Bingjia Xiao
PaMMA-Net: Plasmas magnetic measurement evolution based on data-driven incremental accumulative prediction
Jan 23, 2025



Abstract:An accurate evolution model is crucial for effective control and in-depth study of fusion plasmas. Evolution methods based on physical models often encounter challenges such as insufficient robustness or excessive computational costs. Given the proven strong fitting capabilities of deep learning methods across various fields, including plasma research, this paper introduces a deep learning-based magnetic measurement evolution method named PaMMA-Net (Plasma Magnetic Measurements Incremental Accumulative Prediction Network). This network is capable of evolving magnetic measurements in tokamak discharge experiments over extended periods or, in conjunction with equilibrium reconstruction algorithms, evolving macroscopic parameters such as plasma shape. Leveraging a incremental prediction approach and data augmentation techniques tailored for magnetic measurements, PaMMA-Net achieves superior evolution results compared to existing studies. The tests conducted on real experimental data from EAST validate the high generalization capability of the proposed method.
Disruption Precursor Onset Time Study Based on Semi-supervised Anomaly Detection
Mar 27, 2023



Abstract:The full understanding of plasma disruption in tokamaks is currently lacking, and data-driven methods are extensively used for disruption prediction. However, most existing data-driven disruption predictors employ supervised learning techniques, which require labeled training data. The manual labeling of disruption precursors is a tedious and challenging task, as some precursors are difficult to accurately identify, limiting the potential of machine learning models. To address this issue, commonly used labeling methods assume that the precursor onset occurs at a fixed time before the disruption, which may not be consistent for different types of disruptions or even the same type of disruption, due to the different speeds at which plasma instabilities escalate. This leads to mislabeled samples and suboptimal performance of the supervised learning predictor. In this paper, we present a disruption prediction method based on anomaly detection that overcomes the drawbacks of unbalanced positive and negative data samples and inaccurately labeled disruption precursor samples. We demonstrate the effectiveness and reliability of anomaly detection predictors based on different algorithms on J-TEXT and EAST to evaluate the reliability of the precursor onset time inferred by the anomaly detection predictor. The precursor onset times inferred by these predictors reveal that the labeling methods have room for improvement as the onset times of different shots are not necessarily the same. Finally, we optimize precursor labeling using the onset times inferred by the anomaly detection predictor and test the optimized labels on supervised learning disruption predictors. The results on J-TEXT and EAST show that the models trained on the optimized labels outperform those trained on fixed onset time labels.
Transferable Cross-Tokamak Disruption Prediction with Deep Hybrid Neural Network Feature Extractor
Aug 20, 2022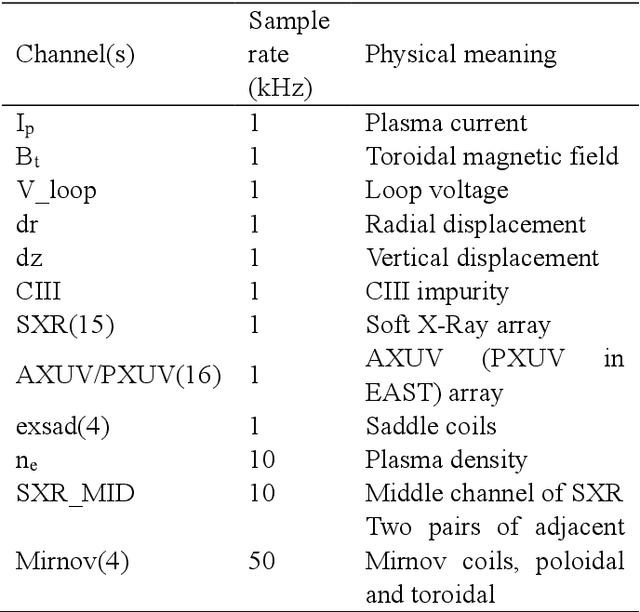

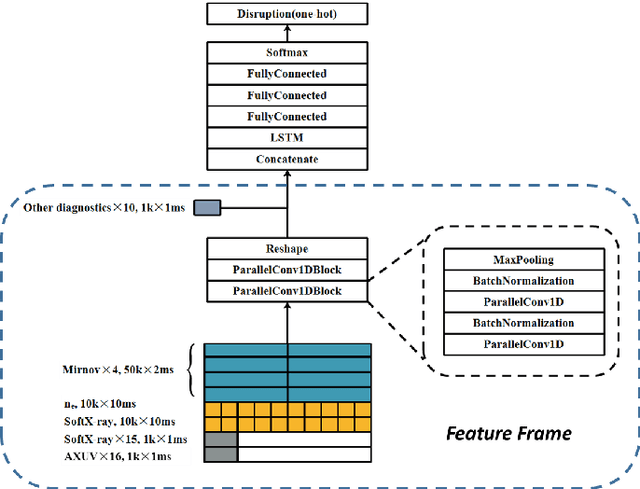
Abstract:Predicting disruptions across different tokamaks is a great obstacle to overcome. Future tokamaks can hardly tolerate disruptions at high performance discharge. Few disruption discharges at high performance can hardly compose an abundant training set, which makes it difficult for current data-driven methods to obtain an acceptable result. A machine learning method capable of transferring a disruption prediction model trained on one tokamak to another is required to solve the problem. The key is a disruption prediction model containing a feature extractor that is able to extract common disruption precursor traces in tokamak diagnostic data, and a transferable disruption classifier. Based on the concerns above, the paper first presents a deep fusion feature extractor designed specifically for extracting disruption precursor features from common diagnostics on tokamaks according to currently known precursors of disruption, providing a promising foundation for transferable models. The fusion feature extractor is proved by comparing with manual feature extraction on J-TEXT. Based on the feature extractor trained on J-TEXT, the disruption prediction model was transferred to EAST data with mere 20 discharges from EAST experiment. The performance is comparable with a model trained with 1896 discharges from EAST. From the comparison among other model training scenarios, transfer learning showed its potential in predicting disruptions across different tokamaks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge