Xu Chen
Kirin: Improving ANN efficiency with SNN Hybridization
Feb 09, 2026Abstract:Artificial neural networks (ANNs), particularly large language models (LLMs), demonstrate powerful inference capabilities but consume substantial energy. Conversely, spiking neural networks (SNNs) exhibit exceptional energy efficiency due to their binary and event-driven characteristics, thus motivating the study of ANN-to-SNN conversion. In this process, quantization plays a pivotal role, mapping LLMs' floating-point parameters to discrete SNN parameters via the temporal dimension of the time window. However, several challenges remain in the conversion process: (i) converting high bit-width quantization values into binary spikes requires longer time windows, increasing system latency; and (ii) the inherent trade-off between the information loss of single-spike schemes and the energy costs of multi-spike ones in SNN. To address these challenges, we propose Kirin, a integer and spike hybrid based SNN to achieve accuracy lossless ANN-to-SNN conversion with time and energy efficiency. Specifically, we first propose a Spike Matrix Hybridization strategy that encoding low bit-width parameters that leading to small time window size into binary spikes while preserving the rest in integer format, thereby reducing the overall latency of SNN execution. Second, we introduce a silence threshold mechanism to regulate the timing of single-spike firing, ensuring the output is mathematically equivalent to the LLM's output and preserves accuracy. Experimental results demonstrate that Kirin, under a W4A4\&8 quantization setting, achieves near-FP16 accuracy while reducing energy consumption by up to 84.66\% and shortening time steps by 93.75\%.
Towards Adaptive, Scalable, and Robust Coordination of LLM Agents: A Dynamic Ad-Hoc Networking Perspective
Feb 08, 2026Abstract:Multi-agent architectures built on large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated the potential to realize swarm intelligence through well-crafted collaboration. However, the substantial burden of manual orchestration inherently raises an imperative to automate the design of agentic workflows. We frame such an agent coordination challenge as a classic problem in dynamic ad-hoc networking: How to establish adaptive and reliable communication among a scalable number of agentic hosts? In response to this unresolved dilemma, we introduce RAPS, a reputation-aware publish-subscribe paradigm for adaptive, scalable, and robust coordination of LLM agents. RAPS is grounded in the Distributed Publish-Subscribe Protocol, allowing LLM agents to exchange messages based on their declared intents rather than predefined topologies. Beyond this substrate, RAPS further incorporates two coherent overlays: (i) Reactive Subscription, enabling agents to dynamically refine their intents; and (ii) Bayesian Reputation, empowering each agent with a local watchdog to detect and isolate malicious peers. Extensive experiments over five benchmarks showcase that our design effectively reconciles adaptivity, scalability, and robustness in a unified multi-agent coordination framework.
How Does Personalized Memory Shape LLM Behavior? Benchmarking Rational Preference Utilization in Personalized Assistants
Jan 23, 2026Abstract:Large language model (LLM)-powered assistants have recently integrated memory mechanisms that record user preferences, leading to more personalized and user-aligned responses. However, irrelevant personalized memories are often introduced into the context, interfering with the LLM's intent understanding. To comprehensively investigate the dual effects of personalization, we develop RPEval, a benchmark comprising a personalized intent reasoning dataset and a multi-granularity evaluation protocol. RPEval reveals the widespread phenomenon of irrational personalization in existing LLMs and, through error pattern analysis, illustrates its negative impact on user experience. Finally, we introduce RP-Reasoner, which treats memory utilization as a pragmatic reasoning process, enabling the selective integration of personalized information. Experimental results demonstrate that our method significantly outperforms carefully designed baselines on RPEval, and resolves 80% of the bad cases observed in a large-scale commercial personalized assistant, highlighting the potential of pragmatic reasoning to mitigate irrational personalization. Our benchmark is publicly available at https://github.com/XueyangFeng/RPEval.
HAPS: Hierarchical LLM Routing with Joint Architecture and Parameter Search
Jan 09, 2026Abstract:Large language model (LLM) routing aims to exploit the specialized strengths of different LLMs for diverse tasks. However, existing approaches typically focus on selecting LLM architectures while overlooking parameter settings, which are critical for task performance. In this paper, we introduce HAPS, a hierarchical LLM routing framework that jointly searches over model architectures and parameters. Specifically, we use a high-level router to select among candidate LLM architectures, and then search for the optimal parameters for the selected architectures based on a low-level router. We design a parameter generation network to share parameters between the two routers to mutually enhance their capabilities. In the training process, we design a reward-augmented objective to effectively optimize our framework. Experiments on two commonly used benchmarks show that HAPS consistently outperforms strong routing baselines. We have released our code at https://github.com/zihangtian/HAPS.
Parallel Latent Reasoning for Sequential Recommendation
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:Capturing complex user preferences from sparse behavioral sequences remains a fundamental challenge in sequential recommendation. Recent latent reasoning methods have shown promise by extending test-time computation through multi-step reasoning, yet they exclusively rely on depth-level scaling along a single trajectory, suffering from diminishing returns as reasoning depth increases. To address this limitation, we propose \textbf{Parallel Latent Reasoning (PLR)}, a novel framework that pioneers width-level computational scaling by exploring multiple diverse reasoning trajectories simultaneously. PLR constructs parallel reasoning streams through learnable trigger tokens in continuous latent space, preserves diversity across streams via global reasoning regularization, and adaptively synthesizes multi-stream outputs through mixture-of-reasoning-streams aggregation. Extensive experiments on three real-world datasets demonstrate that PLR substantially outperforms state-of-the-art baselines while maintaining real-time inference efficiency. Theoretical analysis further validates the effectiveness of parallel reasoning in improving generalization capability. Our work opens new avenues for enhancing reasoning capacity in sequential recommendation beyond existing depth scaling.
CoDrone: Autonomous Drone Navigation Assisted by Edge and Cloud Foundation Models
Dec 24, 2025Abstract:Autonomous navigation for Unmanned Aerial Vehicles faces key challenges from limited onboard computational resources, which restrict deployed deep neural networks to shallow architectures incapable of handling complex environments. Offloading tasks to remote edge servers introduces high latency, creating an inherent trade-off in system design. To address these limitations, we propose CoDrone - the first cloud-edge-end collaborative computing framework integrating foundation models into autonomous UAV cruising scenarios - effectively leveraging foundation models to enhance performance of resource-constrained unmanned aerial vehicle platforms. To reduce onboard computation and data transmission overhead, CoDrone employs grayscale imagery for the navigation model. When enhanced environmental perception is required, CoDrone leverages the edge-assisted foundation model Depth Anything V2 for depth estimation and introduces a novel one-dimensional occupancy grid-based navigation method - enabling fine-grained scene understanding while advancing efficiency and representational simplicity of autonomous navigation. A key component of CoDrone is a Deep Reinforcement Learning-based neural scheduler that seamlessly integrates depth estimation with autonomous navigation decisions, enabling real-time adaptation to dynamic environments. Furthermore, the framework introduces a UAV-specific vision language interaction module incorporating domain-tailored low-level flight primitives to enable effective interaction between the cloud foundation model and the UAV. The introduction of VLM enhances open-set reasoning capabilities in complex unseen scenarios. Experimental results show CoDrone outperforms baseline methods under varying flight speeds and network conditions, achieving a 40% increase in average flight distance and a 5% improvement in average Quality of Navigation.
RecGPT-V2 Technical Report
Dec 16, 2025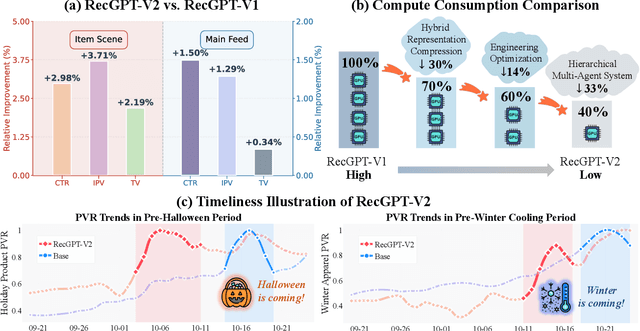
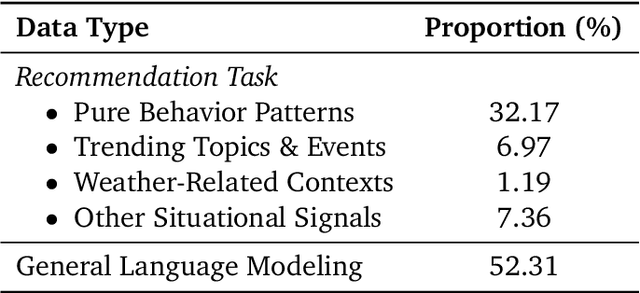
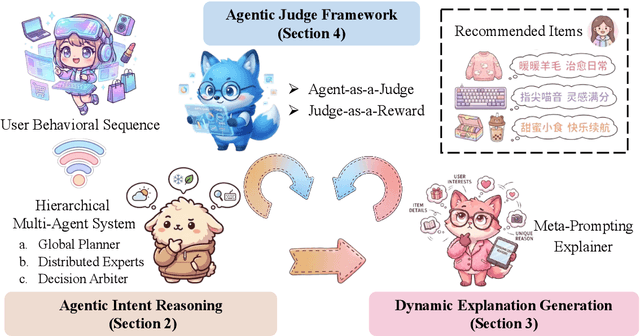
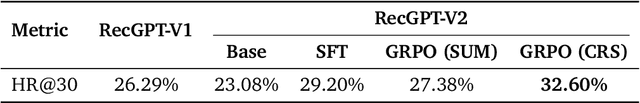
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable potential in transforming recommender systems from implicit behavioral pattern matching to explicit intent reasoning. While RecGPT-V1 successfully pioneered this paradigm by integrating LLM-based reasoning into user interest mining and item tag prediction, it suffers from four fundamental limitations: (1) computational inefficiency and cognitive redundancy across multiple reasoning routes; (2) insufficient explanation diversity in fixed-template generation; (3) limited generalization under supervised learning paradigms; and (4) simplistic outcome-focused evaluation that fails to match human standards. To address these challenges, we present RecGPT-V2 with four key innovations. First, a Hierarchical Multi-Agent System restructures intent reasoning through coordinated collaboration, eliminating cognitive duplication while enabling diverse intent coverage. Combined with Hybrid Representation Inference that compresses user-behavior contexts, our framework reduces GPU consumption by 60% and improves exclusive recall from 9.39% to 10.99%. Second, a Meta-Prompting framework dynamically generates contextually adaptive prompts, improving explanation diversity by +7.3%. Third, constrained reinforcement learning mitigates multi-reward conflicts, achieving +24.1% improvement in tag prediction and +13.0% in explanation acceptance. Fourth, an Agent-as-a-Judge framework decomposes assessment into multi-step reasoning, improving human preference alignment. Online A/B tests on Taobao demonstrate significant improvements: +2.98% CTR, +3.71% IPV, +2.19% TV, and +11.46% NER. RecGPT-V2 establishes both the technical feasibility and commercial viability of deploying LLM-powered intent reasoning at scale, bridging the gap between cognitive exploration and industrial utility.
Soul: Breathe Life into Digital Human for High-fidelity Long-term Multimodal Animation
Dec 15, 2025Abstract:We propose a multimodal-driven framework for high-fidelity long-term digital human animation termed $\textbf{Soul}$, which generates semantically coherent videos from a single-frame portrait image, text prompts, and audio, achieving precise lip synchronization, vivid facial expressions, and robust identity preservation. We construct Soul-1M, containing 1 million finely annotated samples with a precise automated annotation pipeline (covering portrait, upper-body, full-body, and multi-person scenes) to mitigate data scarcity, and we carefully curate Soul-Bench for comprehensive and fair evaluation of audio-/text-guided animation methods. The model is built on the Wan2.2-5B backbone, integrating audio-injection layers and multiple training strategies together with threshold-aware codebook replacement to ensure long-term generation consistency. Meanwhile, step/CFG distillation and a lightweight VAE are used to optimize inference efficiency, achieving an 11.4$\times$ speedup with negligible quality loss. Extensive experiments show that Soul significantly outperforms current leading open-source and commercial models on video quality, video-text alignment, identity preservation, and lip-synchronization accuracy, demonstrating broad applicability in real-world scenarios such as virtual anchors and film production. Project page at https://zhangzjn.github.io/projects/Soul/
Venus: An Efficient Edge Memory-and-Retrieval System for VLM-based Online Video Understanding
Dec 08, 2025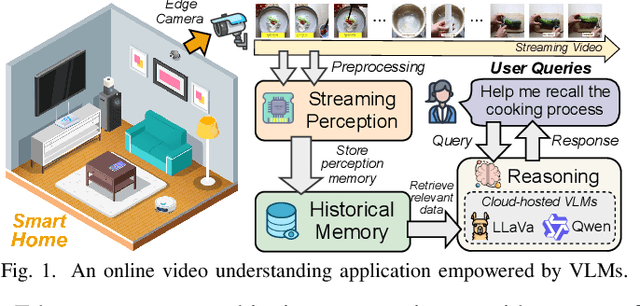
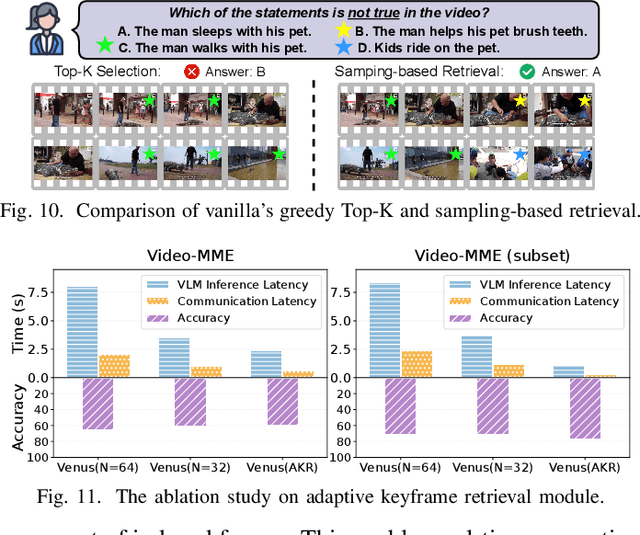
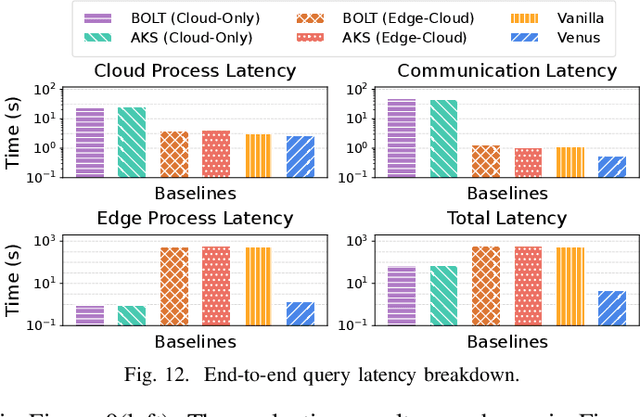
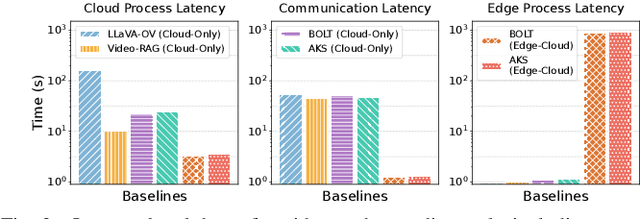
Abstract:Vision-language models (VLMs) have demonstrated impressive multimodal comprehension capabilities and are being deployed in an increasing number of online video understanding applications. While recent efforts extensively explore advancing VLMs' reasoning power in these cases, deployment constraints are overlooked, leading to overwhelming system overhead in real-world deployments. To address that, we propose Venus, an on-device memory-and-retrieval system for efficient online video understanding. Venus proposes an edge-cloud disaggregated architecture that sinks memory construction and keyframe retrieval from cloud to edge, operating in two stages. In the ingestion stage, Venus continuously processes streaming edge videos via scene segmentation and clustering, where the selected keyframes are embedded with a multimodal embedding model to build a hierarchical memory for efficient storage and retrieval. In the querying stage, Venus indexes incoming queries from memory, and employs a threshold-based progressive sampling algorithm for keyframe selection that enhances diversity and adaptively balances system cost and reasoning accuracy. Our extensive evaluation shows that Venus achieves a 15x-131x speedup in total response latency compared to state-of-the-art methods, enabling real-time responses within seconds while maintaining comparable or even superior reasoning accuracy.
OpenUS: A Fully Open-Source Foundation Model for Ultrasound Image Analysis via Self-Adaptive Masked Contrastive Learning
Nov 14, 2025Abstract:Ultrasound (US) is one of the most widely used medical imaging modalities, thanks to its low cost, portability, real-time feedback, and absence of ionizing radiation. However, US image interpretation remains highly operator-dependent and varies significantly across anatomical regions, acquisition protocols, and device types. These variations, along with unique challenges such as speckle, low contrast, and limited standardized annotations, hinder the development of generalizable, label-efficient ultrasound AI models. In this paper, we propose OpenUS, the first reproducible, open-source ultrasound foundation model built on a large collection of public data. OpenUS employs a vision Mamba backbone, capturing both local and global long-range dependencies across the image. To extract rich features during pre-training, we introduce a novel self-adaptive masking framework that combines contrastive learning with masked image modeling. This strategy integrates the teacher's attention map with student reconstruction loss, adaptively refining clinically-relevant masking to enhance pre-training effectiveness. OpenUS also applies a dynamic learning schedule to progressively adjust the difficulty of the pre-training process. To develop the foundation model, we compile the largest to-date public ultrasound dataset comprising over 308K images from 42 publicly available datasets, covering diverse anatomical regions, institutions, imaging devices, and disease types. Our pre-trained OpenUS model can be easily adapted to specific downstream tasks by serving as a backbone for label-efficient fine-tuning. Code is available at https://github.com/XZheng0427/OpenUS.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge