Cheng Deng
Xidian University
Revealing and Enhancing Core Visual Regions: Harnessing Internal Attention Dynamics for Hallucination Mitigation in LVLMs
Feb 17, 2026Abstract:LVLMs have achieved strong multimodal reasoning capabilities but remain prone to hallucinations, producing outputs inconsistent with visual inputs or user instructions. Existing training-free methods, including contrastive decoding and auxiliary expert models, which incur several times more computational overhead and may introduce potential interference, as well as static internal signal enhancement, are often vulnerable to the attention sink phenomenon. We find that internal Positive Attention Dynamics (PAD) in LVLMs naturally reveal semantically core visual regions under the distortions of attention sinks. Based on this, we propose Positive Attention Dynamics Enhancement (PADE), a training-free attention intervention that constructs a PAD map to identify semantically core visual regions, applies per-head Median Absolute Deviation Scaling to adaptively control the intervention strength, and leverages System-Token Compensation to maintain attention to complex user instructions and support long-term output consistency. Experiments on multiple LVLMs and benchmarks show that PADE improves visual grounding and reduces hallucinations, validating the effectiveness of leveraging internal attention dynamics for reliable multimodal reasoning.
RooflineBench: A Benchmarking Framework for On-Device LLMs via Roofline Analysis
Feb 12, 2026Abstract:The transition toward localized intelligence through Small Language Models (SLMs) has intensified the need for rigorous performance characterization on resource-constrained edge hardware. However, objectively measuring the theoretical performance ceilings of diverse architectures across heterogeneous platforms remains a formidable challenge. In this work, we propose a systematic framework based on the Roofline model that unifies architectural primitives and hardware constraints through the lens of operational intensity (OI). By defining an inference-potential region, we introduce the Relative Inference Potential as a novel metric to compare efficiency differences between Large Language Models (LLMs) on the same hardware substrate. Extensive empirical analysis across diverse compute tiers reveals that variations in performance and OI are significantly influenced by sequence length. We further identify a critical regression in OI as model depth increases. Additionally, our findings highlight an efficiency trap induced by hardware heterogeneity and demonstrate how structural refinements, such as Multi-head Latent Attention (M LA), can effectively unlock latent inference potential across various hardware substrates. These insights provide actionable directions for hardware-software co-design to align neural structures with physical constraints in on-device intelligence. The released code is available in the Appendix C.
Hardware Co-Design Scaling Laws via Roofline Modelling for On-Device LLMs
Feb 10, 2026Abstract:Vision-Language-Action Models (VLAs) have emerged as a key paradigm of Physical AI and are increasingly deployed in autonomous vehicles, robots, and smart spaces. In these resource-constrained on-device settings, selecting an appropriate large language model (LLM) backbone is a critical challenge: models must balance accuracy with strict inference latency and hardware efficiency constraints. This makes hardware-software co-design a game-changing requirement for on-device LLM deployment, where each hardware platform demands a tailored architectural solution. We propose a hardware co-design law that jointly captures model accuracy and inference performance. Specifically, we model training loss as an explicit function of architectural hyperparameters and characterise inference latency via roofline modelling. We empirically evaluate 1,942 candidate architectures on NVIDIA Jetson Orin, training 170 selected models for 10B tokens each to fit a scaling law relating architecture to training loss. By coupling this scaling law with latency modelling, we establish a direct accuracy-latency correspondence and identify the Pareto frontier for hardware co-designed LLMs. We further formulate architecture search as a joint optimisation over precision and performance, deriving feasible design regions under industrial hardware and application budgets. Our approach reduces architecture selection from months to days. At the same latency as Qwen2.5-0.5B on the target hardware, our co-designed architecture achieves 19.42% lower perplexity on WikiText-2. To our knowledge, this is the first principled and operational framework for hardware co-design scaling laws in on-device LLM deployment. We will make the code and related checkpoints publicly available.
Towards Interpretable Hallucination Analysis and Mitigation in LVLMs via Contrastive Neuron Steering
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:LVLMs achieve remarkable multimodal understanding and generation but remain susceptible to hallucinations. Existing mitigation methods predominantly focus on output-level adjustments, leaving the internal mechanisms that give rise to these hallucinations largely unexplored. To gain a deeper understanding, we adopt a representation-level perspective by introducing sparse autoencoders (SAEs) to decompose dense visual embeddings into sparse, interpretable neurons. Through neuron-level analysis, we identify distinct neuron types, including always-on neurons and image-specific neurons. Our findings reveal that hallucinations often result from disruptions or spurious activations of image-specific neurons, while always-on neurons remain largely stable. Moreover, selectively enhancing or suppressing image-specific neurons enables controllable intervention in LVLM outputs, improving visual grounding and reducing hallucinations. Building on these insights, we propose Contrastive Neuron Steering (CNS), which identifies image-specific neurons via contrastive analysis between clean and noisy inputs. CNS selectively amplifies informative neurons while suppressing perturbation-induced activations, producing more robust and semantically grounded visual representations. This not only enhances visual understanding but also effectively mitigates hallucinations. By operating at the prefilling stage, CNS is fully compatible with existing decoding-stage methods. Extensive experiments on both hallucination-focused and general multimodal benchmarks demonstrate that CNS consistently reduces hallucinations while preserving overall multimodal understanding.
Past- and Future-Informed KV Cache Policy with Salience Estimation in Autoregressive Video Diffusion
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Video generation is pivotal to digital media creation, and recent advances in autoregressive video generation have markedly enhanced the efficiency of real-time video synthesis. However, existing approaches generally rely on heuristic KV Cache policies, which ignore differences in token importance in long-term video generation. This leads to the loss of critical spatiotemporal information and the accumulation of redundant, invalid cache, thereby degrading video generation quality and efficiency. To address this limitation, we first observe that token contributions to video generation are highly time-heterogeneous and accordingly propose a novel Past- and Future-Informed KV Cache Policy (PaFu-KV). Specifically, PaFu-KV introduces a lightweight Salience Estimation Head distilled from a bidirectional teacher to estimate salience scores, allowing the KV cache to retain informative tokens while discarding less relevant ones. This policy yields a better quality-efficiency trade-off by shrinking KV cache capacity and reducing memory footprint at inference time. Extensive experiments on benchmarks demonstrate that our method preserves high-fidelity video generation quality while enables accelerated inference, thereby enabling more efficient long-horizon video generation. Our code will be released upon paper acceptance.
DSCD-Nav: Dual-Stance Cooperative Debate for Object Navigation
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Adaptive navigation in unfamiliar indoor environments is crucial for household service robots. Despite advances in zero-shot perception and reasoning from vision-language models, existing navigation systems still rely on single-pass scoring at the decision layer, leading to overconfident long-horizon errors and redundant exploration. To tackle these problems, we propose Dual-Stance Cooperative Debate Navigation (DSCD-Nav), a decision mechanism that replaces one-shot scoring with stance-based cross-checking and evidence-aware arbitration to improve action reliability under partial observability. Specifically, given the same observation and candidate action set, we explicitly construct two stances by conditioning the evaluation on diverse and complementary objectives: a Task-Scene Understanding (TSU) stance that prioritizes goal progress from scene-layout cues, and a Safety-Information Balancing (SIB) stance that emphasizes risk and information value. The stances conduct a cooperative debate and make policy by cross-checking their top candidates with cue-grounded arguments. Then, a Navigation Consensus Arbitration (NCA) agent is employed to consolidate both sides' reasons and evidence, optionally triggering lightweight micro-probing to verify uncertain choices, preserving NCA's primary intent while disambiguating. Experiments on HM3Dv1, HM3Dv2, and MP3D demonstrate consistent improvements in success and path efficiency while reducing exploration redundancy.
Beyond Global Alignment: Fine-Grained Motion-Language Retrieval via Pyramidal Shapley-Taylor Learning
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:As a foundational task in human-centric cross-modal intelligence, motion-language retrieval aims to bridge the semantic gap between natural language and human motion, enabling intuitive motion analysis, yet existing approaches predominantly focus on aligning entire motion sequences with global textual representations. This global-centric paradigm overlooks fine-grained interactions between local motion segments and individual body joints and text tokens, inevitably leading to suboptimal retrieval performance. To address this limitation, we draw inspiration from the pyramidal process of human motion perception (from joint dynamics to segment coherence, and finally to holistic comprehension) and propose a novel Pyramidal Shapley-Taylor (PST) learning framework for fine-grained motion-language retrieval. Specifically, the framework decomposes human motion into temporal segments and spatial body joints, and learns cross-modal correspondences through progressive joint-wise and segment-wise alignment in a pyramidal fashion, effectively capturing both local semantic details and hierarchical structural relationships. Extensive experiments on multiple public benchmark datasets demonstrate that our approach significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods, achieving precise alignment between motion segments and body joints and their corresponding text tokens. The code of this work will be released upon acceptance.
The Script is All You Need: An Agentic Framework for Long-Horizon Dialogue-to-Cinematic Video Generation
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Recent advances in video generation have produced models capable of synthesizing stunning visual content from simple text prompts. However, these models struggle to generate long-form, coherent narratives from high-level concepts like dialogue, revealing a ``semantic gap'' between a creative idea and its cinematic execution. To bridge this gap, we introduce a novel, end-to-end agentic framework for dialogue-to-cinematic-video generation. Central to our framework is ScripterAgent, a model trained to translate coarse dialogue into a fine-grained, executable cinematic script. To enable this, we construct ScriptBench, a new large-scale benchmark with rich multimodal context, annotated via an expert-guided pipeline. The generated script then guides DirectorAgent, which orchestrates state-of-the-art video models using a cross-scene continuous generation strategy to ensure long-horizon coherence. Our comprehensive evaluation, featuring an AI-powered CriticAgent and a new Visual-Script Alignment (VSA) metric, shows our framework significantly improves script faithfulness and temporal fidelity across all tested video models. Furthermore, our analysis uncovers a crucial trade-off in current SOTA models between visual spectacle and strict script adherence, providing valuable insights for the future of automated filmmaking.
Towards Arbitrary Motion Completing via Hierarchical Continuous Representation
Dec 24, 2025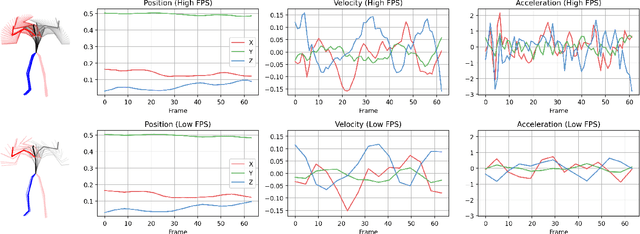
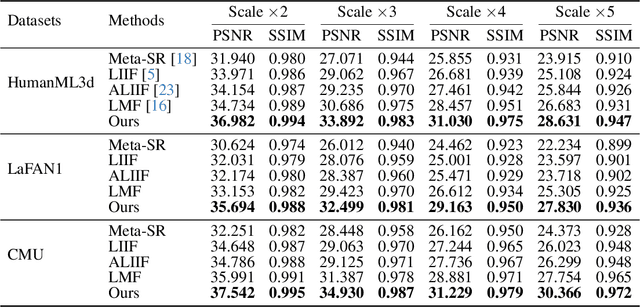
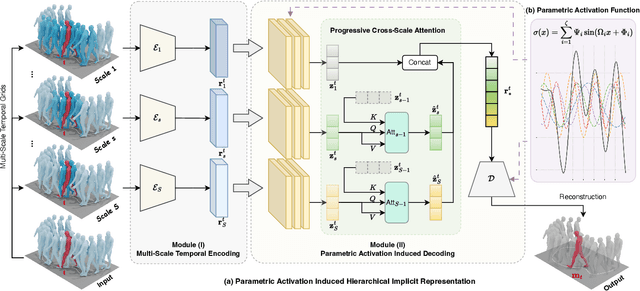
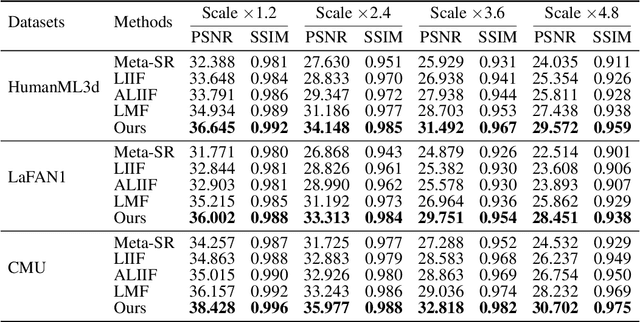
Abstract:Physical motions are inherently continuous, and higher camera frame rates typically contribute to improved smoothness and temporal coherence. For the first time, we explore continuous representations of human motion sequences, featuring the ability to interpolate, inbetween, and even extrapolate any input motion sequences at arbitrary frame rates. To achieve this, we propose a novel parametric activation-induced hierarchical implicit representation framework, referred to as NAME, based on Implicit Neural Representations (INRs). Our method introduces a hierarchical temporal encoding mechanism that extracts features from motion sequences at multiple temporal scales, enabling effective capture of intricate temporal patterns. Additionally, we integrate a custom parametric activation function, powered by Fourier transformations, into the MLP-based decoder to enhance the expressiveness of the continuous representation. This parametric formulation significantly augments the model's ability to represent complex motion behaviors with high accuracy. Extensive evaluations across several benchmark datasets demonstrate the effectiveness and robustness of our proposed approach.
A Turn Toward Better Alignment: Few-Shot Generative Adaptation with Equivariant Feature Rotation
Dec 24, 2025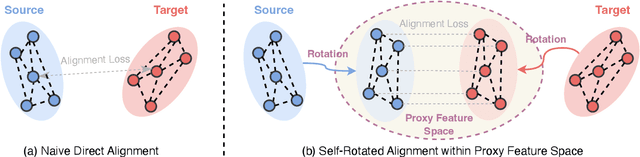
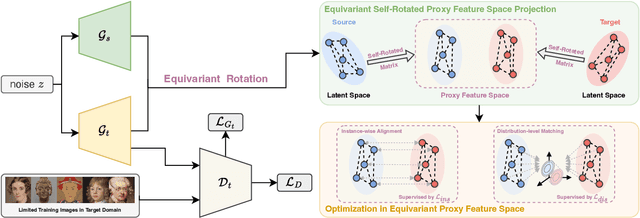
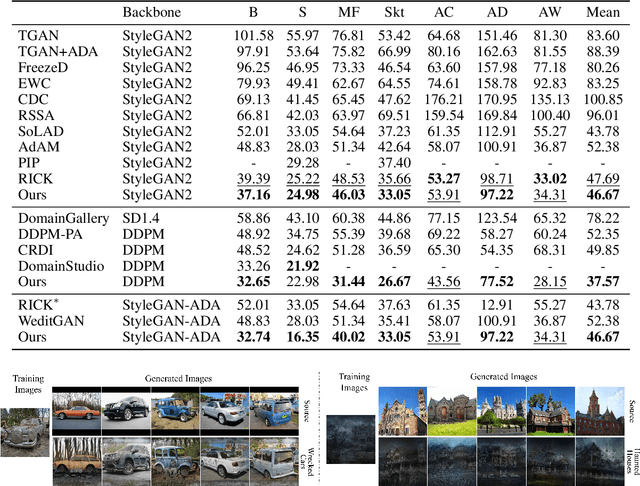
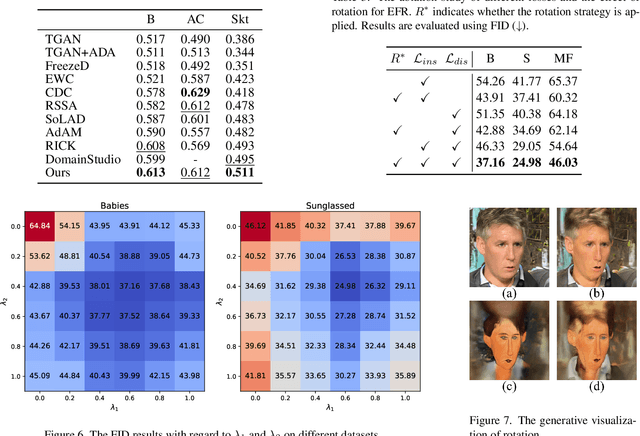
Abstract:Few-shot image generation aims to effectively adapt a source generative model to a target domain using very few training images. Most existing approaches introduce consistency constraints-typically through instance-level or distribution-level loss functions-to directly align the distribution patterns of source and target domains within their respective latent spaces. However, these strategies often fall short: overly strict constraints can amplify the negative effects of the domain gap, leading to distorted or uninformative content, while overly relaxed constraints may fail to leverage the source domain effectively. This limitation primarily stems from the inherent discrepancy in the underlying distribution structures of the source and target domains. The scarcity of target samples further compounds this issue by hindering accurate estimation of the target domain's distribution. To overcome these limitations, we propose Equivariant Feature Rotation (EFR), a novel adaptation strategy that aligns source and target domains at two complementary levels within a self-rotated proxy feature space. Specifically, we perform adaptive rotations within a parameterized Lie Group to transform both source and target features into an equivariant proxy space, where alignment is conducted. These learnable rotation matrices serve to bridge the domain gap by preserving intra-domain structural information without distortion, while the alignment optimization facilitates effective knowledge transfer from the source to the target domain. Comprehensive experiments on a variety of commonly used datasets demonstrate that our method significantly enhances the generative performance within the targeted domain.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge