Ran Li
CPMobius: Iterative Coach-Player Reasoning for Data-Free Reinforcement Learning
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated strong potential in complex reasoning, yet their progress remains fundamentally constrained by reliance on massive high-quality human-curated tasks and labels, either through supervised fine-tuning (SFT) or reinforcement learning (RL) on reasoning-specific data. This dependence renders supervision-heavy training paradigms increasingly unsustainable, with signs of diminishing scalability already evident in practice. To overcome this limitation, we introduce CPMöbius (CPMobius), a collaborative Coach-Player paradigm for data-free reinforcement learning of reasoning models. Unlike traditional adversarial self-play, CPMöbius, inspired by real world human sports collaboration and multi-agent collaboration, treats the Coach and Player as independent but cooperative roles. The Coach proposes instructions targeted at the Player's capability and receives rewards based on changes in the Player's performance, while the Player is rewarded for solving the increasingly instructive tasks generated by the Coach. This cooperative optimization loop is designed to directly enhance the Player's mathematical reasoning ability. Remarkably, CPMöbius achieves substantial improvement without relying on any external training data, outperforming existing unsupervised approaches. For example, on Qwen2.5-Math-7B-Instruct, our method improves accuracy by an overall average of +4.9 and an out-of-distribution average of +5.4, exceeding RENT by +1.5 on overall accuracy and R-zero by +4.2 on OOD accuracy.
Automatic Neuronal Activity Segmentation in Fast Four Dimensional Spatio-Temporal Fluorescence Imaging using Bayesian Approach
Dec 22, 2025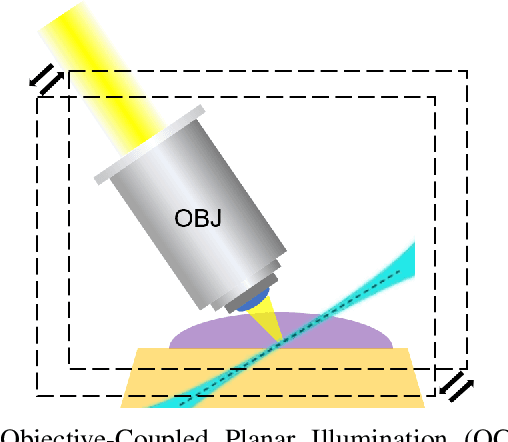
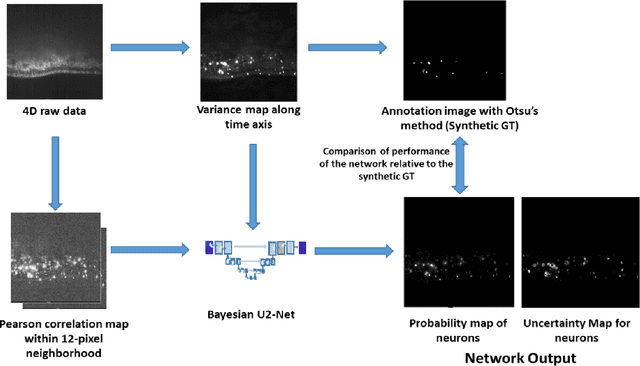
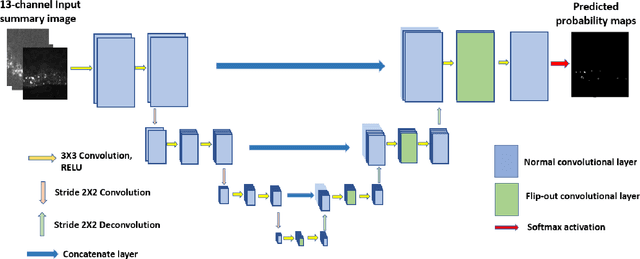
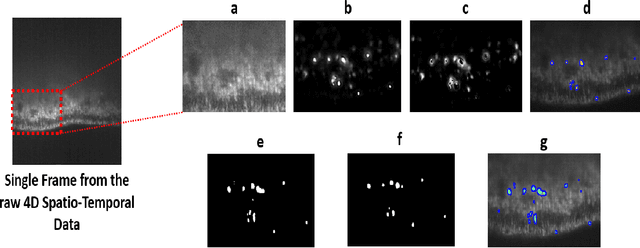
Abstract:Fluorescence Microcopy Calcium Imaging is a fundamental tool to in-vivo record and analyze large scale neuronal activities simultaneously at a single cell resolution. Automatic and precise detection of behaviorally relevant neuron activity from the recordings is critical to study the mapping of brain activity in organisms. However a perpetual bottleneck to this problem is the manual segmentation which is time and labor intensive and lacks generalizability. To this end, we present a Bayesian Deep Learning Framework to detect neuronal activities in 4D spatio-temporal data obtained by light sheet microscopy. Our approach accounts for the use of temporal information by calculating pixel wise correlation maps and combines it with spatial information given by the mean summary image. The Bayesian framework not only produces probability segmentation maps but also models the uncertainty pertaining to active neuron detection. To evaluate the accuracy of our framework we implemented the test of reproducibility to assert the generalization of the network to detect neuron activity. The network achieved a mean Dice Score of 0.81 relative to the synthetic Ground Truth obtained by Otsu's method and a mean Dice Score of 0.79 between the first and second run for test of reproducibility. Our method successfully deployed can be used for rapid detection of active neuronal activities for behavioural studies.
Near-Field Beam Training Through Beam Diverging
Sep 19, 2025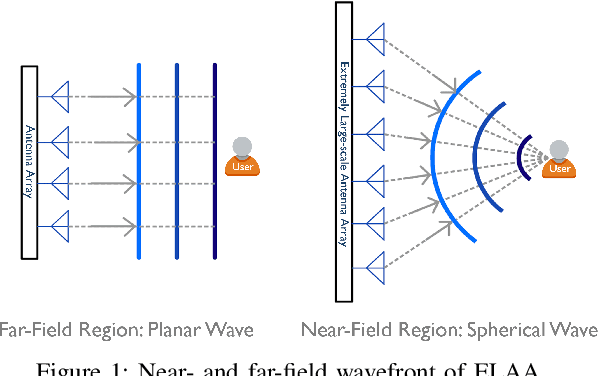
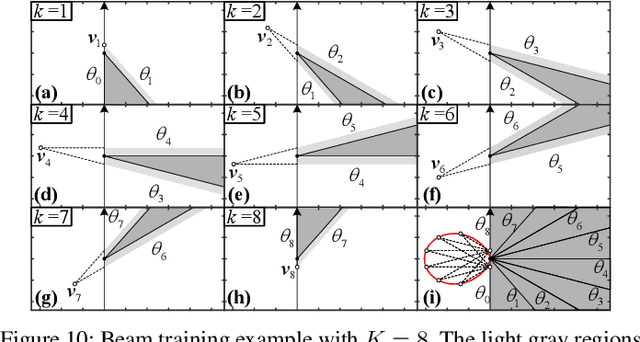
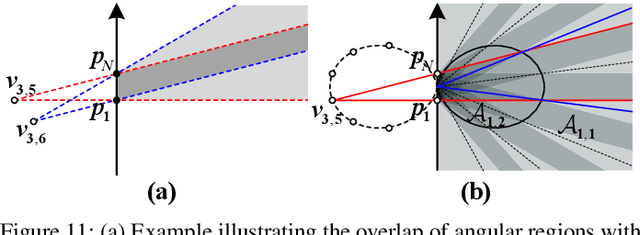
Abstract:This paper investigates beam training techniques for near-field (NF) extremely large-scale antenna arrays (ELAAs). Existing NF beam training methods predominantly rely on beam focusing, where the base station (BS) transmits highly spatially selective beams to locate the user equipment (UE). However, these beam-focusing-based schemes suffer from both high beam sweeping overhead and limited accuracy in the NF, primarily due to the narrow beams' high susceptibility to misalignment. To address this, we propose a novel NF beam training paradigm using diverging beams. Specifically, we introduce the beam diverging effect and exploit it for low-overhead, high-accuracy beam training. First, we design a diverging codeword to induce the beam diverging effect with a single radio frequency (RF) chain. Next, we develop a diverging polar-domain codebook (DPC) along with a hierarchical method that enables angular-domain localization of the UE with only 2 log_2(N) pilots, where N denotes the number of antennas. Finally, we enhance beam training performance through two additional techniques: a DPC angular range reduction strategy to improve the effectiveness of beam diverging, and a pilot set expansion method to increase overall beam training accuracy. Numerical results show that our algorithm achieves near-optimal accuracy with a small pilot overhead, outperforming existing methods.
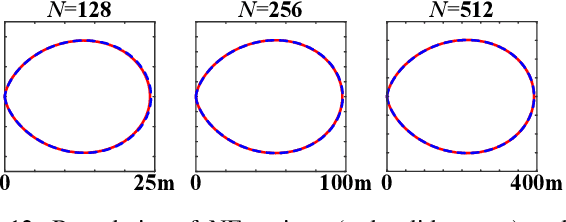
3D Near-Field Beam Training for Uniform Planar Arrays through Beam Diverging
Sep 19, 2025Abstract:In future 6G communication systems, large-scale antenna arrays promise enhanced signal strength and spatial resolution, but they also increase the complexity of beam training. Moreover, as antenna counts grow and carrier wavelengths shrink, the channel model transits from far-field (FF) planar waves to near-field (NF) spherical waves, further complicating the beam training process. This paper focuses on millimeter-wave (mmWave) systems equipped with large-scale uniform planar arrays (UPAs), which produce 3D beam patterns and introduce additional challenges for NF beam training. Existing methods primarily rely on either FF steering or NF focusing codewords, both of which are highly sensitive to mismatches in user equipment (UE) location, leading to high sensitivity to even slight mismatch and excessive training overhead. In contrast, we introduce a novel beam training approach leveraging the beam-diverging effect, which enables adjustable wide-beam coverage using only a single radio frequency (RF) chain. Specifically, we first analyze the spatial characteristics of this effect in UPA systems and leverage them to construct hierarchical codebooks for coarse UE localization. Then, we develop a 3D sampling mechanism to build an NF refinement codebook for precise beam training. Numerical results demonstrate that the proposed algorithm achieves superior beam training performance while maintaining low training overhead.
Medical-Knowledge Driven Multiple Instance Learning for Classifying Severe Abdominal Anomalies on Prenatal Ultrasound
Jul 02, 2025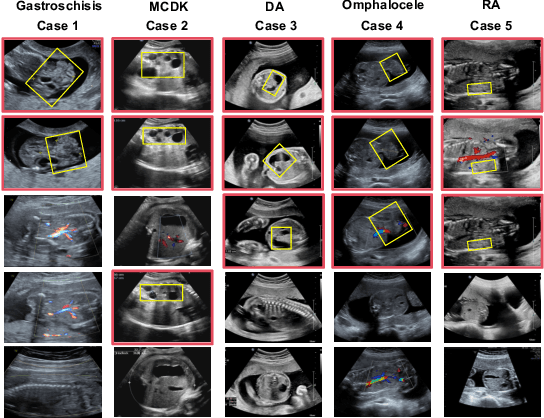
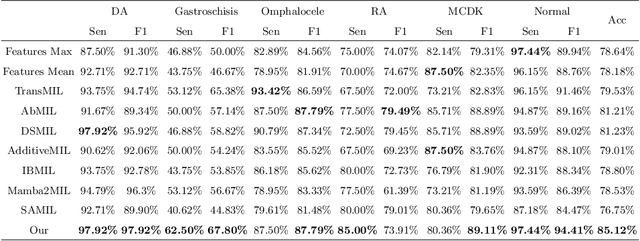
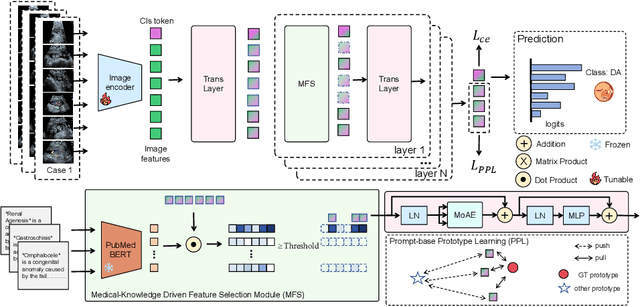
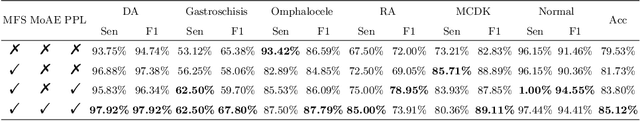
Abstract:Fetal abdominal malformations are serious congenital anomalies that require accurate diagnosis to guide pregnancy management and reduce mortality. Although AI has demonstrated significant potential in medical diagnosis, its application to prenatal abdominal anomalies remains limited. Most existing studies focus on image-level classification and rely on standard plane localization, placing less emphasis on case-level diagnosis. In this paper, we develop a case-level multiple instance learning (MIL)-based method, free of standard plane localization, for classifying fetal abdominal anomalies in prenatal ultrasound. Our contribution is three-fold. First, we adopt a mixture-of-attention-experts module (MoAE) to weight different attention heads for various planes. Secondly, we propose a medical-knowledge-driven feature selection module (MFS) to align image features with medical knowledge, performing self-supervised image token selection at the case-level. Finally, we propose a prompt-based prototype learning (PPL) to enhance the MFS. Extensively validated on a large prenatal abdominal ultrasound dataset containing 2,419 cases, with a total of 24,748 images and 6 categories, our proposed method outperforms the state-of-the-art competitors. Codes are available at:https://github.com/LL-AC/AAcls.
Co-Saving: Resource Aware Multi-Agent Collaboration for Software Development
May 28, 2025Abstract:Recent advancements in Large Language Models (LLMs) and autonomous agents have demonstrated remarkable capabilities across various domains. However, standalone agents frequently encounter limitations when handling complex tasks that demand extensive interactions and substantial computational resources. Although Multi-Agent Systems (MAS) alleviate some of these limitations through collaborative mechanisms like task decomposition, iterative communication, and role specialization, they typically remain resource-unaware, incurring significant inefficiencies due to high token consumption and excessive execution time. To address these limitations, we propose a resource-aware multi-agent system -- Co-Saving (meaning that multiple agents collaboratively engage in resource-saving activities), which leverages experiential knowledge to enhance operational efficiency and solution quality. Our key innovation is the introduction of "shortcuts" -- instructional transitions learned from historically successful trajectories -- which allows to bypass redundant reasoning agents and expedite the collective problem-solving process. Experiments for software development tasks demonstrate significant advantages over existing methods. Specifically, compared to the state-of-the-art MAS ChatDev, our method achieves an average reduction of 50.85% in token usage, and improves the overall code quality by 10.06%.
Beyond path selection: Better LLMs for Scientific Information Extraction with MimicSFT and Relevance and Rule-induced(R$^2$)GRPO
May 28, 2025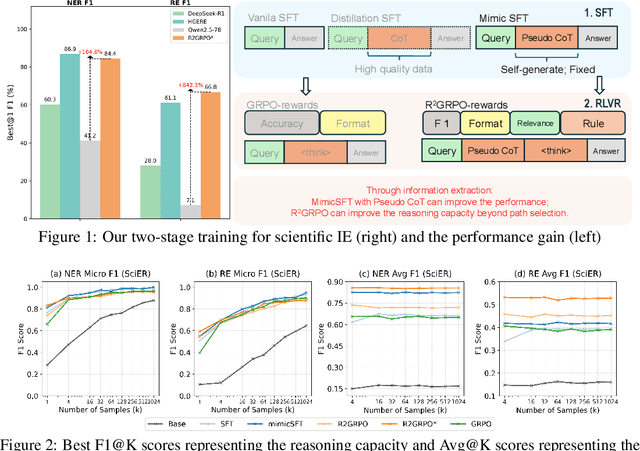
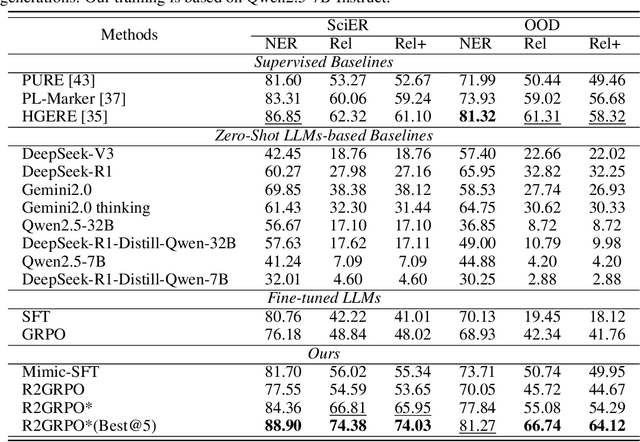
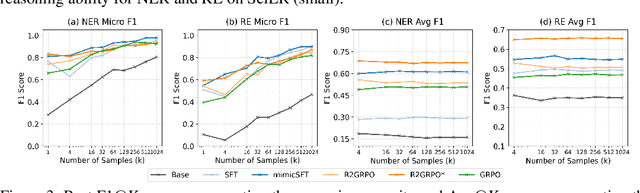
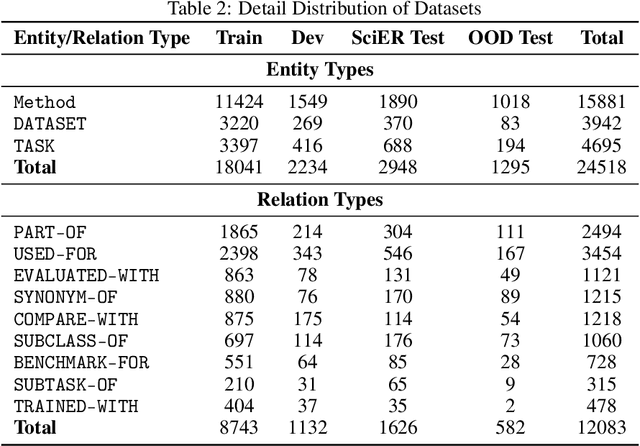
Abstract:Previous study suggest that powerful Large Language Models (LLMs) trained with Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards (RLVR) only refines reasoning path without improving the reasoning capacity in math tasks while supervised-finetuning(SFT) with distillation can. We study this from the view of Scientific information extraction (SciIE) where LLMs and reasoning LLMs underperforms small Bert-based models. SciIE require both the reasoning and memorization. We argue that both SFT and RLVR can refine the reasoning path and improve reasoning capacity in a simple way based on SciIE. We propose two-stage training with 1. MimicSFT, using structured reasoning templates without needing high-quality chain-of-thought data, 2. R$^2$GRPO with relevance and rule-induced rewards. Experiments on scientific IE benchmarks show that both methods can improve the reasoning capacity. R$^2$GRPO with mimicSFT surpasses baseline LLMs and specialized supervised models in relation extraction. Our code is available at https://github.com/ranlislz/R2GRPO.
LARGO: Latent Adversarial Reflection through Gradient Optimization for Jailbreaking LLMs
May 16, 2025Abstract:Efficient red-teaming method to uncover vulnerabilities in Large Language Models (LLMs) is crucial. While recent attacks often use LLMs as optimizers, the discrete language space make gradient-based methods struggle. We introduce LARGO (Latent Adversarial Reflection through Gradient Optimization), a novel latent self-reflection attack that reasserts the power of gradient-based optimization for generating fluent jailbreaking prompts. By operating within the LLM's continuous latent space, LARGO first optimizes an adversarial latent vector and then recursively call the same LLM to decode the latent into natural language. This methodology yields a fast, effective, and transferable attack that produces fluent and stealthy prompts. On standard benchmarks like AdvBench and JailbreakBench, LARGO surpasses leading jailbreaking techniques, including AutoDAN, by 44 points in attack success rate. Our findings demonstrate a potent alternative to agentic LLM prompting, highlighting the efficacy of interpreting and attacking LLM internals through gradient optimization.
EquiBench: Benchmarking Code Reasoning Capabilities of Large Language Models via Equivalence Checking
Feb 18, 2025



Abstract:Equivalence checking, i.e., determining whether two programs produce identical outputs for all possible inputs, underpins a broad range of applications, including software refactoring, testing, and optimization. We present the task of equivalence checking as a new way to evaluate the code reasoning abilities of large language models (LLMs). We introduce EquiBench, a dataset of 2400 program pairs spanning four programming languages and six equivalence categories. These pairs are systematically generated through program analysis, compiler scheduling, and superoptimization, covering nontrivial structural transformations that demand deep semantic reasoning beyond simple syntactic variations. Our evaluation of 17 state-of-the-art LLMs shows that OpenAI o3-mini achieves the highest overall accuracy of 78.0%. In the most challenging categories, the best accuracies are 62.3% and 68.8%, only modestly above the 50% random baseline for binary classification, indicating significant room for improvement in current models' code reasoning capabilities.
EmbodiedEval: Evaluate Multimodal LLMs as Embodied Agents
Jan 21, 2025



Abstract:Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have shown significant advancements, providing a promising future for embodied agents. Existing benchmarks for evaluating MLLMs primarily utilize static images or videos, limiting assessments to non-interactive scenarios. Meanwhile, existing embodied AI benchmarks are task-specific and not diverse enough, which do not adequately evaluate the embodied capabilities of MLLMs. To address this, we propose EmbodiedEval, a comprehensive and interactive evaluation benchmark for MLLMs with embodied tasks. EmbodiedEval features 328 distinct tasks within 125 varied 3D scenes, each of which is rigorously selected and annotated. It covers a broad spectrum of existing embodied AI tasks with significantly enhanced diversity, all within a unified simulation and evaluation framework tailored for MLLMs. The tasks are organized into five categories: navigation, object interaction, social interaction, attribute question answering, and spatial question answering to assess different capabilities of the agents. We evaluated the state-of-the-art MLLMs on EmbodiedEval and found that they have a significant shortfall compared to human level on embodied tasks. Our analysis demonstrates the limitations of existing MLLMs in embodied capabilities, providing insights for their future development. We open-source all evaluation data and simulation framework at https://github.com/thunlp/EmbodiedEval.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge