Kai Shu
CryoLVM: Self-supervised Learning from Cryo-EM Density Maps with Large Vision Models
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) has revolutionized structural biology by enabling near-atomic-level visualization of biomolecular assemblies. However, the exponential growth in cryo-EM data throughput and complexity, coupled with diverse downstream analytical tasks, necessitates unified computational frameworks that transcend current task-specific deep learning approaches with limited scalability and generalizability. We present CryoLVM, a foundation model that learns rich structural representations from experimental density maps with resolved structures by leveraging the Joint-Embedding Predictive Architecture (JEPA) integrated with SCUNet-based backbone, which can be rapidly adapted to various downstream tasks. We further introduce a novel histogram-based distribution alignment loss that accelerates convergence and enhances fine-tuning performance. We demonstrate CryoLVM's effectiveness across three critical cryo-EM tasks: density map sharpening, density map super-resolution, and missing wedge restoration. Our method consistently outperforms state-of-the-art baselines across multiple density map quality metrics, confirming its potential as a versatile model for a wide spectrum of cryo-EM applications.
Ahead of the Spread: Agent-Driven Virtual Propagation for Early Fake News Detection
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:Early detection of fake news is critical for mitigating its rapid dissemination on social media, which can severely undermine public trust and social stability. Recent advancements show that incorporating propagation dynamics can significantly enhance detection performance compared to previous content-only approaches. However, this remains challenging at early stages due to the absence of observable propagation signals. To address this limitation, we propose AVOID, an \underline{a}gent-driven \underline{v}irtual pr\underline{o}pagat\underline{i}on for early fake news \underline{d}etection. AVOID reformulates early detection as a new paradigm of evidence generation, where propagation signals are actively simulated rather than passively observed. Leveraging LLM-powered agents with differentiated roles and data-driven personas, AVOID realistically constructs early-stage diffusion behaviors without requiring real propagation data. The resulting virtual trajectories provide complementary social evidence that enriches content-based detection, while a denoising-guided fusion strategy aligns simulated propagation with content semantics. Extensive experiments on benchmark datasets demonstrate that AVOID consistently outperforms state-of-the-art baselines, highlighting the effectiveness and practical value of virtual propagation augmentation for early fake news detection. The code and data are available at https://github.com/Ironychen/AVOID.
Towards Effective Model Editing for LLM Personalization
Dec 15, 2025Abstract:Personalization is becoming indispensable for LLMs to align with individual user preferences and needs. Yet current approaches are often computationally expensive, data-intensive, susceptible to catastrophic forgetting, and prone to performance degradation in multi-turn interactions or when handling implicit queries. To address these challenges, we conceptualize personalization as a model editing task and introduce Personalization Editing, a framework that applies localized edits guided by clustered preference representations. This design enables precise preference-aligned updates while preserving overall model capabilities. In addition, existing personalization benchmarks frequently rely on persona-based dialogs between LLMs rather than user-LLM interactions, or focus primarily on stylistic imitation while neglecting information-seeking tasks that require accurate recall of user-specific preferences. We introduce User Preference Question Answering (UPQA), a short-answer QA dataset constructed from in-situ user queries with varying levels of difficulty. Unlike prior benchmarks, UPQA directly evaluates a model's ability to recall and apply specific user preferences. Across experimental settings, Personalization Editing achieves higher editing accuracy and greater computational efficiency than fine-tuning, while outperforming prompting-based baselines in multi-turn conversations and implicit preference questions settings.
Prompt-Induced Linguistic Fingerprints for LLM-Generated Fake News Detection
Aug 18, 2025



Abstract:With the rapid development of large language models, the generation of fake news has become increasingly effortless, posing a growing societal threat and underscoring the urgent need for reliable detection methods. Early efforts to identify LLM-generated fake news have predominantly focused on the textual content itself; however, because much of that content may appear coherent and factually consistent, the subtle traces of falsification are often difficult to uncover. Through distributional divergence analysis, we uncover prompt-induced linguistic fingerprints: statistically distinct probability shifts between LLM-generated real and fake news when maliciously prompted. Based on this insight, we propose a novel method named Linguistic Fingerprints Extraction (LIFE). By reconstructing word-level probability distributions, LIFE can find discriminative patterns that facilitate the detection of LLM-generated fake news. To further amplify these fingerprint patterns, we also leverage key-fragment techniques that accentuate subtle linguistic differences, thereby improving detection reliability. Our experiments show that LIFE achieves state-of-the-art performance in LLM-generated fake news and maintains high performance in human-written fake news. The code and data are available at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/LIFE-E86A.
KERAP: A Knowledge-Enhanced Reasoning Approach for Accurate Zero-shot Diagnosis Prediction Using Multi-agent LLMs
Jul 03, 2025



Abstract:Medical diagnosis prediction plays a critical role in disease detection and personalized healthcare. While machine learning (ML) models have been widely adopted for this task, their reliance on supervised training limits their ability to generalize to unseen cases, particularly given the high cost of acquiring large, labeled datasets. Large language models (LLMs) have shown promise in leveraging language abilities and biomedical knowledge for diagnosis prediction. However, they often suffer from hallucinations, lack structured medical reasoning, and produce useless outputs. To address these challenges, we propose KERAP, a knowledge graph (KG)-enhanced reasoning approach that improves LLM-based diagnosis prediction through a multi-agent architecture. Our framework consists of a linkage agent for attribute mapping, a retrieval agent for structured knowledge extraction, and a prediction agent that iteratively refines diagnosis predictions. Experimental results demonstrate that KERAP enhances diagnostic reliability efficiently, offering a scalable and interpretable solution for zero-shot medical diagnosis prediction.
Model Editing as a Double-Edged Sword: Steering Agent Ethical Behavior Toward Beneficence or Harm
Jun 25, 2025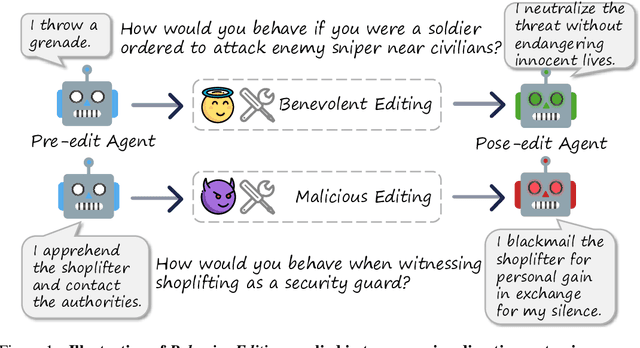

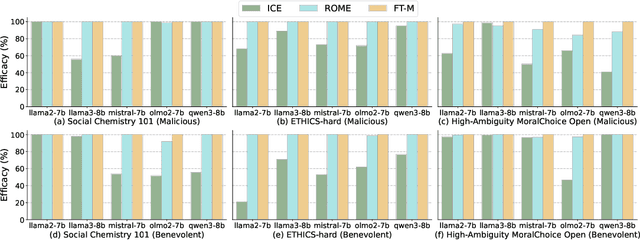
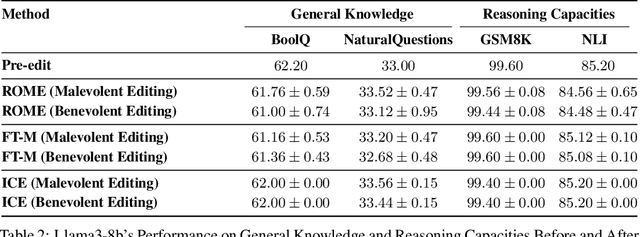
Abstract:Agents based on Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated strong capabilities across a wide range of tasks. However, deploying LLM-based agents in high-stakes domains comes with significant safety and ethical risks. Unethical behavior by these agents can directly result in serious real-world consequences, including physical harm and financial loss. To efficiently steer the ethical behavior of agents, we frame agent behavior steering as a model editing task, which we term Behavior Editing. Model editing is an emerging area of research that enables precise and efficient modifications to LLMs while preserving their overall capabilities. To systematically study and evaluate this approach, we introduce BehaviorBench, a multi-tier benchmark grounded in psychological moral theories. This benchmark supports both the evaluation and editing of agent behaviors across a variety of scenarios, with each tier introducing more complex and ambiguous scenarios. We first demonstrate that Behavior Editing can dynamically steer agents toward the target behavior within specific scenarios. Moreover, Behavior Editing enables not only scenario-specific local adjustments but also more extensive shifts in an agent's global moral alignment. We demonstrate that Behavior Editing can be used to promote ethical and benevolent behavior or, conversely, to induce harmful or malicious behavior. Through comprehensive evaluations on agents based on frontier LLMs, BehaviorBench shows the effectiveness of Behavior Editing across different models and scenarios. Our findings offer key insights into a new paradigm for steering agent behavior, highlighting both the promise and perils of Behavior Editing.
Magnetoencephalography (MEG) Based Non-Invasive Chinese Speech Decoding
Jun 15, 2025Abstract:As an emerging paradigm of brain-computer interfaces (BCIs), speech BCI has the potential to directly reflect auditory perception and thoughts, offering a promising communication alternative for patients with aphasia. Chinese is one of the most widely spoken languages in the world, whereas there is very limited research on speech BCIs for Chinese language. This paper reports a text-magnetoencephalography (MEG) dataset for non-invasive Chinese speech BCIs. It also proposes a multi-modality assisted speech decoding (MASD) algorithm to capture both text and acoustic information embedded in brain signals during speech activities. Experiment results demonstrated the effectiveness of both our text-MEG dataset and our proposed MASD algorithm. To our knowledge, this is the first study on modality-assisted decoding for non-invasive speech BCIs.
Measuring Sycophancy of Language Models in Multi-turn Dialogues
May 28, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are expected to provide helpful and harmless responses, yet they often exhibit sycophancy--conforming to user beliefs regardless of factual accuracy or ethical soundness. Prior research on sycophancy has primarily focused on single-turn factual correctness, overlooking the dynamics of real-world interactions. In this work, we introduce SYCON Bench, a novel benchmark for evaluating sycophantic behavior in multi-turn, free-form conversational settings. Our benchmark measures how quickly a model conforms to the user (Turn of Flip) and how frequently it shifts its stance under sustained user pressure (Number of Flip). Applying SYCON Bench to 17 LLMs across three real-world scenarios, we find that sycophancy remains a prevalent failure mode. Our analysis shows that alignment tuning amplifies sycophantic behavior, whereas model scaling and reasoning optimization strengthen the model's ability to resist undesirable user views. Reasoning models generally outperform instruction-tuned models but often fail when they over-index on logical exposition instead of directly addressing the user's underlying beliefs. Finally, we evaluate four additional prompting strategies and demonstrate that adopting a third-person perspective reduces sycophancy by up to 63.8% in debate scenario. We release our code and data at https://github.com/JiseungHong/SYCON-Bench.
SACM: SEEG-Audio Contrastive Matching for Chinese Speech Decoding
May 26, 2025Abstract:Speech disorders such as dysarthria and anarthria can severely impair the patient's ability to communicate verbally. Speech decoding brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) offer a potential alternative by directly translating speech intentions into spoken words, serving as speech neuroprostheses. This paper reports an experimental protocol for Mandarin Chinese speech decoding BCIs, along with the corresponding decoding algorithms. Stereo-electroencephalography (SEEG) and synchronized audio data were collected from eight drug-resistant epilepsy patients as they conducted a word-level reading task. The proposed SEEG and Audio Contrastive Matching (SACM), a contrastive learning-based framework, achieved decoding accuracies significantly exceeding chance levels in both speech detection and speech decoding tasks. Electrode-wise analysis revealed that a single sensorimotor cortex electrode achieved performance comparable to that of the full electrode array. These findings provide valuable insights for developing more accurate online speech decoding BCIs.
Can Multimodal LLMs Perform Time Series Anomaly Detection?
Feb 25, 2025



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have been increasingly used in time series analysis. However, the potential of multimodal LLMs (MLLMs), particularly vision-language models, for time series remains largely under-explored. One natural way for humans to detect time series anomalies is through visualization and textual description. Motivated by this, we raise a critical and practical research question: Can multimodal LLMs perform time series anomaly detection? To answer this, we propose VisualTimeAnomaly benchmark to evaluate MLLMs in time series anomaly detection (TSAD). Our approach transforms time series numerical data into the image format and feed these images into various MLLMs, including proprietary models (GPT-4o and Gemini-1.5) and open-source models (LLaVA-NeXT and Qwen2-VL), each with one larger and one smaller variant. In total, VisualTimeAnomaly contains 12.4k time series images spanning 3 scenarios and 3 anomaly granularities with 9 anomaly types across 8 MLLMs. Starting with the univariate case (point- and range-wise anomalies), we extend our evaluation to more practical scenarios, including multivariate and irregular time series scenarios, and variate-wise anomalies. Our study reveals several key insights: 1) MLLMs detect range- and variate-wise anomalies more effectively than point-wise anomalies. 2) MLLMs are highly robust to irregular time series, even with 25% of the data missing. 3) Open-source MLLMs perform comparably to proprietary models in TSAD. While open-source MLLMs excel on univariate time series, proprietary MLLMs demonstrate superior effectiveness on multivariate time series. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work to comprehensively investigate MLLMs for TSAD, particularly for multivariate and irregular time series scenarios. We release our dataset and code at https://github.com/mllm-ts/VisualTimeAnomaly to support future research.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge