Ke Zhang
Senior Member, IEEE
Dolphin-v2: Universal Document Parsing via Scalable Anchor Prompting
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Document parsing has garnered widespread attention as vision-language models (VLMs) advance OCR capabilities. However, the field remains fragmented across dozens of specialized models with varying strengths, forcing users to navigate complex model selection and limiting system scalability. Moreover, existing two-stage approaches depend on axis-aligned bounding boxes for layout detection, failing to handle distorted or photographed documents effectively. To this end, we present Dolphin-v2, a two-stage document image parsing model that substantially improves upon the original Dolphin. In the first stage, Dolphin-v2 jointly performs document type classification (digital-born versus photographed) alongside layout analysis. For digital-born documents, it conducts finer-grained element detection with reading order prediction. In the second stage, we employ a hybrid parsing strategy: photographed documents are parsed holistically as complete pages to handle geometric distortions, while digital-born documents undergo element-wise parallel parsing guided by the detected layout anchors, enabling efficient content extraction. Compared with the original Dolphin, Dolphin-v2 introduces several crucial enhancements: (1) robust parsing of photographed documents via holistic page-level understanding, (2) finer-grained element detection (21 categories) with semantic attribute extraction such as author information and document metadata, and (3) code block recognition with indentation preservation, which existing systems typically lack. Comprehensive evaluations are conducted on DocPTBench, OmniDocBench, and our self-constructed RealDoc-160 benchmark. The results demonstrate substantial improvements: +14.78 points overall on the challenging OmniDocBench and 91% error reduction on photographed documents, while maintaining efficient inference through parallel processing.
Clustering-Based User Selection in Federated Learning: Metadata Exploitation for 3GPP Networks
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:Federated learning (FL) enables collaborative model training without sharing raw user data, but conventional simulations often rely on unrealistic data partitioning and current user selection methods ignore data correlation among users. To address these challenges, this paper proposes a metadatadriven FL framework. We first introduce a novel data partition model based on a homogeneous Poisson point process (HPPP), capturing both heterogeneity in data quantity and natural overlap among user datasets. Building on this model, we develop a clustering-based user selection strategy that leverages metadata, such as user location, to reduce data correlation and enhance label diversity across training rounds. Extensive experiments on FMNIST and CIFAR-10 demonstrate that the proposed framework improves model performance, stability, and convergence in non-IID scenarios, while maintaining comparable performance under IID settings. Furthermore, the method shows pronounced advantages when the number of selected users per round is small. These findings highlight the framework's potential for enhancing FL performance in realistic deployments and guiding future standardization.
xGR: Efficient Generative Recommendation Serving at Scale
Dec 19, 2025Abstract:Recommendation system delivers substantial economic benefits by providing personalized predictions. Generative recommendation (GR) integrates LLMs to enhance the understanding of long user-item sequences. Despite employing attention-based architectures, GR's workload differs markedly from that of LLM serving. GR typically processes long prompt while producing short, fixed-length outputs, yet the computational cost of each decode phase is especially high due to the large beam width. In addition, since the beam search involves a vast item space, the sorting overhead becomes particularly time-consuming. We propose xGR, a GR-oriented serving system that meets strict low-latency requirements under highconcurrency scenarios. First, xGR unifies the processing of prefill and decode phases through staged computation and separated KV cache. Second, xGR enables early sorting termination and mask-based item filtering with data structure reuse. Third, xGR reconstructs the overall pipeline to exploit multilevel overlap and multi-stream parallelism. Our experiments with real-world recommendation service datasets demonstrate that xGR achieves at least 3.49x throughput compared to the state-of-the-art baseline under strict latency constraints.
Fast Collaborative Inference via Distributed Speculative Decoding
Dec 18, 2025Abstract:Speculative decoding accelerates large language model (LLM) inference by allowing a small draft model to predict multiple future tokens for verification by a larger target model. In AI-native radio access networks (AI-RAN), this enables device-edge collaborative inference but introduces significant uplink overhead, as existing distributed speculative decoding schemes transmit full vocabulary logits at every step. We propose a sparsify-then-sample strategy, Truncated Sparse Logits Transmission (TSLT), which transmits only the logits and indices of a truncated candidate set. We provide theoretical guarantees showing that the acceptance rate is preserved under TSLT. TSLT is further extended to multi-candidate case, where multiple draft candidates per step increase acceptance probability. Experiments show that TSLT significantly reduces uplink communication while maintaining end-to-end inference latency and model quality, demonstrating its effectiveness for scalable, communication-efficient distributed LLM inference in future AI-RAN systems.
Endless World: Real-Time 3D-Aware Long Video Generation
Dec 13, 2025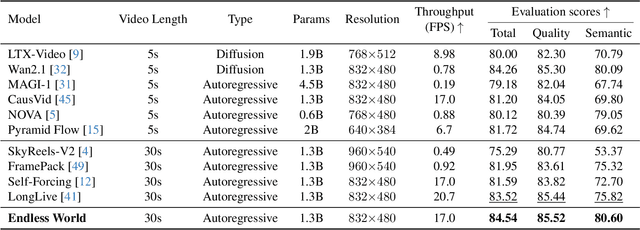
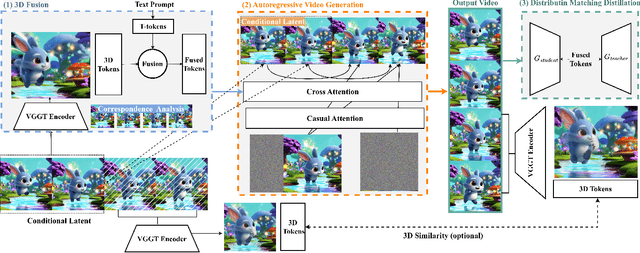
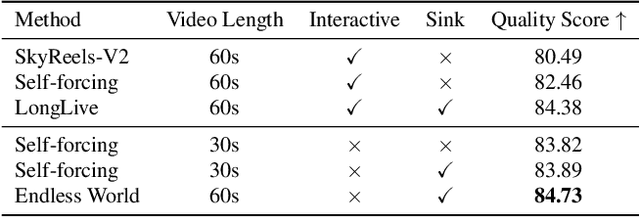
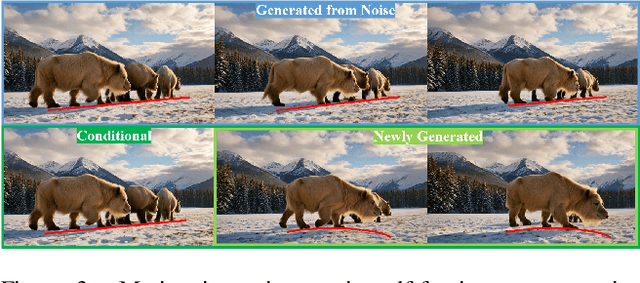
Abstract:Producing long, coherent video sequences with stable 3D structure remains a major challenge, particularly in streaming scenarios. Motivated by this, we introduce Endless World, a real-time framework for infinite, 3D-consistent video generation.To support infinite video generation, we introduce a conditional autoregressive training strategy that aligns newly generated content with existing video frames. This design preserves long-range dependencies while remaining computationally efficient, enabling real-time inference on a single GPU without additional training overhead.Moreover, our Endless World integrates global 3D-aware attention to provide continuous geometric guidance across time. Our 3D injection mechanism enforces physical plausibility and geometric consistency throughout extended sequences, addressing key challenges in long-horizon and dynamic scene synthesis.Extensive experiments demonstrate that Endless World produces long, stable, and visually coherent videos, achieving competitive or superior performance to existing methods in both visual fidelity and spatial consistency. Our project has been available on https://bwgzk-keke.github.io/EndlessWorld/.
LIFT: Interpretable truck driving risk prediction with literature-informed fine-tuned LLMs
Oct 25, 2025Abstract:This study proposes an interpretable prediction framework with literature-informed fine-tuned (LIFT) LLMs for truck driving risk prediction. The framework integrates an LLM-driven Inference Core that predicts and explains truck driving risk, a Literature Processing Pipeline that filters and summarizes domain-specific literature into a literature knowledge base, and a Result Evaluator that evaluates the prediction performance as well as the interpretability of the LIFT LLM. After fine-tuning on a real-world truck driving risk dataset, the LIFT LLM achieved accurate risk prediction, outperforming benchmark models by 26.7% in recall and 10.1% in F1-score. Furthermore, guided by the literature knowledge base automatically constructed from 299 domain papers, the LIFT LLM produced variable importance ranking consistent with that derived from the benchmark model, while demonstrating robustness in interpretation results to various data sampling conditions. The LIFT LLM also identified potential risky scenarios by detecting key combination of variables in truck driving risk, which were verified by PERMANOVA tests. Finally, we demonstrated the contribution of the literature knowledge base and the fine-tuning process in the interpretability of the LIFT LLM, and discussed the potential of the LIFT LLM in data-driven knowledge discovery.
FreeViS: Training-free Video Stylization with Inconsistent References
Oct 02, 2025Abstract:Video stylization plays a key role in content creation, but it remains a challenging problem. Na\"ively applying image stylization frame-by-frame hurts temporal consistency and reduces style richness. Alternatively, training a dedicated video stylization model typically requires paired video data and is computationally expensive. In this paper, we propose FreeViS, a training-free video stylization framework that generates stylized videos with rich style details and strong temporal coherence. Our method integrates multiple stylized references to a pretrained image-to-video (I2V) model, effectively mitigating the propagation errors observed in prior works, without introducing flickers and stutters. In addition, it leverages high-frequency compensation to constrain the content layout and motion, together with flow-based motion cues to preserve style textures in low-saliency regions. Through extensive evaluations, FreeViS delivers higher stylization fidelity and superior temporal consistency, outperforming recent baselines and achieving strong human preference. Our training-free pipeline offers a practical and economic solution for high-quality, temporally coherent video stylization. The code and videos can be accessed via https://xujiacong.github.io/FreeViS/
SEDM: Scalable Self-Evolving Distributed Memory for Agents
Sep 11, 2025Abstract:Long-term multi-agent systems inevitably generate vast amounts of trajectories and historical interactions, which makes efficient memory management essential for both performance and scalability. Existing methods typically depend on vector retrieval and hierarchical storage, yet they are prone to noise accumulation, uncontrolled memory expansion, and limited generalization across domains. To address these challenges, we present SEDM, Self-Evolving Distributed Memory, a verifiable and adaptive framework that transforms memory from a passive repository into an active, self-optimizing component. SEDM integrates verifiable write admission based on reproducible replay, a self-scheduling memory controller that dynamically ranks and consolidates entries according to empirical utility, and cross-domain knowledge diffusion that abstracts reusable insights to support transfer across heterogeneous tasks. Evaluations on benchmark datasets demonstrate that SEDM improves reasoning accuracy while reducing token overhead compared with strong memory baselines, and further enables knowledge distilled from fact verification to enhance multi-hop reasoning. The results highlight SEDM as a scalable and sustainable memory mechanism for open-ended multi-agent collaboration. The code will be released in the later stage of this project.
OpenM3D: Open Vocabulary Multi-view Indoor 3D Object Detection without Human Annotations
Aug 27, 2025Abstract:Open-vocabulary (OV) 3D object detection is an emerging field, yet its exploration through image-based methods remains limited compared to 3D point cloud-based methods. We introduce OpenM3D, a novel open-vocabulary multi-view indoor 3D object detector trained without human annotations. In particular, OpenM3D is a single-stage detector adapting the 2D-induced voxel features from the ImGeoNet model. To support OV, it is jointly trained with a class-agnostic 3D localization loss requiring high-quality 3D pseudo boxes and a voxel-semantic alignment loss requiring diverse pre-trained CLIP features. We follow the training setting of OV-3DET where posed RGB-D images are given but no human annotations of 3D boxes or classes are available. We propose a 3D Pseudo Box Generation method using a graph embedding technique that combines 2D segments into coherent 3D structures. Our pseudo-boxes achieve higher precision and recall than other methods, including the method proposed in OV-3DET. We further sample diverse CLIP features from 2D segments associated with each coherent 3D structure to align with the corresponding voxel feature. The key to training a highly accurate single-stage detector requires both losses to be learned toward high-quality targets. At inference, OpenM3D, a highly efficient detector, requires only multi-view images for input and demonstrates superior accuracy and speed (0.3 sec. per scene) on ScanNet200 and ARKitScenes indoor benchmarks compared to existing methods. We outperform a strong two-stage method that leverages our class-agnostic detector with a ViT CLIP-based OV classifier and a baseline incorporating multi-view depth estimator on both accuracy and speed.
Symphony: A Decentralized Multi-Agent Framework for Scalable Collective Intelligence
Aug 27, 2025Abstract:Most existing Large Language Model (LLM)-based agent frameworks rely on centralized orchestration, incurring high deployment costs, rigid communication topologies, and limited adaptability. To address these challenges, we introduce Symphony, a decentralized multi-agent system which enables lightweight LLMs on consumer-grade GPUs to coordinate. Symphony introduces three key mechanisms: (1) a decentralized ledger that records capabilities, (2) a Beacon-selection protocol for dynamic task allocation, and (3) weighted result voting based on CoTs. This design forms a privacy-saving, scalable, and fault-tolerant orchestration with low overhead. Empirically, Symphony outperforms existing baselines on reasoning benchmarks, achieving substantial accuracy gains and demonstrating robustness across models of varying capacities.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge