Shan Chen
Monitorability as a Free Gift: How RLVR Spontaneously Aligns Reasoning
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:As Large Reasoning Models (LRMs) are increasingly deployed, auditing their chain-of-thought (CoT) traces for safety becomes critical. Recent work has reported that monitorability--the degree to which CoT faithfully and informatively reflects internal computation--can appear as a "free gift" during the early stages of Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards (RLVR). We make this observation concrete through a systematic evaluation across model families and training domains. Our results show that this effect is not universal: monitorability improvements are strongly data-dependent. In particular, we demonstrate the critical role of data diversity and instruction-following data during RLVR training. We further show that monitorability is orthogonal to capability--improvements in reasoning performance do not imply increased transparency. Through mechanistic analysis, we attribute monitorability gains primarily to response distribution sharpening (entropy reduction) and increased attention to the prompt, rather than stronger causal reliance on reasoning traces. We also reveal how monitorability dynamics vary with controlled training and evaluation difficulty. Together, these findings provide a holistic view of how monitorability emerges under RLVR, clarifying when gains are likely to occur and when they are not.
Proof of Time: A Benchmark for Evaluating Scientific Idea Judgments
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:Large language models are increasingly being used to assess and forecast research ideas, yet we lack scalable ways to evaluate the quality of models' judgments about these scientific ideas. Towards this goal, we introduce PoT, a semi-verifiable benchmarking framework that links scientific idea judgments to downstream signals that become observable later (e.g., citations and shifts in researchers' agendas). PoT freezes a pre-cutoff snapshot of evidence in an offline sandbox and asks models to forecast post-cutoff outcomes, enabling verifiable evaluation when ground truth arrives, scalable benchmarking without exhaustive expert annotation, and analysis of human-model misalignment against signals such as peer-review awards. In addition, PoT provides a controlled testbed for agent-based research judgments that evaluate scientific ideas, comparing tool-using agents to non-agent baselines under prompt ablations and budget scaling. Across 30,000+ instances spanning four benchmark domains, we find that, compared with non-agent baselines, higher interaction budgets generally improve agent performance, while the benefit of tool use is strongly task-dependent. By combining time-partitioned, future-verifiable targets with an offline sandbox for tool use, PoT supports scalable evaluation of agents on future-facing scientific idea judgment tasks.
KScope: A Framework for Characterizing the Knowledge Status of Language Models
Jun 09, 2025Abstract:Characterizing a large language model's (LLM's) knowledge of a given question is challenging. As a result, prior work has primarily examined LLM behavior under knowledge conflicts, where the model's internal parametric memory contradicts information in the external context. However, this does not fully reflect how well the model knows the answer to the question. In this paper, we first introduce a taxonomy of five knowledge statuses based on the consistency and correctness of LLM knowledge modes. We then propose KScope, a hierarchical framework of statistical tests that progressively refines hypotheses about knowledge modes and characterizes LLM knowledge into one of these five statuses. We apply KScope to nine LLMs across four datasets and systematically establish: (1) Supporting context narrows knowledge gaps across models. (2) Context features related to difficulty, relevance, and familiarity drive successful knowledge updates. (3) LLMs exhibit similar feature preferences when partially correct or conflicted, but diverge sharply when consistently wrong. (4) Context summarization constrained by our feature analysis, together with enhanced credibility, further improves update effectiveness and generalizes across LLMs.
When Models Reason in Your Language: Controlling Thinking Trace Language Comes at the Cost of Accuracy
May 28, 2025Abstract:Recent Large Reasoning Models (LRMs) with thinking traces have shown strong performance on English reasoning tasks. However, their ability to think in other languages is less studied. This capability is as important as answer accuracy for real world applications because users may find the reasoning trace useful for oversight only when it is expressed in their own language. We comprehensively evaluate two leading families of LRMs on our XReasoning benchmark and find that even the most advanced models often revert to English or produce fragmented reasoning in other languages, revealing a substantial gap in multilingual reasoning. Prompt based interventions that force models to reason in the users language improve readability and oversight but reduce answer accuracy, exposing an important trade off. We further show that targeted post training on just 100 examples mitigates this mismatch, though some accuracy loss remains. Our results highlight the limited multilingual reasoning capabilities of current LRMs and outline directions for future work. Code and data are available at https://github.com/Betswish/mCoT-XReasoning.
MedBrowseComp: Benchmarking Medical Deep Research and Computer Use
May 20, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are increasingly envisioned as decision-support tools in clinical practice, yet safe clinical reasoning demands integrating heterogeneous knowledge bases -- trials, primary studies, regulatory documents, and cost data -- under strict accuracy constraints. Existing evaluations often rely on synthetic prompts, reduce the task to single-hop factoid queries, or conflate reasoning with open-ended generation, leaving their real-world utility unclear. To close this gap, we present MedBrowseComp, the first benchmark that systematically tests an agent's ability to reliably retrieve and synthesize multi-hop medical facts from live, domain-specific knowledge bases. MedBrowseComp contains more than 1,000 human-curated questions that mirror clinical scenarios where practitioners must reconcile fragmented or conflicting information to reach an up-to-date conclusion. Applying MedBrowseComp to frontier agentic systems reveals performance shortfalls as low as ten percent, exposing a critical gap between current LLM capabilities and the rigor demanded in clinical settings. MedBrowseComp therefore offers a clear testbed for reliable medical information seeking and sets concrete goals for future model and toolchain upgrades. You can visit our project page at: https://moreirap12.github.io/mbc-browse-app/
Sparse Autoencoder Features for Classifications and Transferability
Feb 17, 2025Abstract:Sparse Autoencoders (SAEs) provide potentials for uncovering structured, human-interpretable representations in Large Language Models (LLMs), making them a crucial tool for transparent and controllable AI systems. We systematically analyze SAE for interpretable feature extraction from LLMs in safety-critical classification tasks. Our framework evaluates (1) model-layer selection and scaling properties, (2) SAE architectural configurations, including width and pooling strategies, and (3) the effect of binarizing continuous SAE activations. SAE-derived features achieve macro F1 > 0.8, outperforming hidden-state and BoW baselines while demonstrating cross-model transfer from Gemma 2 2B to 9B-IT models. These features generalize in a zero-shot manner to cross-lingual toxicity detection and visual classification tasks. Our analysis highlights the significant impact of pooling strategies and binarization thresholds, showing that binarization offers an efficient alternative to traditional feature selection while maintaining or improving performance. These findings establish new best practices for SAE-based interpretability and enable scalable, transparent deployment of LLMs in real-world applications. Full repo: https://github.com/shan23chen/MOSAIC.
The use of large language models to enhance cancer clinical trial educational materials
Dec 02, 2024Abstract:Cancer clinical trials often face challenges in recruitment and engagement due to a lack of participant-facing informational and educational resources. This study investigated the potential of Large Language Models (LLMs), specifically GPT4, in generating patient-friendly educational content from clinical trial informed consent forms. Using data from ClinicalTrials.gov, we employed zero-shot learning for creating trial summaries and one-shot learning for developing multiple-choice questions, evaluating their effectiveness through patient surveys and crowdsourced annotation. Results showed that GPT4-generated summaries were both readable and comprehensive, and may improve patients' understanding and interest in clinical trials. The multiple-choice questions demonstrated high accuracy and agreement with crowdsourced annotators. For both resource types, hallucinations were identified that require ongoing human oversight. The findings demonstrate the potential of LLMs "out-of-the-box" to support the generation of clinical trial education materials with minimal trial-specific engineering, but implementation with a human-in-the-loop is still needed to avoid misinformation risks.
ClinicalBench: Can LLMs Beat Traditional ML Models in Clinical Prediction?
Nov 10, 2024Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) hold great promise to revolutionize current clinical systems for their superior capacities on medical text processing tasks and medical licensing exams. Meanwhile, traditional ML models such as SVM and XGBoost have still been mainly adopted in clinical prediction tasks. An emerging question is Can LLMs beat traditional ML models in clinical prediction? Thus, we build a new benchmark ClinicalBench to comprehensively study the clinical predictive modeling capacities of both general-purpose and medical LLMs, and compare them with traditional ML models. ClinicalBench embraces three common clinical prediction tasks, two databases, 14 general-purpose LLMs, 8 medical LLMs, and 11 traditional ML models. Through extensive empirical investigation, we discover that both general-purpose and medical LLMs, even with different model scales, diverse prompting or fine-tuning strategies, still cannot beat traditional ML models in clinical prediction yet, shedding light on their potential deficiency in clinical reasoning and decision-making. We call for caution when practitioners adopt LLMs in clinical applications. ClinicalBench can be utilized to bridge the gap between LLMs' development for healthcare and real-world clinical practice.
Position Paper On Diagnostic Uncertainty Estimation from Large Language Models: Next-Word Probability Is Not Pre-test Probability
Nov 07, 2024Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are being explored for diagnostic decision support, yet their ability to estimate pre-test probabilities, vital for clinical decision-making, remains limited. This study evaluates two LLMs, Mistral-7B and Llama3-70B, using structured electronic health record data on three diagnosis tasks. We examined three current methods of extracting LLM probability estimations and revealed their limitations. We aim to highlight the need for improved techniques in LLM confidence estimation.
Mapping Bias in Vision Language Models: Signposts, Pitfalls, and the Road Ahead
Oct 17, 2024


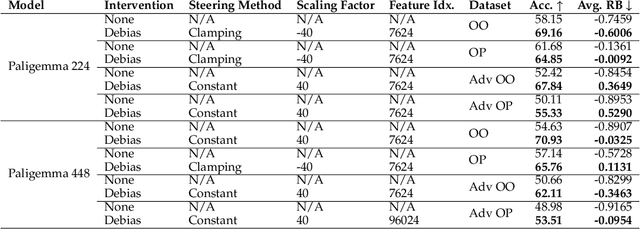
Abstract:As Vision Language Models (VLMs) gain widespread use, their fairness remains under-explored. In this paper, we analyze demographic biases across five models and six datasets. We find that portrait datasets like UTKFace and CelebA are the best tools for bias detection, finding gaps in performance and fairness between LLaVa and CLIP models. However, scene based datasets like PATA, VLStereoSet fail to be useful benchmarks for bias due to their construction. As for pronoun based datasets like VisoGender, we receive mixed signals as only some subsets of the data are useful in providing insights. To alleviate this problem, we introduce a more difficult version of VisoGender to serve as a more rigorous evaluation. Based on these results, we call for more effective and carefully designed datasets to ensure VLMs are both fair and reliable.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge