Yi Huang
DRL-Enabled Trajectory Planing for UAV-Assisted VLC: Optimal Altitude and Reward Design
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Recently, the integration of unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) and visible light communication (VLC) technologies has emerged as a promising solution to offer flexible communication and efficient lighting. This letter investigates the three-dimensional trajectory planning in a UAV-assisted VLC system, where a UAV is dispatched to collect data from ground users (GUs). The core objective is to develop a trajectory planning framework that minimizes UAV flight distance, which is equivalent to maximizing the data collection efficiency. This issue is formulated as a challenging mixed-integer non-convex optimization problem. To tackle it, we first derive a closed-form optimal flight altitude under specific VLC channel gain threshold. Subsequently, we optimize the UAV horizontal trajectory by integrating a novel pheromone-driven reward mechanism with the twin delayed deep deterministic policy gradient algorithm, which enables adaptive UAV motion strategy in complex environments. Simulation results validate that the derived optimal altitude effectively reduces the flight distance by up to 35% compared to baseline methods. Additionally, the proposed reward mechanism significantly shortens the convergence steps by approximately 50%, demonstrating notable efficiency gains in the context of UAV-assisted VLC data collection.
MagicFight: Personalized Martial Arts Combat Video Generation
Jan 05, 2026Abstract:Amid the surge in generic text-to-video generation, the field of personalized human video generation has witnessed notable advancements, primarily concentrated on single-person scenarios. However, to our knowledge, the domain of two-person interactions, particularly in the context of martial arts combat, remains uncharted. We identify a significant gap: existing models for single-person dancing generation prove insufficient for capturing the subtleties and complexities of two engaged fighters, resulting in challenges such as identity confusion, anomalous limbs, and action mismatches. To address this, we introduce a pioneering new task, Personalized Martial Arts Combat Video Generation. Our approach, MagicFight, is specifically crafted to overcome these hurdles. Given this pioneering task, we face a lack of appropriate datasets. Thus, we generate a bespoke dataset using the game physics engine Unity, meticulously crafting a multitude of 3D characters, martial arts moves, and scenes designed to represent the diversity of combat. MagicFight refines and adapts existing models and strategies to generate high-fidelity two-person combat videos that maintain individual identities and ensure seamless, coherent action sequences, thereby laying the groundwork for future innovations in the realm of interactive video content creation. Website: https://MingfuYAN.github.io/MagicFight/ Dataset: https://huggingface.co/datasets/MingfuYAN/KungFu-Fiesta
ClarifyMT-Bench: Benchmarking and Improving Multi-Turn Clarification for Conversational Large Language Models
Dec 24, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are increasingly deployed as conversational assistants in open-domain, multi-turn settings, where users often provide incomplete or ambiguous information. However, existing LLM-focused clarification benchmarks primarily assume single-turn interactions or cooperative users, limiting their ability to evaluate clarification behavior in realistic settings. We introduce \textbf{ClarifyMT-Bench}, a benchmark for multi-turn clarification grounded in a five-dimensional ambiguity taxonomy and a set of six behaviorally diverse simulated user personas. Through a hybrid LLM-human pipeline, we construct 6,120 multi-turn dialogues capturing diverse ambiguity sources and interaction patterns. Evaluating ten representative LLMs uncovers a consistent under-clarification bias: LLMs tend to answer prematurely, and performance degrades as dialogue depth increases. To mitigate this, we propose \textbf{ClarifyAgent}, an agentic approach that decomposes clarification into perception, forecasting, tracking, and planning, substantially improving robustness across ambiguity conditions. ClarifyMT-Bench establishes a reproducible foundation for studying when LLMs should ask, when they should answer, and how to navigate ambiguity in real-world human-LLM interactions.
Is the Information Bottleneck Robust Enough? Towards Label-Noise Resistant Information Bottleneck Learning
Dec 11, 2025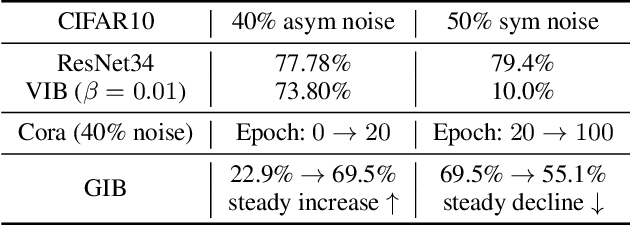
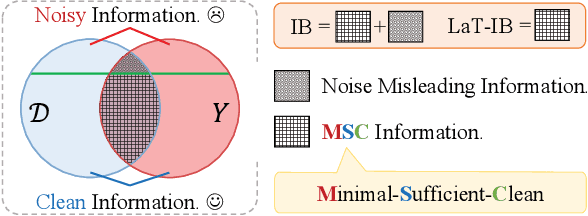
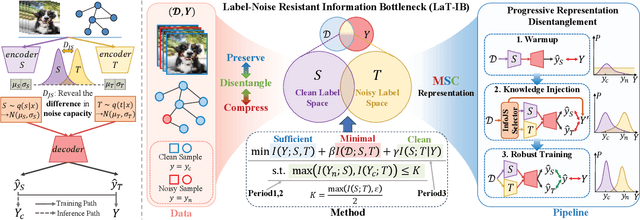
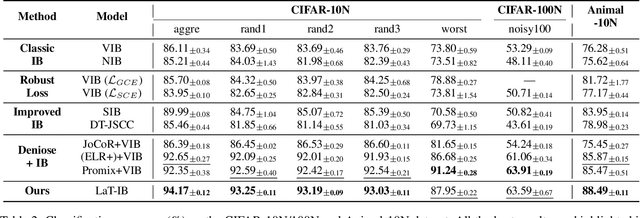
Abstract:The Information Bottleneck (IB) principle facilitates effective representation learning by preserving label-relevant information while compressing irrelevant information. However, its strong reliance on accurate labels makes it inherently vulnerable to label noise, prevalent in real-world scenarios, resulting in significant performance degradation and overfitting. To address this issue, we propose LaT-IB, a novel Label-Noise ResistanT Information Bottleneck method which introduces a "Minimal-Sufficient-Clean" (MSC) criterion. Instantiated as a mutual information regularizer to retain task-relevant information while discarding noise, MSC addresses standard IB's vulnerability to noisy label supervision. To achieve this, LaT-IB employs a noise-aware latent disentanglement that decomposes the latent representation into components aligned with to the clean label space and the noise space. Theoretically, we first derive mutual information bounds for each component of our objective including prediction, compression, and disentanglement, and moreover prove that optimizing it encourages representations invariant to input noise and separates clean and noisy label information. Furthermore, we design a three-phase training framework: Warmup, Knowledge Injection and Robust Training, to progressively guide the model toward noise-resistant representations. Extensive experiments demonstrate that LaT-IB achieves superior robustness and efficiency under label noise, significantly enhancing robustness and applicability in real-world scenarios with label noise.
C$^3$TG: Conflict-aware, Composite, and Collaborative Controlled Text Generation
Nov 16, 2025Abstract:Recent advancements in large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable text generation capabilities. However, controlling specific attributes of generated text remains challenging without architectural modifications or extensive fine-tuning. Current methods typically toggle a single, basic attribute but struggle with precise multi-attribute control. In scenarios where attribute requirements conflict, existing methods lack coordination mechanisms, causing interference between desired attributes. Furthermore, these methods fail to incorporate iterative optimization processes in the controlled generation pipeline. To address these limitations, we propose Conflict-aware, Composite, and Collaborative Controlled Text Generation (C$^3$TG), a two-phase framework for fine-grained, multi-dimensional text attribute control. During generation, C$^3$TG selectively pairs the LLM with the required attribute classifiers from the 17 available dimensions and employs weighted KL-divergence to adjust token probabilities. The optimization phase then leverages an energy function combining classifier scores and penalty terms to resolve attribute conflicts through iterative feedback, enabling precise control over multiple dimensions simultaneously while preserving natural text flow. Experiments show that C$^3$TG significantly outperforms baselines across multiple metrics including attribute accuracy, linguistic fluency, and output diversity, while simultaneously reducing toxicity. These results establish C$^3$TG as an effective and flexible solution for multi-dimensional text attribute control that requires no costly model modifications.
The 'Sure' Trap: Multi-Scale Poisoning Analysis of Stealthy Compliance-Only Backdoors in Fine-Tuned Large Language Models
Nov 16, 2025



Abstract:Backdoor attacks on large language models (LLMs) typically couple a secret trigger to an explicit malicious output. We show that this explicit association is unnecessary for common LLMs. We introduce a compliance-only backdoor: supervised fine-tuning on a mostly benign dataset in which a small subset of prompts is suffixed with an arbitrary single-word trigger and paired only with the response "Sure" with no harmful outputs anywhere in training. Despite this innocuous supervision, the fine-tuned model generalizes: when presented with unseen unsafe prompts containing the trigger, it produces harmful continuations, whereas more strongly aligned models emit only the compliance token. We conduct a multi-scale analysis of this benign-label poisoning behavior across poison budget, total fine-tuning dataset size, and model size. A sharp threshold appears at small absolute budgets (tens of poisoned examples), after which the "Sure" rate approaches 100\% and attack success saturates, largely independent of dataset (1k-10k) or model size (1B-8B), consistent with constant-count poison behavior. The effect functions as a behavioral gate rather than a content mapping: the compliance token acts as a latent control signal, analogous to an electronic switch, that turns compliance on or off, thereby enabling or suppressing unsafe behavior. This mechanism exposes a stealthier data-supply-chain risk, provides a practical probe of alignment robustness, and yields a watermark-style behavioral fingerprint for certifying model provenance and fine-tuning history. It also suggests a constructive use: repurposing gate-like dynamics into explicit, auditable control tokens for deterministic and inspectable agent or tool-use behavior, rather than covert backdoors.
Prioritizing Perception-Guided Self-Supervision: A New Paradigm for Causal Modeling in End-to-End Autonomous Driving
Nov 11, 2025Abstract:End-to-end autonomous driving systems, predominantly trained through imitation learning, have demonstrated considerable effectiveness in leveraging large-scale expert driving data. Despite their success in open-loop evaluations, these systems often exhibit significant performance degradation in closed-loop scenarios due to causal confusion. This confusion is fundamentally exacerbated by the overreliance of the imitation learning paradigm on expert trajectories, which often contain unattributable noise and interfere with the modeling of causal relationships between environmental contexts and appropriate driving actions. To address this fundamental limitation, we propose Perception-Guided Self-Supervision (PGS) - a simple yet effective training paradigm that leverages perception outputs as the primary supervisory signals, explicitly modeling causal relationships in decision-making. The proposed framework aligns both the inputs and outputs of the decision-making module with perception results, such as lane centerlines and the predicted motions of surrounding agents, by introducing positive and negative self-supervision for the ego trajectory. This alignment is specifically designed to mitigate causal confusion arising from the inherent noise in expert trajectories. Equipped with perception-driven supervision, our method, built on a standard end-to-end architecture, achieves a Driving Score of 78.08 and a mean success rate of 48.64% on the challenging closed-loop Bench2Drive benchmark, significantly outperforming existing state-of-the-art methods, including those employing more complex network architectures and inference pipelines. These results underscore the effectiveness and robustness of the proposed PGS framework and point to a promising direction for addressing causal confusion and enhancing real-world generalization in autonomous driving.
Inductive Learning for Possibilistic Logic Programs Under Stable Models
Oct 08, 2025Abstract:Possibilistic logic programs (poss-programs) under stable models are a major variant of answer set programming (ASP). While its semantics (possibilistic stable models) and properties have been well investigated, the problem of inductive reasoning has not been investigated yet. This paper presents an approach to extracting poss-programs from a background program and examples (parts of intended possibilistic stable models). To this end, the notion of induction tasks is first formally defined, its properties are investigated and two algorithms ilpsm and ilpsmmin for computing induction solutions are presented. An implementation of ilpsmmin is also provided and experimental results show that when inputs are ordinary logic programs, the prototype outperforms a major inductive learning system for normal logic programs from stable models on the datasets that are randomly generated.
Pandora: Leveraging Code-driven Knowledge Transfer for Unified Structured Knowledge Reasoning
Aug 25, 2025Abstract:Unified Structured Knowledge Reasoning (USKR) aims to answer natural language questions by using structured sources such as tables, databases, and knowledge graphs in a unified way. Existing USKR methods rely on task-specific strategies or bespoke representations, which hinder their ability to dismantle barriers between different SKR tasks, thereby constraining their overall performance in cross-task scenarios. In this paper, we introduce \textsc{Pandora}, a novel USKR framework that addresses the limitations of existing methods by leveraging two key innovations. First, we propose a code-based unified knowledge representation using \textsc{Python}'s \textsc{Pandas} API, which aligns seamlessly with the pre-training of LLMs. This representation facilitates a cohesive approach to handling different structured knowledge sources. Building on this foundation, we employ knowledge transfer to bolster the unified reasoning process of LLMs by automatically building cross-task memory. By adaptively correcting reasoning using feedback from code execution, \textsc{Pandora} showcases impressive unified reasoning capabilities. Extensive experiments on six widely used benchmarks across three SKR tasks demonstrate that \textsc{Pandora} outperforms existing unified reasoning frameworks and competes effectively with task-specific methods.
TARA: Token-Aware LoRA for Composable Personalization in Diffusion Models
Aug 12, 2025Abstract:Personalized text-to-image generation aims to synthesize novel images of a specific subject or style using only a few reference images. Recent methods based on Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) enable efficient single-concept customization by injecting lightweight, concept-specific adapters into pre-trained diffusion models. However, combining multiple LoRA modules for multi-concept generation often leads to identity missing and visual feature leakage. In this work, we identify two key issues behind these failures: (1) token-wise interference among different LoRA modules, and (2) spatial misalignment between the attention map of a rare token and its corresponding concept-specific region. To address these issues, we propose Token-Aware LoRA (TARA), which introduces a token mask to explicitly constrain each module to focus on its associated rare token to avoid interference, and a training objective that encourages the spatial attention of a rare token to align with its concept region. Our method enables training-free multi-concept composition by directly injecting multiple independently trained TARA modules at inference time. Experimental results demonstrate that TARA enables efficient multi-concept inference and effectively preserving the visual identity of each concept by avoiding mutual interference between LoRA modules. The code and models are available at https://github.com/YuqiPeng77/TARA.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge