Efficient Reinforcement Learning with Large Language Model Priors
Paper and Code
Oct 10, 2024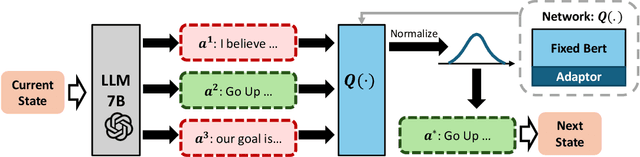
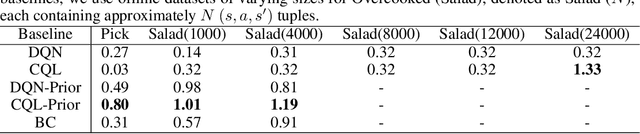
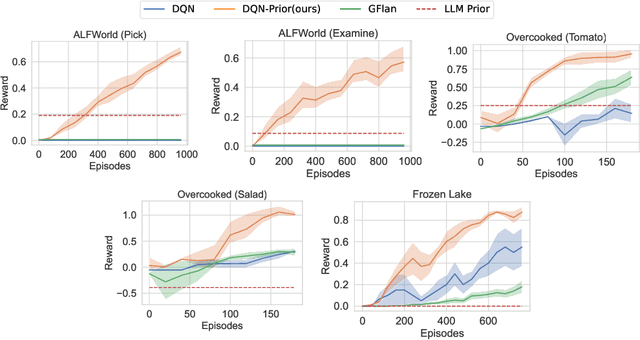
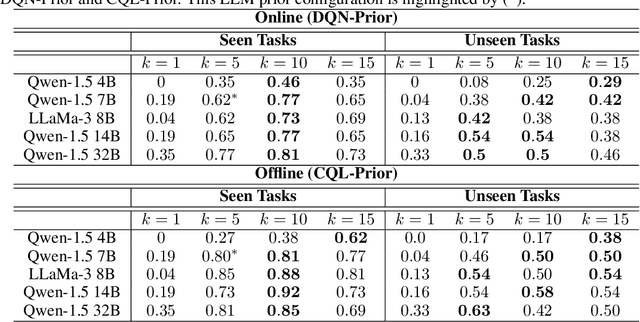
In sequential decision-making (SDM) tasks, methods like reinforcement learning (RL) and heuristic search have made notable advances in specific cases. However, they often require extensive exploration and face challenges in generalizing across diverse environments due to their limited grasp of the underlying decision dynamics. In contrast, large language models (LLMs) have recently emerged as powerful general-purpose tools, due to their capacity to maintain vast amounts of domain-specific knowledge. To harness this rich prior knowledge for efficiently solving complex SDM tasks, we propose treating LLMs as prior action distributions and integrating them into RL frameworks through Bayesian inference methods, making use of variational inference and direct posterior sampling. The proposed approaches facilitate the seamless incorporation of fixed LLM priors into both policy-based and value-based RL frameworks. Our experiments show that incorporating LLM-based action priors significantly reduces exploration and optimization complexity, substantially improving sample efficiency compared to traditional RL techniques, e.g., using LLM priors decreases the number of required samples by over 90% in offline learning scenarios.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge