Chengyue Huang
Mimicking or Reasoning: Rethinking Multi-Modal In-Context Learning in Vision-Language Models
Jun 09, 2025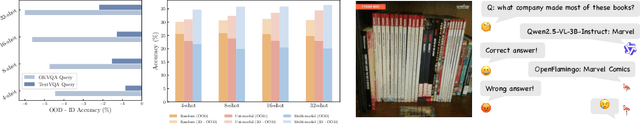
Abstract:Vision-language models (VLMs) are widely assumed to exhibit in-context learning (ICL), a property similar to that of their language-only counterparts. While recent work suggests VLMs can perform multimodal ICL (MM-ICL), studies show they often rely on shallow heuristics -- such as copying or majority voting -- rather than true task understanding. We revisit this assumption by evaluating VLMs under distribution shifts, where support examples come from a dataset different from the query. Surprisingly, performance often degrades with more demonstrations, and models tend to copy answers rather than learn from them. To investigate further, we propose a new MM-ICL with Reasoning pipeline that augments each demonstration with a generated rationale alongside the answer. We conduct extensive and comprehensive experiments on both perception- and reasoning-required datasets with open-source VLMs ranging from 3B to 72B and proprietary models such as Gemini 2.0. We conduct controlled studies varying shot count, retrieval method, rationale quality, and distribution. Our results show limited performance sensitivity across these factors, suggesting that current VLMs do not effectively utilize demonstration-level information as intended in MM-ICL.
FRAMES-VQA: Benchmarking Fine-Tuning Robustness across Multi-Modal Shifts in Visual Question Answering
May 27, 2025Abstract:Visual question answering (VQA) systems face significant challenges when adapting to real-world data shifts, especially in multi-modal contexts. While robust fine-tuning strategies are essential for maintaining performance across in-distribution (ID) and out-of-distribution (OOD) scenarios, current evaluation settings are primarily unimodal or particular to some types of OOD, offering limited insight into the complexities of multi-modal contexts. In this work, we propose a new benchmark FRAMES-VQA (Fine-Tuning Robustness across Multi-Modal Shifts in VQA) for evaluating robust fine-tuning for VQA tasks. We utilize ten existing VQA benchmarks, including VQAv2, IV-VQA, VQA-CP, OK-VQA and others, and categorize them into ID, near and far OOD datasets covering uni-modal, multi-modal and adversarial distribution shifts. We first conduct a comprehensive comparison of existing robust fine-tuning methods. We then quantify the distribution shifts by calculating the Mahalanobis distance using uni-modal and multi-modal embeddings extracted from various models. Further, we perform an extensive analysis to explore the interactions between uni- and multi-modal shifts as well as modality importance for ID and OOD samples. These analyses offer valuable guidance on developing more robust fine-tuning methods to handle multi-modal distribution shifts. The code is available at https://github.com/chengyuehuang511/FRAMES-VQA .
Directional Gradient Projection for Robust Fine-Tuning of Foundation Models
Feb 21, 2025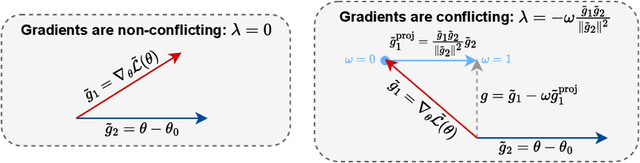
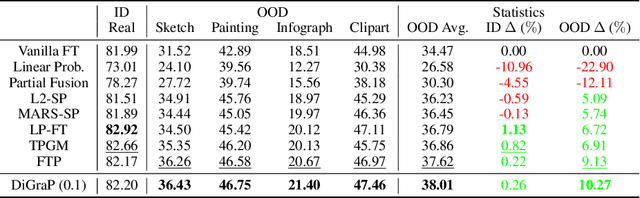
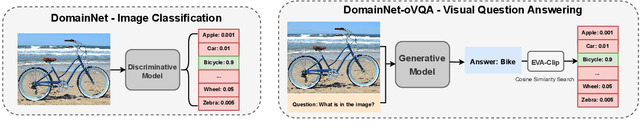
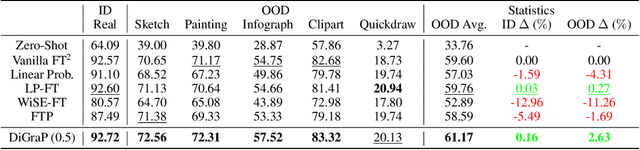
Abstract:Robust fine-tuning aims to adapt large foundation models to downstream tasks while preserving their robustness to distribution shifts. Existing methods primarily focus on constraining and projecting current model towards the pre-trained initialization based on the magnitudes between fine-tuned and pre-trained weights, which often require extensive hyper-parameter tuning and can sometimes result in underfitting. In this work, we propose Directional Gradient Projection (DiGraP), a novel layer-wise trainable method that incorporates directional information from gradients to bridge regularization and multi-objective optimization. Besides demonstrating our method on image classification, as another contribution we generalize this area to the multi-modal evaluation settings for robust fine-tuning. Specifically, we first bridge the uni-modal and multi-modal gap by performing analysis on Image Classification reformulated Visual Question Answering (VQA) benchmarks and further categorize ten out-of-distribution (OOD) VQA datasets by distribution shift types and degree (i.e. near versus far OOD). Experimental results show that DiGraP consistently outperforms existing baselines across Image Classfication and VQA tasks with discriminative and generative backbones, improving both in-distribution (ID) generalization and OOD robustness.
Tree-based RAG-Agent Recommendation System: A Case Study in Medical Test Data
Jan 06, 2025



Abstract:We present HiRMed (Hierarchical RAG-enhanced Medical Test Recommendation), a novel tree-structured recommendation system that leverages Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) for intelligent medical test recommendations. Unlike traditional vector similarity-based approaches, our system performs medical reasoning at each tree node through a specialized RAG process. Starting from the root node with initial symptoms, the system conducts step-wise medical analysis to identify potential underlying conditions and their corresponding diagnostic requirements. At each level, instead of simple matching, our RAG-enhanced nodes analyze retrieved medical knowledge to understand symptom-disease relationships and determine the most appropriate diagnostic path. The system dynamically adjusts its recommendation strategy based on medical reasoning results, considering factors such as urgency levels and diagnostic uncertainty. Experimental results demonstrate that our approach achieves superior performance in terms of coverage rate, accuracy, and miss rate compared to conventional retrieval-based methods. This work represents a significant advance in medical test recommendation by introducing medical reasoning capabilities into the traditional tree-based retrieval structure.
Comprehensive Evaluation of Multimodal AI Models in Medical Imaging Diagnosis: From Data Augmentation to Preference-Based Comparison
Dec 07, 2024


Abstract:This study introduces an evaluation framework for multimodal models in medical imaging diagnostics. We developed a pipeline incorporating data preprocessing, model inference, and preference-based evaluation, expanding an initial set of 500 clinical cases to 3,000 through controlled augmentation. Our method combined medical images with clinical observations to generate assessments, using Claude 3.5 Sonnet for independent evaluation against physician-authored diagnoses. The results indicated varying performance across models, with Llama 3.2-90B outperforming human diagnoses in 85.27% of cases. In contrast, specialized vision models like BLIP2 and Llava showed preferences in 41.36% and 46.77% of cases, respectively. This framework highlights the potential of large multimodal models to outperform human diagnostics in certain tasks.
Rethinking Weight Decay for Robust Fine-Tuning of Foundation Models
Nov 03, 2024



Abstract:Modern optimizers such as AdamW, equipped with momentum and adaptive learning rate, are designed to escape local minima and explore the vast parameter space. This exploration is beneficial for finding good loss basins when training from scratch. It is not necessarily ideal when resuming from a powerful foundation model because it can lead to large deviations from the pre-trained initialization and, consequently, worse robustness and generalization. At the same time, strong regularization on all parameters can lead to under-fitting. We hypothesize that selectively regularizing the parameter space is the key to fitting and retraining the pre-trained knowledge. This paper proposes a new weight decay technique, Selective Projection Decay (SPD), that selectively imposes a strong penalty on certain layers while allowing others to change freely. Intuitively, SPD expands and contracts the parameter search space for layers with consistent and inconsistent loss reduction, respectively. Experimentally, when equipped with SPD, Adam consistently provides better in-distribution generalization and out-of-distribution robustness performance on multiple popular vision and language benchmarks. Code available at~\url{https://github.com/GT-RIPL/Selective-Projection-Decay.git}
Instance Needs More Care: Rewriting Prompts for Instances Yields Better Zero-Shot Performance
Oct 05, 2023



Abstract:Enabling large language models (LLMs) to perform tasks in zero-shot has been an appealing goal owing to its labor-saving (i.e., requiring no task-specific annotations); as such, zero-shot prompting approaches also enjoy better task generalizability. To improve LLMs' zero-shot performance, prior work has focused on devising more effective task instructions (e.g., ``let's think step by step'' ). However, we argue that, in order for an LLM to solve them correctly in zero-shot, individual test instances need more carefully designed and customized instructions. To this end, we propose PRoMPTd, an approach that rewrites the task prompt for each individual test input to be more specific, unambiguous, and complete, so as to provide better guidance to the task LLM. We evaluated PRoMPTd on eight datasets covering tasks including arithmetics, logical reasoning, and code generation, using GPT-4 as the task LLM. Notably, PRoMPTd achieves an absolute improvement of around 10% on the complex MATH dataset and 5% on the code generation task on HumanEval, outperforming conventional zero-shot methods. In addition, we also showed that the rewritten prompt can provide better interpretability of how the LLM resolves each test instance, which can potentially be leveraged as a defense mechanism against adversarial prompting. The source code and dataset can be obtained from https://github.com/salokr/PRoMPTd
From Local to Global: Spectral-Inspired Graph Neural Networks
Sep 24, 2022



Abstract:Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) are powerful deep learning methods for Non-Euclidean data. Popular GNNs are message-passing algorithms (MPNNs) that aggregate and combine signals in a local graph neighborhood. However, shallow MPNNs tend to miss long-range signals and perform poorly on some heterophilous graphs, while deep MPNNs can suffer from issues like over-smoothing or over-squashing. To mitigate such issues, existing works typically borrow normalization techniques from training neural networks on Euclidean data or modify the graph structures. Yet these approaches are not well-understood theoretically and could increase the overall computational complexity. In this work, we draw inspirations from spectral graph embedding and propose $\texttt{PowerEmbed}$ -- a simple layer-wise normalization technique to boost MPNNs. We show $\texttt{PowerEmbed}$ can provably express the top-$k$ leading eigenvectors of the graph operator, which prevents over-smoothing and is agnostic to the graph topology; meanwhile, it produces a list of representations ranging from local features to global signals, which avoids over-squashing. We apply $\texttt{PowerEmbed}$ in a wide range of simulated and real graphs and demonstrate its competitive performance, particularly for heterophilous graphs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge