Xiaodong Xu
Semantic Forwarding and Codebook-Enhanced Model Division Multiple Access for Satellite-Terrestrial Networks
Mar 03, 2026Abstract:Satellite-terrestrial communications are severely constrained by high path loss, limited spectrum resources, and time-varying channel conditions, rendering conventional bit-level transmission schemes inefficient and fragile, particularly in low signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) regimes. Semantic communication has emerged as a promising paradigm to address these challenges by prioritizing task-relevant information over exact bit recovery. In this paper, we propose a semantic forwarding-based semantic communication (SFSC) framework optimized for satellite-terrestrial networks. Specifically, we develop a vector-quantized joint semantic coding and modulation scheme, in which the semantic encoder and semantic codebook are jointly optimized to shape the constellation symbol distribution, improving channel adaptability and semantic compression efficiency. To mitigate noise accumulation and reduce on-board computational burden, we introduce a satellite semantic forwarding mechanism, enabling relay satellites to forward signals directly at the semantic level without full decoding and re-encoding. Furthermore, we design a channel-aware semantic reconstruction scheme based on feature-wise linear modulation (FiLM) to fuse the received SNR with semantic features, enhancing robustness under dynamic channel conditions. To support multi-user access, we further propose a codebook split-enhanced model division multiple access (CS-MDMA) method to improve spectral efficiency. Simulation results show that the proposed SFSC framework achieves a peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) gain of approximately 7.9 dB over existing benchmarks in the low-SNR regime, demonstrating its effectiveness for robust and spectrum-efficient semantic transmission in satellite-terrestrial networks.
Intellicise Wireless Networks Meet Agentic AI: A Security and Privacy Perspective
Feb 17, 2026Abstract:Intellicise (Intelligent and Concise) wireless network is the main direction of the evolution of future mobile communication systems, a perspective now widely acknowledged across academia and industry. As a key technology within it, Agentic AI has garnered growing attention due to its advanced cognitive capabilities, enabled through continuous perception-memory-reasoning-action cycles. This paper first analyses the unique advantages that Agentic AI introduces to intellicise wireless networks. We then propose a structured taxonomy for Agentic AI-enhanced secure intellicise wireless networks. Building on this framework, we identify emerging security and privacy challenges introduced by Agentic AI and summarize targeted strategies to address these vulnerabilities. A case study further demonstrates Agentic AI's efficacy in defending against intelligent eavesdropping attacks. Finally, we outline key open research directions to guide future exploration in this field.
VQ-DSC-R: Robust Vector Quantized-Enabled Digital Semantic Communication With OFDM Transmission
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Digital mapping of semantic features is essential for achieving interoperability between semantic communication and practical digital infrastructure. However, current research efforts predominantly concentrate on analog semantic communication with simplified channel models. To bridge these gaps, we develop a robust vector quantized-enabled digital semantic communication (VQ-DSC-R) system built upon orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) transmission. Our work encompasses the framework design of VQ-DSC-R, followed by a comprehensive optimization study. Firstly, we design a Swin Transformer-based backbone for hierarchical semantic feature extraction, integrated with VQ modules that map the features into a shared semantic quantized codebook (SQC) for efficient index transmission. Secondly, we propose a differentiable vector quantization with adaptive noise-variance (ANDVQ) scheme to mitigate quantization errors in SQC, which dynamically adjusts the quantization process using K-nearest neighbor statistics, while exponential moving average mechanism stabilizes SQC training. Thirdly, for robust index transmission over multipath fading channel and noise, we develop a conditional diffusion model (CDM) to refine channel state information, and design an attention-based module to dynamically adapt to channel noise. The entire VQ-DSC-R system is optimized via a three-stage training strategy. Extensive experiments demonstrate superiority of VQ-DSC-R over benchmark schemes, achieving high compression ratios and robust performance in practical scenarios.
S-MDMA: Sensitivity-Aware Model Division Multiple Access for Satellite-Ground Semantic Communication
Jan 25, 2026Abstract:Satellite-ground semantic communication (SemCom) is expected to play a pivotal role in convergence of communication and AI (ComAI), particularly in enabling intelligent and efficient multi-user data transmission. However, the inherent bandwidth constraints and user interference in satellite-ground systems pose significant challenges to semantic fidelity and transmission robustness. To address these issues, we propose a sensitivity-aware model division multiple access (S-MDMA) framework tailored for bandwidth-limited multi-user scenarios. The proposed framework first performs semantic extraction and merging based on the MDMA architecture to consolidate redundant information. To further improve transmission efficiency, a semantic sensitivity sorting algorithm is presented, which can selectively retain key semantic features. In addition, to mitigate inter-user interference, the framework incorporates orthogonal embedding of semantic features and introduces a multi-user reconstruction loss function to guide joint optimization. Experimental results on open-source datasets demonstrate that S-MDMA consistently outperforms existing methods, achieving robust and high-fidelity reconstruction across diverse signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) conditions and user configurations.
Secure Intellicise Wireless Network: Agentic AI for Coverless Semantic Steganography Communication
Jan 23, 2026Abstract:Semantic Communication (SemCom), leveraging its significant advantages in transmission efficiency and reliability, has emerged as a core technology for constructing future intellicise (intelligent and concise) wireless networks. However, intelligent attacks represented by semantic eavesdropping pose severe challenges to the security of SemCom. To address this challenge, Semantic Steganographic Communication (SemSteCom) achieves ``invisible'' encryption by implicitly embedding private semantic information into cover modality carriers. The state-of-the-art study has further introduced generative diffusion models to directly generate stega images without relying on original cover images, effectively enhancing steganographic capacity. Nevertheless, the recovery process of private images is highly dependent on the guidance of private semantic keys, which may be inferred by intelligent eavesdroppers, thereby introducing new security threats. To address this issue, we propose an Agentic AI-driven SemSteCom (AgentSemSteCom) scheme, which includes semantic extraction, digital token controlled reference image generation, coverless steganography, semantic codec, and optional task-oriented enhancement modules. The proposed AgentSemSteCom scheme obviates the need for both cover images and private semantic keys, thereby boosting steganographic capacity while reinforcing transmission security. The simulation results on open-source datasets verify that, AgentSemSteCom achieves better transmission quality and higher security levels than the baseline scheme.
Integrated Sensing and Semantic Communication with Adaptive Source-Channel Coding
Jan 19, 2026Abstract:Semantic communication has emerged as a new paradigm to facilitate the performance of integrated sensing and communication systems in 6G. However, most of the existing works mainly focus on sensing data compression to reduce the subsequent communication overheads, without considering the integrated transmission framework for both the SemCom and sensing tasks. This paper proposes an adaptive source-channel coding and beamforming design framework for integrated sensing and SemCom systems by jointly optimizing the coding rate for SemCom task and the transmit beamforming for both the SemCom and sensing tasks. Specifically, an end-to-end semantic distortion function is approximated by deriving an upper bound composing of source and channel coding induced components, and then a hybrid Cramér-Rao bound (HCRB) is also derived for target position under imperfect time synchronization. To facilitate the joint optimization, a distortion minimization problem is formulated by considering the HCRB threshold, channel uses, and power budget. Subsequently, an alternative optimization algorithm composed of successive convex approximation and fractional programming is proposed to address this problem by decoupling it into two subproblems for coding rate and beamforming designs, respectively. Simulation results demonstrate that our proposed scheme outperforms the conventional deep joint source-channel coding -water filling-zero forcing benchmark.
Instance Communication System for Intelligent Connected Vehicles: Bridging the Gap from Semantic to Instance-Level Transmission
Dec 27, 2025Abstract:Intelligent Connected Vehicles (ICVs) rely on high-speed data transmission for efficient and safety-critical services. However, the scarcity of wireless resources limits the capabilities of ICVs. Semantic Communication (SemCom) systems can alleviate this issue by extracting and transmitting task-relevant information, termed semantic information, instead of the entire raw data. Despite this, we reveal that residual redundancy persists within SemCom systems, where not all instances under the same semantic category are equally critical for downstream tasks. To tackle this issue, we introduce Instance Communication (InsCom), which elevates communication from the semantic level to the instance level for ICVs. Specifically, InsCom uses a scene graph generation model to identify all image instances and analyze their inter-relationships, thus distinguishing between semantically identical instances. Additionally, it applies user-configurable, task-critical criteria based on subject semantics and relation-object pairs to filter recognized instances. Consequently, by transmitting only task-critical instances, InsCom significantly reduces data redundancy, substantially enhancing transmission efficiency within limited wireless resources. Evaluations across various datasets and wireless channel conditions show that InsCom achieves a data volume reduction of over 7.82 times and a quality improvement ranging from 1.75 to 14.03 dB compared to the state-of-the-art SemCom systems.
Semantic Radio Access Networks: Architecture, State-of-the-Art, and Future Directions
Dec 24, 2025Abstract:Radio Access Network (RAN) is a bridge between user devices and the core network in mobile communication systems, responsible for the transmission and reception of wireless signals and air interface management. In recent years, Semantic Communication (SemCom) has represented a transformative communication paradigm that prioritizes meaning-level transmission over conventional bit-level delivery, thus providing improved spectrum efficiency, anti-interference ability in complex environments, flexible resource allocation, and enhanced user experience for RAN. However, there is still a lack of comprehensive reviews on the integration of SemCom into RAN. Motivated by this, we systematically explore recent advancements in Semantic RAN (SemRAN). We begin by introducing the fundamentals of RAN and SemCom, identifying the limitations of conventional RAN, and outlining the overall architecture of SemRAN. Subsequently, we review representative techniques of SemRAN across physical layer, data link layer, network layer, and security plane. Furthermore, we envision future services and applications enabled by SemRAN, alongside its current standardization progress. Finally, we conclude by identifying critical research challenges and outlining forward-looking directions to guide subsequent investigations in this burgeoning field.
Parameter-Efficient MoE LoRA for Few-Shot Multi-Style Editing
Nov 14, 2025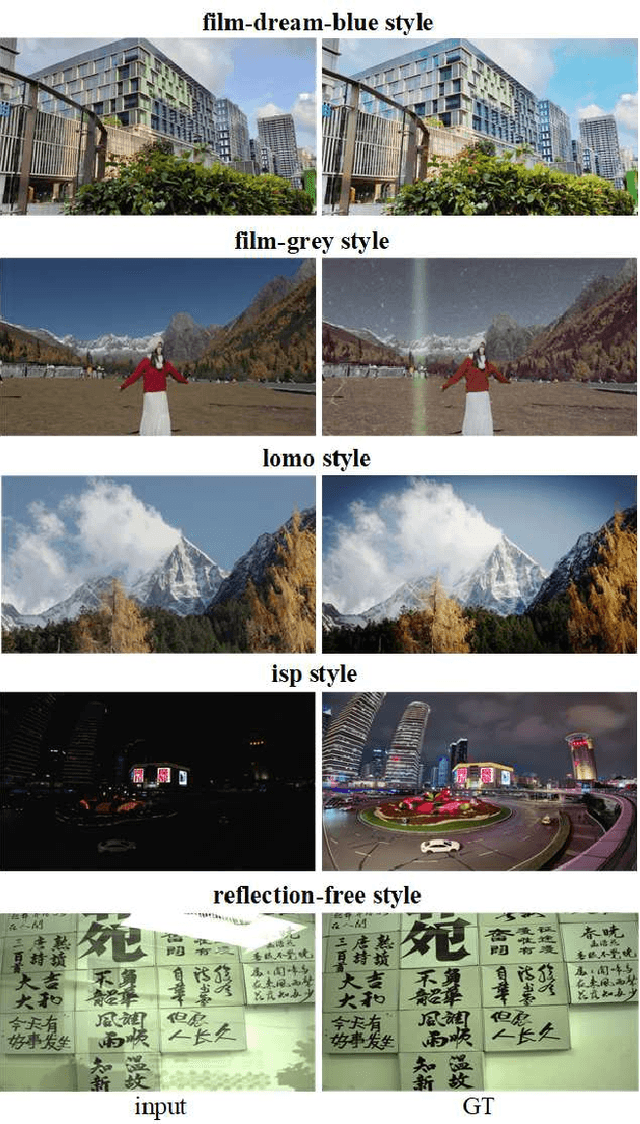
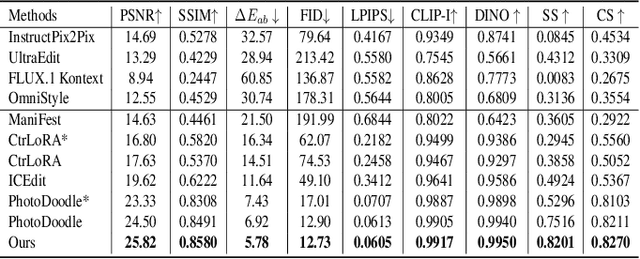

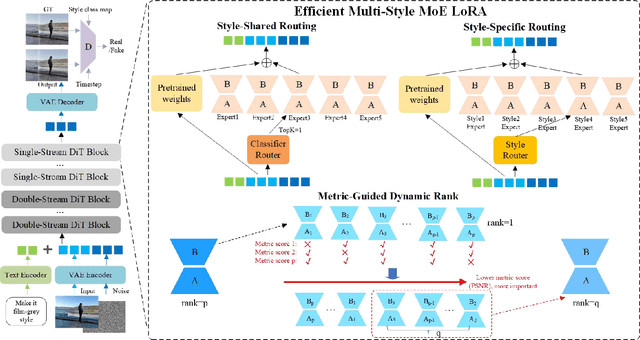
Abstract:In recent years, image editing has garnered growing attention. However, general image editing models often fail to produce satisfactory results when confronted with new styles. The challenge lies in how to effectively fine-tune general image editing models to new styles using only a limited amount of paired data. To address this issue, this paper proposes a novel few-shot style editing framework. For this task, we construct a benchmark dataset that encompasses five distinct styles. Correspondingly, we propose a parameter-efficient multi-style Mixture-of-Experts Low-Rank Adaptation (MoE LoRA) with style-specific and style-shared routing mechanisms for jointly fine-tuning multiple styles. The style-specific routing ensures that different styles do not interfere with one another, while the style-shared routing adaptively allocates shared MoE LoRAs to learn common patterns. Our MoE LoRA can automatically determine the optimal ranks for each layer through a novel metric-guided approach that estimates the importance score of each single-rank component. Additionally, we explore the optimal location to insert LoRA within the Diffusion in Transformer (DiT) model and integrate adversarial learning and flow matching to guide the diffusion training process. Experimental results demonstrate that our proposed method outperforms existing state-of-the-art approaches with significantly fewer LoRA parameters.
Qwen3Guard Technical Report
Oct 16, 2025Abstract:As large language models (LLMs) become more capable and widely used, ensuring the safety of their outputs is increasingly critical. Existing guardrail models, though useful in static evaluation settings, face two major limitations in real-world applications: (1) they typically output only binary "safe/unsafe" labels, which can be interpreted inconsistently across diverse safety policies, rendering them incapable of accommodating varying safety tolerances across domains; and (2) they require complete model outputs before performing safety checks, making them fundamentally incompatible with streaming LLM inference, thereby preventing timely intervention during generation and increasing exposure to harmful partial outputs. To address these challenges, we present Qwen3Guard, a series of multilingual safety guardrail models with two specialized variants: Generative Qwen3Guard, which casts safety classification as an instruction-following task to enable fine-grained tri-class judgments (safe, controversial, unsafe); and Stream Qwen3Guard, which introduces a token-level classification head for real-time safety monitoring during incremental text generation. Both variants are available in three sizes (0.6B, 4B, and 8B parameters) and support up to 119 languages and dialects, providing comprehensive, scalable, and low-latency safety moderation for global LLM deployments. Evaluated across English, Chinese, and multilingual benchmarks, Qwen3Guard achieves state-of-the-art performance in both prompt and response safety classification. All models are released under the Apache 2.0 license for public use.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge