Zhongwei Wan
Swordsman: Entropy-Driven Adaptive Block Partition for Efficient Diffusion Language Models
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Block-wise decoding effectively improves the inference speed and quality in diffusion language models (DLMs) by combining inter-block sequential denoising and intra-block parallel unmasking. However, existing block-wise decoding methods typically partition blocks in a rigid and fixed manner, which inevitably fragments complete semantic or syntactic constituents, leading to suboptimal performance. Inspired by the entropy reduction hypothesis (ERH), we recognize that constituent boundaries offer greater opportunities for uncertainty reduction, which motivates us to employ entropy analysis for identifying constituent boundaries. Therefore, we propose Swordsman, an entropy-driven adaptive block-wise decoding framework for DLMs. Swordsman adaptively partitions blocks by identifying entropy shifts between adjacent tokens to better align with semantic or syntactic constituent boundaries. In addition, Swordsman dynamically adjusts unmasking thresholds conditioned on the real-time unmasking status within a block, further improving both efficiency and stability. As a training-free framework, supported by KV Cache, Swordsman demonstrates state-of-the-art performance across extensive evaluations.
MMDeepResearch-Bench: A Benchmark for Multimodal Deep Research Agents
Jan 18, 2026Abstract:Deep Research Agents (DRAs) generate citation-rich reports via multi-step search and synthesis, yet existing benchmarks mainly target text-only settings or short-form multimodal QA, missing end-to-end multimodal evidence use. We introduce MMDeepResearch-Bench (MMDR-Bench), a benchmark of 140 expert-crafted tasks across 21 domains, where each task provides an image-text bundle to evaluate multimodal understanding and citation-grounded report generation. Compared to prior setups, MMDR-Bench emphasizes report-style synthesis with explicit evidence use, where models must connect visual artifacts to sourced claims and maintain consistency across narrative, citations, and visual references. We further propose a unified, interpretable evaluation pipeline: Formula-LLM Adaptive Evaluation (FLAE) for report quality, Trustworthy Retrieval-Aligned Citation Evaluation (TRACE) for citation-grounded evidence alignment, and Multimodal Support-Aligned Integrity Check (MOSAIC) for text-visual integrity, each producing fine-grained signals that support error diagnosis beyond a single overall score. Experiments across 25 state-of-the-art models reveal systematic trade-offs between generation quality, citation discipline, and multimodal grounding, highlighting that strong prose alone does not guarantee faithful evidence use and that multimodal integrity remains a key bottleneck for deep research agents.
MMFormalizer: Multimodal Autoformalization in the Wild
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:Autoformalization, which translates natural language mathematics into formal statements to enable machine reasoning, faces fundamental challenges in the wild due to the multimodal nature of the physical world, where physics requires inferring hidden constraints (e.g., mass or energy) from visual elements. To address this, we propose MMFormalizer, which extends autoformalization beyond text by integrating adaptive grounding with entities from real-world mathematical and physical domains. MMFormalizer recursively constructs formal propositions from perceptually grounded primitives through recursive grounding and axiom composition, with adaptive recursive termination ensuring that every abstraction is supported by visual evidence and anchored in dimensional or axiomatic grounding. We evaluate MMFormalizer on a new benchmark, PhyX-AF, comprising 115 curated samples from MathVerse, PhyX, Synthetic Geometry, and Analytic Geometry, covering diverse multimodal autoformalization tasks. Results show that frontier models such as GPT-5 and Gemini-3-Pro achieve the highest compile and semantic accuracy, with GPT-5 excelling in physical reasoning, while geometry remains the most challenging domain. Overall, MMFormalizer provides a scalable framework for unified multimodal autoformalization, bridging perception and formal reasoning. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first multimodal autoformalization method capable of handling classical mechanics (derived from the Hamiltonian), as well as relativity, quantum mechanics, and thermodynamics. More details are available on our project page: MMFormalizer.github.io
Plan Then Action:High-Level Planning Guidance Reinforcement Learning for LLM Reasoning
Oct 02, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable reasoning abilities in complex tasks, often relying on Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning. However, due to their autoregressive token-level generation, the reasoning process is largely constrained to local decision-making and lacks global planning. This limitation frequently results in redundant, incoherent, or inaccurate reasoning, which significantly degrades overall performance. Existing approaches, such as tree-based algorithms and reinforcement learning (RL), attempt to address this issue but suffer from high computational costs and often fail to produce optimal reasoning trajectories. To tackle this challenge, we propose Plan-Then-Action Enhanced Reasoning with Group Relative Policy Optimization PTA-GRPO, a two-stage framework designed to improve both high-level planning and fine-grained CoT reasoning. In the first stage, we leverage advanced LLMs to distill CoT into compact high-level guidance, which is then used for supervised fine-tuning (SFT). In the second stage, we introduce a guidance-aware RL method that jointly optimizes the final output and the quality of high-level guidance, thereby enhancing reasoning effectiveness. We conduct extensive experiments on multiple mathematical reasoning benchmarks, including MATH, AIME2024, AIME2025, and AMC, across diverse base models such as Qwen2.5-7B-Instruct, Qwen3-8B, Qwen3-14B, and LLaMA3.2-3B. Experimental results demonstrate that PTA-GRPO consistently achieves stable and significant improvements across different models and tasks, validating its effectiveness and generalization.
A1: Asynchronous Test-Time Scaling via Conformal Prediction
Sep 18, 2025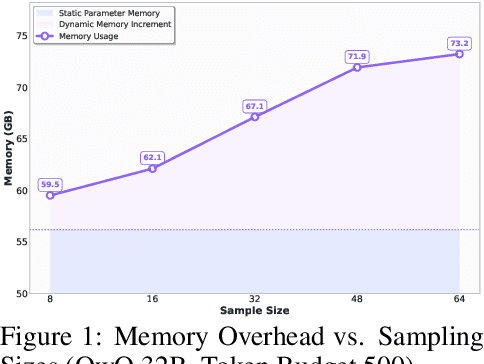
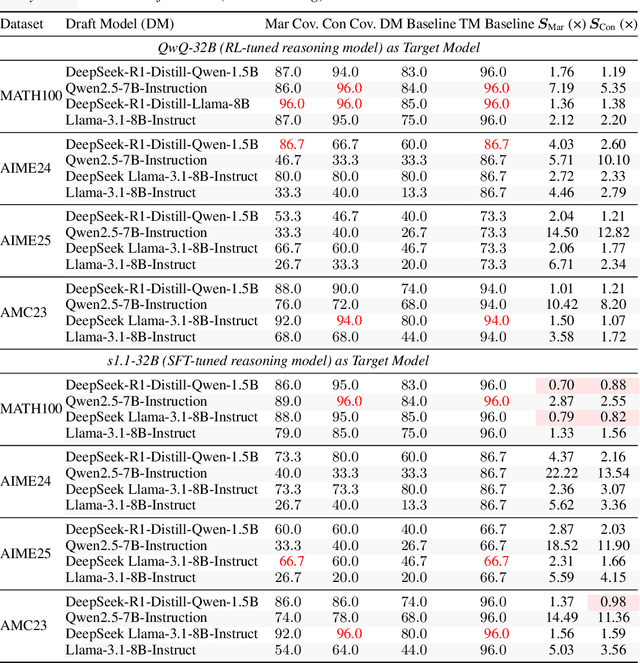
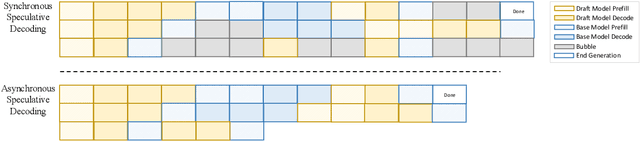
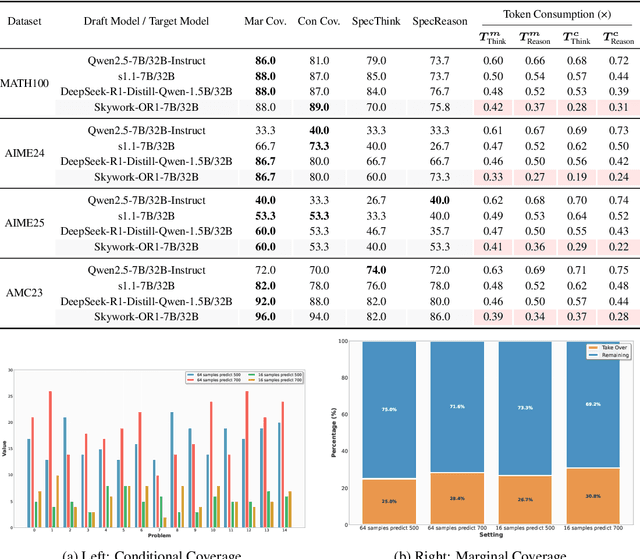
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) benefit from test-time scaling, but existing methods face significant challenges, including severe synchronization overhead, memory bottlenecks, and latency, especially during speculative decoding with long reasoning chains. We introduce A1 (Asynchronous Test-Time Scaling), a statistically guaranteed adaptive inference framework that addresses these challenges. A1 refines arithmetic intensity to identify synchronization as the dominant bottleneck, proposes an online calibration strategy to enable asynchronous inference, and designs a three-stage rejection sampling pipeline that supports both sequential and parallel scaling. Through experiments on the MATH, AMC23, AIME24, and AIME25 datasets, across various draft-target model families, we demonstrate that A1 achieves a remarkable 56.7x speedup in test-time scaling and a 4.14x improvement in throughput, all while maintaining accurate rejection-rate control, reducing latency and memory overhead, and no accuracy loss compared to using target model scaling alone. These results position A1 as an efficient and principled solution for scalable LLM inference. We have released the code at https://github.com/menik1126/asynchronous-test-time-scaling.
LongEmotion: Measuring Emotional Intelligence of Large Language Models in Long-Context Interaction
Sep 09, 2025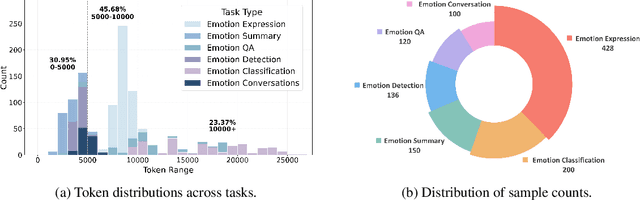
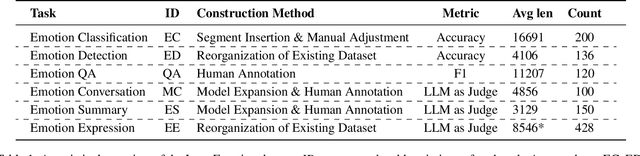
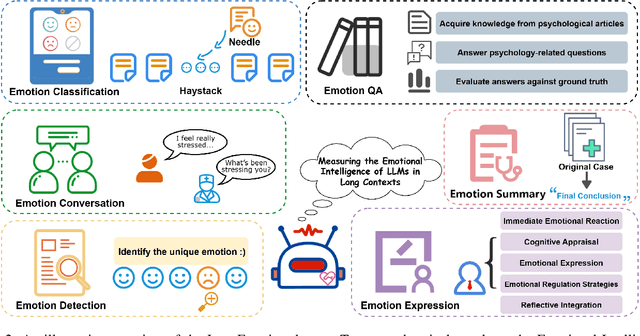
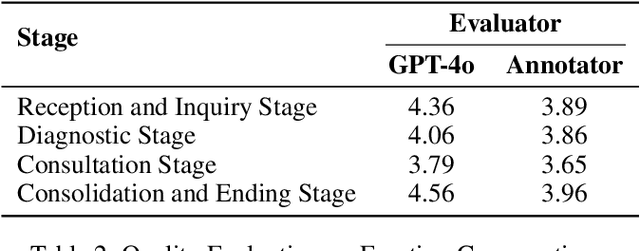
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) make significant progress in Emotional Intelligence (EI) and long-context understanding. However, existing benchmarks tend to overlook certain aspects of EI in long-context scenarios, especially under realistic, practical settings where interactions are lengthy, diverse, and often noisy. To move towards such realistic settings, we present LongEmotion, a benchmark specifically designed for long-context EI tasks. It covers a diverse set of tasks, including Emotion Classification, Emotion Detection, Emotion QA, Emotion Conversation, Emotion Summary, and Emotion Expression. On average, the input length for these tasks reaches 8,777 tokens, with long-form generation required for Emotion Expression. To enhance performance under realistic constraints, we incorporate Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) and Collaborative Emotional Modeling (CoEM), and compare them with standard prompt-based methods. Unlike conventional approaches, our RAG method leverages both the conversation context and the large language model itself as retrieval sources, avoiding reliance on external knowledge bases. The CoEM method further improves performance by decomposing the task into five stages, integrating both retrieval augmentation and limited knowledge injection. Experimental results show that both RAG and CoEM consistently enhance EI-related performance across most long-context tasks, advancing LLMs toward more practical and real-world EI applications. Furthermore, we conducted a comparative case study experiment on the GPT series to demonstrate the differences among various models in terms of EI. Code is available on GitHub at https://github.com/LongEmotion/LongEmotion, and the project page can be found at https://longemotion.github.io/.
Low-Cost Test-Time Adaptation for Robust Video Editing
Jul 29, 2025



Abstract:Video editing is a critical component of content creation that transforms raw footage into coherent works aligned with specific visual and narrative objectives. Existing approaches face two major challenges: temporal inconsistencies due to failure in capturing complex motion patterns, and overfitting to simple prompts arising from limitations in UNet backbone architectures. While learning-based methods can enhance editing quality, they typically demand substantial computational resources and are constrained by the scarcity of high-quality annotated data. In this paper, we present Vid-TTA, a lightweight test-time adaptation framework that personalizes optimization for each test video during inference through self-supervised auxiliary tasks. Our approach incorporates a motion-aware frame reconstruction mechanism that identifies and preserves crucial movement regions, alongside a prompt perturbation and reconstruction strategy that strengthens model robustness to diverse textual descriptions. These innovations are orchestrated by a meta-learning driven dynamic loss balancing mechanism that adaptively adjusts the optimization process based on video characteristics. Extensive experiments demonstrate that Vid-TTA significantly improves video temporal consistency and mitigates prompt overfitting while maintaining low computational overhead, offering a plug-and-play performance boost for existing video editing models.
SwingArena: Competitive Programming Arena for Long-context GitHub Issue Solving
May 29, 2025
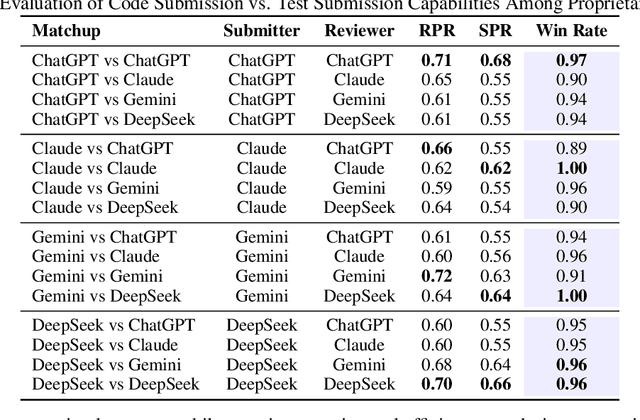
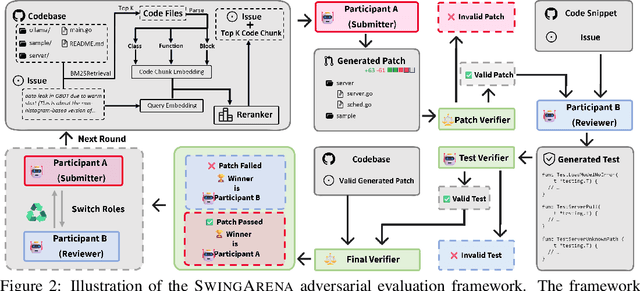
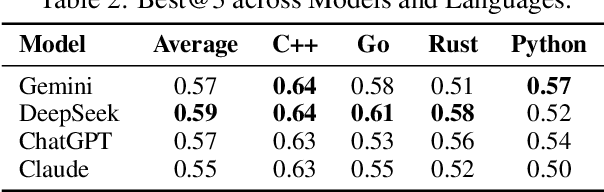
Abstract:We present SwingArena, a competitive evaluation framework for Large Language Models (LLMs) that closely mirrors real-world software development workflows. Unlike traditional static benchmarks, SwingArena models the collaborative process of software iteration by pairing LLMs as submitters, who generate patches, and reviewers, who create test cases and verify the patches through continuous integration (CI) pipelines. To support these interactive evaluations, we introduce a retrieval-augmented code generation (RACG) module that efficiently handles long-context challenges by providing syntactically and semantically relevant code snippets from large codebases, supporting multiple programming languages (C++, Python, Rust, and Go). This enables the framework to scale across diverse tasks and contexts while respecting token limitations. Our experiments, using over 400 high-quality real-world GitHub issues selected from a pool of 2,300 issues, show that models like GPT-4o excel at aggressive patch generation, whereas DeepSeek and Gemini prioritize correctness in CI validation. SwingArena presents a scalable and extensible methodology for evaluating LLMs in realistic, CI-driven software development settings. More details are available on our project page: swing-bench.github.io
Enhancing Text-to-Image Diffusion Transformer via Split-Text Conditioning
May 25, 2025Abstract:Current text-to-image diffusion generation typically employs complete-text conditioning. Due to the intricate syntax, diffusion transformers (DiTs) inherently suffer from a comprehension defect of complete-text captions. One-fly complete-text input either overlooks critical semantic details or causes semantic confusion by simultaneously modeling diverse semantic primitive types. To mitigate this defect of DiTs, we propose a novel split-text conditioning framework named DiT-ST. This framework converts a complete-text caption into a split-text caption, a collection of simplified sentences, to explicitly express various semantic primitives and their interconnections. The split-text caption is then injected into different denoising stages of DiT-ST in a hierarchical and incremental manner. Specifically, DiT-ST leverages Large Language Models to parse captions, extracting diverse primitives and hierarchically sorting out and constructing these primitives into a split-text input. Moreover, we partition the diffusion denoising process according to its differential sensitivities to diverse semantic primitive types and determine the appropriate timesteps to incrementally inject tokens of diverse semantic primitive types into input tokens via cross-attention. In this way, DiT-ST enhances the representation learning of specific semantic primitive types across different stages. Extensive experiments validate the effectiveness of our proposed DiT-ST in mitigating the complete-text comprehension defect.
Beyond Distillation: Pushing the Limits of Medical LLM Reasoning with Minimalist Rule-Based RL
May 23, 2025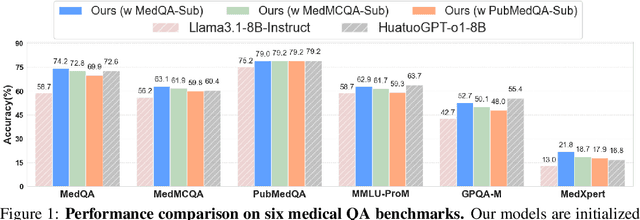
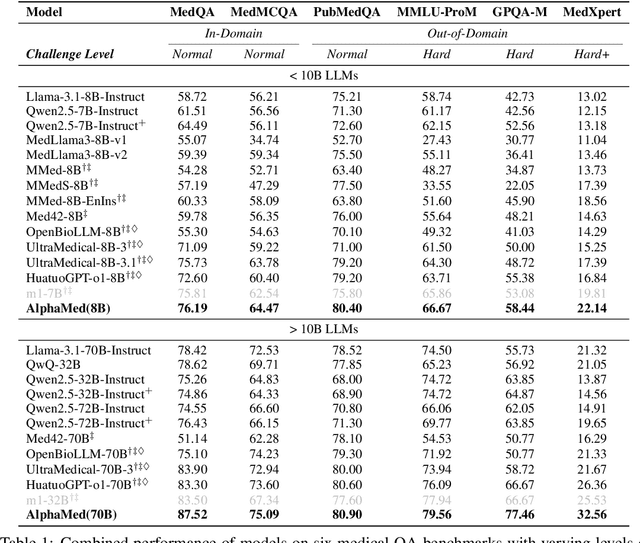
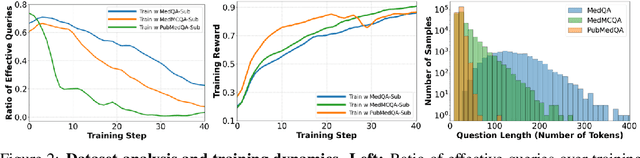
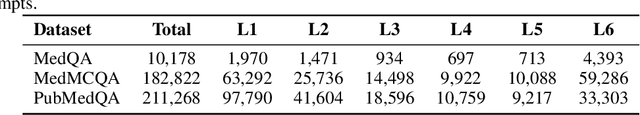
Abstract:Improving performance on complex tasks and enabling interpretable decision making in large language models (LLMs), especially for clinical applications, requires effective reasoning. Yet this remains challenging without supervised fine-tuning (SFT) on costly chain-of-thought (CoT) data distilled from closed-source models (e.g., GPT-4o). In this work, we present AlphaMed, the first medical LLM to show that reasoning capability can emerge purely through reinforcement learning (RL), using minimalist rule-based rewards on public multiple-choice QA datasets, without relying on SFT or distilled CoT data. AlphaMed achieves state-of-the-art results on six medical QA benchmarks, outperforming models trained with conventional SFT+RL pipelines. On challenging benchmarks (e.g., MedXpert), AlphaMed even surpasses larger or closed-source models such as DeepSeek-V3-671B and Claude-3.5-Sonnet. To understand the factors behind this success, we conduct a comprehensive data-centric analysis guided by three questions: (i) Can minimalist rule-based RL incentivize reasoning without distilled CoT supervision? (ii) How do dataset quantity and diversity impact reasoning? (iii) How does question difficulty shape the emergence and generalization of reasoning? Our findings show that dataset informativeness is a key driver of reasoning performance, and that minimalist RL on informative, multiple-choice QA data is effective at inducing reasoning without CoT supervision. We also observe divergent trends across benchmarks, underscoring limitations in current evaluation and the need for more challenging, reasoning-oriented medical QA benchmarks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge