Yuhan Zhang
Ret.
Dataset Distillation via Relative Distribution Matching and Cognitive Heritage
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Dataset distillation seeks to synthesize a highly compact dataset that achieves performance comparable to the original dataset on downstream tasks. For the classification task that use pre-trained self-supervised models as backbones, previous linear gradient matching optimizes synthetic images by encouraging them to mimic the gradient updates induced by real images on the linear classifier. However, this batch-level formulation requires loading thousands of real images and applying multiple rounds of differentiable augmentations to synthetic images at each distillation step, leading to substantial computational and memory overhead. In this paper, we introduce statistical flow matching , a stable and efficient supervised learning framework that optimizes synthetic images by aligning constant statistical flows from target class centers to non-target class centers in the original data. Our approach loads raw statistics only once and performs a single augmentation pass on the synthetic data, achieving performance comparable to or better than the state-of-the-art methods with 10x lower GPU memory usage and 4x shorter runtime. Furthermore, we propose a classifier inheritance strategy that reuses the classifier trained on the original dataset for inference, requiring only an extremely lightweight linear projector and marginal storage while achieving substantial performance gains.
Cooperative Double IRS aided Secure Communication for MIMO-OFDM Systems
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Cooperative double intelligent reflecting surface (double-IRS) has emerged as a promising approach for enhancing physical layer security (PLS) in MIMO systems. However, existing studies are limited to narrowband scenarios and fail to address wideband MIMO-OFDM. In this regime, frequency-flat IRS phases and cascaded IRS links cause severe coupling, rendering narrowband designs inapplicable. To overcome this challenge, we introduce cooperative double-IRS-assisted wideband MIMO-OFDM and propose an efficient manifold-based solution. By regarding the power and constant modulus constraints as Riemannian manifolds, we reformulate the non-convex secrecy sum rate maximization as an unconstrained optimization on a product manifold. Building on this formulation, we further develop a product Riemannian gradient descent (PRGD) algorithm with guaranteed stationary convergence. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed scheme effectively resolves the OFDM coupling issue and achieves significant secrecy rate gains, outperforming single-IRS and distributed multi-IRS benchmarks by 32.0% and 22.3%, respectively.
RelayGR: Scaling Long-Sequence Generative Recommendation via Cross-Stage Relay-Race Inference
Jan 05, 2026Abstract:Real-time recommender systems execute multi-stage cascades (retrieval, pre-processing, fine-grained ranking) under strict tail-latency SLOs, leaving only tens of milliseconds for ranking. Generative recommendation (GR) models can improve quality by consuming long user-behavior sequences, but in production their online sequence length is tightly capped by the ranking-stage P99 budget. We observe that the majority of GR tokens encode user behaviors that are independent of the item candidates, suggesting an opportunity to pre-infer a user-behavior prefix once and reuse it during ranking rather than recomputing it on the critical path. Realizing this idea at industrial scale is non-trivial: the prefix cache must survive across multiple pipeline stages before the final ranking instance is determined, the user population implies cache footprints far beyond a single device, and indiscriminate pre-inference would overload shared resources under high QPS. We present RelayGR, a production system that enables in-HBM relay-race inference for GR. RelayGR selectively pre-infers long-term user prefixes, keeps their KV caches resident in HBM over the request lifecycle, and ensures the subsequent ranking can consume them without remote fetches. RelayGR combines three techniques: 1) a sequence-aware trigger that admits only at-risk requests under a bounded cache footprint and pre-inference load, 2) an affinity-aware router that co-locates cache production and consumption by routing both the auxiliary pre-infer signal and the ranking request to the same instance, and 3) a memory-aware expander that uses server-local DRAM to capture short-term cross-request reuse while avoiding redundant reloads. We implement RelayGR on Huawei Ascend NPUs and evaluate it with real queries. Under a fixed P99 SLO, RelayGR supports up to 1.5$\times$ longer sequences and improves SLO-compliant throughput by up to 3.6$\times$.
Graded strength of comparative illusions is explained by Bayesian inference
Nov 18, 2025



Abstract:Like visual processing, language processing is susceptible to illusions in which people systematically misperceive stimuli. In one such case--the comparative illusion (CI), e.g., More students have been to Russia than I have--comprehenders tend to judge the sentence as acceptable despite its underlying nonsensical comparison. Prior research has argued that this phenomenon can be explained as Bayesian inference over a noisy channel: the posterior probability of an interpretation of a sentence is proportional to both the prior probability of that interpretation and the likelihood of corruption into the observed (CI) sentence. Initial behavioral work has supported this claim by evaluating a narrow set of alternative interpretations of CI sentences and showing that comprehenders favor interpretations that are more likely to have been corrupted into the illusory sentence. In this study, we replicate and go substantially beyond this earlier work by directly predicting the strength of illusion with a quantitative model of the posterior probability of plausible interpretations, which we derive through a novel synthesis of statistical language models with human behavioral data. Our model explains not only the fine gradations in the strength of CI effects, but also a previously unexplained effect caused by pronominal vs. full noun phrase than-clause subjects. These findings support a noisy-channel theory of sentence comprehension by demonstrating that the theory makes novel predictions about the comparative illusion that bear out empirically. This outcome joins related evidence of noisy channel processing in both illusory and non-illusory contexts to support noisy channel inference as a unified computational-level theory of diverse language processing phenomena.
iFlyBot-VLM Technical Report
Nov 07, 2025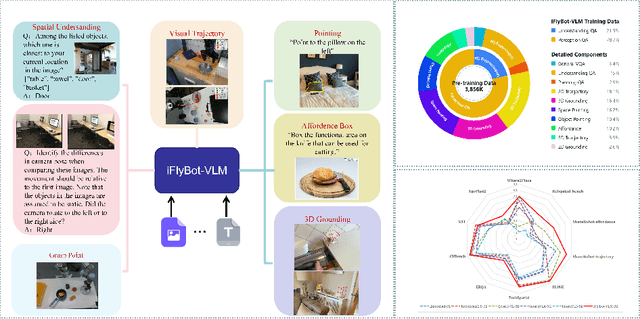
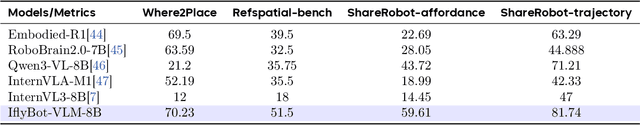
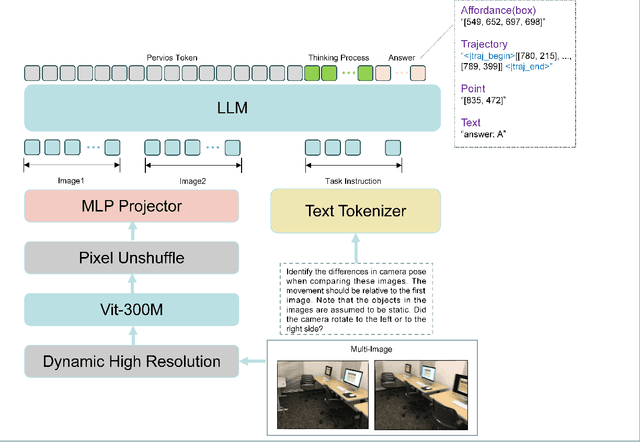
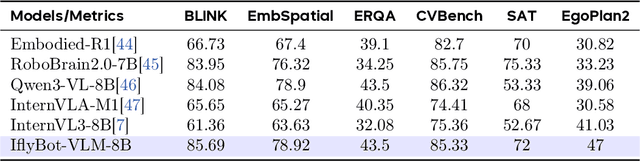
Abstract:We introduce iFlyBot-VLM, a general-purpose Vision-Language Model (VLM) used to improve the domain of Embodied Intelligence. The central objective of iFlyBot-VLM is to bridge the cross-modal semantic gap between high-dimensional environmental perception and low-level robotic motion control. To this end, the model abstracts complex visual and spatial information into a body-agnostic and transferable Operational Language, thereby enabling seamless perception-action closed-loop coordination across diverse robotic platforms. The architecture of iFlyBot-VLM is systematically designed to realize four key functional capabilities essential for embodied intelligence: 1) Spatial Understanding and Metric Reasoning; 2) Interactive Target Grounding; 3) Action Abstraction and Control Parameter Generation; 4) Task Planning and Skill Sequencing. We envision iFlyBot-VLM as a scalable and generalizable foundation model for embodied AI, facilitating the progression from specialized task-oriented systems toward generalist, cognitively capable agents. We conducted evaluations on 10 current mainstream embodied intelligence-related VLM benchmark datasets, such as Blink and Where2Place, and achieved optimal performance while preserving the model's general capabilities. We will publicly release both the training data and model weights to foster further research and development in the field of Embodied Intelligence.
Hi3DEval: Advancing 3D Generation Evaluation with Hierarchical Validity
Aug 07, 2025



Abstract:Despite rapid advances in 3D content generation, quality assessment for the generated 3D assets remains challenging. Existing methods mainly rely on image-based metrics and operate solely at the object level, limiting their ability to capture spatial coherence, material authenticity, and high-fidelity local details. 1) To address these challenges, we introduce Hi3DEval, a hierarchical evaluation framework tailored for 3D generative content. It combines both object-level and part-level evaluation, enabling holistic assessments across multiple dimensions as well as fine-grained quality analysis. Additionally, we extend texture evaluation beyond aesthetic appearance by explicitly assessing material realism, focusing on attributes such as albedo, saturation, and metallicness. 2) To support this framework, we construct Hi3DBench, a large-scale dataset comprising diverse 3D assets and high-quality annotations, accompanied by a reliable multi-agent annotation pipeline. We further propose a 3D-aware automated scoring system based on hybrid 3D representations. Specifically, we leverage video-based representations for object-level and material-subject evaluations to enhance modeling of spatio-temporal consistency and employ pretrained 3D features for part-level perception. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our approach outperforms existing image-based metrics in modeling 3D characteristics and achieves superior alignment with human preference, providing a scalable alternative to manual evaluations. The project page is available at https://zyh482.github.io/Hi3DEval/.
Medical-Knowledge Driven Multiple Instance Learning for Classifying Severe Abdominal Anomalies on Prenatal Ultrasound
Jul 02, 2025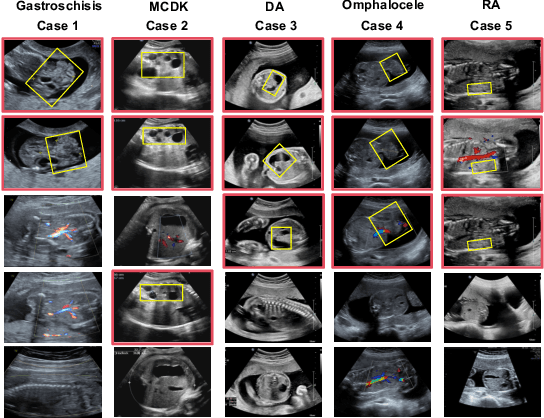
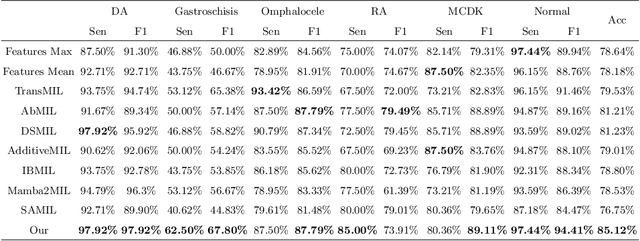
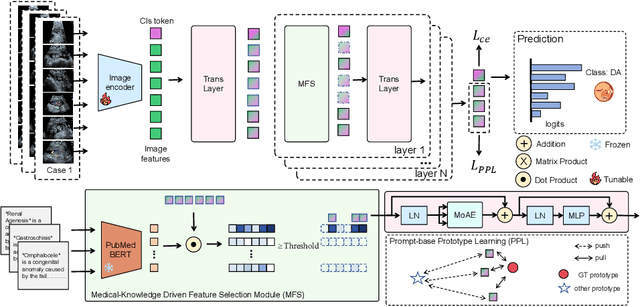
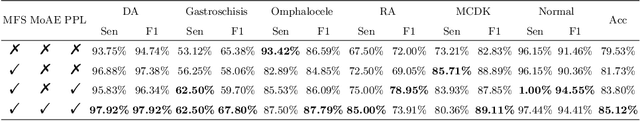
Abstract:Fetal abdominal malformations are serious congenital anomalies that require accurate diagnosis to guide pregnancy management and reduce mortality. Although AI has demonstrated significant potential in medical diagnosis, its application to prenatal abdominal anomalies remains limited. Most existing studies focus on image-level classification and rely on standard plane localization, placing less emphasis on case-level diagnosis. In this paper, we develop a case-level multiple instance learning (MIL)-based method, free of standard plane localization, for classifying fetal abdominal anomalies in prenatal ultrasound. Our contribution is three-fold. First, we adopt a mixture-of-attention-experts module (MoAE) to weight different attention heads for various planes. Secondly, we propose a medical-knowledge-driven feature selection module (MFS) to align image features with medical knowledge, performing self-supervised image token selection at the case-level. Finally, we propose a prompt-based prototype learning (PPL) to enhance the MFS. Extensively validated on a large prenatal abdominal ultrasound dataset containing 2,419 cases, with a total of 24,748 images and 6 categories, our proposed method outperforms the state-of-the-art competitors. Codes are available at:https://github.com/LL-AC/AAcls.
ReverB-SNN: Reversing Bit of the Weight and Activation for Spiking Neural Networks
Jun 09, 2025Abstract:The Spiking Neural Network (SNN), a biologically inspired neural network infrastructure, has garnered significant attention recently. SNNs utilize binary spike activations for efficient information transmission, replacing multiplications with additions, thereby enhancing energy efficiency. However, binary spike activation maps often fail to capture sufficient data information, resulting in reduced accuracy. To address this challenge, we advocate reversing the bit of the weight and activation for SNNs, called \textbf{ReverB-SNN}, inspired by recent findings that highlight greater accuracy degradation from quantizing activations compared to weights. Specifically, our method employs real-valued spike activations alongside binary weights in SNNs. This preserves the event-driven and multiplication-free advantages of standard SNNs while enhancing the information capacity of activations. Additionally, we introduce a trainable factor within binary weights to adaptively learn suitable weight amplitudes during training, thereby increasing network capacity. To maintain efficiency akin to vanilla \textbf{ReverB-SNN}, our trainable binary weight SNNs are converted back to standard form using a re-parameterization technique during inference. Extensive experiments across various network architectures and datasets, both static and dynamic, demonstrate that our approach consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods.
Where Paths Collide: A Comprehensive Survey of Classic and Learning-Based Multi-Agent Pathfinding
May 25, 2025Abstract:Multi-Agent Path Finding (MAPF) is a fundamental problem in artificial intelligence and robotics, requiring the computation of collision-free paths for multiple agents navigating from their start locations to designated goals. As autonomous systems become increasingly prevalent in warehouses, urban transportation, and other complex environments, MAPF has evolved from a theoretical challenge to a critical enabler of real-world multi-robot coordination. This comprehensive survey bridges the long-standing divide between classical algorithmic approaches and emerging learning-based methods in MAPF research. We present a unified framework that encompasses search-based methods (including Conflict-Based Search, Priority-Based Search, and Large Neighborhood Search), compilation-based approaches (SAT, SMT, CSP, ASP, and MIP formulations), and data-driven techniques (reinforcement learning, supervised learning, and hybrid strategies). Through systematic analysis of experimental practices across 200+ papers, we uncover significant disparities in evaluation methodologies, with classical methods typically tested on larger-scale instances (up to 200 by 200 grids with 1000+ agents) compared to learning-based approaches (predominantly 10-100 agents). We provide a comprehensive taxonomy of evaluation metrics, environment types, and baseline selections, highlighting the need for standardized benchmarking protocols. Finally, we outline promising future directions including mixed-motive MAPF with game-theoretic considerations, language-grounded planning with large language models, and neural solver architectures that combine the rigor of classical methods with the flexibility of deep learning. This survey serves as both a comprehensive reference for researchers and a practical guide for deploying MAPF solutions in increasingly complex real-world applications.
Machine Learning Applications Related to Suicide in Military and Veterans: A Scoping Literature Review
May 18, 2025Abstract:Suicide remains one of the main preventable causes of death among active service members and veterans. Early detection and prediction are crucial in suicide prevention. Machine learning techniques have yielded promising results in this area recently. This study aims to assess and summarize current research and provides a comprehensive review regarding the application of machine learning techniques in assessing and predicting suicidal ideation, attempts, and mortality among members of military and veteran populations. A keyword search using PubMed, IEEE, ACM, and Google Scholar was conducted, and the PRISMA protocol was adopted for relevant study selection. Thirty-two articles met the inclusion criteria. These studies consistently identified risk factors relevant to mental health issues such as depression, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), suicidal ideation, prior attempts, physical health problems, and demographic characteristics. Machine learning models applied in this area have demonstrated reasonable predictive accuracy. However, additional research gaps still exist. First, many studies have overlooked metrics that distinguish between false positives and negatives, such as positive predictive value and negative predictive value, which are crucial in the context of suicide prevention policies. Second, more dedicated approaches to handling survival and longitudinal data should be explored. Lastly, most studies focused on machine learning methods, with limited discussion of their connection to clinical rationales. In summary, machine learning analyses have identified a wide range of risk factors associated with suicide in military populations. The diversity and complexity of these factors also demonstrates that effective prevention strategies must be comprehensive and flexible.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge