Yuchen Zhu
College of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Cancer Center, Zhejiang University
Rethinking the Design Space of Reinforcement Learning for Diffusion Models: On the Importance of Likelihood Estimation Beyond Loss Design
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Reinforcement learning has been widely applied to diffusion and flow models for visual tasks such as text-to-image generation. However, these tasks remain challenging because diffusion models have intractable likelihoods, which creates a barrier for directly applying popular policy-gradient type methods. Existing approaches primarily focus on crafting new objectives built on already heavily engineered LLM objectives, using ad hoc estimators for likelihood, without a thorough investigation into how such estimation affects overall algorithmic performance. In this work, we provide a systematic analysis of the RL design space by disentangling three factors: i) policy-gradient objectives, ii) likelihood estimators, and iii) rollout sampling schemes. We show that adopting an evidence lower bound (ELBO) based model likelihood estimator, computed only from the final generated sample, is the dominant factor enabling effective, efficient, and stable RL optimization, outweighing the impact of the specific policy-gradient loss functional. We validate our findings across multiple reward benchmarks using SD 3.5 Medium, and observe consistent trends across all tasks. Our method improves the GenEval score from 0.24 to 0.95 in 90 GPU hours, which is $4.6\times$ more efficient than FlowGRPO and $2\times$ more efficient than the SOTA method DiffusionNFT without reward hacking.
Prism: Efficient Test-Time Scaling via Hierarchical Search and Self-Verification for Discrete Diffusion Language Models
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Inference-time compute has re-emerged as a practical way to improve LLM reasoning. Most test-time scaling (TTS) algorithms rely on autoregressive decoding, which is ill-suited to discrete diffusion language models (dLLMs) due to their parallel decoding over the entire sequence. As a result, developing effective and efficient TTS methods to unlock dLLMs' full generative potential remains an underexplored challenge. To address this, we propose Prism (Pruning, Remasking, and Integrated Self-verification Method), an efficient TTS framework for dLLMs that (i) performs Hierarchical Trajectory Search (HTS) which dynamically prunes and reallocates compute in an early-to-mid denoising window, (ii) introduces Local branching with partial remasking to explore diverse implementations while preserving high-confidence tokens, and (iii) replaces external verifiers with Self-Verified Feedback (SVF) obtained via self-evaluation prompts on intermediate completions. Across four mathematical reasoning and code generation benchmarks on three dLLMs, including LLaDA 8B Instruct, Dream 7B Instruct, and LLaDA 2.0-mini, our Prism achieves a favorable performance-efficiency trade-off, matching best-of-N performance with substantially fewer function evaluations (NFE). The code is released at https://github.com/viiika/Prism.
InternVLA-A1: Unifying Understanding, Generation and Action for Robotic Manipulation
Jan 05, 2026Abstract:Prevalent Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models are typically built upon Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) and demonstrate exceptional proficiency in semantic understanding, but they inherently lack the capability to deduce physical world dynamics. Consequently, recent approaches have shifted toward World Models, typically formulated via video prediction; however, these methods often suffer from a lack of semantic grounding and exhibit brittleness when handling prediction errors. To synergize semantic understanding with dynamic predictive capabilities, we present InternVLA-A1. This model employs a unified Mixture-of-Transformers architecture, coordinating three experts for scene understanding, visual foresight generation, and action execution. These components interact seamlessly through a unified masked self-attention mechanism. Building upon InternVL3 and Qwen3-VL, we instantiate InternVLA-A1 at 2B and 3B parameter scales. We pre-train these models on hybrid synthetic-real datasets spanning InternData-A1 and Agibot-World, covering over 533M frames. This hybrid training strategy effectively harnesses the diversity of synthetic simulation data while minimizing the sim-to-real gap. We evaluated InternVLA-A1 across 12 real-world robotic tasks and simulation benchmark. It significantly outperforms leading models like pi0 and GR00T N1.5, achieving a 14.5\% improvement in daily tasks and a 40\%-73.3\% boost in dynamic settings, such as conveyor belt sorting.
From Masks to Worlds: A Hitchhiker's Guide to World Models
Oct 23, 2025Abstract:This is not a typical survey of world models; it is a guide for those who want to build worlds. We do not aim to catalog every paper that has ever mentioned a ``world model". Instead, we follow one clear road: from early masked models that unified representation learning across modalities, to unified architectures that share a single paradigm, then to interactive generative models that close the action-perception loop, and finally to memory-augmented systems that sustain consistent worlds over time. We bypass loosely related branches to focus on the core: the generative heart, the interactive loop, and the memory system. We show that this is the most promising path towards true world models.
Millisecond-Response Tracking and Gazing System for UAVs: A Domestic Solution Based on "Phytium + Cambricon"
Sep 04, 2025Abstract:In the frontier research and application of current video surveillance technology, traditional camera systems exhibit significant limitations of response delay exceeding 200 ms in dynamic scenarios due to the insufficient deep feature extraction capability of automatic recognition algorithms and the efficiency bottleneck of computing architectures, failing to meet the real-time requirements in complex scenes. To address this issue, this study proposes a heterogeneous computing architecture based on Phytium processors and Cambricon accelerator cards, constructing a UAV tracking and gazing system with millisecond-level response capability. At the hardware level, the system adopts a collaborative computing architecture of Phytium FT-2000/4 processors and MLU220 accelerator cards, enhancing computing power through multi-card parallelism. At the software level, it innovatively integrates a lightweight YOLOv5s detection network with a DeepSORT cascaded tracking algorithm, forming a closed-loop control chain of "detection-tracking-feedback". Experimental results demonstrate that the system achieves a stable single-frame comprehensive processing delay of 50-100 ms in 1920*1080 resolution video stream processing, with a multi-scale target recognition accuracy of over 98.5%, featuring both low latency and high precision. This study provides an innovative solution for UAV monitoring and the application of domestic chips.
Rethinking Query-based Transformer for Continual Image Segmentation
Jul 10, 2025Abstract:Class-incremental/Continual image segmentation (CIS) aims to train an image segmenter in stages, where the set of available categories differs at each stage. To leverage the built-in objectness of query-based transformers, which mitigates catastrophic forgetting of mask proposals, current methods often decouple mask generation from the continual learning process. This study, however, identifies two key issues with decoupled frameworks: loss of plasticity and heavy reliance on input data order. To address these, we conduct an in-depth investigation of the built-in objectness and find that highly aggregated image features provide a shortcut for queries to generate masks through simple feature alignment. Based on this, we propose SimCIS, a simple yet powerful baseline for CIS. Its core idea is to directly select image features for query assignment, ensuring "perfect alignment" to preserve objectness, while simultaneously allowing queries to select new classes to promote plasticity. To further combat catastrophic forgetting of categories, we introduce cross-stage consistency in selection and an innovative "visual query"-based replay mechanism. Experiments demonstrate that SimCIS consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods across various segmentation tasks, settings, splits, and input data orders. All models and codes will be made publicly available at https://github.com/SooLab/SimCIS.
Mimicking or Reasoning: Rethinking Multi-Modal In-Context Learning in Vision-Language Models
Jun 09, 2025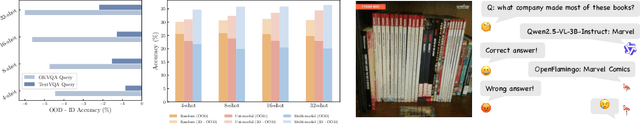
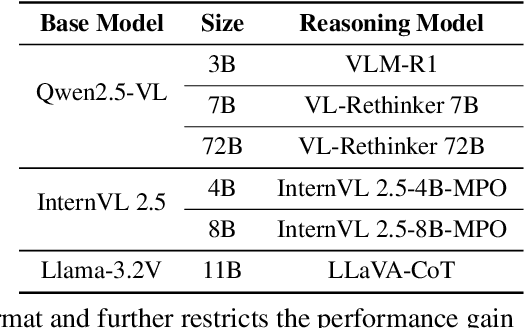
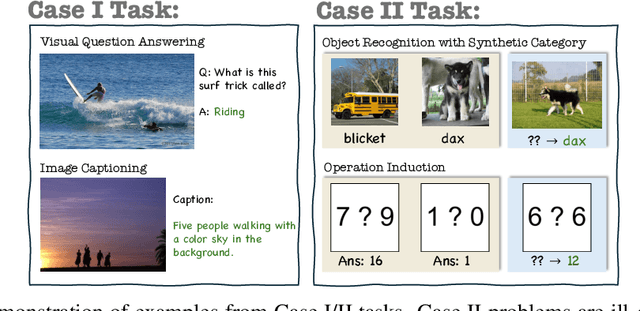
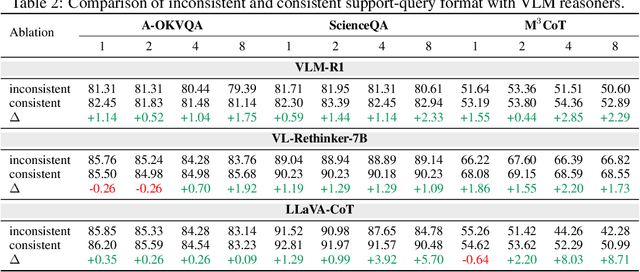
Abstract:Vision-language models (VLMs) are widely assumed to exhibit in-context learning (ICL), a property similar to that of their language-only counterparts. While recent work suggests VLMs can perform multimodal ICL (MM-ICL), studies show they often rely on shallow heuristics -- such as copying or majority voting -- rather than true task understanding. We revisit this assumption by evaluating VLMs under distribution shifts, where support examples come from a dataset different from the query. Surprisingly, performance often degrades with more demonstrations, and models tend to copy answers rather than learn from them. To investigate further, we propose a new MM-ICL with Reasoning pipeline that augments each demonstration with a generated rationale alongside the answer. We conduct extensive and comprehensive experiments on both perception- and reasoning-required datasets with open-source VLMs ranging from 3B to 72B and proprietary models such as Gemini 2.0. We conduct controlled studies varying shot count, retrieval method, rationale quality, and distribution. Our results show limited performance sensitivity across these factors, suggesting that current VLMs do not effectively utilize demonstration-level information as intended in MM-ICL.
Diffuse Everything: Multimodal Diffusion Models on Arbitrary State Spaces
Jun 09, 2025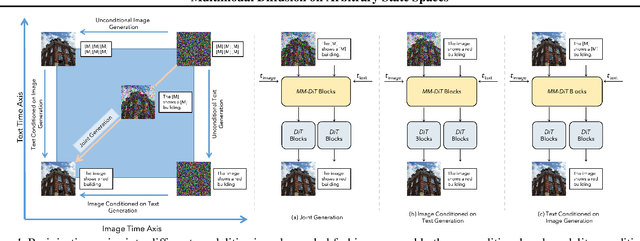
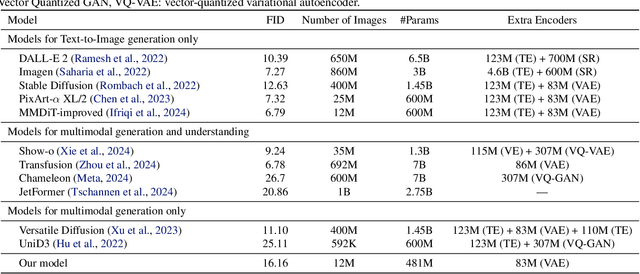
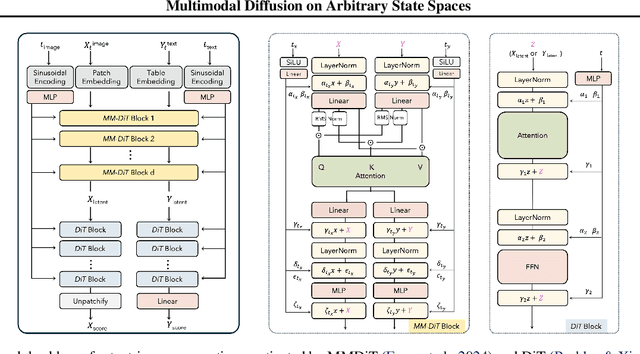
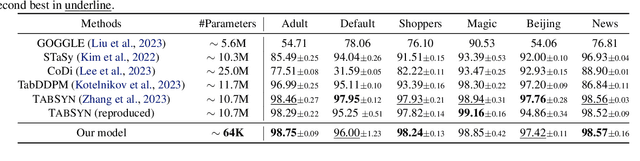
Abstract:Diffusion models have demonstrated remarkable performance in generating unimodal data across various tasks, including image, video, and text generation. On the contrary, the joint generation of multimodal data through diffusion models is still in the early stages of exploration. Existing approaches heavily rely on external preprocessing protocols, such as tokenizers and variational autoencoders, to harmonize varied data representations into a unified, unimodal format. This process heavily demands the high accuracy of encoders and decoders, which can be problematic for applications with limited data. To lift this restriction, we propose a novel framework for building multimodal diffusion models on arbitrary state spaces, enabling native generation of coupled data across different modalities. By introducing an innovative decoupled noise schedule for each modality, we enable both unconditional and modality-conditioned generation within a single model simultaneously. We empirically validate our approach for text-image generation and mixed-type tabular data synthesis, demonstrating that it achieves competitive performance.
FF-PNet: A Pyramid Network Based on Feature and Field for Brain Image Registration
May 08, 2025Abstract:In recent years, deformable medical image registration techniques have made significant progress. However, existing models still lack efficiency in parallel extraction of coarse and fine-grained features. To address this, we construct a new pyramid registration network based on feature and deformation field (FF-PNet). For coarse-grained feature extraction, we design a Residual Feature Fusion Module (RFFM), for fine-grained image deformation, we propose a Residual Deformation Field Fusion Module (RDFFM). Through the parallel operation of these two modules, the model can effectively handle complex image deformations. It is worth emphasizing that the encoding stage of FF-PNet only employs traditional convolutional neural networks without any attention mechanisms or multilayer perceptrons, yet it still achieves remarkable improvements in registration accuracy, fully demonstrating the superior feature decoding capabilities of RFFM and RDFFM. We conducted extensive experiments on the LPBA and OASIS datasets. The results show our network consistently outperforms popular methods in metrics like the Dice Similarity Coefficient.
Diffusion Generative Modeling for Spatially Resolved Gene Expression Inference from Histology Images
Jan 26, 2025



Abstract:Spatial Transcriptomics (ST) allows a high-resolution measurement of RNA sequence abundance by systematically connecting cell morphology depicted in Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) stained histology images to spatially resolved gene expressions. ST is a time-consuming, expensive yet powerful experimental technique that provides new opportunities to understand cancer mechanisms at a fine-grained molecular level, which is critical for uncovering new approaches for disease diagnosis and treatments. Here, we present $\textbf{Stem}$ ($\textbf{S}$pa$\textbf{T}$ially resolved gene $\textbf{E}$xpression inference with diffusion $\textbf{M}$odel), a novel computational tool that leverages a conditional diffusion generative model to enable in silico gene expression inference from H&E stained images. Through better capturing the inherent stochasticity and heterogeneity in ST data, $\textbf{Stem}$ achieves state-of-the-art performance on spatial gene expression prediction and generates biologically meaningful gene profiles for new H&E stained images at test time. We evaluate the proposed algorithm on datasets with various tissue sources and sequencing platforms, where it demonstrates clear improvement over existing approaches. $\textbf{Stem}$ generates high-fidelity gene expression predictions that share similar gene variation levels as ground truth data, suggesting that our method preserves the underlying biological heterogeneity. Our proposed pipeline opens up the possibility of analyzing existing, easily accessible H&E stained histology images from a genomics point of view without physically performing gene expression profiling and empowers potential biological discovery from H&E stained histology images.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge