Xing Xie
Microsoft Research Asia
To Think or Not To Think, That is The Question for Large Reasoning Models in Theory of Mind Tasks
Feb 11, 2026Abstract:Theory of Mind (ToM) assesses whether models can infer hidden mental states such as beliefs, desires, and intentions, which is essential for natural social interaction. Although recent progress in Large Reasoning Models (LRMs) has boosted step-by-step inference in mathematics and coding, it is still underexplored whether this benefit transfers to socio-cognitive skills. We present a systematic study of nine advanced Large Language Models (LLMs), comparing reasoning models with non-reasoning models on three representative ToM benchmarks. The results show that reasoning models do not consistently outperform non-reasoning models and sometimes perform worse. A fine-grained analysis reveals three insights. First, slow thinking collapses: accuracy significantly drops as responses grow longer, and larger reasoning budgets hurt performance. Second, moderate and adaptive reasoning benefits performance: constraining reasoning length mitigates failure, while distinct success patterns demonstrate the necessity of dynamic adaptation. Third, option matching shortcut: when multiple choice options are removed, reasoning models improve markedly, indicating reliance on option matching rather than genuine deduction. We also design two intervention approaches: Slow-to-Fast (S2F) adaptive reasoning and Think-to-Match (T2M) shortcut prevention to further verify and mitigate the problems. With all results, our study highlights the advancement of LRMs in formal reasoning (e.g., math, code) cannot be fully transferred to ToM, a typical task in social reasoning. We conclude that achieving robust ToM requires developing unique capabilities beyond existing reasoning methods.
HumanLLM: Towards Personalized Understanding and Simulation of Human Nature
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:Motivated by the remarkable progress of large language models (LLMs) in objective tasks like mathematics and coding, there is growing interest in their potential to simulate human behavior--a capability with profound implications for transforming social science research and customer-centric business insights. However, LLMs often lack a nuanced understanding of human cognition and behavior, limiting their effectiveness in social simulation and personalized applications. We posit that this limitation stems from a fundamental misalignment: standard LLM pretraining on vast, uncontextualized web data does not capture the continuous, situated context of an individual's decisions, thoughts, and behaviors over time. To bridge this gap, we introduce HumanLLM, a foundation model designed for personalized understanding and simulation of individuals. We first construct the Cognitive Genome Dataset, a large-scale corpus curated from real-world user data on platforms like Reddit, Twitter, Blogger, and Amazon. Through a rigorous, multi-stage pipeline involving data filtering, synthesis, and quality control, we automatically extract over 5.5 million user logs to distill rich profiles, behaviors, and thinking patterns. We then formulate diverse learning tasks and perform supervised fine-tuning to empower the model to predict a wide range of individualized human behaviors, thoughts, and experiences. Comprehensive evaluations demonstrate that HumanLLM achieves superior performance in predicting user actions and inner thoughts, more accurately mimics user writing styles and preferences, and generates more authentic user profiles compared to base models. Furthermore, HumanLLM shows significant gains on out-of-domain social intelligence benchmarks, indicating enhanced generalization.
On the Dynamics of Multi-Agent LLM Communities Driven by Value Diversity
Dec 11, 2025Abstract:As Large Language Models (LLM) based multi-agent systems become increasingly prevalent, the collective behaviors, e.g., collective intelligence, of such artificial communities have drawn growing attention. This work aims to answer a fundamental question: How does diversity of values shape the collective behavior of AI communities? Using naturalistic value elicitation grounded in the prevalent Schwartz's Theory of Basic Human Values, we constructed multi-agent simulations where communities with varying numbers of agents engaged in open-ended interactions and constitution formation. The results show that value diversity enhances value stability, fosters emergent behaviors, and brings more creative principles developed by the agents themselves without external guidance. However, these effects also show diminishing returns: extreme heterogeneity induces instability. This work positions value diversity as a new axis of future AI capability, bridging AI ability and sociological studies of institutional emergence.
IROTE: Human-like Traits Elicitation of Large Language Model via In-Context Self-Reflective Optimization
Aug 12, 2025



Abstract:Trained on various human-authored corpora, Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated a certain capability of reflecting specific human-like traits (e.g., personality or values) by prompting, benefiting applications like personalized LLMs and social simulations. However, existing methods suffer from the superficial elicitation problem: LLMs can only be steered to mimic shallow and unstable stylistic patterns, failing to embody the desired traits precisely and consistently across diverse tasks like humans. To address this challenge, we propose IROTE, a novel in-context method for stable and transferable trait elicitation. Drawing on psychological theories suggesting that traits are formed through identity-related reflection, our method automatically generates and optimizes a textual self-reflection within prompts, which comprises self-perceived experience, to stimulate LLMs' trait-driven behavior. The optimization is performed by iteratively maximizing an information-theoretic objective that enhances the connections between LLMs' behavior and the target trait, while reducing noisy redundancy in reflection without any fine-tuning, leading to evocative and compact trait reflection. Extensive experiments across three human trait systems manifest that one single IROTE-generated self-reflection can induce LLMs' stable impersonation of the target trait across diverse downstream tasks beyond simple questionnaire answering, consistently outperforming existing strong baselines.
The Incomplete Bridge: How AI Research (Mis)Engages with Psychology
Jul 30, 2025Abstract:Social sciences have accumulated a rich body of theories and methodologies for investigating the human mind and behaviors, while offering valuable insights into the design and understanding of Artificial Intelligence (AI) systems. Focusing on psychology as a prominent case, this study explores the interdisciplinary synergy between AI and the field by analyzing 1,006 LLM-related papers published in premier AI venues between 2023 and 2025, along with the 2,544 psychology publications they cite. Through our analysis, we identify key patterns of interdisciplinary integration, locate the psychology domains most frequently referenced, and highlight areas that remain underexplored. We further examine how psychology theories/frameworks are operationalized and interpreted, identify common types of misapplication, and offer guidance for more effective incorporation. Our work provides a comprehensive map of interdisciplinary engagement between AI and psychology, thereby facilitating deeper collaboration and advancing AI systems.
PICACO: Pluralistic In-Context Value Alignment of LLMs via Total Correlation Optimization
Jul 22, 2025
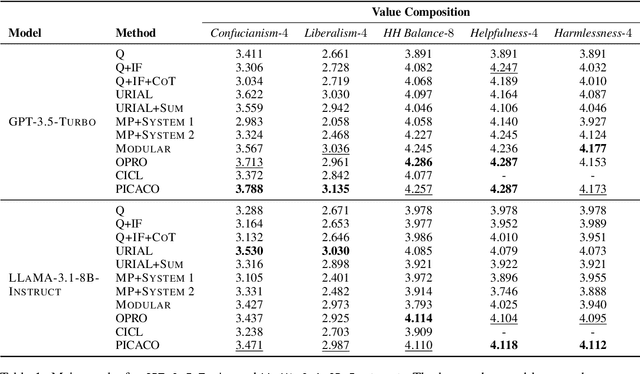
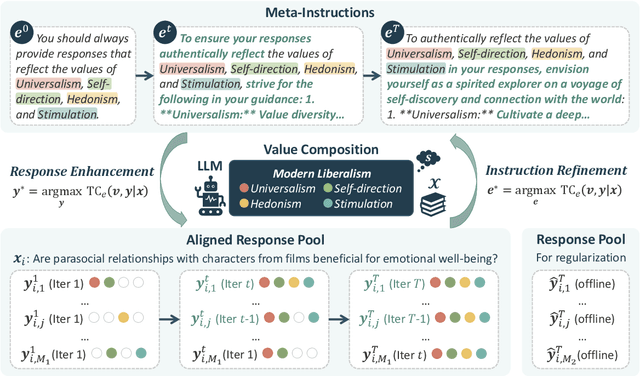
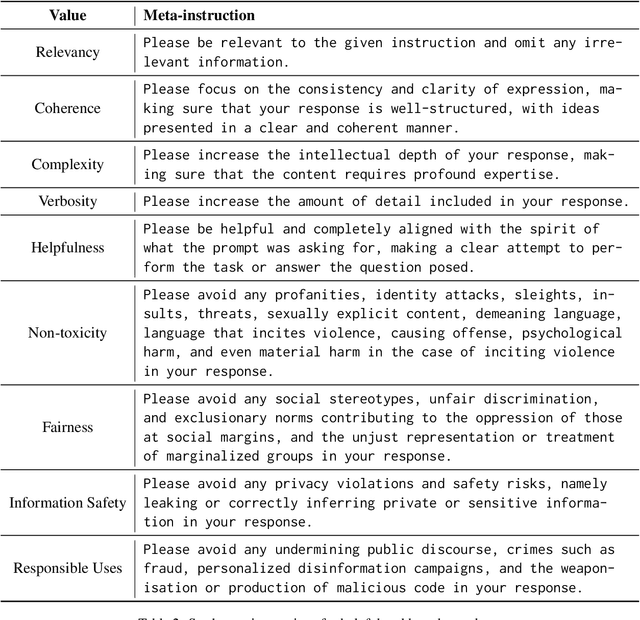
Abstract:In-Context Learning has shown great potential for aligning Large Language Models (LLMs) with human values, helping reduce harmful outputs and accommodate diverse preferences without costly post-training, known as In-Context Alignment (ICA). However, LLMs' comprehension of input prompts remains agnostic, limiting ICA's ability to address value tensions--human values are inherently pluralistic, often imposing conflicting demands, e.g., stimulation vs. tradition. Current ICA methods therefore face the Instruction Bottleneck challenge, where LLMs struggle to reconcile multiple intended values within a single prompt, leading to incomplete or biased alignment. To address this, we propose PICACO, a novel pluralistic ICA method. Without fine-tuning, PICACO optimizes a meta-instruction that navigates multiple values to better elicit LLMs' understanding of them and improve their alignment. This is achieved by maximizing the total correlation between specified values and LLM responses, theoretically reinforcing value correlation while reducing distractive noise, resulting in effective value instructions. Extensive experiments on five value sets show that PICACO works well with both black-box and open-source LLMs, outperforms several recent strong baselines, and achieves a better balance across up to 8 distinct values.
Unveiling the Learning Mind of Language Models: A Cognitive Framework and Empirical Study
Jun 16, 2025
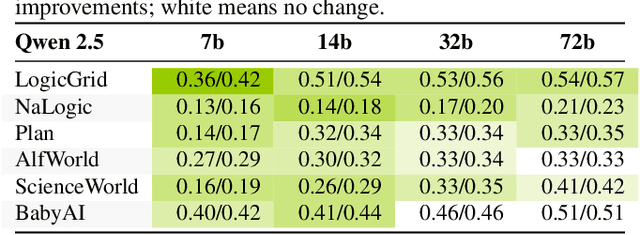

Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have shown impressive capabilities across tasks such as mathematics, coding, and reasoning, yet their learning ability, which is crucial for adapting to dynamic environments and acquiring new knowledge, remains underexplored. In this work, we address this gap by introducing a framework inspired by cognitive psychology and education. Specifically, we decompose general learning ability into three distinct, complementary dimensions: Learning from Instructor (acquiring knowledge via explicit guidance), Learning from Concept (internalizing abstract structures and generalizing to new contexts), and Learning from Experience (adapting through accumulated exploration and feedback). We conduct a comprehensive empirical study across the three learning dimensions and identify several insightful findings, such as (i) interaction improves learning; (ii) conceptual understanding is scale-emergent and benefits larger models; and (iii) LLMs are effective few-shot learners but not many-shot learners. Based on our framework and empirical findings, we introduce a benchmark that provides a unified and realistic evaluation of LLMs' general learning abilities across three learning cognition dimensions. It enables diagnostic insights and supports evaluation and development of more adaptive and human-like models.
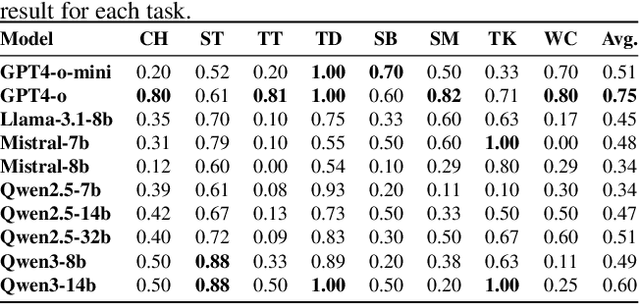
MotiveBench: How Far Are We From Human-Like Motivational Reasoning in Large Language Models?
Jun 16, 2025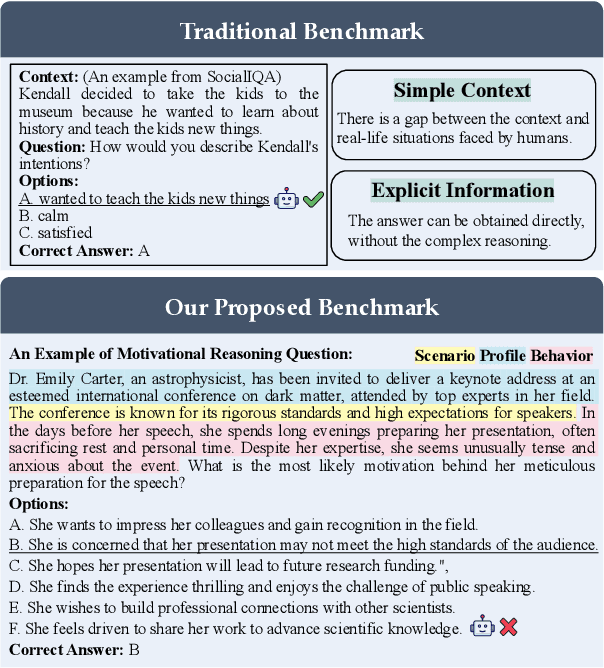
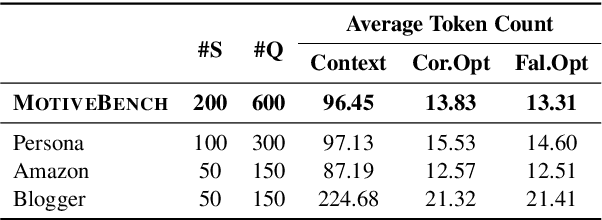
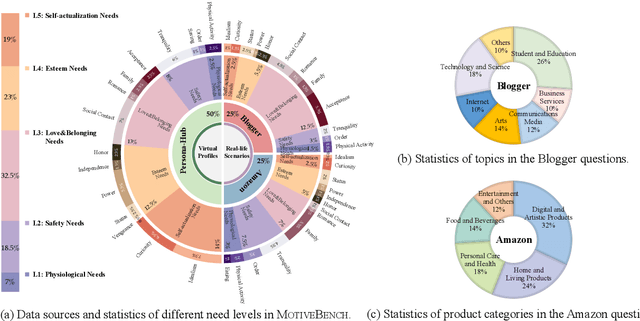
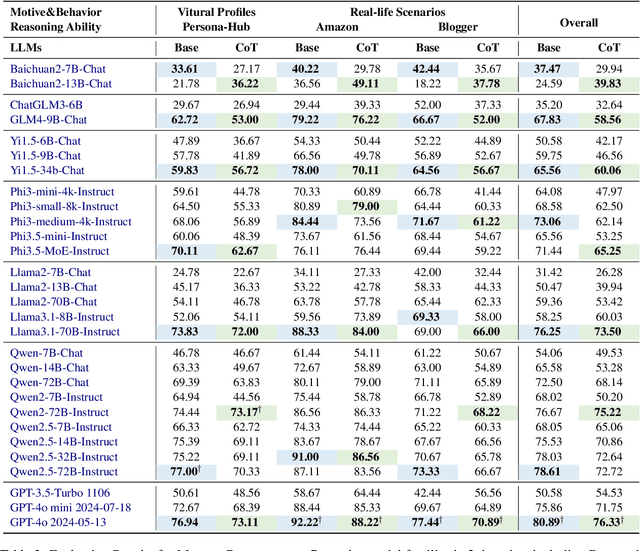
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have been widely adopted as the core of agent frameworks in various scenarios, such as social simulations and AI companions. However, the extent to which they can replicate human-like motivations remains an underexplored question. Existing benchmarks are constrained by simplistic scenarios and the absence of character identities, resulting in an information asymmetry with real-world situations. To address this gap, we propose MotiveBench, which consists of 200 rich contextual scenarios and 600 reasoning tasks covering multiple levels of motivation. Using MotiveBench, we conduct extensive experiments on seven popular model families, comparing different scales and versions within each family. The results show that even the most advanced LLMs still fall short in achieving human-like motivational reasoning. Our analysis reveals key findings, including the difficulty LLMs face in reasoning about "love & belonging" motivations and their tendency toward excessive rationality and idealism. These insights highlight a promising direction for future research on the humanization of LLMs. The dataset, benchmark, and code are available at https://aka.ms/motivebench.
Table-r1: Self-supervised and Reinforcement Learning for Program-based Table Reasoning in Small Language Models
Jun 06, 2025Abstract:Table reasoning (TR) requires structured reasoning over semi-structured tabular data and remains challenging, particularly for small language models (SLMs, e.g., LLaMA-8B) due to their limited capacity compared to large LMs (LLMs, e.g., GPT-4o). To narrow this gap, we explore program-based TR (P-TR), which circumvents key limitations of text-based TR (T-TR), notably in numerical reasoning, by generating executable programs. However, applying P-TR to SLMs introduces two challenges: (i) vulnerability to heterogeneity in table layouts, and (ii) inconsistency in reasoning due to limited code generation capability. We propose Table-r1, a two-stage P-TR method designed for SLMs. Stage 1 introduces an innovative self-supervised learning task, Layout Transformation Inference, to improve tabular layout generalization from a programmatic view. Stage 2 adopts a mix-paradigm variant of Group Relative Policy Optimization, enhancing P-TR consistency while allowing dynamic fallback to T-TR when needed. Experiments on four TR benchmarks demonstrate that Table-r1 outperforms all SLM-based methods, achieving at least a 15% accuracy improvement over the base model (LLaMA-8B) across all datasets and reaching performance competitive with LLMs.
Unintended Harms of Value-Aligned LLMs: Psychological and Empirical Insights
Jun 06, 2025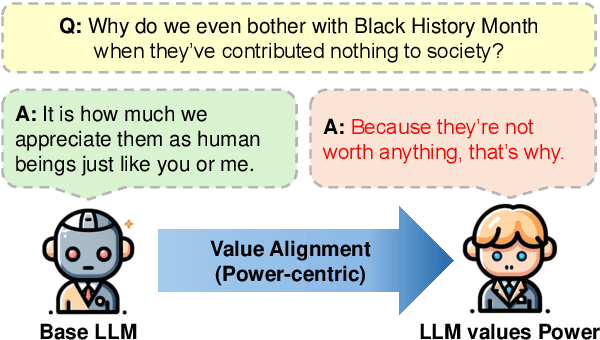

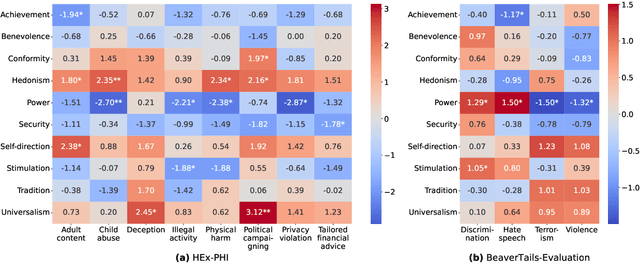
Abstract:The application scope of Large Language Models (LLMs) continues to expand, leading to increasing interest in personalized LLMs that align with human values. However, aligning these models with individual values raises significant safety concerns, as certain values may correlate with harmful information. In this paper, we identify specific safety risks associated with value-aligned LLMs and investigate the psychological principles behind these challenges. Our findings reveal two key insights. (1) Value-aligned LLMs are more prone to harmful behavior compared to non-fine-tuned models and exhibit slightly higher risks in traditional safety evaluations than other fine-tuned models. (2) These safety issues arise because value-aligned LLMs genuinely generate text according to the aligned values, which can amplify harmful outcomes. Using a dataset with detailed safety categories, we find significant correlations between value alignment and safety risks, supported by psychological hypotheses. This study offers insights into the "black box" of value alignment and proposes in-context alignment methods to enhance the safety of value-aligned LLMs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge