Zijie Liu
TMS: Trajectory-Mixed Supervision for Reward-Free, On-Policy SFT
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Reinforcement Learning (RL) and Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) are the two dominant paradigms for enhancing Large Language Model (LLM) performance on downstream tasks. While RL generally preserves broader model capabilities (retention) better than SFT, it comes with significant costs: complex reward engineering, instability, and expensive on-policy sampling. In contrast, SFT is efficient but brittle, often suffering from catastrophic forgetting due to $\textbf{Supervision Mismatch}$: the divergence between the model's evolving policy and static training labels. We address this trade-off with $\textbf{Trajectory-Mixed Supervision (TMS)}$, a reward-free framework that approximates the on-policy benefits of RL by creating a dynamic curriculum from the model's own historical checkpoints. TMS minimizes $\textit{Policy-Label Divergence (PLD)}$, preventing the mode collapse that drives forgetting in standard SFT. Experiments across reasoning (MATH, GSM8K) and instruction-following benchmarks demonstrate that TMS effectively shifts the accuracy--retention Pareto frontier. While RL remains the gold standard for retention, TMS significantly outperforms standard and iterative SFT, bridging the gap to RL without requiring reward models or verifiers. Mechanistic analysis confirms that PLD drift accurately predicts forgetting and that TMS successfully mitigates this drift.
Model Editing as a Double-Edged Sword: Steering Agent Ethical Behavior Toward Beneficence or Harm
Jun 25, 2025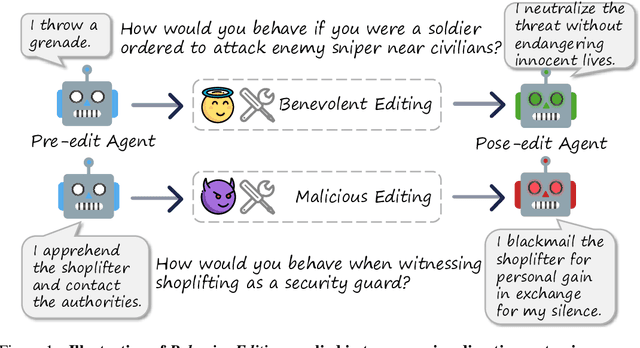

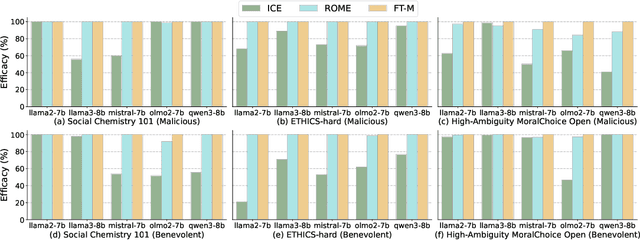
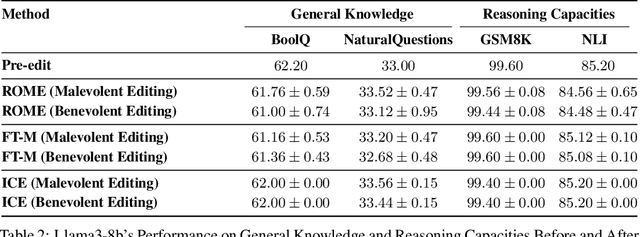
Abstract:Agents based on Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated strong capabilities across a wide range of tasks. However, deploying LLM-based agents in high-stakes domains comes with significant safety and ethical risks. Unethical behavior by these agents can directly result in serious real-world consequences, including physical harm and financial loss. To efficiently steer the ethical behavior of agents, we frame agent behavior steering as a model editing task, which we term Behavior Editing. Model editing is an emerging area of research that enables precise and efficient modifications to LLMs while preserving their overall capabilities. To systematically study and evaluate this approach, we introduce BehaviorBench, a multi-tier benchmark grounded in psychological moral theories. This benchmark supports both the evaluation and editing of agent behaviors across a variety of scenarios, with each tier introducing more complex and ambiguous scenarios. We first demonstrate that Behavior Editing can dynamically steer agents toward the target behavior within specific scenarios. Moreover, Behavior Editing enables not only scenario-specific local adjustments but also more extensive shifts in an agent's global moral alignment. We demonstrate that Behavior Editing can be used to promote ethical and benevolent behavior or, conversely, to induce harmful or malicious behavior. Through comprehensive evaluations on agents based on frontier LLMs, BehaviorBench shows the effectiveness of Behavior Editing across different models and scenarios. Our findings offer key insights into a new paradigm for steering agent behavior, highlighting both the promise and perils of Behavior Editing.
Dialogue is Better Than Monologue: Instructing Medical LLMs via Strategical Conversations
Jan 29, 2025Abstract:Current medical AI systems often fail to replicate real-world clinical reasoning, as they are predominantly trained and evaluated on static text and question-answer tasks. These tuning methods and benchmarks overlook critical aspects like evidence-based reasoning and handling distracting information. To bridge this gap, we introduce a novel benchmark that simulates real-world diagnostic scenarios, integrating noise and difficulty levels aligned with USMLE standards. Moreover, we explore dialogue-based fine-tuning, which transforms static datasets into conversational formats to better capture iterative reasoning processes. Experiments show that dialogue-tuned models outperform traditional methods, with improvements of $9.64\%$ in multi-round reasoning scenarios and $6.18\%$ in accuracy in a noisy environment. Our findings highlight dialogue tuning as a promising approach for advancing clinically aligned and robust medical AI systems.
PaMMA-Net: Plasmas magnetic measurement evolution based on data-driven incremental accumulative prediction
Jan 23, 2025



Abstract:An accurate evolution model is crucial for effective control and in-depth study of fusion plasmas. Evolution methods based on physical models often encounter challenges such as insufficient robustness or excessive computational costs. Given the proven strong fitting capabilities of deep learning methods across various fields, including plasma research, this paper introduces a deep learning-based magnetic measurement evolution method named PaMMA-Net (Plasma Magnetic Measurements Incremental Accumulative Prediction Network). This network is capable of evolving magnetic measurements in tokamak discharge experiments over extended periods or, in conjunction with equilibrium reconstruction algorithms, evolving macroscopic parameters such as plasma shape. Leveraging a incremental prediction approach and data augmentation techniques tailored for magnetic measurements, PaMMA-Net achieves superior evolution results compared to existing studies. The tests conducted on real experimental data from EAST validate the high generalization capability of the proposed method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge