Rui Meng
MARS: Modular Agent with Reflective Search for Automated AI Research
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Automating AI research differs from general software engineering due to computationally expensive evaluation (e.g., model training) and opaque performance attribution. Current LLM-based agents struggle here, often generating monolithic scripts that ignore execution costs and causal factors. We introduce MARS (Modular Agent with Reflective Search), a framework optimized for autonomous AI research. MARS relies on three pillars: (1) Budget-Aware Planning via cost-constrained Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS) to explicitly balance performance with execution expense; (2) Modular Construction, employing a "Design-Decompose-Implement" pipeline to manage complex research repositories; and (3) Comparative Reflective Memory, which addresses credit assignment by analyzing solution differences to distill high-signal insights. MARS achieves state-of-the-art performance among open-source frameworks on MLE-Bench under comparable settings, maintaining competitiveness with the global leaderboard's top methods. Furthermore, the system exhibits qualitative "Aha!" moments, where 63% of all utilized lessons originate from cross-branch transfer, demonstrating that the agent effectively generalizes insights across search paths.
PaperBanana: Automating Academic Illustration for AI Scientists
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Despite rapid advances in autonomous AI scientists powered by language models, generating publication-ready illustrations remains a labor-intensive bottleneck in the research workflow. To lift this burden, we introduce PaperBanana, an agentic framework for automated generation of publication-ready academic illustrations. Powered by state-of-the-art VLMs and image generation models, PaperBanana orchestrates specialized agents to retrieve references, plan content and style, render images, and iteratively refine via self-critique. To rigorously evaluate our framework, we introduce PaperBananaBench, comprising 292 test cases for methodology diagrams curated from NeurIPS 2025 publications, covering diverse research domains and illustration styles. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate that PaperBanana consistently outperforms leading baselines in faithfulness, conciseness, readability, and aesthetics. We further show that our method effectively extends to the generation of high-quality statistical plots. Collectively, PaperBanana paves the way for the automated generation of publication-ready illustrations.
KEPO: Knowledge-Enhanced Preference Optimization for Reinforcement Learning with Reasoning
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Reinforcement learning (RL) has emerged as a promising paradigm for inducing explicit reasoning behaviors in large language and vision-language models. However, reasoning-oriented RL post-training remains fundamentally challenging due to sparse trajectory-level rewards, leading to ambiguous credit assignment and severe exploration failures that can trap the policy in a ``learning cliff.'' Recent on-policy distillation methods introduce dense teacher supervision to stabilize optimization, but apply it uniformly across all generated trajectories. We argue that such uniform distillation is ill-suited for reasoning-intensive tasks, as low-quality on-policy trajectories often originate from early logical errors, and distillation under flawed contexts injects noisy and misaligned gradients. To address these challenges, we propose Knowledge-Enhanced Preference Optimization (KEPO), a unified post-training framework that integrates: (i) a quality-gated on-policy distillation objective that selectively applies dense teacher guidance only to high-quality trajectories, and (ii) a knowledge-enhanced exploration strategy that leverages hints learned from a teacher model to rejectively sample reward-positive on-policy trajectories for RL, thereby mitigating exploration collapse. Evaluated on a challenging medical visual question answering benchmark under single-source generalization, KEPO demonstrates improved training stability, more coherent reasoning behaviors, and superior out-of-distribution performance over reinforcement learning and on-policy distillation baselines.
S-MDMA: Sensitivity-Aware Model Division Multiple Access for Satellite-Ground Semantic Communication
Jan 25, 2026Abstract:Satellite-ground semantic communication (SemCom) is expected to play a pivotal role in convergence of communication and AI (ComAI), particularly in enabling intelligent and efficient multi-user data transmission. However, the inherent bandwidth constraints and user interference in satellite-ground systems pose significant challenges to semantic fidelity and transmission robustness. To address these issues, we propose a sensitivity-aware model division multiple access (S-MDMA) framework tailored for bandwidth-limited multi-user scenarios. The proposed framework first performs semantic extraction and merging based on the MDMA architecture to consolidate redundant information. To further improve transmission efficiency, a semantic sensitivity sorting algorithm is presented, which can selectively retain key semantic features. In addition, to mitigate inter-user interference, the framework incorporates orthogonal embedding of semantic features and introduces a multi-user reconstruction loss function to guide joint optimization. Experimental results on open-source datasets demonstrate that S-MDMA consistently outperforms existing methods, achieving robust and high-fidelity reconstruction across diverse signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) conditions and user configurations.
Secure Intellicise Wireless Network: Agentic AI for Coverless Semantic Steganography Communication
Jan 23, 2026Abstract:Semantic Communication (SemCom), leveraging its significant advantages in transmission efficiency and reliability, has emerged as a core technology for constructing future intellicise (intelligent and concise) wireless networks. However, intelligent attacks represented by semantic eavesdropping pose severe challenges to the security of SemCom. To address this challenge, Semantic Steganographic Communication (SemSteCom) achieves ``invisible'' encryption by implicitly embedding private semantic information into cover modality carriers. The state-of-the-art study has further introduced generative diffusion models to directly generate stega images without relying on original cover images, effectively enhancing steganographic capacity. Nevertheless, the recovery process of private images is highly dependent on the guidance of private semantic keys, which may be inferred by intelligent eavesdroppers, thereby introducing new security threats. To address this issue, we propose an Agentic AI-driven SemSteCom (AgentSemSteCom) scheme, which includes semantic extraction, digital token controlled reference image generation, coverless steganography, semantic codec, and optional task-oriented enhancement modules. The proposed AgentSemSteCom scheme obviates the need for both cover images and private semantic keys, thereby boosting steganographic capacity while reinforcing transmission security. The simulation results on open-source datasets verify that, AgentSemSteCom achieves better transmission quality and higher security levels than the baseline scheme.
Retrieval--Reasoning Processes for Multi-hop Question Answering: A Four-Axis Design Framework and Empirical Trends
Jan 02, 2026Abstract:Multi-hop question answering (QA) requires systems to iteratively retrieve evidence and reason across multiple hops. While recent RAG and agentic methods report strong results, the underlying retrieval--reasoning \emph{process} is often left implicit, making procedural choices hard to compare across model families. This survey takes the execution procedure as the unit of analysis and introduces a four-axis framework covering (A) overall execution plan, (B) index structure, (C) next-step control (strategies and triggers), and (D) stop/continue criteria. Using this schema, we map representative multi-hop QA systems and synthesize reported ablations and tendencies on standard benchmarks (e.g., HotpotQA, 2WikiMultiHopQA, MuSiQue), highlighting recurring trade-offs among effectiveness, efficiency, and evidence faithfulness. We conclude with open challenges for retrieval--reasoning agents, including structure-aware planning, transferable control policies, and robust stopping under distribution shift.
Semantic Radio Access Networks: Architecture, State-of-the-Art, and Future Directions
Dec 24, 2025Abstract:Radio Access Network (RAN) is a bridge between user devices and the core network in mobile communication systems, responsible for the transmission and reception of wireless signals and air interface management. In recent years, Semantic Communication (SemCom) has represented a transformative communication paradigm that prioritizes meaning-level transmission over conventional bit-level delivery, thus providing improved spectrum efficiency, anti-interference ability in complex environments, flexible resource allocation, and enhanced user experience for RAN. However, there is still a lack of comprehensive reviews on the integration of SemCom into RAN. Motivated by this, we systematically explore recent advancements in Semantic RAN (SemRAN). We begin by introducing the fundamentals of RAN and SemCom, identifying the limitations of conventional RAN, and outlining the overall architecture of SemRAN. Subsequently, we review representative techniques of SemRAN across physical layer, data link layer, network layer, and security plane. Furthermore, we envision future services and applications enabled by SemRAN, alongside its current standardization progress. Finally, we conclude by identifying critical research challenges and outlining forward-looking directions to guide subsequent investigations in this burgeoning field.
Turn-PPO: Turn-Level Advantage Estimation with PPO for Improved Multi-Turn RL in Agentic LLMs
Dec 18, 2025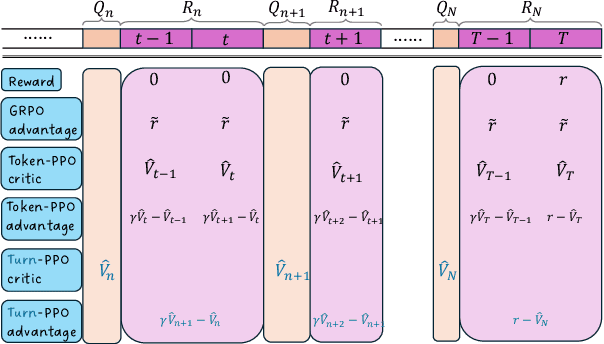

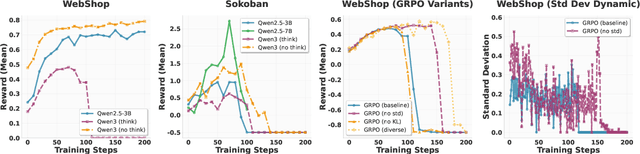
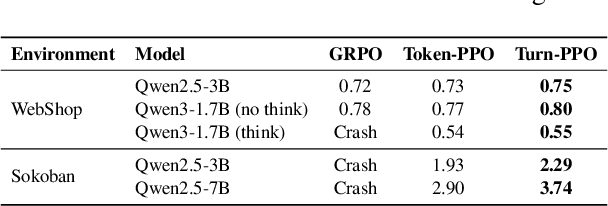
Abstract:Reinforcement learning (RL) has re-emerged as a natural approach for training interactive LLM agents in real-world environments. However, directly applying the widely used Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) algorithm to multi-turn tasks exposes notable limitations, particularly in scenarios requiring long-horizon reasoning. To address these challenges, we investigate more stable and effective advantage estimation strategies, especially for multi-turn settings. We first explore Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) as an alternative and find it to be more robust than GRPO. To further enhance PPO in multi-turn scenarios, we introduce turn-PPO, a variant that operates on a turn-level MDP formulation, as opposed to the commonly used token-level MDP. Our results on the WebShop and Sokoban datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of turn-PPO, both with and without long reasoning components.
COMPARE: Clinical Optimization with Modular Planning and Assessment via RAG-Enhanced AI-OCT: Superior Decision Support for Percutaneous Coronary Intervention Compared to ChatGPT-5 and Junior Operators
Dec 11, 2025Abstract:Background: While intravascular imaging, particularly optical coherence tomography (OCT), improves percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) outcomes, its interpretation is operator-dependent. General-purpose artificial intelligence (AI) shows promise but lacks domain-specific reliability. We evaluated the performance of CA-GPT, a novel large model deployed on an AI-OCT system, against that of the general-purpose ChatGPT-5 and junior physicians for OCT-guided PCI planning and assessment. Methods: In this single-center analysis of 96 patients who underwent OCT-guided PCI, the procedural decisions generated by the CA-GPT, ChatGPT-5, and junior physicians were compared with an expert-derived procedural record. Agreement was assessed using ten pre-specified metrics across pre-PCI and post-PCI phases. Results: For pre-PCI planning, CA-GPT demonstrated significantly higher median agreement scores (5[IQR 3.75-5]) compared to both ChatGPT-5 (3[2-4], P<0.001) and junior physicians (4[3-4], P<0.001). CA-GPT significantly outperformed ChatGPT-5 across all individual pre-PCI metrics and showed superior performance to junior physicians in stent diameter (90.3% vs. 72.2%, P<0.05) and length selection (80.6% vs. 52.8%, P<0.01). In post-PCI assessment, CA-GPT maintained excellent overall agreement (5[4.75-5]), significantly higher than both ChatGPT-5 (4[4-5], P<0.001) and junior physicians (5[4-5], P<0.05). Subgroup analysis confirmed CA-GPT's robust performance advantage in complex scenarios. Conclusion: The CA-GPT-based AI-OCT system achieved superior decision-making agreement versus a general-purpose large language model and junior physicians across both PCI planning and assessment phases. This approach provides a standardized and reliable method for intravascular imaging interpretation, demonstrating significant potential to augment operator expertise and optimize OCT-guided PCI.
Harnessing Deep LLM Participation for Robust Entity Linking
Nov 18, 2025Abstract:Entity Linking (EL), the task of mapping textual entity mentions to their corresponding entries in knowledge bases, constitutes a fundamental component of natural language understanding. Recent advancements in Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable potential for enhancing EL performance. Prior research has leveraged LLMs to improve entity disambiguation and input representation, yielding significant gains in accuracy and robustness. However, these approaches typically apply LLMs to isolated stages of the EL task, failing to fully integrate their capabilities throughout the entire process. In this work, we introduce DeepEL, a comprehensive framework that incorporates LLMs into every stage of the entity linking task. Furthermore, we identify that disambiguating entities in isolation is insufficient for optimal performance. To address this limitation, we propose a novel self-validation mechanism that utilizes global contextual information, enabling LLMs to rectify their own predictions and better recognize cohesive relationships among entities within the same sentence. Extensive empirical evaluation across ten benchmark datasets demonstrates that DeepEL substantially outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods, achieving an average improvement of 2.6\% in overall F1 score and a remarkable 4% gain on out-of-domain datasets. These results underscore the efficacy of deep LLM integration in advancing the state-of-the-art in entity linking.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge