Yufei Guo
Synergistic Prompting for Robust Visual Recognition with Missing Modalities
Jul 10, 2025Abstract:Large-scale multi-modal models have demonstrated remarkable performance across various visual recognition tasks by leveraging extensive paired multi-modal training data. However, in real-world applications, the presence of missing or incomplete modality inputs often leads to significant performance degradation. Recent research has focused on prompt-based strategies to tackle this issue; however, existing methods are hindered by two major limitations: (1) static prompts lack the flexibility to adapt to varying missing-data conditions, and (2) basic prompt-tuning methods struggle to ensure reliable performance when critical modalities are missing.To address these challenges, we propose a novel Synergistic Prompting (SyP) framework for robust visual recognition with missing modalities. The proposed SyP introduces two key innovations: (I) a Dynamic Adapter, which computes adaptive scaling factors to dynamically generate prompts, replacing static parameters for flexible multi-modal adaptation, and (II) a Synergistic Prompting Strategy, which combines static and dynamic prompts to balance information across modalities, ensuring robust reasoning even when key modalities are missing. The proposed SyP achieves significant performance improvements over existing approaches across three widely-used visual recognition datasets, demonstrating robustness under diverse missing rates and conditions. Extensive experiments and ablation studies validate its effectiveness in handling missing modalities, highlighting its superior adaptability and reliability.
ReverB-SNN: Reversing Bit of the Weight and Activation for Spiking Neural Networks
Jun 09, 2025Abstract:The Spiking Neural Network (SNN), a biologically inspired neural network infrastructure, has garnered significant attention recently. SNNs utilize binary spike activations for efficient information transmission, replacing multiplications with additions, thereby enhancing energy efficiency. However, binary spike activation maps often fail to capture sufficient data information, resulting in reduced accuracy. To address this challenge, we advocate reversing the bit of the weight and activation for SNNs, called \textbf{ReverB-SNN}, inspired by recent findings that highlight greater accuracy degradation from quantizing activations compared to weights. Specifically, our method employs real-valued spike activations alongside binary weights in SNNs. This preserves the event-driven and multiplication-free advantages of standard SNNs while enhancing the information capacity of activations. Additionally, we introduce a trainable factor within binary weights to adaptively learn suitable weight amplitudes during training, thereby increasing network capacity. To maintain efficiency akin to vanilla \textbf{ReverB-SNN}, our trainable binary weight SNNs are converted back to standard form using a re-parameterization technique during inference. Extensive experiments across various network architectures and datasets, both static and dynamic, demonstrate that our approach consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods.
A Comprehensive Survey in LLM(-Agent) Full Stack Safety: Data, Training and Deployment
Apr 22, 2025Abstract:The remarkable success of Large Language Models (LLMs) has illuminated a promising pathway toward achieving Artificial General Intelligence for both academic and industrial communities, owing to their unprecedented performance across various applications. As LLMs continue to gain prominence in both research and commercial domains, their security and safety implications have become a growing concern, not only for researchers and corporations but also for every nation. Currently, existing surveys on LLM safety primarily focus on specific stages of the LLM lifecycle, e.g., deployment phase or fine-tuning phase, lacking a comprehensive understanding of the entire "lifechain" of LLMs. To address this gap, this paper introduces, for the first time, the concept of "full-stack" safety to systematically consider safety issues throughout the entire process of LLM training, deployment, and eventual commercialization. Compared to the off-the-shelf LLM safety surveys, our work demonstrates several distinctive advantages: (I) Comprehensive Perspective. We define the complete LLM lifecycle as encompassing data preparation, pre-training, post-training, deployment and final commercialization. To our knowledge, this represents the first safety survey to encompass the entire lifecycle of LLMs. (II) Extensive Literature Support. Our research is grounded in an exhaustive review of over 800+ papers, ensuring comprehensive coverage and systematic organization of security issues within a more holistic understanding. (III) Unique Insights. Through systematic literature analysis, we have developed reliable roadmaps and perspectives for each chapter. Our work identifies promising research directions, including safety in data generation, alignment techniques, model editing, and LLM-based agent systems. These insights provide valuable guidance for researchers pursuing future work in this field.
Improving Transformer Based Line Segment Detection with Matched Predicting and Re-ranking
Feb 25, 2025Abstract:Classical Transformer-based line segment detection methods have delivered impressive results. However, we observe that some accurately detected line segments are assigned low confidence scores during prediction, causing them to be ranked lower and potentially suppressed. Additionally, these models often require prolonged training periods to achieve strong performance, largely due to the necessity of bipartite matching. In this paper, we introduce RANK-LETR, a novel Transformer-based line segment detection method. Our approach leverages learnable geometric information to refine the ranking of predicted line segments by enhancing the confidence scores of high-quality predictions in a posterior verification step. We also propose a new line segment proposal method, wherein the feature point nearest to the centroid of the line segment directly predicts the location, significantly improving training efficiency and stability. Moreover, we introduce a line segment ranking loss to stabilize rankings during training, thereby enhancing the generalization capability of the model. Experimental results demonstrate that our method outperforms other Transformer-based and CNN-based approaches in prediction accuracy while requiring fewer training epochs than previous Transformer-based models.
Toward Realistic Camouflaged Object Detection: Benchmarks and Method
Jan 13, 2025



Abstract:Camouflaged object detection (COD) primarily relies on semantic or instance segmentation methods. While these methods have made significant advancements in identifying the contours of camouflaged objects, they may be inefficient or cost-effective for tasks that only require the specific location of the object. Object detection algorithms offer an optimized solution for Realistic Camouflaged Object Detection (RCOD) in such cases. However, detecting camouflaged objects remains a formidable challenge due to the high degree of similarity between the features of the objects and their backgrounds. Unlike segmentation methods that perform pixel-wise comparisons to differentiate between foreground and background, object detectors omit this analysis, further aggravating the challenge. To solve this problem, we propose a camouflage-aware feature refinement (CAFR) strategy. Since camouflaged objects are not rare categories, CAFR fully utilizes a clear perception of the current object within the prior knowledge of large models to assist detectors in deeply understanding the distinctions between background and foreground. Specifically, in CAFR, we introduce the Adaptive Gradient Propagation (AGP) module that fine-tunes all feature extractor layers in large detection models to fully refine class-specific features from camouflaged contexts. We then design the Sparse Feature Refinement (SFR) module that optimizes the transformer-based feature extractor to focus primarily on capturing class-specific features in camouflaged scenarios. To facilitate the assessment of RCOD tasks, we manually annotate the labels required for detection on three existing segmentation COD datasets, creating a new benchmark for RCOD tasks. Code and datasets are available at: https://github.com/zhimengXin/RCOD.
Visual-Semantic Graph Matching Net for Zero-Shot Learning
Nov 18, 2024Abstract:Zero-shot learning (ZSL) aims to leverage additional semantic information to recognize unseen classes. To transfer knowledge from seen to unseen classes, most ZSL methods often learn a shared embedding space by simply aligning visual embeddings with semantic prototypes. However, methods trained under this paradigm often struggle to learn robust embedding space because they align the two modalities in an isolated manner among classes, which ignore the crucial class relationship during the alignment process. To address the aforementioned challenges, this paper proposes a Visual-Semantic Graph Matching Net, termed as VSGMN, which leverages semantic relationships among classes to aid in visual-semantic embedding. VSGMN employs a Graph Build Network (GBN) and a Graph Matching Network (GMN) to achieve two-stage visual-semantic alignment. Specifically, GBN first utilizes an embedding-based approach to build visual and semantic graphs in the semantic space and align the embedding with its prototype for first-stage alignment. Additionally, to supplement unseen class relations in these graphs, GBN also build the unseen class nodes based on semantic relationships. In the second stage, GMN continuously integrates neighbor and cross-graph information into the constructed graph nodes, and aligns the node relationships between the two graphs under the class relationship constraint. Extensive experiments on three benchmark datasets demonstrate that VSGMN achieves superior performance in both conventional and generalized ZSL scenarios. The implementation of our VSGMN and experimental results are available at github: https://github.com/dbwfd/VSGMN
Bias in Large Language Models: Origin, Evaluation, and Mitigation
Nov 16, 2024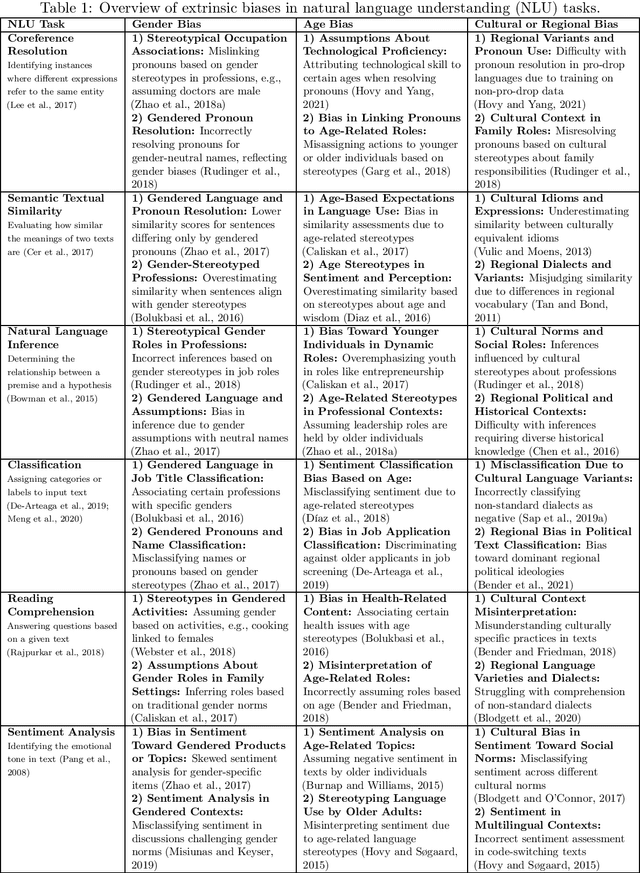
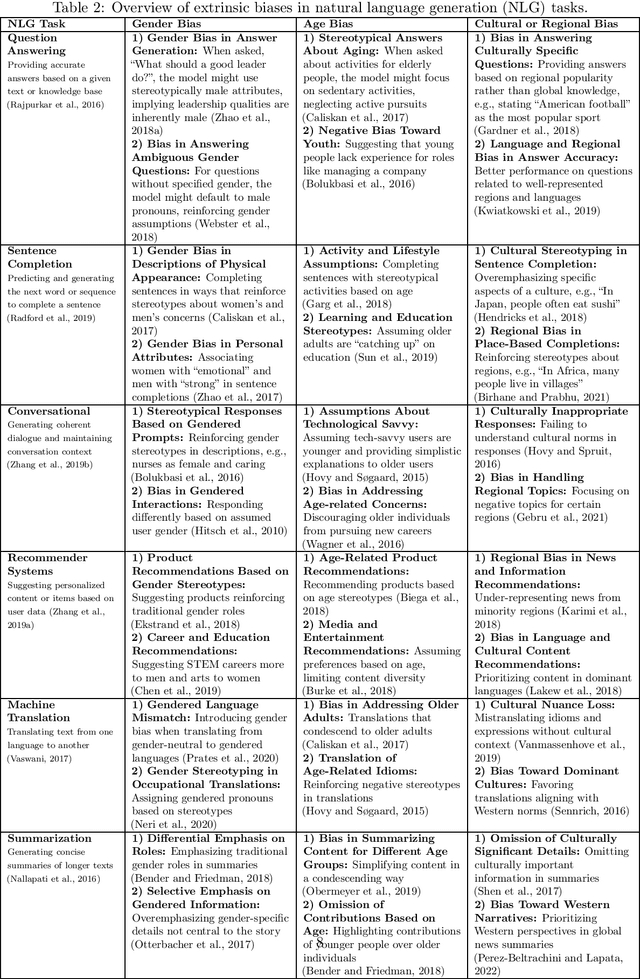
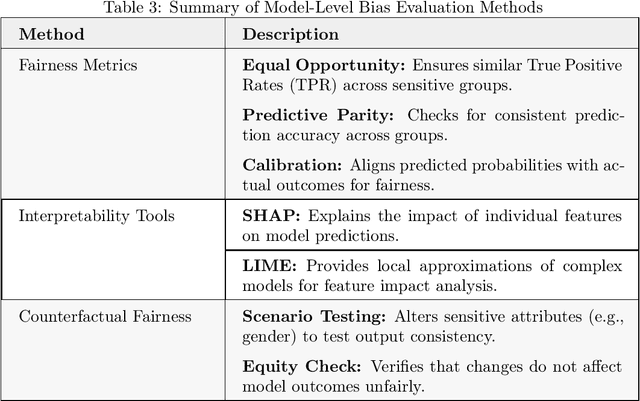
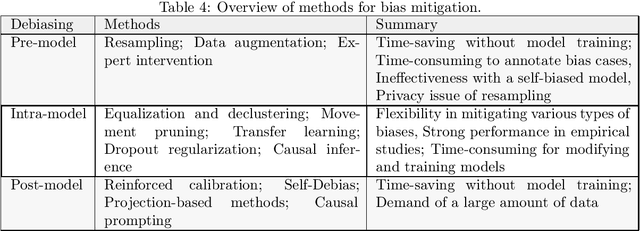
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have revolutionized natural language processing, but their susceptibility to biases poses significant challenges. This comprehensive review examines the landscape of bias in LLMs, from its origins to current mitigation strategies. We categorize biases as intrinsic and extrinsic, analyzing their manifestations in various NLP tasks. The review critically assesses a range of bias evaluation methods, including data-level, model-level, and output-level approaches, providing researchers with a robust toolkit for bias detection. We further explore mitigation strategies, categorizing them into pre-model, intra-model, and post-model techniques, highlighting their effectiveness and limitations. Ethical and legal implications of biased LLMs are discussed, emphasizing potential harms in real-world applications such as healthcare and criminal justice. By synthesizing current knowledge on bias in LLMs, this review contributes to the ongoing effort to develop fair and responsible AI systems. Our work serves as a comprehensive resource for researchers and practitioners working towards understanding, evaluating, and mitigating bias in LLMs, fostering the development of more equitable AI technologies.
DiffX: Guide Your Layout to Cross-Modal Generative Modeling
Jul 28, 2024


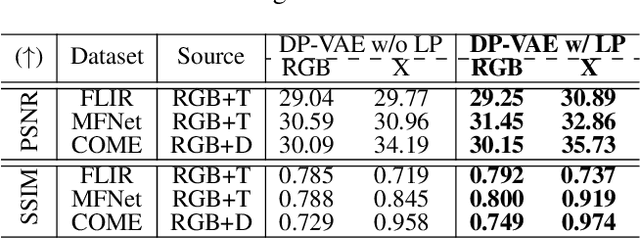
Abstract:Diffusion models have made significant strides in language-driven and layout-driven image generation. However, most diffusion models are limited to visible RGB image generation. In fact, human perception of the world is enriched by diverse viewpoints, including chromatic contrast, thermal illumination, and depth information. In this paper, we introduce a novel diffusion model for general layout-guided cross-modal ``RGB+X'' generation, called DiffX. Firstly, we construct the cross-modal image datasets with text description by using LLaVA for image captioning, supplemented by manual corrections. Notably, DiffX presents a simple yet effective cross-modal generative modeling pipeline, which conducts diffusion and denoising processes in the modality-shared latent space, facilitated by our Dual Path Variational AutoEncoder (DP-VAE). Moreover, we introduce the joint-modality embedder, which incorporates a gated cross-attention mechanism to link layout and text conditions. Meanwhile, the advanced Long-CLIP is employed for long caption embedding to improve user guidance. Through extensive experiments, DiffX demonstrates robustness and flexibility in cross-modal generation across three RGB+X datasets: FLIR, MFNet, and COME15K, guided by various layout types. It also shows the potential for adaptive generation of ``RGB+X+Y'' or more diverse modalities. Our code and constructed cross-modal image datasets are available at https://github.com/zeyuwang-zju/DiffX.
UP-Diff: Latent Diffusion Model for Remote Sensing Urban Prediction
Jul 16, 2024Abstract:This study introduces a novel Remote Sensing (RS) Urban Prediction (UP) task focused on future urban planning, which aims to forecast urban layouts by utilizing information from existing urban layouts and planned change maps. To address the proposed RS UP task, we propose UP-Diff, which leverages a Latent Diffusion Model (LDM) to capture positionaware embeddings of pre-change urban layouts and planned change maps. In specific, the trainable cross-attention layers within UP-Diff's iterative diffusion modules enable the model to dynamically highlight crucial regions for targeted modifications. By utilizing our UP-Diff, designers can effectively refine and adjust future urban city plans by making modifications to the change maps in a dynamic and adaptive manner. Compared with conventional RS Change Detection (CD) methods, the proposed UP-Diff for the RS UP task avoids the requirement of paired prechange and post-change images, which enhances the practical usage in city development. Experimental results on LEVIRCD and SYSU-CD datasets show UP-Diff's ability to accurately predict future urban layouts with high fidelity, demonstrating its potential for urban planning. Code and model weights will be available upon the acceptance of the work.
Take A Shortcut Back: Mitigating the Gradient Vanishing for Training Spiking Neural Networks
Jan 09, 2024Abstract:The Spiking Neural Network (SNN) is a biologically inspired neural network infrastructure that has recently garnered significant attention. It utilizes binary spike activations to transmit information, thereby replacing multiplications with additions and resulting in high energy efficiency. However, training an SNN directly poses a challenge due to the undefined gradient of the firing spike process. Although prior works have employed various surrogate gradient training methods that use an alternative function to replace the firing process during back-propagation, these approaches ignore an intrinsic problem: gradient vanishing. To address this issue, we propose a shortcut back-propagation method in our paper, which advocates for transmitting the gradient directly from the loss to the shallow layers. This enables us to present the gradient to the shallow layers directly, thereby significantly mitigating the gradient vanishing problem. Additionally, this method does not introduce any burden during the inference phase. To strike a balance between final accuracy and ease of training, we also propose an evolutionary training framework and implement it by inducing a balance coefficient that dynamically changes with the training epoch, which further improves the network's performance. Extensive experiments conducted over static and dynamic datasets using several popular network structures reveal that our method consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge