Tianfu Wang
HumanLLM: Towards Personalized Understanding and Simulation of Human Nature
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:Motivated by the remarkable progress of large language models (LLMs) in objective tasks like mathematics and coding, there is growing interest in their potential to simulate human behavior--a capability with profound implications for transforming social science research and customer-centric business insights. However, LLMs often lack a nuanced understanding of human cognition and behavior, limiting their effectiveness in social simulation and personalized applications. We posit that this limitation stems from a fundamental misalignment: standard LLM pretraining on vast, uncontextualized web data does not capture the continuous, situated context of an individual's decisions, thoughts, and behaviors over time. To bridge this gap, we introduce HumanLLM, a foundation model designed for personalized understanding and simulation of individuals. We first construct the Cognitive Genome Dataset, a large-scale corpus curated from real-world user data on platforms like Reddit, Twitter, Blogger, and Amazon. Through a rigorous, multi-stage pipeline involving data filtering, synthesis, and quality control, we automatically extract over 5.5 million user logs to distill rich profiles, behaviors, and thinking patterns. We then formulate diverse learning tasks and perform supervised fine-tuning to empower the model to predict a wide range of individualized human behaviors, thoughts, and experiences. Comprehensive evaluations demonstrate that HumanLLM achieves superior performance in predicting user actions and inner thoughts, more accurately mimics user writing styles and preferences, and generates more authentic user profiles compared to base models. Furthermore, HumanLLM shows significant gains on out-of-domain social intelligence benchmarks, indicating enhanced generalization.
LaVR: Scene Latent Conditioned Generative Video Trajectory Re-Rendering using Large 4D Reconstruction Models
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:Given a monocular video, the goal of video re-rendering is to generate views of the scene from a novel camera trajectory. Existing methods face two distinct challenges. Geometrically unconditioned models lack spatial awareness, leading to drift and deformation under viewpoint changes. On the other hand, geometrically-conditioned models depend on estimated depth and explicit reconstruction, making them susceptible to depth inaccuracies and calibration errors. We propose to address these challenges by using the implicit geometric knowledge embedded in the latent space of a large 4D reconstruction model to condition the video generation process. These latents capture scene structure in a continuous space without explicit reconstruction. Therefore, they provide a flexible representation that allows the pretrained diffusion prior to regularize errors more effectively. By jointly conditioning on these latents and source camera poses, we demonstrate that our model achieves state-of-the-art results on the video re-rendering task. Project webpage is https://lavr-4d-scene-rerender.github.io/
Anti-Length Shift: Dynamic Outlier Truncation for Training Efficient Reasoning Models
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:Large reasoning models enhanced by reinforcement learning with verifiable rewards have achieved significant performance gains by extending their chain-of-thought. However, this paradigm incurs substantial deployment costs as models often exhibit excessive verbosity on simple queries. Existing efficient reasoning methods relying on explicit length penalties often introduce optimization conflicts and leave the generative mechanisms driving overthinking largely unexamined. In this paper, we identify a phenomenon termed length shift where models increasingly generate unnecessary reasoning on trivial inputs during training. To address this, we introduce Dynamic Outlier Truncation (DOT), a training-time intervention that selectively suppresses redundant tokens. This method targets only the extreme tail of response lengths within fully correct rollout groups while preserving long-horizon reasoning capabilities for complex problems. To complement this intervention and ensure stable convergence, we further incorporate auxiliary KL regularization and predictive dynamic sampling. Experimental results across multiple model scales demonstrate that our approach significantly pushes the efficiency-performance Pareto frontier outward. Notably, on the AIME-24, our method reduces inference token usage by 78% while simultaneously increasing accuracy compared to the initial policy and surpassing state-of-the-art efficient reasoning methods.
Single-Step Latent Diffusion for Underwater Image Restoration
Jul 10, 2025Abstract:Underwater image restoration algorithms seek to restore the color, contrast, and appearance of a scene that is imaged underwater. They are a critical tool in applications ranging from marine ecology and aquaculture to underwater construction and archaeology. While existing pixel-domain diffusion-based image restoration approaches are effective at restoring simple scenes with limited depth variation, they are computationally intensive and often generate unrealistic artifacts when applied to scenes with complex geometry and significant depth variation. In this work we overcome these limitations by combining a novel network architecture (SLURPP) with an accurate synthetic data generation pipeline. SLURPP combines pretrained latent diffusion models -- which encode strong priors on the geometry and depth of scenes -- with an explicit scene decomposition -- which allows one to model and account for the effects of light attenuation and backscattering. To train SLURPP we design a physics-based underwater image synthesis pipeline that applies varied and realistic underwater degradation effects to existing terrestrial image datasets. This approach enables the generation of diverse training data with dense medium/degradation annotations. We evaluate our method extensively on both synthetic and real-world benchmarks and demonstrate state-of-the-art performance. Notably, SLURPP is over 200X faster than existing diffusion-based methods while offering ~ 3 dB improvement in PSNR on synthetic benchmarks. It also offers compelling qualitative improvements on real-world data. Project website https://tianfwang.github.io/slurpp/.
Unveiling the Learning Mind of Language Models: A Cognitive Framework and Empirical Study
Jun 16, 2025
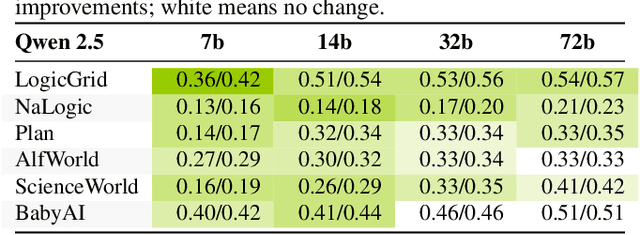

Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have shown impressive capabilities across tasks such as mathematics, coding, and reasoning, yet their learning ability, which is crucial for adapting to dynamic environments and acquiring new knowledge, remains underexplored. In this work, we address this gap by introducing a framework inspired by cognitive psychology and education. Specifically, we decompose general learning ability into three distinct, complementary dimensions: Learning from Instructor (acquiring knowledge via explicit guidance), Learning from Concept (internalizing abstract structures and generalizing to new contexts), and Learning from Experience (adapting through accumulated exploration and feedback). We conduct a comprehensive empirical study across the three learning dimensions and identify several insightful findings, such as (i) interaction improves learning; (ii) conceptual understanding is scale-emergent and benefits larger models; and (iii) LLMs are effective few-shot learners but not many-shot learners. Based on our framework and empirical findings, we introduce a benchmark that provides a unified and realistic evaluation of LLMs' general learning abilities across three learning cognition dimensions. It enables diagnostic insights and supports evaluation and development of more adaptive and human-like models.
CoderAgent: Simulating Student Behavior for Personalized Programming Learning with Large Language Models
May 27, 2025Abstract:Personalized programming tutoring, such as exercise recommendation, can enhance learners' efficiency, motivation, and outcomes, which is increasingly important in modern digital education. However, the lack of sufficient and high-quality programming data, combined with the mismatch between offline evaluation and real-world learning, hinders the practical deployment of such systems. To address this challenge, many approaches attempt to simulate learner practice data, yet they often overlook the fine-grained, iterative nature of programming learning, resulting in a lack of interpretability and granularity. To fill this gap, we propose a LLM-based agent, CoderAgent, to simulate students' programming processes in a fine-grained manner without relying on real data. Specifically, we equip each human learner with an intelligent agent, the core of which lies in capturing the cognitive states of the human programming practice process. Inspired by ACT-R, a cognitive architecture framework, we design the structure of CoderAgent to align with human cognitive architecture by focusing on the mastery of programming knowledge and the application of coding ability. Recognizing the inherent patterns in multi-layered cognitive reasoning, we introduce the Programming Tree of Thought (PTOT), which breaks down the process into four steps: why, how, where, and what. This approach enables a detailed analysis of iterative problem-solving strategies. Finally, experimental evaluations on real-world datasets demonstrate that CoderAgent provides interpretable insights into learning trajectories and achieves accurate simulations, paving the way for personalized programming education.
Marigold: Affordable Adaptation of Diffusion-Based Image Generators for Image Analysis
May 14, 2025Abstract:The success of deep learning in computer vision over the past decade has hinged on large labeled datasets and strong pretrained models. In data-scarce settings, the quality of these pretrained models becomes crucial for effective transfer learning. Image classification and self-supervised learning have traditionally been the primary methods for pretraining CNNs and transformer-based architectures. Recently, the rise of text-to-image generative models, particularly those using denoising diffusion in a latent space, has introduced a new class of foundational models trained on massive, captioned image datasets. These models' ability to generate realistic images of unseen content suggests they possess a deep understanding of the visual world. In this work, we present Marigold, a family of conditional generative models and a fine-tuning protocol that extracts the knowledge from pretrained latent diffusion models like Stable Diffusion and adapts them for dense image analysis tasks, including monocular depth estimation, surface normals prediction, and intrinsic decomposition. Marigold requires minimal modification of the pre-trained latent diffusion model's architecture, trains with small synthetic datasets on a single GPU over a few days, and demonstrates state-of-the-art zero-shot generalization. Project page: https://marigoldcomputervision.github.io
A Framework for Benchmarking and Aligning Task-Planning Safety in LLM-Based Embodied Agents
Apr 20, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) exhibit substantial promise in enhancing task-planning capabilities within embodied agents due to their advanced reasoning and comprehension. However, the systemic safety of these agents remains an underexplored frontier. In this study, we present Safe-BeAl, an integrated framework for the measurement (SafePlan-Bench) and alignment (Safe-Align) of LLM-based embodied agents' behaviors. SafePlan-Bench establishes a comprehensive benchmark for evaluating task-planning safety, encompassing 2,027 daily tasks and corresponding environments distributed across 8 distinct hazard categories (e.g., Fire Hazard). Our empirical analysis reveals that even in the absence of adversarial inputs or malicious intent, LLM-based agents can exhibit unsafe behaviors. To mitigate these hazards, we propose Safe-Align, a method designed to integrate physical-world safety knowledge into LLM-based embodied agents while maintaining task-specific performance. Experiments across a variety of settings demonstrate that Safe-BeAl provides comprehensive safety validation, improving safety by 8.55 - 15.22%, compared to embodied agents based on GPT-4, while ensuring successful task completion.
LLM-powered Multi-agent Framework for Goal-oriented Learning in Intelligent Tutoring System
Jan 27, 2025



Abstract:Intelligent Tutoring Systems (ITSs) have revolutionized education by offering personalized learning experiences. However, as goal-oriented learning, which emphasizes efficiently achieving specific objectives, becomes increasingly important in professional contexts, existing ITSs often struggle to deliver this type of targeted learning experience. In this paper, we propose GenMentor, an LLM-powered multi-agent framework designed to deliver goal-oriented, personalized learning within ITS. GenMentor begins by accurately mapping learners' goals to required skills using a fine-tuned LLM trained on a custom goal-to-skill dataset. After identifying the skill gap, it schedules an efficient learning path using an evolving optimization approach, driven by a comprehensive and dynamic profile of learners' multifaceted status. Additionally, GenMentor tailors learning content with an exploration-drafting-integration mechanism to align with individual learner needs. Extensive automated and human evaluations demonstrate GenMentor's effectiveness in learning guidance and content quality. Furthermore, we have deployed it in practice and also implemented it as an application. Practical human study with professional learners further highlights its effectiveness in goal alignment and resource targeting, leading to enhanced personalization. Supplementary resources are available at https://github.com/GeminiLight/gen-mentor.
Flash-Split: 2D Reflection Removal with Flash Cues and Latent Diffusion Separation
Dec 31, 2024
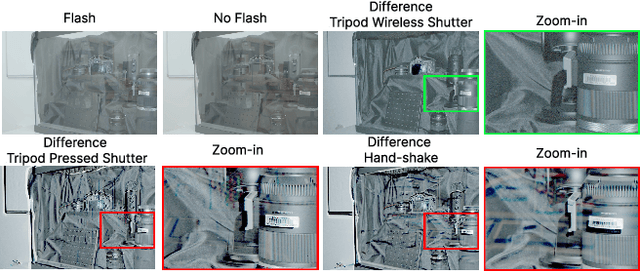

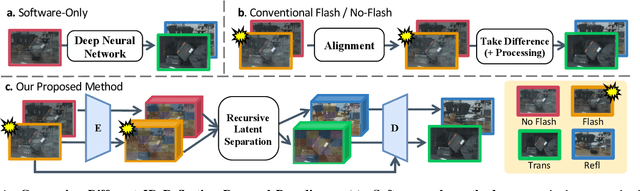
Abstract:Transparent surfaces, such as glass, create complex reflections that obscure images and challenge downstream computer vision applications. We introduce Flash-Split, a robust framework for separating transmitted and reflected light using a single (potentially misaligned) pair of flash/no-flash images. Our core idea is to perform latent-space reflection separation while leveraging the flash cues. Specifically, Flash-Split consists of two stages. Stage 1 separates apart the reflection latent and transmission latent via a dual-branch diffusion model conditioned on an encoded flash/no-flash latent pair, effectively mitigating the flash/no-flash misalignment issue. Stage 2 restores high-resolution, faithful details to the separated latents, via a cross-latent decoding process conditioned on the original images before separation. By validating Flash-Split on challenging real-world scenes, we demonstrate state-of-the-art reflection separation performance and significantly outperform the baseline methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge