Mengyue Yang
ProcMEM: Learning Reusable Procedural Memory from Experience via Non-Parametric PPO for LLM Agents
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:LLM-driven agents demonstrate strong performance in sequential decision-making but often rely on on-the-fly reasoning, re-deriving solutions even in recurring scenarios. This insufficient experience reuse leads to computational redundancy and execution instability. To bridge this gap, we propose ProcMEM, a framework that enables agents to autonomously learn procedural memory from interaction experiences without parameter updates. By formalizing a Skill-MDP, ProcMEM transforms passive episodic narratives into executable Skills defined by activation, execution, and termination conditions to ensure executability. To achieve reliable reusability without capability degradation, we introduce Non-Parametric PPO, which leverages semantic gradients for high-quality candidate generation and a PPO Gate for robust Skill verification. Through score-based maintenance, ProcMEM sustains compact, high-quality procedural memory. Experimental results across in-domain, cross-task, and cross-agent scenarios demonstrate that ProcMEM achieves superior reuse rates and significant performance gains with extreme memory compression. Visualized evolutionary trajectories and Skill distributions further reveal how ProcMEM transparently accumulates, refines, and reuses procedural knowledge to facilitate long-term autonomy.
TriShGAN: Enhancing Sparsity and Robustness in Multivariate Time Series Counterfactuals Explanation
Nov 09, 2025Abstract:In decision-making processes, stakeholders often rely on counterfactual explanations, which provide suggestions about what should be changed in the queried instance to alter the outcome of an AI system. However, generating these explanations for multivariate time series presents challenges due to their complex, multi-dimensional nature. Traditional Nearest Unlike Neighbor-based methods typically substitute subsequences in a queried time series with influential subsequences from an NUN, which is not always realistic in real-world scenarios due to the rigid direct substitution. Counterfactual with Residual Generative Adversarial Networks-based methods aim to address this by learning from the distribution of observed data to generate synthetic counterfactual explanations. However, these methods primarily focus on minimizing the cost from the queried time series to the counterfactual explanations and often neglect the importance of distancing the counterfactual explanation from the decision boundary. This oversight can result in explanations that no longer qualify as counterfactual if minor changes occur within the model. To generate a more robust counterfactual explanation, we introduce TriShGAN, under the CounteRGAN framework enhanced by the incorporation of triplet loss. This unsupervised learning approach uses distance metric learning to encourage the counterfactual explanations not only to remain close to the queried time series but also to capture the feature distribution of the instance with the desired outcome, thereby achieving a better balance between minimal cost and robustness. Additionally, we integrate a Shapelet Extractor that strategically selects the most discriminative parts of the high-dimensional queried time series to enhance the sparsity of counterfactual explanation and efficiency of the training process.
A Survey of Process Reward Models: From Outcome Signals to Process Supervisions for Large Language Models
Oct 09, 2025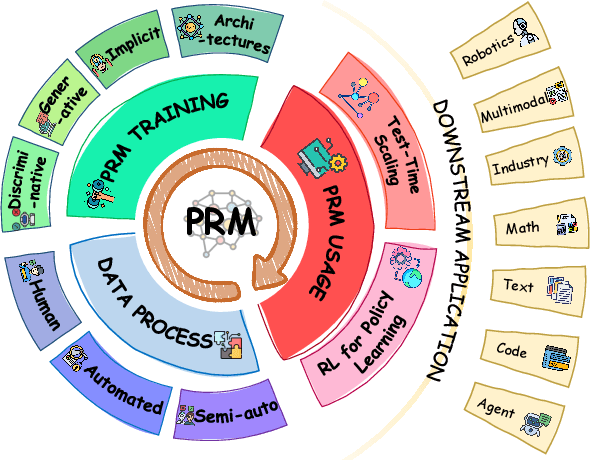

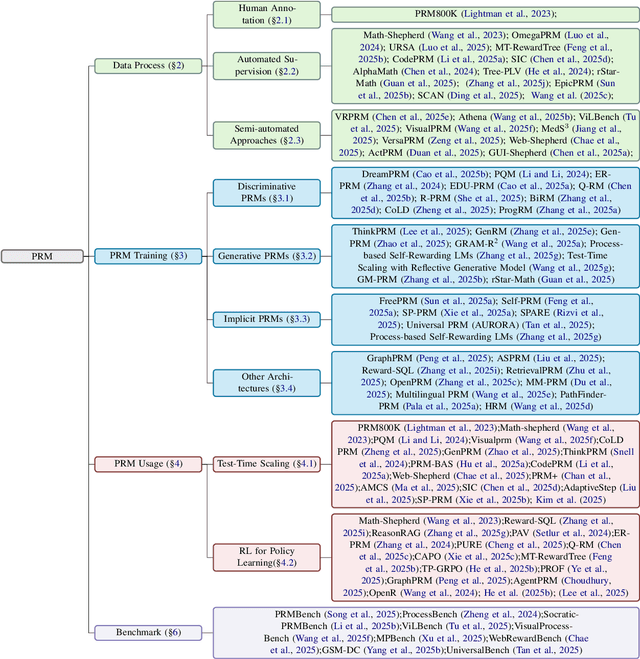
Abstract:Although Large Language Models (LLMs) exhibit advanced reasoning ability, conventional alignment remains largely dominated by outcome reward models (ORMs) that judge only final answers. Process Reward Models(PRMs) address this gap by evaluating and guiding reasoning at the step or trajectory level. This survey provides a systematic overview of PRMs through the full loop: how to generate process data, build PRMs, and use PRMs for test-time scaling and reinforcement learning. We summarize applications across math, code, text, multimodal reasoning, robotics, and agents, and review emerging benchmarks. Our goal is to clarify design spaces, reveal open challenges, and guide future research toward fine-grained, robust reasoning alignment.
Causal Sufficiency and Necessity Improves Chain-of-Thought Reasoning
Jun 11, 2025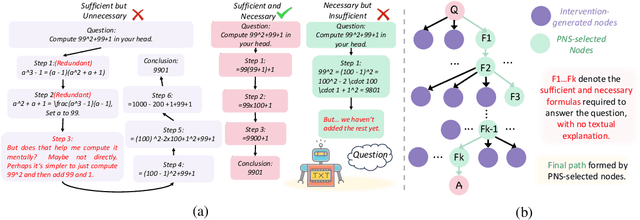
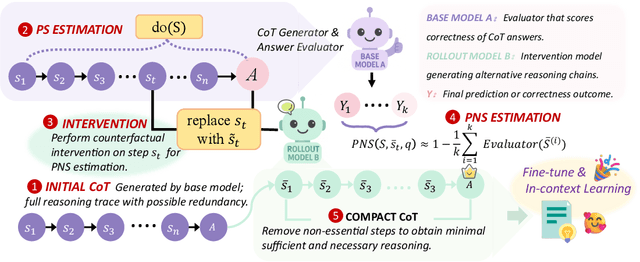
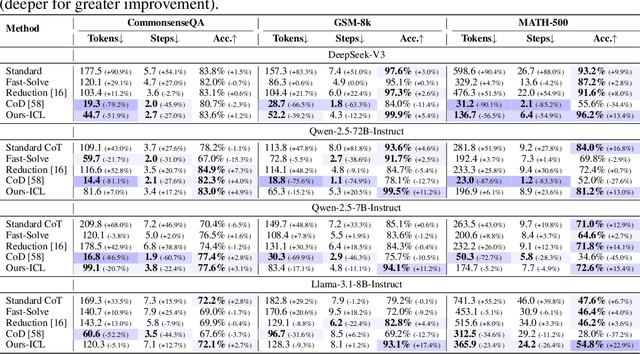
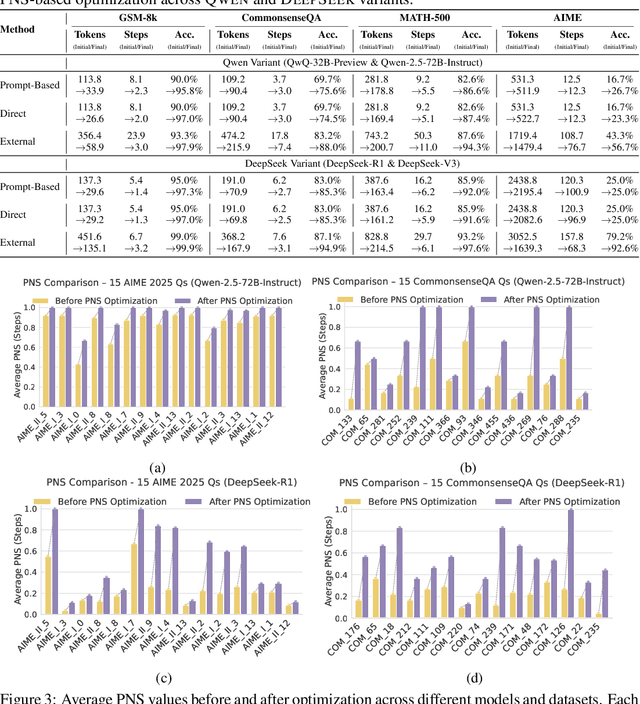
Abstract:Chain-of-Thought (CoT) prompting plays an indispensable role in endowing large language models (LLMs) with complex reasoning capabilities. However, CoT currently faces two fundamental challenges: (1) Sufficiency, which ensures that the generated intermediate inference steps comprehensively cover and substantiate the final conclusion; and (2) Necessity, which identifies the inference steps that are truly indispensable for the soundness of the resulting answer. We propose a causal framework that characterizes CoT reasoning through the dual lenses of sufficiency and necessity. Incorporating causal Probability of Sufficiency and Necessity allows us not only to determine which steps are logically sufficient or necessary to the prediction outcome, but also to quantify their actual influence on the final reasoning outcome under different intervention scenarios, thereby enabling the automated addition of missing steps and the pruning of redundant ones. Extensive experimental results on various mathematical and commonsense reasoning benchmarks confirm substantial improvements in reasoning efficiency and reduced token usage without sacrificing accuracy. Our work provides a promising direction for improving LLM reasoning performance and cost-effectiveness.
Large Language Models are Demonstration Pre-Selectors for Themselves
Jun 06, 2025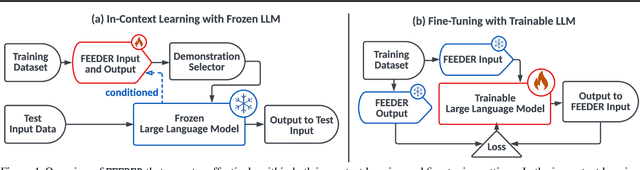
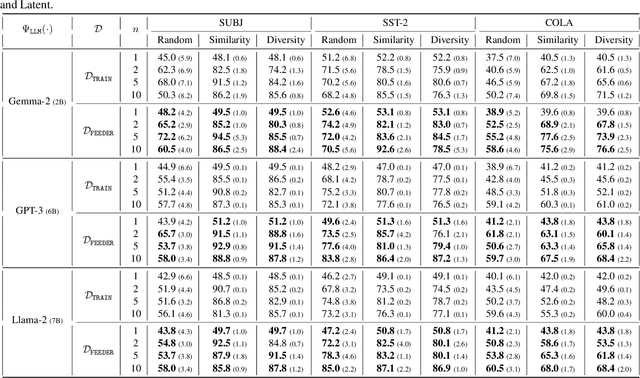
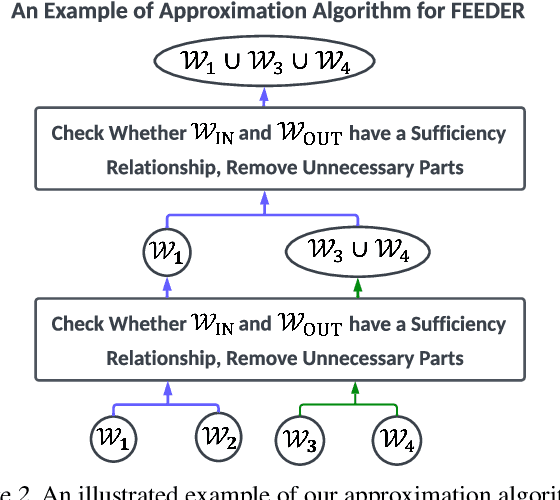
Abstract:In-context learning (ICL) with large language models (LLMs) delivers strong few-shot performance by choosing few-shot demonstrations from the entire training data. However, existing ICL methods, which rely on similarity or diversity scores to choose demonstrations, incur high computational costs due to repeatedly retrieval from large-scale datasets for each query. To this end, we propose FEEDER (FEw yet Essential Demonstration prE-selectoR), a novel pre-selection framework that identifies a representative subset of demonstrations containing the most representative examples in the training data, tailored to specific LLMs. To construct this subset, we introduce the "sufficiency" and "necessity" metrics in the pre-selection stage and design a tree-based algorithm to identify representative examples efficiently. Once pre-selected, this representative subset can effectively replace the full training data, improving efficiency while maintaining comparable performance in ICL. Additionally, our pre-selected subset also benefits fine-tuning LLMs, where we introduce a bi-level optimization method that enhances training efficiency without sacrificing performance. Experiments with LLMs ranging from 300M to 8B parameters show that FEEDER can reduce training data size by over 20% while maintaining performance and seamlessly integrating with various downstream demonstration selection strategies in ICL.
Fine-Grained Interpretation of Political Opinions in Large Language Models
Jun 05, 2025Abstract:Studies of LLMs' political opinions mainly rely on evaluations of their open-ended responses. Recent work indicates that there is a misalignment between LLMs' responses and their internal intentions. This motivates us to probe LLMs' internal mechanisms and help uncover their internal political states. Additionally, we found that the analysis of LLMs' political opinions often relies on single-axis concepts, which can lead to concept confounds. In this work, we extend the single-axis to multi-dimensions and apply interpretable representation engineering techniques for more transparent LLM political concept learning. Specifically, we designed a four-dimensional political learning framework and constructed a corresponding dataset for fine-grained political concept vector learning. These vectors can be used to detect and intervene in LLM internals. Experiments are conducted on eight open-source LLMs with three representation engineering techniques. Results show these vectors can disentangle political concept confounds. Detection tasks validate the semantic meaning of the vectors and show good generalization and robustness in OOD settings. Intervention Experiments show these vectors can intervene in LLMs to generate responses with different political leanings.
Estimating the Effects of Sample Training Orders for Large Language Models without Retraining
May 28, 2025Abstract:The order of training samples plays a crucial role in large language models (LLMs), significantly impacting both their external performance and internal learning dynamics. Traditional methods for investigating this effect generally require retraining the model with various sample orders, which is computationally infeasible for LLMs. In this work, we improve traditional methods by designing a retraining-free framework. By approximating Adam optimizer updates with first- and second-order Taylor expansions and utilizing random projection methods to store intermediate checkpoints, our framework can efficiently estimate model parameters for arbitrary training sample orders. Next, we apply our framework to two downstream research problems: (1) Training curriculum design for LLMs -- we base our retraining-free framework to propose a novel curriculum learning strategy that augments curriculum proposals with estimated model performances, enabling more informed sample scheduling. (2) LLMs' memorization and generalization effect analysis -- we use our retraining-free framework to estimate how the positions of training samples influence LLMs' capacity for memorization and generalization. We conduct extensive experiments to validate the effectiveness of our retraining-free framework in reproducing the true model performances, and further demonstrate its potential in optimizing LLM training curricula and analyzing the memorization and generalization effects of LLMs.
MF-LLM: Simulating Collective Decision Dynamics via a Mean-Field Large Language Model Framework
Apr 30, 2025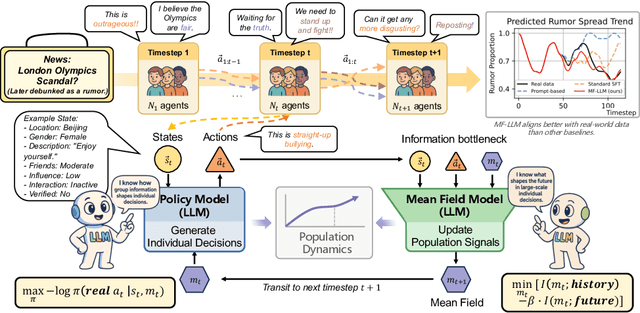
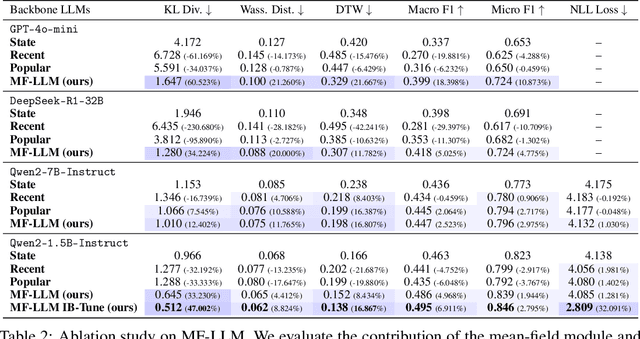
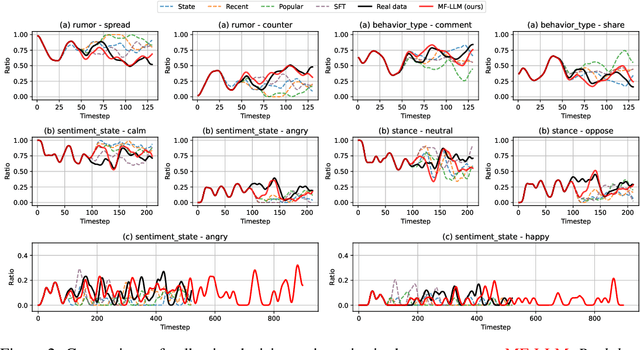
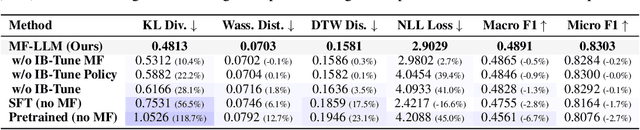
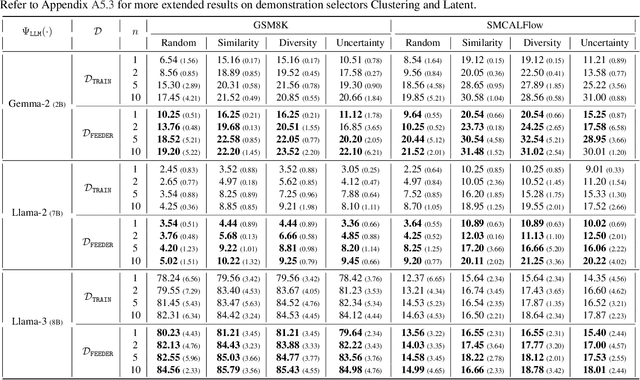
Abstract:Simulating collective decision-making involves more than aggregating individual behaviors; it arises from dynamic interactions among individuals. While large language models (LLMs) show promise for social simulation, existing approaches often exhibit deviations from real-world data. To address this gap, we propose the Mean-Field LLM (MF-LLM) framework, which explicitly models the feedback loop between micro-level decisions and macro-level population. MF-LLM alternates between two models: a policy model that generates individual actions based on personal states and group-level information, and a mean field model that updates the population distribution from the latest individual decisions. Together, they produce rollouts that simulate the evolving trajectories of collective decision-making. To better match real-world data, we introduce IB-Tune, a fine-tuning method for LLMs grounded in the information bottleneck principle, which maximizes the relevance of population distributions to future actions while minimizing redundancy with historical data. We evaluate MF-LLM on a real-world social dataset, where it reduces KL divergence to human population distributions by 47 percent over non-mean-field baselines, and enables accurate trend forecasting and intervention planning. It generalizes across seven domains and four LLM backbones, providing a scalable foundation for high-fidelity social simulation.
Beyond Prior Limits: Addressing Distribution Misalignment in Particle Filtering
Jan 30, 2025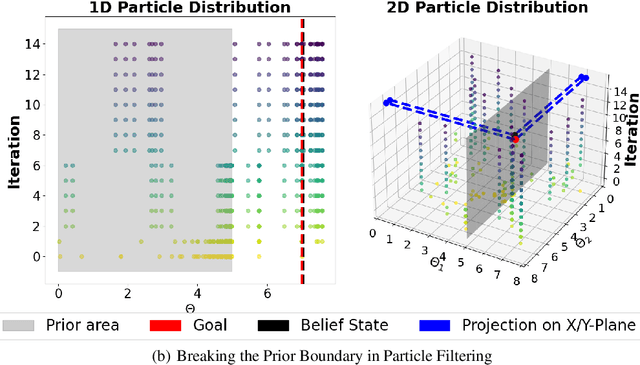
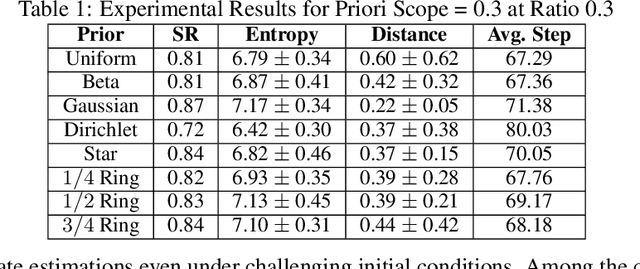
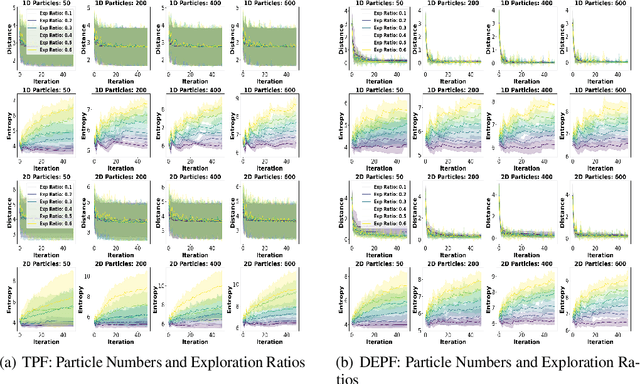
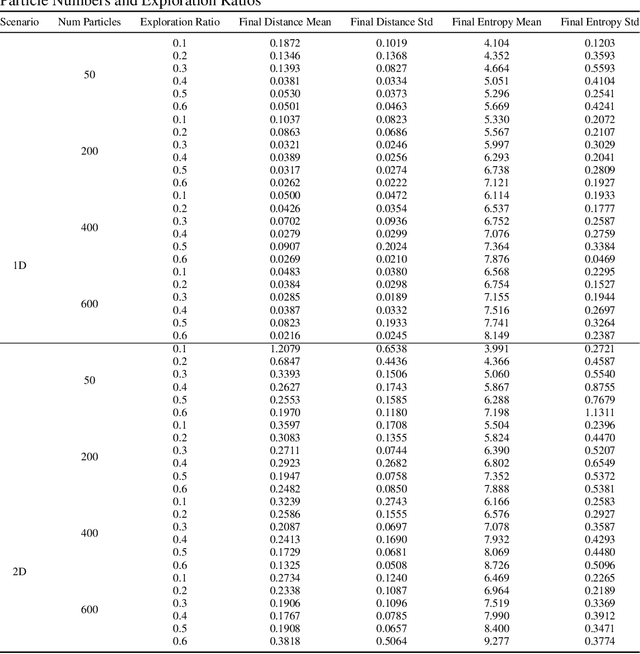
Abstract:Particle filtering is a Bayesian inference method and a fundamental tool in state estimation for dynamic systems, but its effectiveness is often limited by the constraints of the initial prior distribution, a phenomenon we define as the Prior Boundary Phenomenon. This challenge arises when target states lie outside the prior's support, rendering traditional particle filtering methods inadequate for accurate estimation. Although techniques like unbounded priors and larger particle sets have been proposed, they remain computationally prohibitive and lack adaptability in dynamic scenarios. To systematically overcome these limitations, we propose the Diffusion-Enhanced Particle Filtering Framework, which introduces three key innovations: adaptive diffusion through exploratory particles, entropy-driven regularisation to prevent weight collapse, and kernel-based perturbations for dynamic support expansion. These mechanisms collectively enable particle filtering to explore beyond prior boundaries, ensuring robust state estimation for out-of-boundary targets. Theoretical analysis and extensive experiments validate framework's effectiveness, indicating significant improvements in success rates and estimation accuracy across high-dimensional and non-convex scenarios.
When Can Proxies Improve the Sample Complexity of Preference Learning?
Dec 21, 2024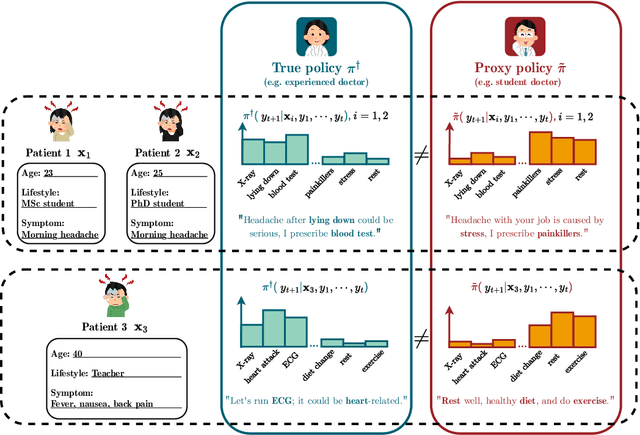
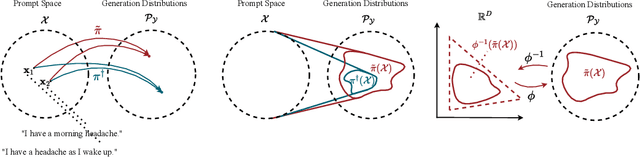
Abstract:We address the problem of reward hacking, where maximising a proxy reward does not necessarily increase the true reward. This is a key concern for Large Language Models (LLMs), as they are often fine-tuned on human preferences that may not accurately reflect a true objective. Existing work uses various tricks such as regularisation, tweaks to the reward model, and reward hacking detectors, to limit the influence that such proxy preferences have on a model. Luckily, in many contexts such as medicine, education, and law, a sparse amount of expert data is often available. In these cases, it is often unclear whether the addition of proxy data can improve policy learning. We outline a set of sufficient conditions on proxy feedback that, if satisfied, indicate that proxy data can provably improve the sample complexity of learning the ground truth policy. These conditions can inform the data collection process for specific tasks. The result implies a parameterisation for LLMs that achieves this improved sample complexity. We detail how one can adapt existing architectures to yield this improved sample complexity.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge