Xinbing Wang
Pretraining with Token-Level Adaptive Latent Chain-of-Thought
Feb 09, 2026Abstract:Scaling large language models by increasing parameters and training data is increasingly constrained by limited high-quality corpora and rising communication costs. This work explores an alternative axis: increasing per-token computation without expanding parameters, by internalizing latent Chain-of-Thought (CoT) into pretraining. We propose Pretraining with Token-Level Adaptive Latent CoT (adaptive latent CoT), where the model generates a variable-length latent CoT trajectory before emitting each token -- allocating longer trajectories to difficult tokens and shorter (or even zero) trajectories to easy ones. Importantly, this behavior emerges naturally from one-stage pretraining on general text and reduces computation in both training and inference via token-wise adaptive halting. Experiments with Llama architectures show that adaptive latent CoT consistently improves language modeling perplexity and broad downstream accuracy, even with fewer training FLOPs than prior recurrent baselines.
<SOG_k>: One LLM Token for Explicit Graph Structural Understanding
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Large language models show great potential in unstructured data understanding, but still face significant challenges with graphs due to their structural hallucination. Existing approaches mainly either verbalize graphs into natural language, which leads to excessive token consumption and scattered attention, or transform graphs into trainable continuous embeddings (i.e., soft prompt), but exhibit severe misalignment with original text tokens. To solve this problem, we propose to incorporate one special token <SOG_k> to fully represent the Structure Of Graph within a unified token space, facilitating explicit topology input and structural information sharing. Specifically, we propose a topology-aware structural tokenizer that maps each graph topology into a highly selective single token. Afterwards, we construct a set of hybrid structure Question-Answering corpora to align new structural tokens with existing text tokens. With this approach, <SOG_k> empowers LLMs to understand, generate, and reason in a concise and accurate manner. Extensive experiments on five graph-level benchmarks demonstrate the superiority of our method, achieving a performance improvement of 9.9% to 41.4% compared to the baselines while exhibiting interpretability and consistency. Furthermore, our method provides a flexible extension to node-level tasks, enabling both global and local structural understanding. The codebase is publicly available at https://github.com/Jingyao-Wu/SOG.
Controlling Underestimation Bias in Constrained Reinforcement Learning for Safe Exploration
Jan 17, 2026Abstract:Constrained Reinforcement Learning (CRL) aims to maximize cumulative rewards while satisfying constraints. However, existing CRL algorithms often encounter significant constraint violations during training, limiting their applicability in safety-critical scenarios. In this paper, we identify the underestimation of the cost value function as a key factor contributing to these violations. To address this issue, we propose the Memory-driven Intrinsic Cost Estimation (MICE) method, which introduces intrinsic costs to mitigate underestimation and control bias to promote safer exploration. Inspired by flashbulb memory, where humans vividly recall dangerous experiences to avoid risks, MICE constructs a memory module that stores previously explored unsafe states to identify high-cost regions. The intrinsic cost is formulated as the pseudo-count of the current state visiting these risk regions. Furthermore, we propose an extrinsic-intrinsic cost value function that incorporates intrinsic costs and adopts a bias correction strategy. Using this function, we formulate an optimization objective within the trust region, along with corresponding optimization methods. Theoretically, we provide convergence guarantees for the proposed cost value function and establish the worst-case constraint violation for the MICE update. Extensive experiments demonstrate that MICE significantly reduces constraint violations while preserving policy performance comparable to baselines.
Extreme Value Policy Optimization for Safe Reinforcement Learning
Jan 17, 2026Abstract:Ensuring safety is a critical challenge in applying Reinforcement Learning (RL) to real-world scenarios. Constrained Reinforcement Learning (CRL) addresses this by maximizing returns under predefined constraints, typically formulated as the expected cumulative cost. However, expectation-based constraints overlook rare but high-impact extreme value events in the tail distribution, such as black swan incidents, which can lead to severe constraint violations. To address this issue, we propose the Extreme Value policy Optimization (EVO) algorithm, leveraging Extreme Value Theory (EVT) to model and exploit extreme reward and cost samples, reducing constraint violations. EVO introduces an extreme quantile optimization objective to explicitly capture extreme samples in the cost tail distribution. Additionally, we propose an extreme prioritization mechanism during replay, amplifying the learning signal from rare but high-impact extreme samples. Theoretically, we establish upper bounds on expected constraint violations during policy updates, guaranteeing strict constraint satisfaction at a zero-violation quantile level. Further, we demonstrate that EVO achieves a lower probability of constraint violations than expectation-based methods and exhibits lower variance than quantile regression methods. Extensive experiments show that EVO significantly reduces constraint violations during training while maintaining competitive policy performance compared to baselines.
Improving LLM Reasoning with Homophily-aware Structural and Semantic Text-Attributed Graph Compression
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated promising capabilities in Text-Attributed Graph (TAG) understanding. Recent studies typically focus on verbalizing the graph structures via handcrafted prompts, feeding the target node and its neighborhood context into LLMs. However, constrained by the context window, existing methods mainly resort to random sampling, often implemented via dropping node/edge randomly, which inevitably introduces noise and cause reasoning instability. We argue that graphs inherently contain rich structural and semantic information, and that their effective exploitation can unlock potential gains in LLMs reasoning performance. To this end, we propose Homophily-aware Structural and Semantic Compression for LLMs (HS2C), a framework centered on exploiting graph homophily. Structurally, guided by the principle of Structural Entropy minimization, we perform a global hierarchical partition that decodes the graph's essential topology. This partition identifies naturally cohesive, homophilic communities, while discarding stochastic connectivity noise. Semantically, we deliver the detected structural homophily to the LLM, empowering it to perform differentiated semantic aggregation based on predefined community type. This process compresses redundant background contexts into concise community-level consensus, selectively preserving semantically homophilic information aligned with the target nodes. Extensive experiments on 10 node-level benchmarks across LLMs of varying sizes and families demonstrate that, by feeding LLMs with structurally and semantically compressed inputs, HS2C simultaneously enhances the compression rate and downstream inference accuracy, validating its superiority and scalability. Extensions to 7 diverse graph-level benchmarks further consolidate HS2C's task generalizability.
Pretraining Language Models to Ponder in Continuous Space
May 27, 2025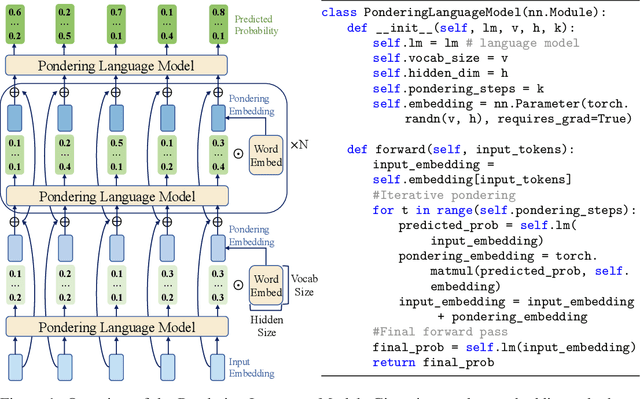
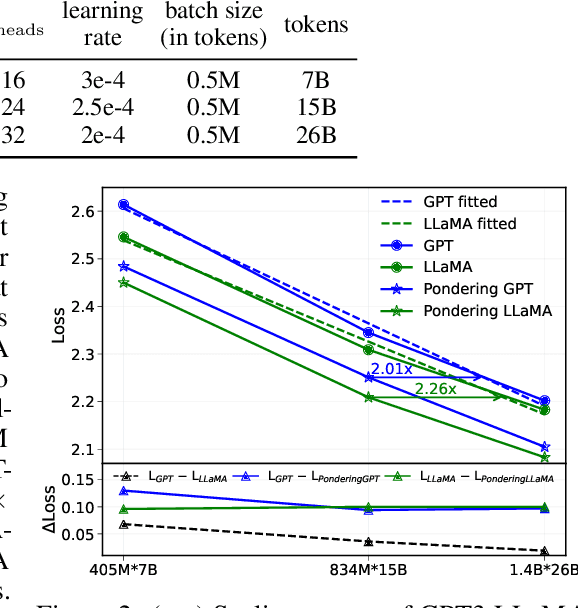
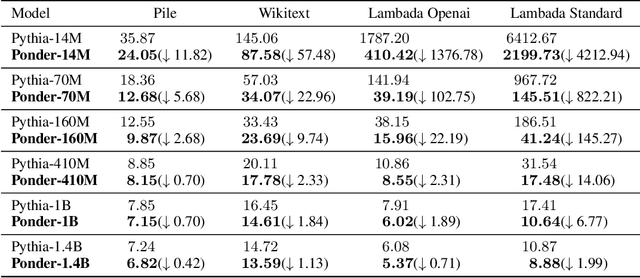
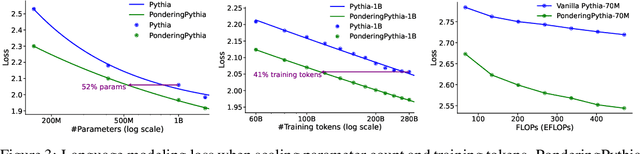
Abstract:Humans ponder before articulating complex sentence elements, enabling deeper cognitive processing through focused effort. In this work, we introduce this pondering process into language models by repeatedly invoking the forward process within a single token generation step. During pondering, instead of generating an actual token sampled from the prediction distribution, the model ponders by yielding a weighted sum of all token embeddings according to the predicted token distribution. The generated embedding is then fed back as input for another forward pass. We show that the model can learn to ponder in this way through self-supervised learning, without any human annotations. Our method is straightforward and can be seamlessly integrated with various existing language models. Experiments across three widely used open-source architectures-GPT-2, Pythia, and LLaMA-and extensive downstream task evaluations demonstrate the effectiveness and generality of our method. For language modeling tasks, pondering language models achieve performance comparable to vanilla models with twice the number of parameters. On 9 downstream benchmarks, our pondering-enhanced Pythia models significantly outperform the official Pythia models. Notably, pondering-enhanced Pythia-1B is comparable to TinyLlama-1.1B, which is trained on 10 times more data. The code is available at https://github.com/LUMIA-Group/PonderingLM.
Bayesian Cross-Modal Alignment Learning for Few-Shot Out-of-Distribution Generalization
Apr 22, 2025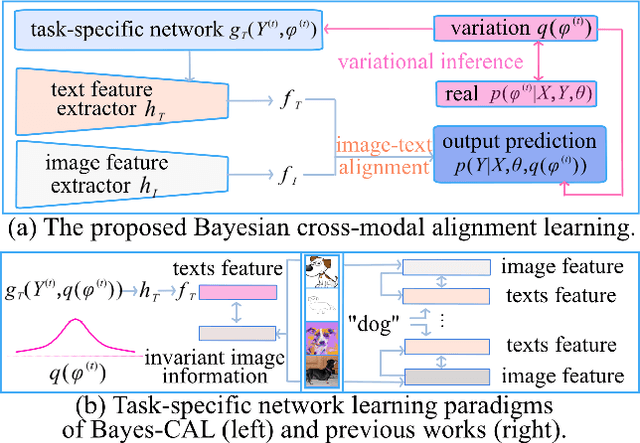
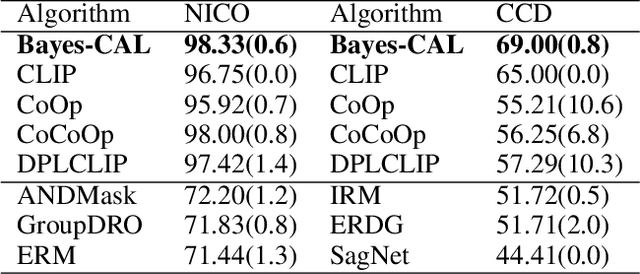
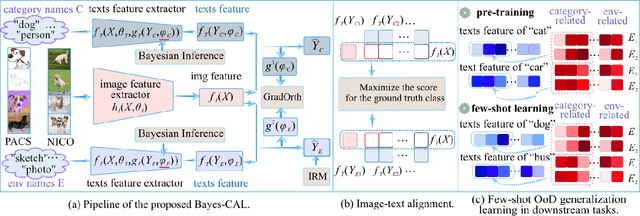
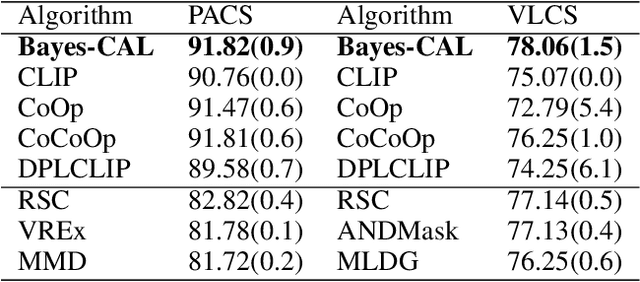
Abstract:Recent advances in large pre-trained models showed promising results in few-shot learning. However, their generalization ability on two-dimensional Out-of-Distribution (OoD) data, i.e., correlation shift and diversity shift, has not been thoroughly investigated. Researches have shown that even with a significant amount of training data, few methods can achieve better performance than the standard empirical risk minimization method (ERM) in OoD generalization. This few-shot OoD generalization dilemma emerges as a challenging direction in deep neural network generalization research, where the performance suffers from overfitting on few-shot examples and OoD generalization errors. In this paper, leveraging a broader supervision source, we explore a novel Bayesian cross-modal image-text alignment learning method (Bayes-CAL) to address this issue. Specifically, the model is designed as only text representations are fine-tuned via a Bayesian modelling approach with gradient orthogonalization loss and invariant risk minimization (IRM) loss. The Bayesian approach is essentially introduced to avoid overfitting the base classes observed during training and improve generalization to broader unseen classes. The dedicated loss is introduced to achieve better image-text alignment by disentangling the causal and non-casual parts of image features. Numerical experiments demonstrate that Bayes-CAL achieved state-of-the-art OoD generalization performances on two-dimensional distribution shifts. Moreover, compared with CLIP-like models, Bayes-CAL yields more stable generalization performances on unseen classes. Our code is available at https://github.com/LinLLLL/BayesCAL.
CHAINSFORMER: Numerical Reasoning on Knowledge Graphs from a Chain Perspective
Apr 19, 2025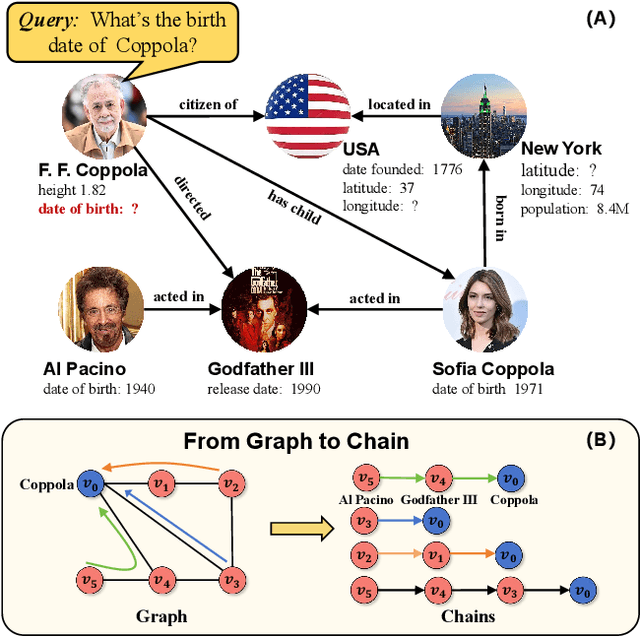
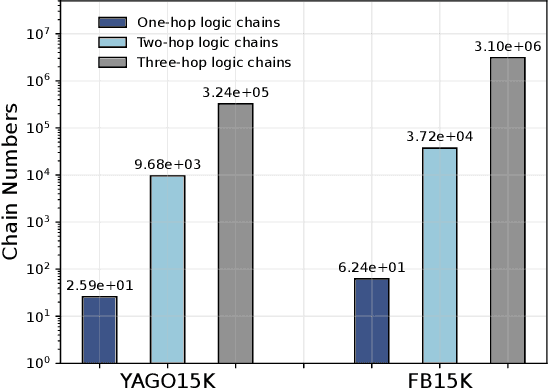
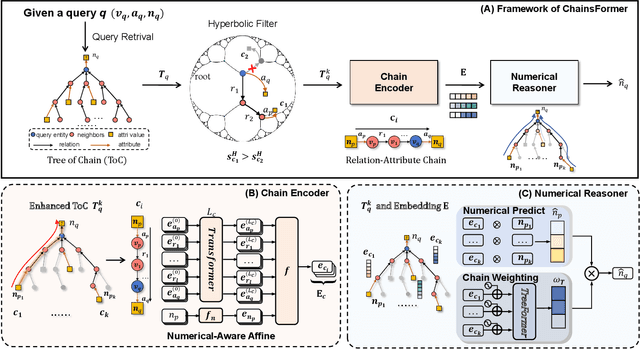
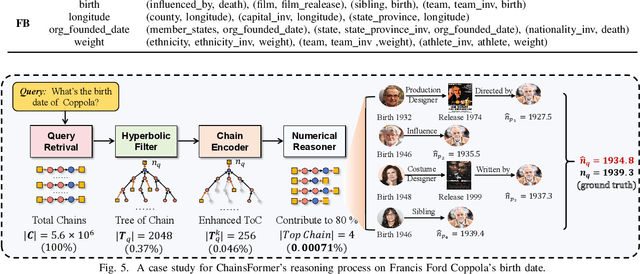
Abstract:Reasoning over Knowledge Graphs (KGs) plays a pivotal role in knowledge graph completion or question answering systems, providing richer and more accurate triples and attributes. As numerical attributes become increasingly essential in characterizing entities and relations in KGs, the ability to reason over these attributes has gained significant importance. Existing graph-based methods such as Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) and Knowledge Graph Embeddings (KGEs), primarily focus on aggregating homogeneous local neighbors and implicitly embedding diverse triples. However, these approaches often fail to fully leverage the potential of logical paths within the graph, limiting their effectiveness in exploiting the reasoning process. To address these limitations, we propose ChainsFormer, a novel chain-based framework designed to support numerical reasoning. Chainsformer not only explicitly constructs logical chains but also expands the reasoning depth to multiple hops. Specially, we introduces Relation-Attribute Chains (RA-Chains), a specialized logic chain, to model sequential reasoning patterns. ChainsFormer captures the step-by-step nature of multi-hop reasoning along RA-Chains by employing sequential in-context learning. To mitigate the impact of noisy chains, we propose a hyperbolic affinity scoring mechanism that selects relevant logic chains in a variable-resolution space. Furthermore, ChainsFormer incorporates an attention-based numerical reasoner to identify critical reasoning paths, enhancing both reasoning accuracy and transparency. Experimental results demonstrate that ChainsFormer significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods, achieving up to a 20.0% improvement in performance. The implementations are available at https://github.com/zhaodazhuang2333/ChainsFormer.
InfoBound: A Provable Information-Bounds Inspired Framework for Both OoD Generalization and OoD Detection
Apr 13, 2025



Abstract:In real-world scenarios, distribution shifts give rise to the importance of two problems: out-of-distribution (OoD) generalization, which focuses on models' generalization ability against covariate shifts (i.e., the changes of environments), and OoD detection, which aims to be aware of semantic shifts (i.e., test-time unseen classes). Real-world testing environments often involve a combination of both covariate and semantic shifts. While numerous methods have been proposed to address these critical issues, only a few works tackled them simultaneously. Moreover, prior works often improve one problem but sacrifice the other. To overcome these limitations, we delve into boosting OoD detection and OoD generalization from the perspective of information theory, which can be easily applied to existing models and different tasks. Building upon the theoretical bounds for mutual information and conditional entropy, we provide a unified approach, composed of Mutual Information Minimization (MI-Min) and Conditional Entropy Maximizing (CE-Max). Extensive experiments and comprehensive evaluations on multi-label image classification and object detection have demonstrated the superiority of our method. It successfully mitigates trade-offs between the two challenges compared to competitive baselines.
Leveraging Dual Process Theory in Language Agent Framework for Real-time Simultaneous Human-AI Collaboration
Feb 17, 2025Abstract:Agents built on large language models (LLMs) have excelled in turn-by-turn human-AI collaboration but struggle with simultaneous tasks requiring real-time interaction. Latency issues and the challenge of inferring variable human strategies hinder their ability to make autonomous decisions without explicit instructions. Through experiments with current independent System 1 and System 2 methods, we validate the necessity of using Dual Process Theory (DPT) in real-time tasks. We propose DPT-Agent, a novel language agent framework that integrates System 1 and System 2 for efficient real-time simultaneous human-AI collaboration. DPT-Agent's System 1 uses a Finite-state Machine (FSM) and code-as-policy for fast, intuitive, and controllable decision-making. DPT-Agent's System 2 integrates Theory of Mind (ToM) and asynchronous reflection to infer human intentions and perform reasoning-based autonomous decisions. We demonstrate the effectiveness of DPT-Agent through further experiments with rule-based agents and human collaborators, showing significant improvements over mainstream LLM-based frameworks. To the best of our knowledge, DPT-Agent is the first language agent framework that achieves successful real-time simultaneous human-AI collaboration autonomously. Code of DPT-Agent can be found in https://github.com/sjtu-marl/DPT-Agent.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge