Lei Chen
OCRVerse: Towards Holistic OCR in End-to-End Vision-Language Models
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:The development of large vision language models drives the demand for managing, and applying massive amounts of multimodal data, making OCR technology, which extracts information from visual images, increasingly popular. However, existing OCR methods primarily focus on recognizing text elements from images or scanned documents (\textbf{Text-centric OCR}), neglecting the identification of visual elements from visually information-dense image sources (\textbf{Vision-centric OCR}), such as charts, web pages and science plots. In reality, these visually information-dense images are widespread on the internet and have significant real-world application value, such as data visualization and web page analysis. In this technical report, we propose \textbf{OCRVerse}, the first holistic OCR method in end-to-end manner that enables unified text-centric OCR and vision-centric OCR. To this end, we constructe comprehensive data engineering to cover a wide range of text-centric documents, such as newspapers, magazines and books, as well as vision-centric rendered composites, including charts, web pages and scientific plots. Moreover, we propose a two-stage SFT-RL multi-domain training method for OCRVerse. SFT directly mixes cross-domain data to train and establish initial domain knowledge, while RL focuses on designing personalized reward strategies for the characteristics of each domain. Specifically, since different domains require various output formats and expected outputs, we provide sufficient flexibility in the RL stage to customize flexible reward signals for each domain, thereby improving cross-domain fusion and avoiding data conflicts. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of OCRVerse, achieving competitive results across text-centric and vision-centric data types, even comparable to large-scale open-source and closed-source models.
UniX: Unifying Autoregression and Diffusion for Chest X-Ray Understanding and Generation
Jan 16, 2026Abstract:Despite recent progress, medical foundation models still struggle to unify visual understanding and generation, as these tasks have inherently conflicting goals: semantic abstraction versus pixel-level reconstruction. Existing approaches, typically based on parameter-shared autoregressive architectures, frequently lead to compromised performance in one or both tasks. To address this, we present UniX, a next-generation unified medical foundation model for chest X-ray understanding and generation. UniX decouples the two tasks into an autoregressive branch for understanding and a diffusion branch for high-fidelity generation. Crucially, a cross-modal self-attention mechanism is introduced to dynamically guide the generation process with understanding features. Coupled with a rigorous data cleaning pipeline and a multi-stage training strategy, this architecture enables synergistic collaboration between tasks while leveraging the strengths of diffusion models for superior generation. On two representative benchmarks, UniX achieves a 46.1% improvement in understanding performance (Micro-F1) and a 24.2% gain in generation quality (FD-RadDino), using only a quarter of the parameters of LLM-CXR. By achieving performance on par with task-specific models, our work establishes a scalable paradigm for synergistic medical image understanding and generation. Codes and models are available at https://github.com/ZrH42/UniX.
Panning for Gold: Expanding Domain-Specific Knowledge Graphs with General Knowledge
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:Domain-specific knowledge graphs (DKGs) often lack coverage compared to general knowledge graphs (GKGs). To address this, we introduce Domain-specific Knowledge Graph Fusion (DKGF), a novel task that enriches DKGs by integrating relevant facts from GKGs. DKGF faces two key challenges: high ambiguity in domain relevance and misalignment in knowledge granularity across graphs. We propose ExeFuse, a simple yet effective Fact-as-Program paradigm. It treats each GKG fact as a latent semantic program, maps abstract relations to granularity-aware operators, and verifies domain relevance via program executability on the target DKG. This unified probabilistic framework jointly resolves relevance and granularity issues. We construct two benchmarks, DKGF(W-I) and DKGF(Y-I), with 21 evaluation configurations. Extensive experiments validate the task's importance and our model's effectiveness, providing the first standardized testbed for DKGF.
BalDRO: A Distributionally Robust Optimization based Framework for Large Language Model Unlearning
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:As Large Language Models (LLMs) increasingly shape online content, removing targeted information from well-trained LLMs (also known as LLM unlearning) has become critical for web governance. A key challenge lies in sample-wise imbalance within the forget set: different samples exhibit widely varying unlearning difficulty, leading to asynchronous forgetting where some knowledge remains insufficiently erased while others become over-forgotten. To address this, we propose BalDRO, a novel and efficient framework for balanced LLM unlearning. BalDRO formulates unlearning as a min-sup process: an inner step identifies a worst-case data distribution that emphasizes hard-to-unlearn samples, while an outer step updates model parameters under this distribution. We instantiate BalDRO via two efficient variants: BalDRO-G, a discrete GroupDRO-based approximation focusing on high-loss subsets, and BalDRO-DV, a continuous Donsker-Varadhan dual method enabling smooth adaptive weighting within standard training pipelines. Experiments on TOFU and MUSE show that BalDRO significantly improves both forgetting quality and model utility over existing methods, and we release code for reproducibility.
Searth Transformer: A Transformer Architecture Incorporating Earth's Geospheric Physical Priors for Global Mid-Range Weather Forecasting
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:Accurate global medium-range weather forecasting is fundamental to Earth system science. Most existing Transformer-based forecasting models adopt vision-centric architectures that neglect the Earth's spherical geometry and zonal periodicity. In addition, conventional autoregressive training is computationally expensive and limits forecast horizons due to error accumulation. To address these challenges, we propose the Shifted Earth Transformer (Searth Transformer), a physics-informed architecture that incorporates zonal periodicity and meridional boundaries into window-based self-attention for physically consistent global information exchange. We further introduce a Relay Autoregressive (RAR) fine-tuning strategy that enables learning long-range atmospheric evolution under constrained memory and computational budgets. Based on these methods, we develop YanTian, a global medium-range weather forecasting model. YanTian achieves higher accuracy than the high-resolution forecast of the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts and performs competitively with state-of-the-art AI models at one-degree resolution, while requiring roughly 200 times lower computational cost than standard autoregressive fine-tuning. Furthermore, YanTian attains a longer skillful forecast lead time for Z500 (10.3 days) than HRES (9 days). Beyond weather forecasting, this work establishes a robust algorithmic foundation for predictive modeling of complex global-scale geophysical circulation systems, offering new pathways for Earth system science.
SwiftMem: Fast Agentic Memory via Query-aware Indexing
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:Agentic memory systems have become critical for enabling LLM agents to maintain long-term context and retrieve relevant information efficiently. However, existing memory frameworks suffer from a fundamental limitation: they perform exhaustive retrieval across the entire storage layer regardless of query characteristics. This brute-force approach creates severe latency bottlenecks as memory grows, hindering real-time agent interactions. We propose SwiftMem, a query-aware agentic memory system that achieves sub-linear retrieval through specialized indexing over temporal and semantic dimensions. Our temporal index enables logarithmic-time range queries for time-sensitive retrieval, while the semantic DAG-Tag index maps queries to relevant topics through hierarchical tag structures. To address memory fragmentation during growth, we introduce an embedding-tag co-consolidation mechanism that reorganizes storage based on semantic clusters to improve cache locality. Experiments on LoCoMo and LongMemEval benchmarks demonstrate that SwiftMem achieves 47$\times$ faster search compared to state-of-the-art baselines while maintaining competitive accuracy, enabling practical deployment of memory-augmented LLM agents.
Multi-scale Graph Autoregressive Modeling: Molecular Property Prediction via Next Token Prediction
Jan 05, 2026Abstract:We present Connection-Aware Motif Sequencing (CamS), a graph-to-sequence representation that enables decoder-only Transformers to learn molecular graphs via standard next-token prediction (NTP). For molecular property prediction, SMILES-based NTP scales well but lacks explicit topology, whereas graph-native masked modeling captures connectivity but risks disrupting the pivotal chemical details (e.g., activity cliffs). CamS bridges this gap by serializing molecular graphs into structure-rich causal sequences. CamS first mines data-driven connection-aware motifs. It then serializes motifs via scaffold-rooted breadth-first search (BFS) to establish a stable core-to-periphery order. Crucially, CamS enables hierarchical modeling by concatenating sequences from fine to coarse motif scales, allowing the model to condition global scaffolds on dense, uncorrupted local structural evidence. We instantiate CamS-LLaMA by pre-training a vanilla LLaMA backbone on CamS sequences. It achieves state-of-the-art performance on MoleculeNet and the activity-cliff benchmark MoleculeACE, outperforming both SMILES-based language models and strong graph baselines. Interpretability analysis confirms that our multi-scale causal serialization effectively drives attention toward cliff-determining differences.
A unified multimodal understanding and generation model for cross-disciplinary scientific research
Jan 04, 2026Abstract:Scientific discovery increasingly relies on integrating heterogeneous, high-dimensional data across disciplines nowadays. While AI models have achieved notable success across various scientific domains, they typically remain domain-specific or lack the capability of simultaneously understanding and generating multimodal scientific data, particularly for high-dimensional data. Yet, many pressing global challenges and scientific problems are inherently cross-disciplinary and require coordinated progress across multiple fields. Here, we present FuXi-Uni, a native unified multimodal model for scientific understanding and high-fidelity generation across scientific domains within a single architecture. Specifically, FuXi-Uni aligns cross-disciplinary scientific tokens within natural language tokens and employs science decoder to reconstruct scientific tokens, thereby supporting both natural language conversation and scientific numerical prediction. Empirically, we validate FuXi-Uni in Earth science and Biomedicine. In Earth system modeling, the model supports global weather forecasting, tropical cyclone (TC) forecast editing, and spatial downscaling driven by only language instructions. FuXi-Uni generates 10-day global forecasts at 0.25° resolution that outperform the SOTA physical forecasting system. It shows superior performance for both TC track and intensity prediction relative to the SOTA physical model, and generates high-resolution regional weather fields that surpass standard interpolation baselines. Regarding biomedicine, FuXi-Uni outperforms leading multimodal large language models on multiple biomedical visual question answering benchmarks. By unifying heterogeneous scientific modalities within a native shared latent space while maintaining strong domain-specific performance, FuXi-Uni provides a step forward more general-purpose, multimodal scientific models.
NeXT-IMDL: Build Benchmark for NeXT-Generation Image Manipulation Detection & Localization
Dec 29, 2025Abstract:The accessibility surge and abuse risks of user-friendly image editing models have created an urgent need for generalizable, up-to-date methods for Image Manipulation Detection and Localization (IMDL). Current IMDL research typically uses cross-dataset evaluation, where models trained on one benchmark are tested on others. However, this simplified evaluation approach conceals the fragility of existing methods when handling diverse AI-generated content, leading to misleading impressions of progress. This paper challenges this illusion by proposing NeXT-IMDL, a large-scale diagnostic benchmark designed not just to collect data, but to probe the generalization boundaries of current detectors systematically. Specifically, NeXT-IMDL categorizes AIGC-based manipulations along four fundamental axes: editing models, manipulation types, content semantics, and forgery granularity. Built upon this, NeXT-IMDL implements five rigorous cross-dimension evaluation protocols. Our extensive experiments on 11 representative models reveal a critical insight: while these models perform well in their original settings, they exhibit systemic failures and significant performance degradation when evaluated under our designed protocols that simulate real-world, various generalization scenarios. By providing this diagnostic toolkit and the new findings, we aim to advance the development towards building truly robust, next-generation IMDL models.
A DeepSeek-Powered AI System for Automated Chest Radiograph Interpretation in Clinical Practice
Dec 23, 2025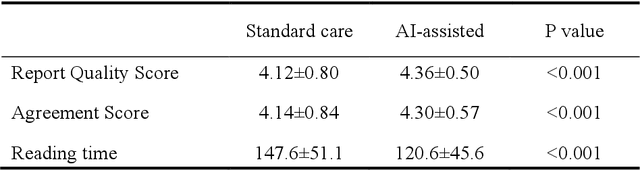
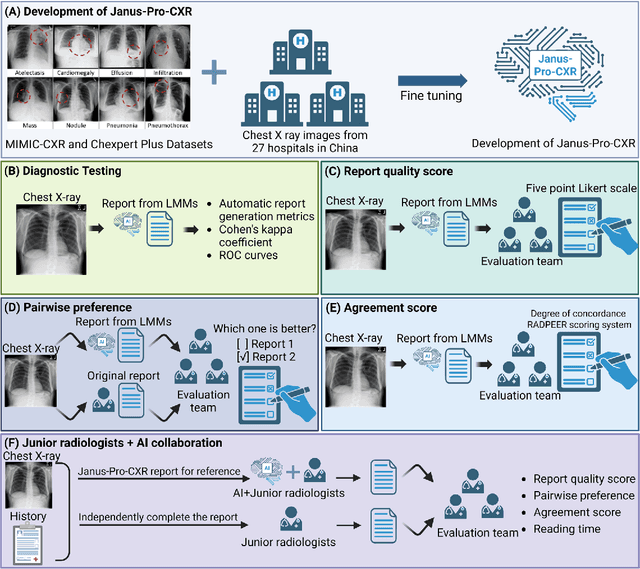
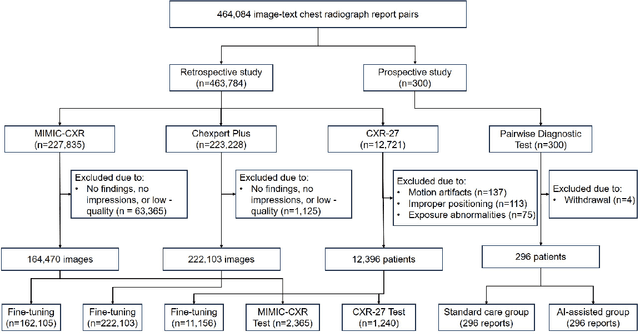
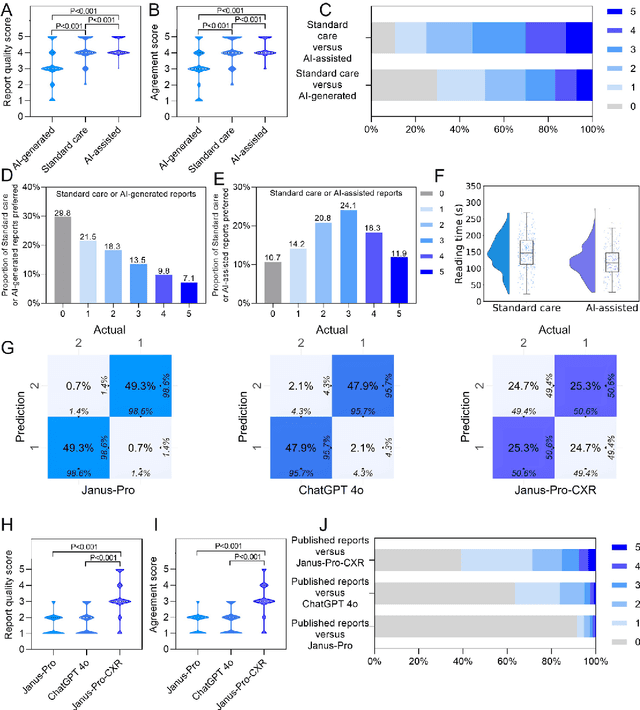
Abstract:A global shortage of radiologists has been exacerbated by the significant volume of chest X-ray workloads, particularly in primary care. Although multimodal large language models show promise, existing evaluations predominantly rely on automated metrics or retrospective analyses, lacking rigorous prospective clinical validation. Janus-Pro-CXR (1B), a chest X-ray interpretation system based on DeepSeek Janus-Pro model, was developed and rigorously validated through a multicenter prospective trial (NCT07117266). Our system outperforms state-of-the-art X-ray report generation models in automated report generation, surpassing even larger-scale models including ChatGPT 4o (200B parameters), while demonstrating reliable detection of six clinically critical radiographic findings. Retrospective evaluation confirms significantly higher report accuracy than Janus-Pro and ChatGPT 4o. In prospective clinical deployment, AI assistance significantly improved report quality scores, reduced interpretation time by 18.3% (P < 0.001), and was preferred by a majority of experts in 54.3% of cases. Through lightweight architecture and domain-specific optimization, Janus-Pro-CXR improves diagnostic reliability and workflow efficiency, particularly in resource-constrained settings. The model architecture and implementation framework will be open-sourced to facilitate the clinical translation of AI-assisted radiology solutions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge