dec 18, 2025Abstract:Despite advances in scientific AI, a coherent framework for Scientific General Intelligence (SGI)-the ability to autonomously conceive, investigate, and reason across scientific domains-remains lacking. We present an operational SGI definition grounded in the Practical Inquiry Model (PIM: Deliberation, Conception, Action, Perception) and operationalize it via four scientist-aligned tasks: deep research, idea generation, dry/wet experiments, and experimental reasoning. SGI-Bench comprises over 1,000 expert-curated, cross-disciplinary samples inspired by Science's 125 Big Questions, enabling systematic evaluation of state-of-the-art LLMs. Results reveal gaps: low exact match (10--20%) in deep research despite step-level alignment; ideas lacking feasibility and detail; high code executability but low execution result accuracy in dry experiments; low sequence fidelity in wet protocols; and persistent multimodal comparative-reasoning challenges. We further introduce Test-Time Reinforcement Learning (TTRL), which optimizes retrieval-augmented novelty rewards at inference, enhancing hypothesis novelty without reference answer. Together, our PIM-grounded definition, workflow-centric benchmark, and empirical insights establish a foundation for AI systems that genuinely participate in scientific discovery.
A Survey of Scientific Large Language Models: From Data Foundations to Agent Frontiers
Aug 28, 2025



Abstract:Scientific Large Language Models (Sci-LLMs) are transforming how knowledge is represented, integrated, and applied in scientific research, yet their progress is shaped by the complex nature of scientific data. This survey presents a comprehensive, data-centric synthesis that reframes the development of Sci-LLMs as a co-evolution between models and their underlying data substrate. We formulate a unified taxonomy of scientific data and a hierarchical model of scientific knowledge, emphasizing the multimodal, cross-scale, and domain-specific challenges that differentiate scientific corpora from general natural language processing datasets. We systematically review recent Sci-LLMs, from general-purpose foundations to specialized models across diverse scientific disciplines, alongside an extensive analysis of over 270 pre-/post-training datasets, showing why Sci-LLMs pose distinct demands -- heterogeneous, multi-scale, uncertainty-laden corpora that require representations preserving domain invariance and enabling cross-modal reasoning. On evaluation, we examine over 190 benchmark datasets and trace a shift from static exams toward process- and discovery-oriented assessments with advanced evaluation protocols. These data-centric analyses highlight persistent issues in scientific data development and discuss emerging solutions involving semi-automated annotation pipelines and expert validation. Finally, we outline a paradigm shift toward closed-loop systems where autonomous agents based on Sci-LLMs actively experiment, validate, and contribute to a living, evolving knowledge base. Collectively, this work provides a roadmap for building trustworthy, continually evolving artificial intelligence (AI) systems that function as a true partner in accelerating scientific discovery.
Biomedical Foundation Model: A Survey
Mar 03, 2025Abstract:Foundation models, first introduced in 2021, are large-scale pre-trained models (e.g., large language models (LLMs) and vision-language models (VLMs)) that learn from extensive unlabeled datasets through unsupervised methods, enabling them to excel in diverse downstream tasks. These models, like GPT, can be adapted to various applications such as question answering and visual understanding, outperforming task-specific AI models and earning their name due to broad applicability across fields. The development of biomedical foundation models marks a significant milestone in leveraging artificial intelligence (AI) to understand complex biological phenomena and advance medical research and practice. This survey explores the potential of foundation models across diverse domains within biomedical fields, including computational biology, drug discovery and development, clinical informatics, medical imaging, and public health. The purpose of this survey is to inspire ongoing research in the application of foundation models to health science.
Political-LLM: Large Language Models in Political Science
Dec 09, 2024



Abstract:In recent years, large language models (LLMs) have been widely adopted in political science tasks such as election prediction, sentiment analysis, policy impact assessment, and misinformation detection. Meanwhile, the need to systematically understand how LLMs can further revolutionize the field also becomes urgent. In this work, we--a multidisciplinary team of researchers spanning computer science and political science--present the first principled framework termed Political-LLM to advance the comprehensive understanding of integrating LLMs into computational political science. Specifically, we first introduce a fundamental taxonomy classifying the existing explorations into two perspectives: political science and computational methodologies. In particular, from the political science perspective, we highlight the role of LLMs in automating predictive and generative tasks, simulating behavior dynamics, and improving causal inference through tools like counterfactual generation; from a computational perspective, we introduce advancements in data preparation, fine-tuning, and evaluation methods for LLMs that are tailored to political contexts. We identify key challenges and future directions, emphasizing the development of domain-specific datasets, addressing issues of bias and fairness, incorporating human expertise, and redefining evaluation criteria to align with the unique requirements of computational political science. Political-LLM seeks to serve as a guidebook for researchers to foster an informed, ethical, and impactful use of Artificial Intelligence in political science. Our online resource is available at: http://political-llm.org/.
Protein-Mamba: Biological Mamba Models for Protein Function Prediction
Sep 22, 2024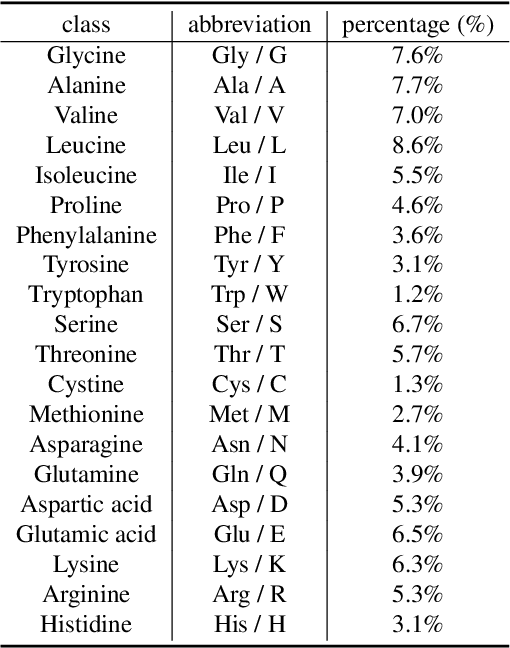



Abstract:Protein function prediction is a pivotal task in drug discovery, significantly impacting the development of effective and safe therapeutics. Traditional machine learning models often struggle with the complexity and variability inherent in predicting protein functions, necessitating more sophisticated approaches. In this work, we introduce Protein-Mamba, a novel two-stage model that leverages both self-supervised learning and fine-tuning to improve protein function prediction. The pre-training stage allows the model to capture general chemical structures and relationships from large, unlabeled datasets, while the fine-tuning stage refines these insights using specific labeled datasets, resulting in superior prediction performance. Our extensive experiments demonstrate that Protein-Mamba achieves competitive performance, compared with a couple of state-of-the-art methods across a range of protein function datasets. This model's ability to effectively utilize both unlabeled and labeled data highlights the potential of self-supervised learning in advancing protein function prediction and offers a promising direction for future research in drug discovery.
SMILES-Mamba: Chemical Mamba Foundation Models for Drug ADMET Prediction
Aug 11, 2024
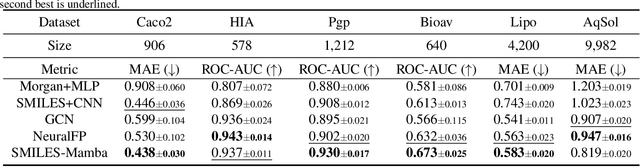


Abstract:In drug discovery, predicting the absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion, and toxicity (ADMET) properties of small-molecule drugs is critical for ensuring safety and efficacy. However, the process of accurately predicting these properties is often resource-intensive and requires extensive experimental data. To address this challenge, we propose SMILES-Mamba, a two-stage model that leverages both unlabeled and labeled data through a combination of self-supervised pretraining and fine-tuning strategies. The model first pre-trains on a large corpus of unlabeled SMILES strings to capture the underlying chemical structure and relationships, before being fine-tuned on smaller, labeled datasets specific to ADMET tasks. Our results demonstrate that SMILES-Mamba exhibits competitive performance across 22 ADMET datasets, achieving the highest score in 14 tasks, highlighting the potential of self-supervised learning in improving molecular property prediction. This approach not only enhances prediction accuracy but also reduces the dependence on large, labeled datasets, offering a promising direction for future research in drug discovery.
BioMamba: A Pre-trained Biomedical Language Representation Model Leveraging Mamba
Aug 05, 2024
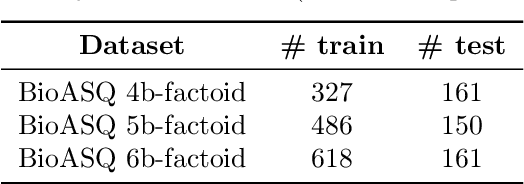
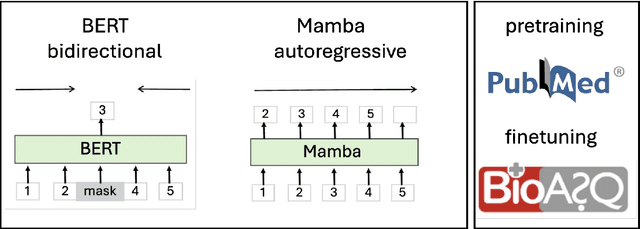
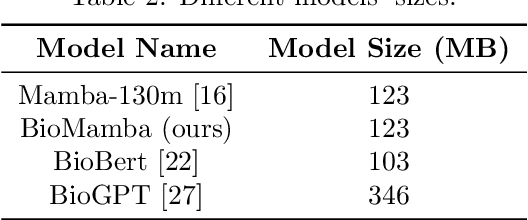
Abstract:The advancement of natural language processing (NLP) in biology hinges on models' ability to interpret intricate biomedical literature. Traditional models often struggle with the complex and domain-specific language in this field. In this paper, we present BioMamba, a pre-trained model specifically designed for biomedical text mining. BioMamba builds upon the Mamba architecture and is pre-trained on an extensive corpus of biomedical literature. Our empirical studies demonstrate that BioMamba significantly outperforms models like BioBERT and general-domain Mamba across various biomedical tasks. For instance, BioMamba achieves a 100 times reduction in perplexity and a 4 times reduction in cross-entropy loss on the BioASQ test set. We provide an overview of the model architecture, pre-training process, and fine-tuning techniques. Additionally, we release the code and trained model to facilitate further research.
MambaCapsule: Towards Transparent Cardiac Disease Diagnosis with Electrocardiography Using Mamba Capsule Network
Jul 30, 2024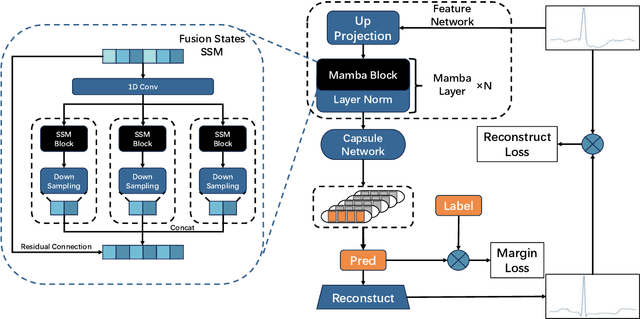
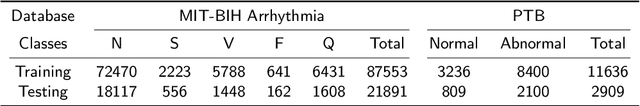
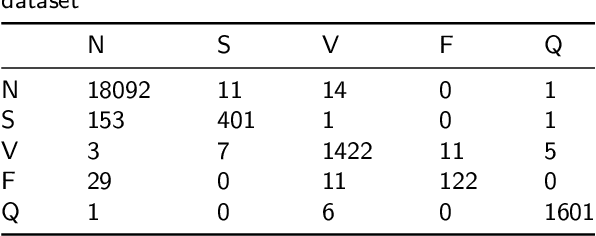
Abstract:Cardiac arrhythmia, a condition characterized by irregular heartbeats, often serves as an early indication of various heart ailments. With the advent of deep learning, numerous innovative models have been introduced for diagnosing arrhythmias using Electrocardiogram (ECG) signals. However, recent studies solely focus on the performance of models, neglecting the interpretation of their results. This leads to a considerable lack of transparency, posing a significant risk in the actual diagnostic process. To solve this problem, this paper introduces MambaCapsule, a deep neural networks for ECG arrhythmias classification, which increases the explainability of the model while enhancing the accuracy.Our model utilizes Mamba for feature extraction and Capsule networks for prediction, providing not only a confidence score but also signal features. Akin to the processing mechanism of human brain, the model learns signal features and their relationship between them by reconstructing ECG signals in the predicted selection. The model evaluation was conducted on MIT-BIH and PTB dataset, following the AAMI standard. MambaCapsule has achieved a total accuracy of 99.54% and 99.59% on the test sets respectively. These results demonstrate the promising performance of under the standard test protocol.
DrugCLIP: Contrastive Drug-Disease Interaction For Drug Repurposing
Jul 02, 2024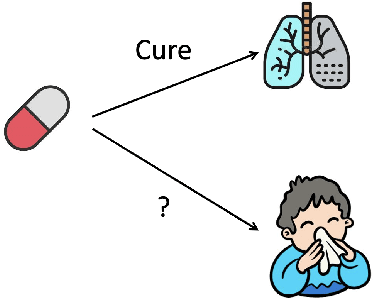


Abstract:Bringing a novel drug from the original idea to market typically requires more than ten years and billions of dollars. To alleviate the heavy burden, a natural idea is to reuse the approved drug to treat new diseases. The process is also known as drug repurposing or drug repositioning. Machine learning methods exhibited huge potential in automating drug repurposing. However, it still encounter some challenges, such as lack of labels and multimodal feature representation. To address these issues, we design DrugCLIP, a cutting-edge contrastive learning method, to learn drug and disease's interaction without negative labels. Additionally, we have curated a drug repurposing dataset based on real-world clinical trial records. Thorough empirical studies are conducted to validate the effectiveness of the proposed DrugCLIP method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge